# HEAVY.AI Installation on RHEL
This is an end-to-end recipe for installing HEAVY.AI on a Red Hat Enterprise 8.x machine using CPU and GPU devices.
The order of these instructions is significant. To avoid problems, install each component in the order presented.
The same instructions can be used to install on RL / RHEL 9, which some minor modifications.
## Assumptions
These instructions assume the following:
* You are installing a "clean" Rocky Linux / RHEL 8 host machine with only the operating system.
* Your HEAVY.AI host only runs the daemons and services required to support HEAVY.AI.
* Your HEAVY.AI host is connected to the Internet.
## Preparation
Prepare your machine by updating your system and optionally enabling or configuring a firewall.
## Update and Reboot
Update the entire system and reboot the system if needed.
```bash
sudo dnf -y update
sudo reboot
```
Install the utilities needed to create HEAVY.AI repositories and download installation binaries.
```bash
sudo dnf -y install dnf-utils curl libldap2-dev
```
## JDK
Follow these instructions to install a headless JDK and configure an environment variable with a path to the library. The “headless” Java Development Kit does not provide support for keyboard, mouse, or display systems. It has fewer dependencies and is best suited for a server host. For more information, see [https://openjdk.java.net](https://openjdk.java.net/).
1. Open a terminal on the host machine.
2. Install the headless JDK using the following command:
```bash
sudo dnf -y install java-1.8.0-openjdk-headless
```
## Create the HEAVY.AI User
Create a group called `heavyai` and a user named `heavyai`, who will own HEAVY.AI software and data on the file system.
You can create the group, user, and home directory using the `useradd` command with the `--user-group` and `--create-home` switches:
```bash
sudo useradd --user-group --create-home --groups wheel heavyai
```
Set a password for the user using the passwd command.
```bash
sudo passwd heavyai
```
Log in with the newly created user.
```bash
sudo su - heavyai
```
## Installation
There are two ways to install the heavy.ai software
* [DNF Installation](/installation-and-configuration/installation/installing-on-rocky-linux-rhel/heavy.ai-installation-on-rhel#installing-with-dnf)\
To install software using DNF's package manager, you can utilize DNF's package management capabilities to search for and then install the desired software. This method provides a convenient and efficient way to manage software installations and dependencies on your system.\\
* [Tarball Installation](/installation-and-configuration/installation/installing-on-rocky-linux-rhel/heavy.ai-installation-on-rhel#installing-on-centos-with-a-tarball)\
Installing via a tarball involves obtaining a compressed archive file (tarball) from the software's official source or repository. After downloading the tarball, you would need to extract its contents and follow the installation instructions provided by the software developers. This method allows for manual installation and customization of the software.
Using the DNF package manager for installation is highly recommended due to its ability to handle dependencies and streamline the installation process, making it a preferred choice for many users.
### Install NVIDIA Drivers ᴳᴾᵁ ᴼᴾᵀᴵᴼᴺ
If your system includes NVIDIA GPUs but the drivers are not installed, it is advisable to install them before proceeding with the suite installation.
See I[nstall NVIDIA Drivers and Vukan on Rocky Linux and RHEL](/installation-and-configuration/installation/installing-on-rocky-linux-rhel/install-nvidia-drivers-and-vulkan-on-rocky-linux-and-rhel) for details.
### Installing with DNF
Create a DNF repository depending on the edition (Enterprise, Free, or Open Source) and execution device (GPU or CPU) you will use.
```bash
sudo dnf config-manager --add-repo \
https://releases.heavy.ai/ee/yum/stable/cuda
```
```bash
sudo yum-config-manager --add-repo \
https://releases.heavy.ai/ee/yum/stable/cpu
```
```bash
sudo yum-config-manager --add-repo \
https://releases.heavy.ai/os/yum/stable/cuda
```
```bash
sudo yum-config-manager --add-repo \
https://releases.heavy.ai/os/yum/stable/cpu
```
Add the GPG-key to the newly added repository.
```bash
sudo dnf config-manager --save \
--setopt="releases.heavy*.gpgkey=https://releases.heavy.ai/GPG-KEY-heavyai"
```
Use `DNF` to install the latest version of HEAVY.AI.
```bash
sudo dnf -y install heavyai.x86_64
```
You can use the DNF package manager to list the available packages when installing a specific version of HEAVY.AI, such as when a multistep upgrade is necessary, or a specific version is needed for any other reason.\
\
`sudo``dnf --showduplicates``list``heavyai`\
\
Select the version needed from the list (e.g. 7.0.0) and install using the command.
\
`sudo``dnf``install``heavyai-7.0.0_20230501_be4f51b048-1.x86_64`
### Installing with a Tarball
Let's begin by creating the installation directory.
```bash
sudo mkdir /opt/heavyai && sudo chown $USER /opt/heavyai
```
Download the archive and install the latest version of the software. The appropriate archive is downloaded based on the edition (Enterprise, Free, or Open Source) and the device used for runtime.
```bash
curl \
https://releases.heavy.ai/ee/tar/heavyai-ee-latest-Linux-x86_64-render.tar.gz \
| sudo tar zxf - --strip-components=1 -C /opt/heavyai
```
```bash
curl \
https://releases.heavy.ai/ee/tar/heavyai-ee-latest-Linux-x86_64-cpu.tar.gz \
| sudo tar zxf - --strip-components=1 -C /opt/heavyai
```
```bash
curl \
https://releases.heavy.ai/os/tar/heavyai-os-latest-Linux-x86_64.tar.gz \
| sudo tar zxf - --strip-components=1 -C /opt/heavyai
```
```bash
curl \
https://releases.heavy.ai/os/tar/heavyai-os-latest-Linux-x86_64-cpu.tar.gz \
| sudo tar zxf - --strip-components=1 -C /opt/heavyai
```
## Configuration
Follow these steps to configure your HEAVY.AI environment.
### Set Environment Variables
For your convenience, you can update .bashrc with these environment variables
```bash
echo "# HEAVY.AI variable and paths
export HEAVYAI_PATH=/opt/heavyai
export HEAVYAI_BASE=/var/lib/heavyai
export HEAVYAI_LOG=\$HEAVYAI_BASE/storage/log
export PATH=\$HEAVYAI_PATH/bin:$PATH" \
>> ~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrc
```
Although this step is optional, you will find references to the HEAVYAI\_BASE and HEAVYAI\_PATH variables.\
These variables contain the paths where configuration, license, and data files are stored and the location of the software installation. It is strongly recommended that you set them up.
### Initialization
Run the script that will initialize the HEAVY.AI services and database storage located in the systemd folder.
```bash
cd $HEAVYAI_PATH/systemd
./install_heavy_systemd.sh
```
Accept the default values provided or make changes as needed.
This step will take a few minutes if you are installing a CUDA-enabled version of the software because the shaders must be compiled.
The script creates a data directory in `$HEAVYAI_BASE/storage` (typically `/var/lib/heavyai`) with the directories `catalogs`, `data`and `log`, which will contain the metadata, the data of the database tables, and the log files from Immerse's web server and the database.\
The log folder is particularly important for database administrators. It contains data about the system's health, performance, and user activities.
### Activation
The first step to activate the system is starting HeavyDB and the Web Server service that Heavy Immerse needs. [¹](/installation-and-configuration/installation/installing-on-rocky-linux-rhel/heavy.ai-installation-on-rhel#in-the-os-edition-heavy-immerse-service-is-unavailable.)
Heavy Immerse is not available in the OS Edition.
Start the services and enable the automatic startup of the service at reboot and start the HEAVY.AI services.
```bash
sudo systemctl enable heavydb --now
sudo systemctl enable heavy_web_server --now
```
```bash
sudo systemctl enable heavydb --now
```
### Configure the Firewall OPTIONAL
If a firewall is not already installed and you want to harden your system, install and start `firewalld`.
```bash
sudo dnf -y install firewalld
sudo systemctl start firewalld
sudo systemctl enable firewalld
sudo systemctl status firewalld
```
To use Heavy Immerse or other third-party tools, you must prepare your host machine to accept incoming HTTP(S) connections. Configure your firewall for external access:
```bash
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=6273-6274/tcp --add-port=6278/tcp --permanent
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
```
Most cloud providers use a different mechanism for firewall configuration. The commands above might not run in cloud deployments.
For more information, see [https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Firewalld?rd=FirewallD](https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Firewalld?rd=FirewallD).
### Licensing HEAVY.AI ee-free only
If you are on **Enterprise** or **Free Edition**, you need to validate your HEAVY.AI instance with your license key. You can skip this section if you are using Open Source Edition. [²](/installation-and-configuration/installation/installing-on-rocky-linux-rhel/heavy.ai-installation-on-rhel#in-the-os-edition-heavy-immerse-service-is-unavailable.-1)
1. Copy your license key from the registration email message. If you have not received your license key, contact your Sales Representative or register for your 30-day trial [here](https://www.omnisci.com/platform/downloads/).
2. Connect to Heavy Immerse using a web browser connected to your host machine on port 6273. For example, `http://heavyai.mycompany.com:6273`.
3. When prompted, paste your license key in the text box and click **Apply**.
4. Log into Heavy Immerse by entering the default username (`admin`) and password (`HyperInteractive`), and then click **Connect**.
The \$HEAVYAI\_BASE directory must be dedicated to HEAVYAI; do not set it to a directory shared by other packages.
### **Final Checks**
To verify that everything is working, load some sample data, perform a `heavysql` query, and generate a Pointmap using Heavy Immerse. [¹](/installation-and-configuration/installation/installing-on-rocky-linux-rhel/heavy.ai-installation-on-rhel#in-the-os-edition-heavy-immerse-service-is-unavailable.)
#### Load Sample Data and Run a Simple Query
HEAVY.AI ships with two sample datasets of airline flight information collected in 2008, and a census of New York City trees. To install sample data, run the following command.
```bash
cd $HEAVYAI_PATH
sudo ./insert_sample_data --data /var/lib/heavyai/storage
```
```bash
# Enter dataset number to download, or 'q' to quit:
Dataset Rows Table Name File Name
1) Flights (2008) 7M flights_2008_7M flights_2008_7M.tar.gz
2) Flights (2008) 10k flights_2008_10k flights_2008_10k.tar.gz
3) NYC Tree Census (2015) 683k nyc_trees_2015_683k nyc_trees_2015_683k.tar.gz
```
Connect to HeavyDB by entering the following command in a terminal on the host machine (default password is `HyperInteractive`):
```bash
$HEAVYAI_PATH/bin/heavysql -p HyperInteractive
```
anEnter a SQL query such as the following:
```sql
SELECT origin_city AS "Origin",
dest_city AS "Destination",
AVG(airtime) AS "Average Airtime"
FROM flights_2008_10k WHERE distance < 175
GROUP BY origin_city, dest_city;
```
The results should be similar to the results below.
```sql
Origin|Destination|Average Airtime
Austin|Houston|33.055556
Norfolk|Baltimore|36.071429
Ft. Myers|Orlando|28.666667
Orlando|Ft. Myers|32.583333
Houston|Austin|29.611111
Baltimore|Norfolk|31.714286
```
### Create a Dashboard Using Heavy Immerse ee-free only [¹](/installation-and-configuration/installation/installing-on-rocky-linux-rhel/heavy.ai-installation-on-rhel#in-the-os-edition-heavy-immerse-service-is-unavailable.)
After installing Enterprise or Free Edition, check if Heavy Immerse is running as intended.
1. Connect to Heavy Immerse using a web browser connected to your host machine on port 6273. For example, `http://heavyai.mycompany.com:6273`.
2. Log into Heavy Immerse by entering the default username (`admin`) and password (`HyperInteractive`), and then click **Connect**.
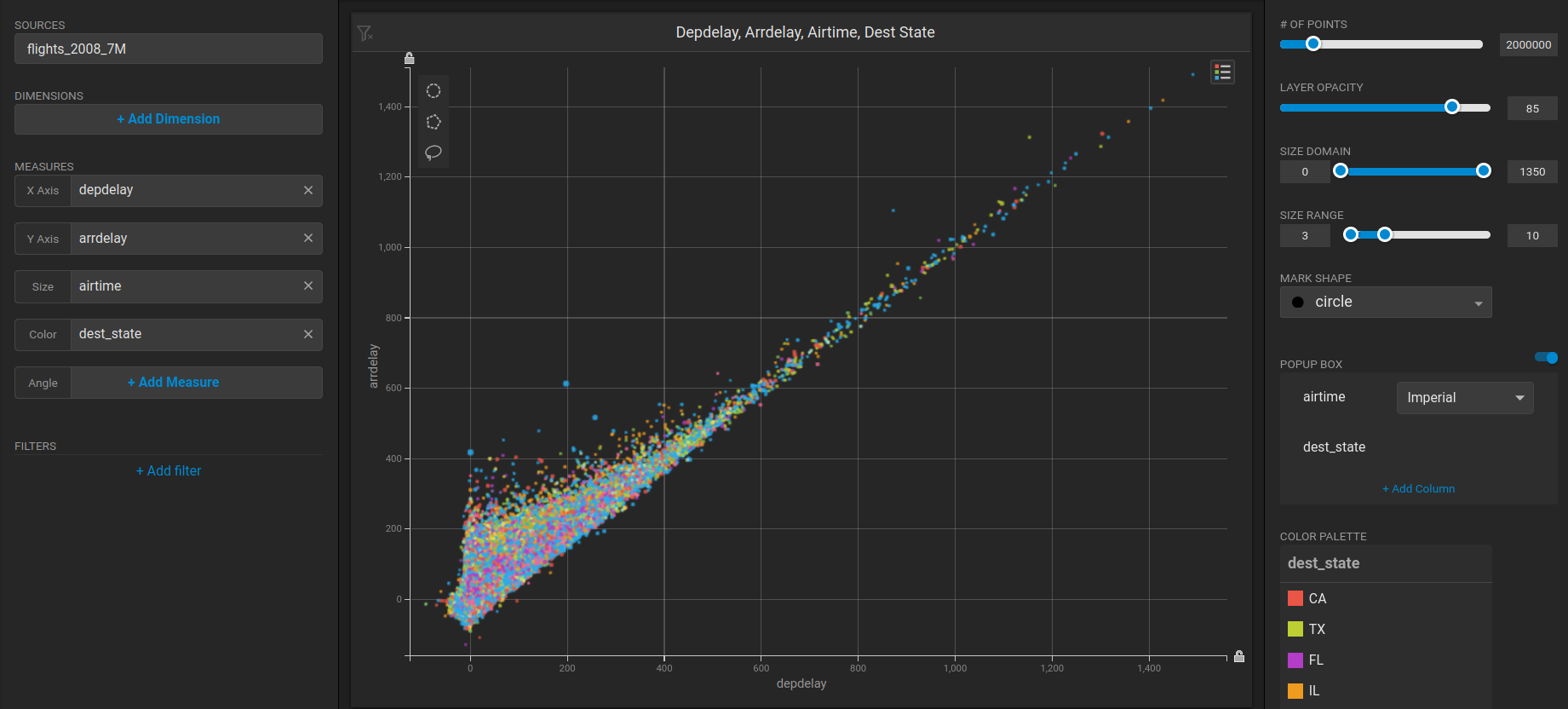
Create a new dashboard and a Scatter Plot to verify that **backend rendering** is working.
1. Click **New Dashboard**.
2. Click **Add Chart**.
3. Click **SCATTER**.
4. Click **Add Data Source**.
5. Choose the *flights\_2008\_10k* table as the data source.
6. Click **X Axis +Add Measure**.
7. Choose *depdelay*.
8. Click **Y Axis +Add Measure**.
9. Choose *arrdelay*.
10. Click Size **+Add Measure**.
11. Choose *airtime.*
12. Click Color **+Add Measure**.
13. Choose *dest\_state.*
The resulting chart clearly demonstrates that there is a direct correlation between departure delay and arrival delay. This insight can help in identifying areas for improvement and implementing strategies to minimize delays and enhance overall efficiency.\\
Create a new dashboard and a Table chart to verify that Heavy Immerse is working.
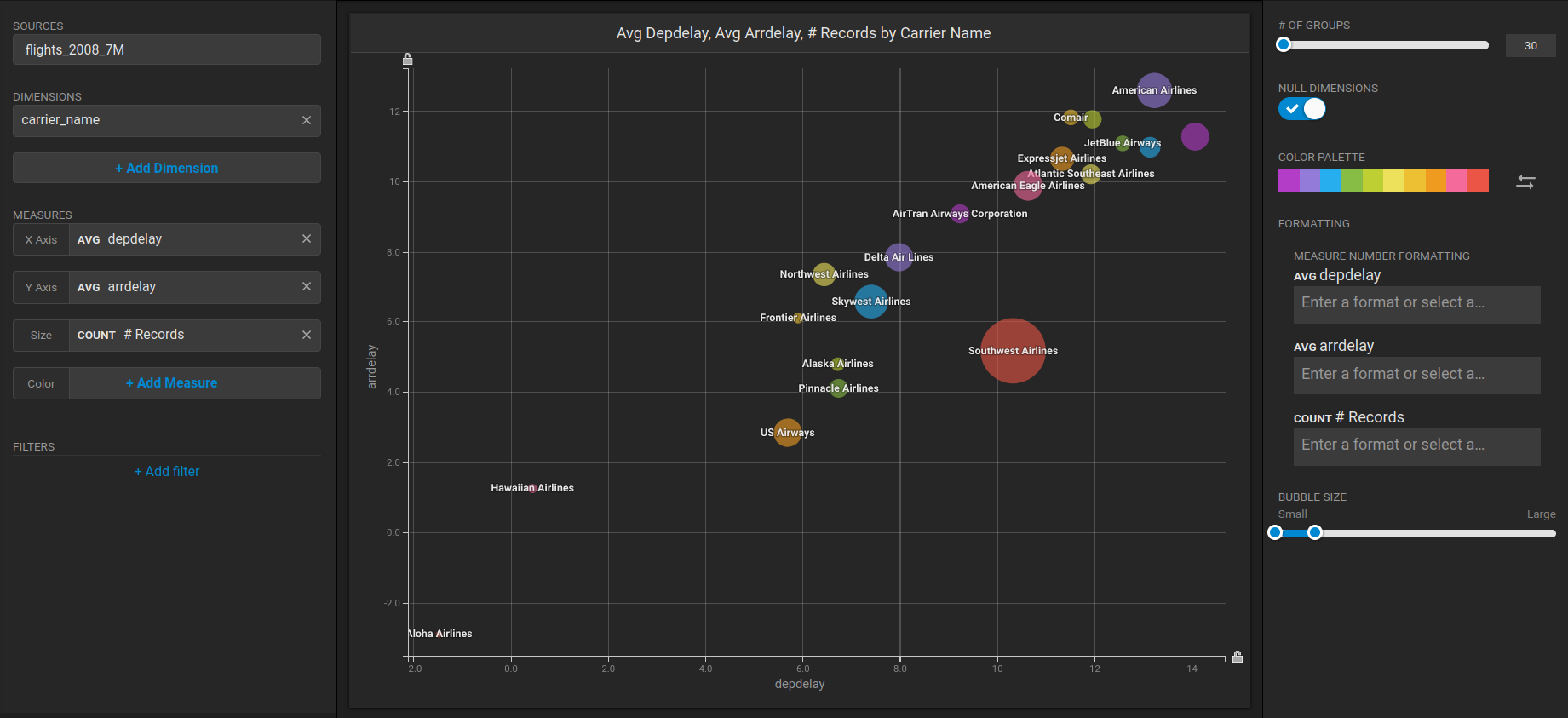
1. Click **New Dashboard**.
2. Click **Add Chart**.
3. Click **Bubble**.
4. Click **Select Data Source**.
5. Choose the *flights\_2008\_10k* table as the data source
6. Click **Add Dimension**.
7. Choose *carrier\_name*.
8. Click **Add Measure**.
9. Choose *depdelay*.
10. Click **Add Measure**.
11. Choose *arrdelay*.
12. Click **Add Measure**.
13. Choose *#Records.*
The resulting chart shows, unsurprisingly, that also the average departure delay is correlated to the average of arrival delay, while there is quite a difference between Carriers.\\
#### ¹ In the OS Edition, Heavy Immerse is unavailable.
#### ² The OS Edition does not require a license key.