Attention#
Scaled Dot Product Attention#
This operation computes the scaled dot product attention (SDPA), as
\(\text{Attention}(Q, K, V) = \text{softmax}\left(\frac{QK^T}{\sqrt{d}}\right)V\)
using the FlashAttention-2 algorithm as described in the paper FlashAttention-2: Faster Attention with Better Parallelism and Work Partitioning. It is applicable for both training and inference phases, with an option to generate a stats tensor to be used for backwards training computation.
Support Matrix#
cudnn SDPA operation requires SM80 (Ampere) or newer architectures and cuda toolkit 12.x or newer.
The support matrix is based on the latest cudnn backend version 9.18.1
Arch |
Datatype |
Layout |
Paged |
Masking |
Deterministic |
Head dim |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Ampere/Ada |
fp16, bf16 |
BHSD, BSHD, Interleaved¹, |
Yes |
Yes⁴ |
Yes |
d <= 256 |
Ampere/Ada |
fp16, bf16 |
BHSD, BSHD, Interleaved, |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
d <= 128 |
Ampere/Ada |
fp16, bf16 |
BHSD, BSHD, Interleaved, |
NA |
Yes |
Yes |
d <= 128 |
Hopper |
fp8, fp16, bf16 |
BHSD, BSHD, Interleaved, |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
d <= 256⁵ |
Hopper |
fp8, fp16, bf16 |
BHSD, BSHD, Interleaved, |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
d <= 256 |
Hopper |
fp8, fp16, bf16 |
BHSD, BSHD, Interleaved, |
NA |
Yes |
Yes |
d <= 256 |
Blackwell (B200/B300) |
fp8, fp16, bf16 |
BHSD, BSHD, Interleaved, |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
d <= 256 |
Blackwell (B200/B300) |
fp8, fp16, bf16 |
BHSD, BSHD, Interleaved, |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
d <= 128 |
Blackwell (B200/B300) |
fp8, fp16, bf16 |
BHSD, BSHD, Interleaved, |
NA |
Yes |
Yes |
d <= 128 |
Blackwell (Consumer) |
fp16, bf16 |
BHSD, BSHD, Interleaved, |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
d <= 256 |
Blackwell (Consumer) |
fp16, bf16 |
BHSD, BSHD, Interleaved, |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
d <= 128 |
Blackwell (Consumer) |
fp16, bf16 |
BHSD, BSHD, Interleaved, |
NA |
Yes |
Yes |
d <= 128 |
Glossary#
¹ Interleaved q,k,v tensors. Generally they have layouts as BS3HD, B3SHD.
² Padded, variable length sequences (requires padding mask). When sequences in a batch have different lengths, use use_padding_mask=True with sequence length tensors.
Setup:
- Set use_padding_mask=True
- Provide seq_len_q tensor of shape (B, 1, 1, 1) with actual query sequence lengths
- Provide seq_len_kv tensor of shape (B, 1, 1, 1) with actual key/value sequence lengths
Example:
Batch with sequences “aa” (length 2) and “bbb” (length 3), max length S=8:
seq_len_q = [2, 3]seq_len_kv = [2, 3]Q[b=0] = aa000000 (6 padding tokens) Q[b=1] = bbb00000 (5 padding tokens)
Dimensions: \([B=2, H=1, S=8, D=64]\)
Strides: \([512, 64, 64, 1]\) (standard BHSD)
cuDNN automatically masks out padding tokens during attention computation.
³ Ragged Layout.
For memory efficiency, variable-length sequences can be packed together without padding. This is called THD layout where \(T = \sum(\text{seq\_len})\) is the total number of valid tokens.
Requirements:
Must set ragged offset tensor via
tensor.set_ragged_offset(ragged_offset_tensor)
Ragged Offset Tensor:
Shape: \((B + 1, 1, 1, 1)\)
Contains cumulative token offsets in elements (not bytes)
Last element is the total number of tokens
Memory Layout visualization:
Example:
Same sequences “aa” and “bbb” packed together:
seq_len_q = [2, 3]seq_len_kv = [2, 3]Q = aabbb (no padding, T=5 total tokens)
Dimensions: \([B=2, H=1, S=8, D=64]\) (S is still max sequence length)
Strides: \([512, 64, 64, 1]\) (strides unchanged, but ignored for ragged)
Ragged offset: \([0, 2 \times H \times D, 5 \times H \times D] = [0, 128, 320]\)
Partially Packed Layout:
Tokens within each batch can be contiguous without being globally packed.
Ragged offset: \([0, 4 \times H \times D, 7 \times H \times D] = [0, 256, 448]\)
Q = aa00bbb0 (batch 0 at offset 0, batch 1 at offset 4)
Not Supported:
Tokens that are not contiguous within a batch cannot be represented.
seq_len_q = [2, 3]Q = a0abbb00bb000000 (tokens interleaved - NOT SUPPORTED)
Note that Q,K,V and their gradients can be individually ragged or not.
Backward Pass with THD:
When using THD layout with cudnn, maximum total tokens are needed for efficient workspace allocation. If not set, defaults to \(B \times S\) which may overallocate memory.
⁴ None, Causal, Sliding window, Additive Bias, Softcap, Arbitrary masking.
⁵ d_qo should be equal to d_kv. (Except when d_qk == 192 and d_vo = 128, which is also supported.)
Important Notes on Support Surface#
All attention flavors MHA, MQA, GQA are supported.
The head dim (d) should be a multiple of 8 for fp16/bf16 and multiple of 16 for fp8 data-types.
The seqlens s_q, and s_kv can have arbitrary value.
The layout of q,k,v,o and dq, dk, dv, do can be independent of each other.
Dropout: Randomly zeros some of the attention weights after the softmax as a form of regularization. You can configure dropout in two ways:
Philox RNG dropout (more performant): Provide:
An RNG seed tensor (INT32 or INT64)
An RNG offset tensor (INT32 or INT64)
A float representing the dropout probability (probability that any weight is set to zero)
(Debug only) Output RNG dump tensor to capture the generated dropout mask
Custom dropout mask: Provide:
A
dropout masktensor matching the attention weights’ dimensions. Dimensions set to 1 will broadcast.A
dropout scaletensor to adjust remaining weights, typically \(1 / (1 - \text{dropout probability})\).
Stats from fprop is supported (Max, Sum). In addition QKClip required for KimiK2, Qwen are also supported optionally.
Benchmarks#
To run the sdpa benchmarks, refer to benchmarks/sdpa folder. Current results:
GB200 - Llama 3.1 Causal (top_left)#
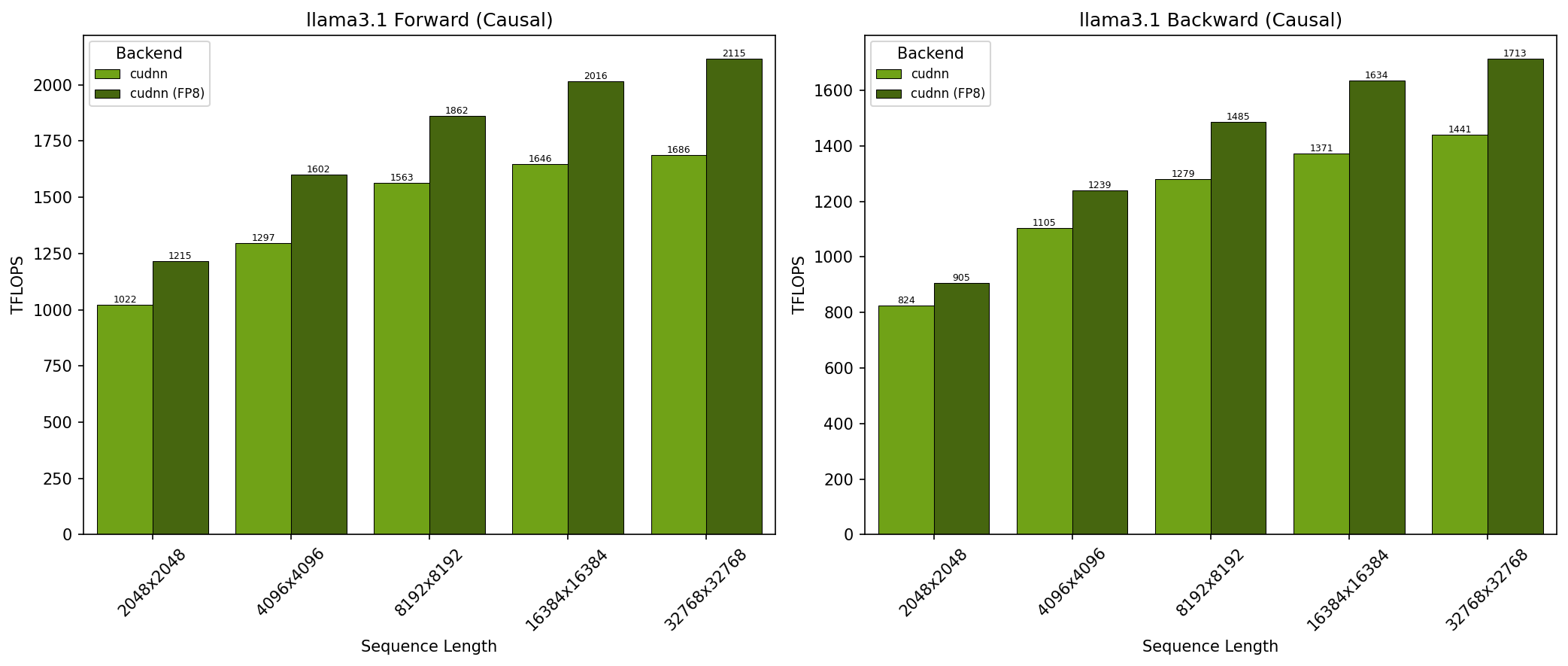
SDPA parameters:
batch=1; num_q_heads=64; num_kv_heads=8; head_dim=128; is_causal=TrueSequence lengths shown on x-axis
Results obtained on NVIDIA GB200 GPU
GB200 - Llama 3.1 Non-Causal (no_mask)#
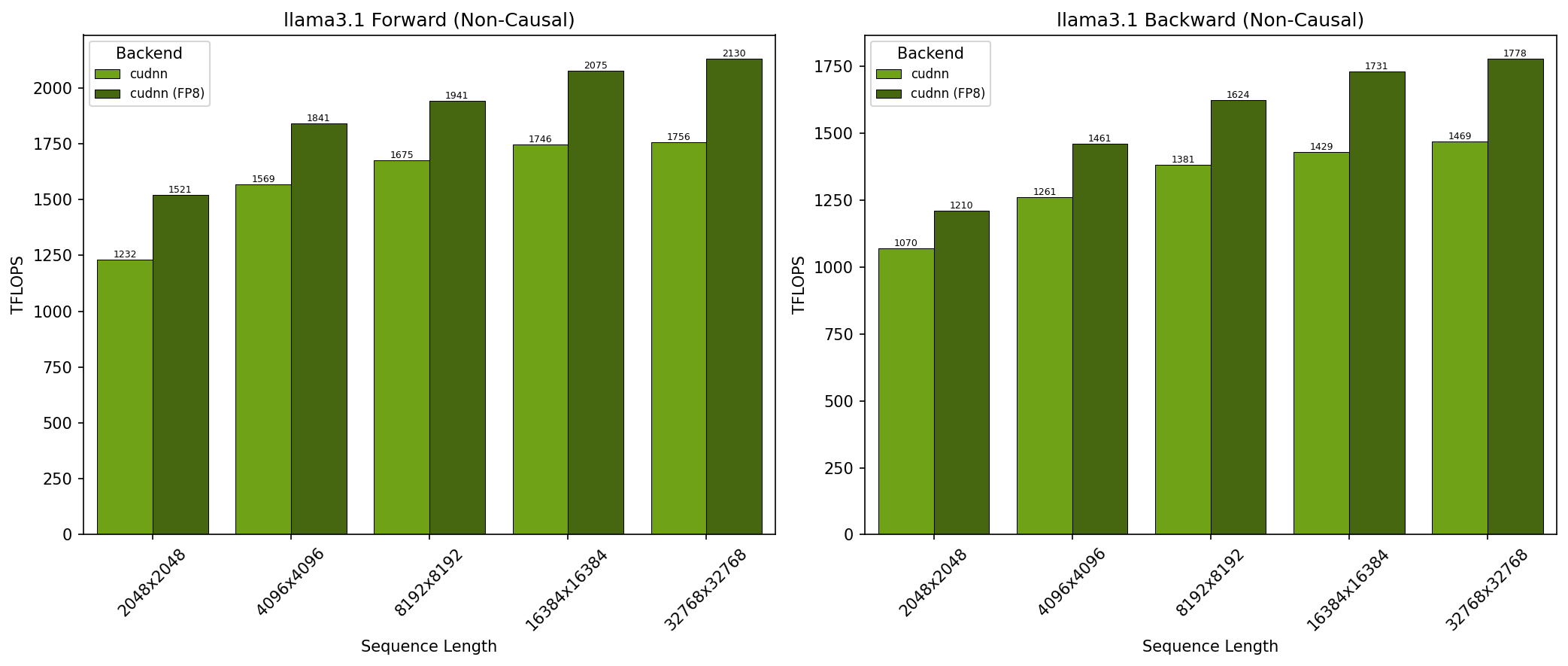
SDPA parameters:
batch=1; num_q_heads=64; num_kv_heads=8; head_dim=128; is_causal=FalseSequence lengths shown on x-axis
Results obtained on NVIDIA GB200 GPU
GB200 - DeepSeek V3 Causal (top_left)#
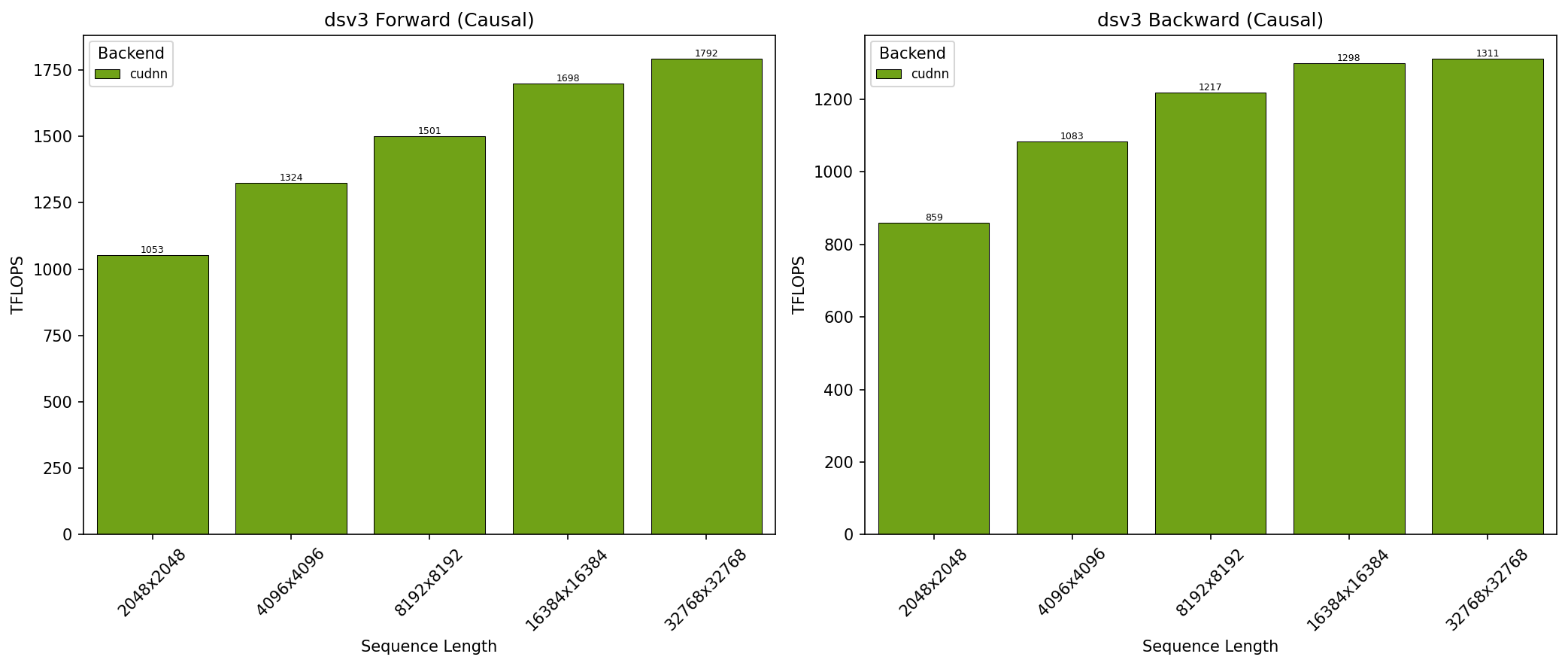
SDPA parameters:
batch=1; num_q_heads=128; num_kv_heads=128; head_dim_qk=192; head_dim_vo=128; is_causal=TrueSequence lengths shown on x-axis
Results obtained on NVIDIA GB200 GPU
GB300 - Llama 3.1 Causal (top_left)#
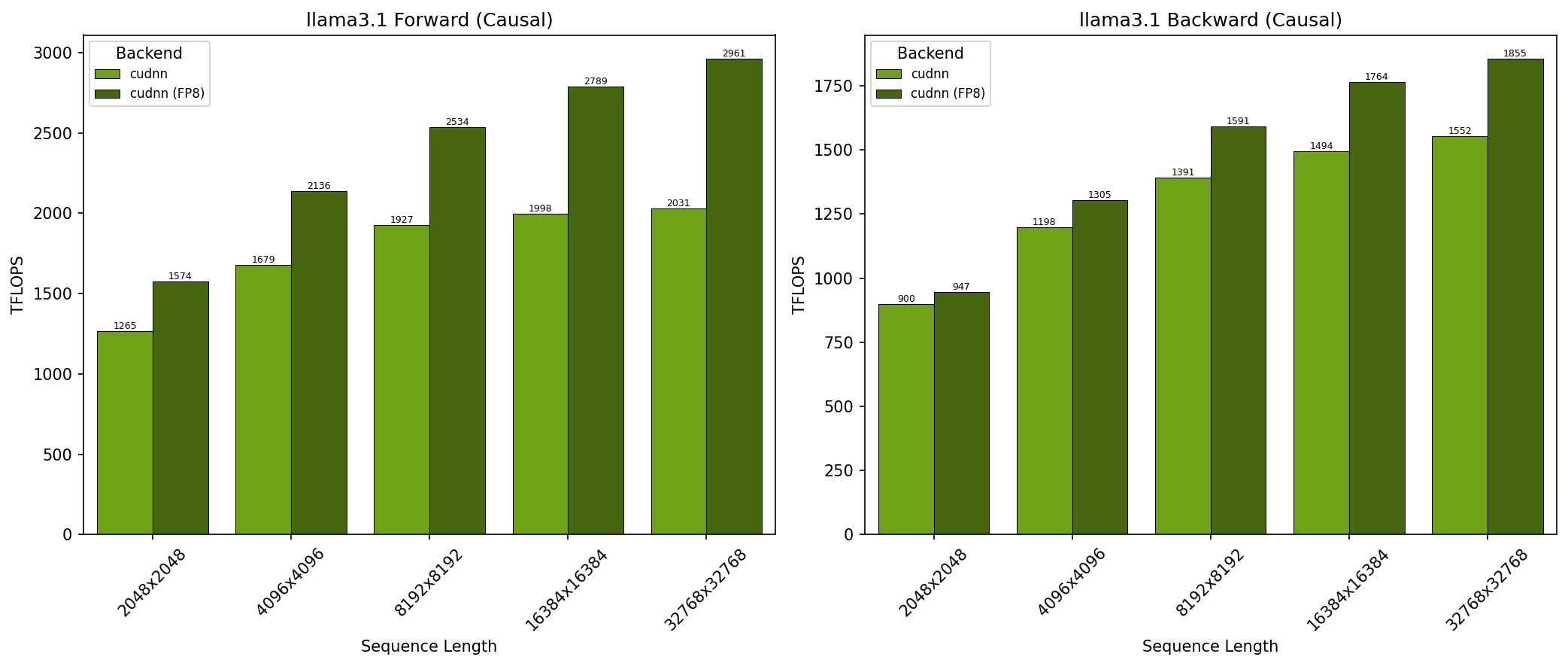
SDPA parameters:
batch=1; num_q_heads=64; num_kv_heads=8; head_dim=128; is_causal=TrueSequence lengths shown on x-axis
Results obtained on NVIDIA GB300 GPU
GB300 - Llama 3.1 Non-Causal (no_mask)#
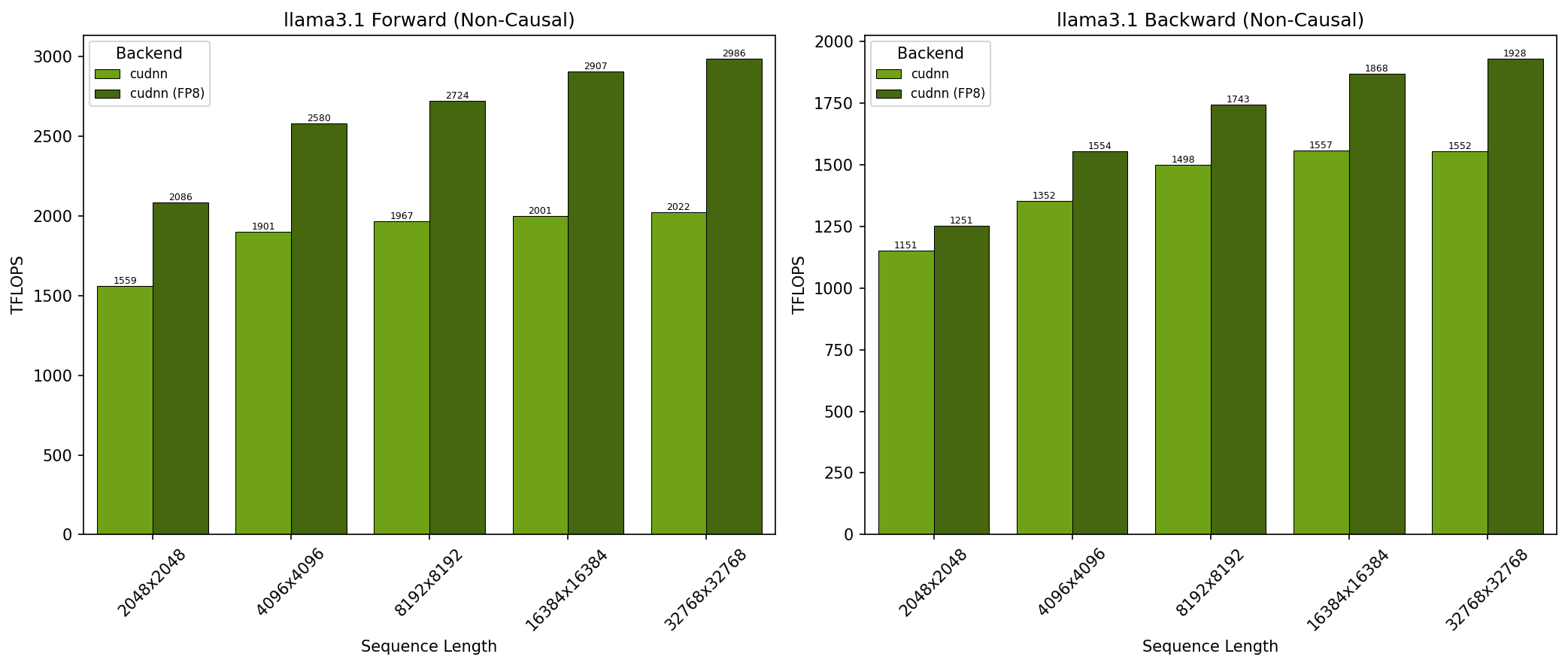
SDPA parameters:
batch=1; num_q_heads=64; num_kv_heads=8; head_dim=128; is_causal=FalseSequence lengths shown on x-axis
Results obtained on NVIDIA GB300 GPU
GB300 - DeepSeek V3 Causal (top_left)#
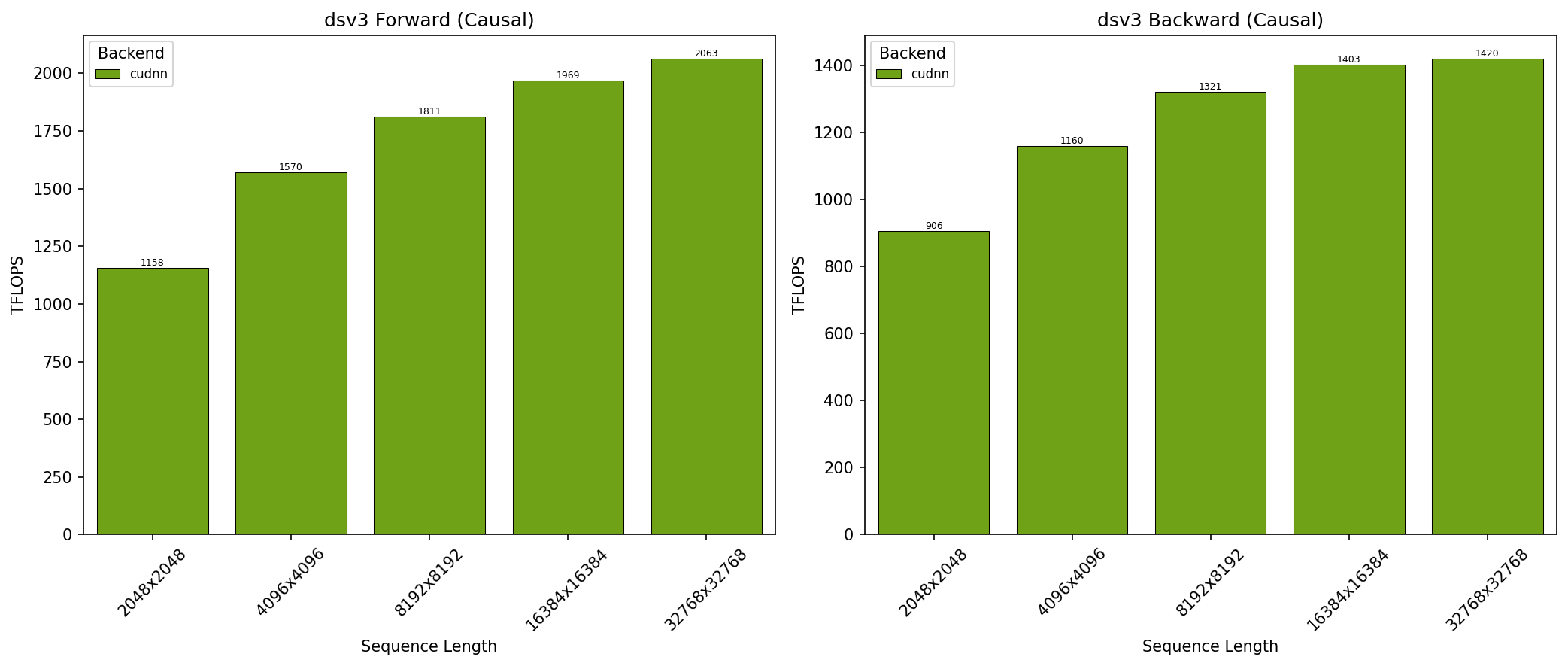
SDPA parameters:
batch=1; num_q_heads=128; num_kv_heads=128; head_dim_qk=192; head_dim_vo=128; is_causal=TrueSequence lengths shown on x-axis
Results obtained on NVIDIA GB300 GPU
API#
SDPA FP16/BF16 Forward#
C++ API#
// returns [output, softmax_stats]
std::array<std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes>, 2>
sdpa(std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> q,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> k,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> v,
SDPA_attributes options);
The options parameter of type SDPA_attributes is used to control the attributes of the forward operation, as detailed below:
// Indicates that softmax_stats should be generated (useful during training).
// If false, the softmax_stats output will be nullptr.
SDPA_attributes& set_generate_stats(bool const value);
// Indicates whether the kernel should output max of attention score
// and numerically stable sum of exponents using normalized values wrt max score
SDPA_attributes& set_logit_max(std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> value);
SDPA_attributes& set_score_sum_exp(std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> value);
SDPA_attributes& set_attn_scale(std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> value);
SDPA_attributes& set_attn_scale(float const value);
// DEPRECATED
// Calls set_generate_stats(!value) (note the negation of `value`).
SDPA_attributes& set_is_inference(bool const value);
// ========================== BEGIN paged attn options =====================
SDPA_attributes& set_paged_attention_k_table(std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> value);
SDPA_attributes& set_paged_attention_v_table(std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> value);
SDPA_attributes& set_paged_attention_max_seq_len_kv(int const value);
// ========================== END paged attn options =====================
// ========================== BEGIN var len options =====================
SDPA_attributes& set_padding_mask(bool const value);
// integer tensor that specifies the sequence length of each batch
SDPA_attributes& set_seq_len_q(std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> value);
SDPA_attributes& set_seq_len_kv(std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> value);
// ========================== END var len options =====================
// ========================== BEGIN score mod options =====================
SDPA_attributes& set_score_mod(std::function<Tensor_t(Graph_t, Tensor_t)>);
// Use in combination to set diagonal masking
SDPA_attributes& set_diagonal_alignment(DiagonalAlignment_t const alignment);
SDPA_attributes& set_diagonal_band_left_bound(int const value);
SDPA_attributes& set_diagonal_band_right_bound(int const value);
// DEPRECATED
// Sets the diagonal position to TOP_LEFT
// calls set_diagonal_band_right_bound(0) if no right_bound was specified
SDPA_attributes& set_causal_mask(bool const value);
// DEPRECATED
// Sets the diagonal position to BOTTOM_RIGHT
// and calls set_diagonal_band_right_bound(0) if no right_bound was specified
SDPA_attributes& set_causal_mask_bottom_right(bool const value);
// DEPRECATED
// calls set_diagonal_band_left_bound(value)
SDPA_attributes& set_sliding_window_length(int const value);
SDPA_attributes& set_bias(std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> value);
SDPA_attributes& set_block_mask(std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> value);
SDPA_attributes& set_alibi_mask(bool const value);
// ========================== END score mod options =====================
// ========================== BEGIN dropout options =====================
SDPA_attributes& set_dropout(float const probability,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> seed,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> offset);
SDPA_attributes& set_dropout(std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> mask,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> scale);
// for debugging dropout mask with seed and offset
SDPA_attributes& set_rng_dump(std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> value);
// ========================== END dropout options =====================
// ========================== BEGIN experimental options ================
// Sets the underlying SDPA implementation to use (default is AUTO).
SDPA_attributes& set_implementation(AttentionImplementation_t value);
// ========================== END experimental options ================
SDPA_attributes& set_compute_data_type(DataType_t value);
Python API#
graph.sdpa(
q, # Query tensor
k, # Key tensor (or container for paged attention)
v, # Value tensor (or container for paged attention)
attn_scale=None, # Attention scale factor (float or tensor)
bias=None, # Additive bias mask tensor
block_mask=None, # Block mask tensor (128x128 tiles, UNIFIED only)
use_alibi_mask=False, # Enable ALiBi positional encoding
use_padding_mask=False, # Enable variable sequence length masking
seq_len_q=None, # Per-batch query sequence lengths
seq_len_kv=None, # Per-batch key/value sequence lengths
diagonal_alignment=TOP_LEFT, # Diagonal alignment: TOP_LEFT or BOTTOM_RIGHT
diagonal_band_left_bound=None, # Left bound for sliding window (None = no bound)
diagonal_band_right_bound=None, # Right bound for causal mask (0 = causal, None = no bound)
dropout=None, # Dropout config: (prob, seed, offset) or (mask, scale)
rng_dump=None, # Debug: output tensor for RNG dropout mask
paged_attention_k_table=None, # Page table for K container
paged_attention_v_table=None, # Page table for V container
paged_attention_max_seq_len_kv=None, # Max KV sequence length for paged attention
generate_stats=None, # Output softmax stats for training (True/False)
implementation=AUTO, # SDPA implementation: AUTO, COMPOSITE, UNIFIED
compute_data_type=NOT_SET, # Computation data type
name=None, # Operation name
)
Args:
q(cudnn_tensor): The query data with shape \((B, H_q, S_q, D_{qk})\).k(cudnn_tensor): The key data. Whenpaged_attention_k_tableis provided, this is a container of non-contiguous key blocks.v(cudnn_tensor): The value data. Whenpaged_attention_v_tableis provided, this is a container of non-contiguous value blocks.attn_scale(Optional[Union[float, cudnn_tensor]]): Scale factor for attention scores. Typically \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{d}}\). Default is None (no scaling).bias(Optional[cudnn_tensor]): Additive bias mask for attention scores. Supports broadcasting.block_mask(Optional[cudnn_tensor]): Block-level mask for 128x128 tiles. Only supported with UNIFIED implementation.use_alibi_mask(Optional[bool]): Enable ALiBi (Attention with Linear Biases) positional encoding. Requiresdiagonal_band_right_bound=0.use_padding_mask(Optional[bool]): Enable variable sequence length masking. Must also provideseq_len_qandseq_len_kv.seq_len_q(Optional[cudnn_tensor]): Per-batch query sequence lengths with shape \((B, 1, 1, 1)\).seq_len_kv(Optional[cudnn_tensor]): Per-batch key/value sequence lengths with shape \((B, 1, 1, 1)\).diagonal_alignment(Optional[cudnn.diagonal_alignment]): Alignment for diagonal masking.TOP_LEFTfor standard causal,BOTTOM_RIGHTfor prefix-LM style.diagonal_band_left_bound(Optional[int]): Left bound for sliding window attention. Masks columns at or beforerow_idx - left_bound.diagonal_band_right_bound(Optional[int]): Right bound for causal masking. Set to 0 for causal mask. Masks columns beyondrow_idx + right_bound.dropout(Optional[tuple]): Dropout configuration. Either(probability, seed, offset)for Philox RNG or(mask, scale)for custom mask.rng_dump(Optional[cudnn_tensor]): Debug tensor to capture the Philox RNG dropout mask.paged_attention_k_table(Optional[cudnn_tensor]): Page table with block offsets into the K container.paged_attention_v_table(Optional[cudnn_tensor]): Page table with block offsets into the V container.paged_attention_max_seq_len_kv(Optional[int]): Maximum sequence length for K/V caches. Recommended when using paged attention.generate_stats(Optional[bool]): If True, output softmax statistics for backward pass. Required for training.implementation(Optional[cudnn.attention_implementation]): SDPA implementation to use.AUTO(default),COMPOSITE, orUNIFIED.compute_data_type(Optional[cudnn.data_type]): Data type for internal computation.name(Optional[str]): Name for the operation.
Returns:
o(cudnn_tensor): The output attention data with shape \((B, H_q, S_q, D_v)\).stats(Optional[cudnn_tensor]): Softmax statistics with shape \((B, H_q, S_q, 1)\) whengenerate_stats=True.
Configurable Options#
Attention scale (
attn_scale): Applies a scaling factor to attention scores before the softmax, such as \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{\text{d}}}\). Set to 1.0 by default. Can be passed as a float or as a tensor.Bias mask: Applies an additive bias mask to attention scores. You must pass a bias tensor as specified in the tensors section below. The dimensions that are passed as 1 will apply a broadcasted mask over attention scores.
Block mask: Masks out tiles of attention scores at a 128x128 block granularity. The block mask is a uint8 tensor where each bit represents whether a 128x128 tile should be computed (1) or masked out (0). This is supported with the UNIFIED implementation.
ALiBi mask: Attention with Linear Biases (ALiBi) is an additive mask applied to the attention scores as described in the paper Train Short, Test Long: Attention with Linear Biases Enables Input Length Extrapolation. When using ALiBi,
diagonal_band_right_boundmust be set to exactly 0 (causal masking).Padding mask (Variable Sequence Length): Masks out padded time steps to ignore them in computation. You must pass per-batch sequence length tensors as specified in the tensors section below. In padded or ragged layout (discussed below) where the actual seqlen can be less than the max seqlens of a graph, certain batches can be skipped by setting the actual seqlen of the corresponding batch to 0.
Diagonal masking options: These options control causal and sliding window masking:
Diagonal Alignment (
diagonal_alignment): Specifies where the diagonal starts. Options are:TOP_LEFT: The diagonal starts at the top-left of the attention matrix. Used for standard causal masking.BOTTOM_RIGHT: The diagonal starts at the bottom-right of the attention matrix, aligned with the actual sequence length. Useful for prefix-LM or when \(S_q \neq S_{kv}\).
Diagonal Band Right Bound (
diagonal_band_right_bound): Specifies that attention scores beyond columnrow_idx + right_boundare masked with negative infinity. Setting this to 0 enables causal masking.Diagonal Band Left Bound (
diagonal_band_left_bound): Specifies that attention scores at or before columnrow_idx - left_boundare masked with negative infinity. This enables sliding window attention.Common masking patterns:
Causal mask (top-left):
diagonal_alignment=TOP_LEFT,right_bound=0Causal mask (bottom-right):
diagonal_alignment=BOTTOM_RIGHT,right_bound=0Sliding window: Set
left_boundto window sizeBand attention: Set both
left_boundandright_bound
Paged attention: Enables non-contiguous K/V caches to reduce memory fragmentation. See the PagedAttention paper.
Requirements:
Pass
page_table_ktensor with block offsets into the K container (optional if K is not paged)Pass
page_table_vtensor with block offsets into the V container (optional if V is not paged)Pass sequence length tensors (
seq_len_q,seq_len_kv) for padding maskOptionally pass
paged_attention_max_seq_len_kvfor the maximum KV sequence length (recommended)
Offset calculation:
\(K_{cache}[b,h,s,d] = K_{container}[page\_table\_k[b,1,s / bs_k, 1], h, s \mod bs_k, d]\)
\(V_{cache}[b,h,s,d] = V_{container}[page\_table\_v[b,1,s / bs_v, 1], h, s \mod bs_v, d]\)
Packed page tables: Page tables can also use ragged offsets to pack only the necessary block indices, useful for frameworks that prefer packed representations.
Implementation: Select the underlying SDPA implementation:
AUTO(default): Auto-selects the best implementation. Recommended for most users.COMPOSITE: Standard cuDNN graph representing SDPA as distinct operations.UNIFIED: Optimized fused SDPA operation (cuDNN 9.13.1+). Supports a subset of features including block masking.
Generate stats (
generate_stats): WhenTrue, outputs softmax statistics needed for backward pass during training. Set toTruefor training,Falsefor inference.
Limitations#
Head dimension must be a multiple of 8.
ALiBi requires causal masking (
diagonal_band_right_bound=0).Block masking is only supported with the UNIFIED implementation.
Ampere/Ada architectures are limited to head dimensions up to 256 for prefill, 128 for decode and backward.
Tensors#
Input Tensors#
Tensor Name |
Device |
Data Type |
Dimensions |
|---|---|---|---|
Q |
GPU |
FP16 or BF16 |
\((B, H_{q}, S_{q}, D_{qk})\) |
K |
GPU |
FP16 or BF16 |
\((B, H_{k}, S_{kv}, D_{qk})\), or \((num\_blocks_{k}, H_{k}, bs_{k}, D_{qk})\) in case of paged K cache |
V |
GPU |
FP16 or BF16 |
\((B, H_{v}, S_{kv}, D_{v})\), or \((num\_blocks_{v}, H_{v}, bs_{v}, D_{v})\) in case of paged V cache |
(Bias mask) Bias Mask |
GPU |
FP16 or BF16 |
\((1, 1, S_{q}, S_{kv})\), \((1, H_{q}, S_{q}, S_{kv})\), \((B, 1, S_{q}, S_{kv})\), or \((B, H_{q}, S_{q}, S_{kv})\) |
(Padding mask/Paged Caches) Sequence Length Q |
GPU |
INT32 |
\((B, 1, 1, 1)\) |
(Padding mask/Paged Caches) Sequence Length KV |
GPU |
INT32 |
\((B, 1, 1, 1)\) |
(Philox RNG Dropout) Seed |
CPU or GPU |
INT32 or INT64 |
\((1, 1, 1, 1)\) |
(Philox RNG Dropout) Offset |
CPU or GPU |
INT32 or INT64 |
\((1, 1, 1, 1)\) |
(Custom Dropout Mask) Mask |
GPU |
FP16 or BF16 |
\((1, 1, S_{q}, S_{kv})\), \((1, H_{q}, S_{q}, S_{kv})\), \((B, 1, S_{q}, S_{kv})\), or \((B, H_{q}, S_{q}, S_{kv})\) |
(Custom Dropout Mask) Scale |
GPU |
FP32 |
\((1, 1, 1, 1)\) |
(Packed Layout) Ragged Offset |
GPU |
INT32 |
\((B + 1, 1, 1, 1)\) |
(Paged Attention) Page Table K |
GPU |
INT32 |
\((B, 1, ceil(S_{kv}/bs_{k}), 1)\) |
(Paged Attention) Page Table V |
GPU |
INT32 |
\((B, 1, ceil(S_{kv}/bs_{v}), 1)\) |
(Paged Attention) Max Sequence Length KV |
CPU |
INT32 or INT64 |
\((1, 1, 1, 1)\) |
Output Tensors#
Tensor Name |
Device |
Data Type |
Dimensions |
|---|---|---|---|
O |
GPU |
FP16 or BF16 |
\((B, H_{q}, S_{q}, D_{v})\) |
Stats (training only) |
GPU |
FP32 |
\((B, H_{q}, S_{q}, 1)\) |
(Philox RNG Dropout) RNG Dump |
GPU |
FP32 |
\((B, H_{q}, S_{q}, S_{kv})\) |
Where:
\(B\) is the batch size
\(H_{q}\) is the number of query heads
\(H_{k}\) is the number of key heads
\(H_{v}\) is the number of value heads
\(S_{q}\) is the sequence length of the query
\(S_{kv}\) is the sequence length of the key and value
\(D_{qk}\) is the embedding dimension per head of query and key
\(D_{v}\) is the embedding dimension per head of value
\(bs_{k}\) is the (power of 2) block size of the K container
\(bs_{v}\) is the (power of 2) block size of the V container
\(num\_blocks_{k}\) is the number of blocks in the K container
\(num\_blocks_{v}\) is the number of blocks in the V container
Samples and Tests#
Python forward sample: samples/python/50_sdpa_forward.ipynb
Python backward sample: samples/python/51_sdpa_backward.ipynb
Python prefill sample with paged caches: samples/python/52_sdpa_with_paged_caches.ipynb
Python decode sample with packed paged caches: samples/python/53_sdpa_decode_with_paged_caches.ipynb
C++ sample: samples/cpp/sdpa
Python tests (v2 with randomized configurations): test/python/test_mhas_v2.py
Example Usage:
import cudnn
import torch
import math
# Create graph
graph = cudnn.pygraph(
io_data_type=cudnn.data_type.HALF,
intermediate_data_type=cudnn.data_type.FLOAT,
compute_data_type=cudnn.data_type.FLOAT,
)
# Create tensor descriptors
q = graph.tensor_like(q_gpu)
k = graph.tensor_like(k_gpu)
v = graph.tensor_like(v_gpu)
# Forward pass with causal masking
o, stats = graph.sdpa(
name="sdpa",
q=q,
k=k,
v=v,
attn_scale=1.0 / math.sqrt(d),
generate_stats=True, # For training
diagonal_band_right_bound=0, # Causal mask
diagonal_alignment=cudnn.diagonal_alignment.TOP_LEFT,
)
o.set_output(True).set_dim(shape_o).set_stride(stride_o)
stats.set_output(True).set_data_type(cudnn.data_type.FLOAT)
# Build and execute
graph.build([cudnn.heur_mode.A, cudnn.heur_mode.FALLBACK])
SDPA FP16/BF16 Backward#
This operation computes gradient tensors for scaled dot product attention (SDPA) using the FlashAttention-2 algorithm as described in the paper FlashAttention-2: Faster Attention with Better Parallelism and Work Partitioning. You are required to pass the stats tensor from the forward operation to the backward operation as input.
C++ API#
// returns [dQ, dK, dV]
std::array<std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes>, 3>
sdpa_backward(std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> q,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> k,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> v,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> o,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> dO,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> stats,
SDPA_backward_attributes);
The options parameter of type SDPA_backward_attributes is used to control the attributes of backward operation, as detailed below:
SDPA_backward_attributes& set_attn_scale(std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> value);
SDPA_backward_attributes& set_attn_scale(float const value);
// ========================== BEGIN var len options =====================
SDPA_backward_attributes& set_padding_mask(bool const value);
// integer tensor that specifies the sequence length of each batch
SDPA_backward_attributes& set_seq_len_q(std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> value);
SDPA_backward_attributes& set_seq_len_kv(std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> value);
// the maximum number of sequence tokens for all batches, used for workspace allocation
SDPA_backward_attributes& set_max_total_seq_len_q(int64_t const value);
SDPA_backward_attributes& set_max_total_seq_len_kv(int64_t const value);
// ========================== END var len options =====================
// ========================== BEGIN score mod options =====================
SDPA_backward_attributes& set_score_mod(std::function<Tensor_t(Graph_t, Tensor_t)>);
// Use in combination to set_diagonal_alignment to set (bottom right) causal masking
SDPA_backward_attributes& set_diagonal_alignment(DiagonalAlignment_t const alignment);
SDPA_backward_attributes& set_diagonal_band_left_bound(int const value);
SDPA_backward_attributes& set_diagonal_band_right_bound(int const value);
// DEPRECATED
// Sets the diagonal position to TOP_LEFT
// calls set_diagonal_band_right_bound(0) if no right_bound was specified
SDPA_backward_attributes& set_causal_mask(bool const value);
// DEPRECATED
// Sets the diagonal position to BOTTOM_RIGHT
// and calls set_diagonal_band_right_bound(0) if no right_bound was specified
SDPA_backward_attributes& set_causal_mask_bottom_right(bool const value);
// DEPRECATED
// calls set_diagonal_band_left_bound(value)
SDPA_backward_attributes& set_sliding_window_length(int const value);
SDPA_backward_attributes& set_bias(std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> value);
SDPA_backward_attributes& set_dbias(std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> value);
SDPA_backward_attributes& set_alibi_mask(bool const value);
// ========================== END score modoptions =====================
// ========================== BEGIN dropout options =====================
SDPA_backward_attributes& set_dropout(float const probability,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> seed,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> offset);
SDPA_backward_attributes& set_dropout(std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> mask,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> scale,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> scale_inv);
// for debugging dropout mask with seed and offset
SDPA_backward_attributes& set_rng_dump(std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> value);
// ========================== END dropout options =====================
SDPA_backward_attributes& set_deterministic_algorithm(bool const value);
SDPA_backward_attributes& set_compute_data_type(DataType_t const value);
Python API#
graph.sdpa_backward(
q, # Query tensor from forward pass
k, # Key tensor from forward pass
v, # Value tensor from forward pass
o, # Output tensor from forward pass
dO, # Gradient of output
stats, # Softmax statistics from forward pass
attn_scale=None, # Attention scale factor (must match forward)
bias=None, # Bias tensor from forward pass
dBias=None, # Output tensor for bias gradient
use_alibi_mask=False, # Enable ALiBi (must match forward)
use_padding_mask=False, # Enable variable sequence length masking
seq_len_q=None, # Per-batch query sequence lengths
seq_len_kv=None, # Per-batch key/value sequence lengths
max_total_seq_len_q=None, # Max total tokens for Q (ragged tensors)
max_total_seq_len_kv=None, # Max total tokens for KV (ragged tensors)
diagonal_alignment=TOP_LEFT, # Diagonal alignment (must match forward)
diagonal_band_left_bound=None, # Left bound (must match forward)
diagonal_band_right_bound=None, # Right bound (must match forward)
dropout=None, # Dropout config (must match forward)
use_deterministic_algorithm=False, # Force deterministic gradient computation
compute_data_type=NOT_SET, # Computation data type
name=None, # Operation name
)
Args:
q(cudnn_tensor): The query data from the forward pass.k(cudnn_tensor): The key data from the forward pass.v(cudnn_tensor): The value data from the forward pass.o(cudnn_tensor): The output data from the forward pass.dO(cudnn_tensor): The gradient of the loss with respect to the output.stats(cudnn_tensor): The softmax statistics tensor from the forward pass (generate_stats=True).attn_scale(Optional[Union[float, cudnn_tensor]]): The attention scale factor. Must match the forward pass.bias(Optional[cudnn_tensor]): The bias tensor from the forward pass.dBias(Optional[cudnn_tensor]): Output tensor to store the bias gradient.use_alibi_mask(Optional[bool]): Enable ALiBi. Must match the forward pass configuration.use_padding_mask(Optional[bool]): Enable variable sequence length masking. Must match forward pass.seq_len_q(Optional[cudnn_tensor]): Per-batch query sequence lengths.seq_len_kv(Optional[cudnn_tensor]): Per-batch key/value sequence lengths.max_total_seq_len_q(Optional[int]): Maximum total sequence tokens for Q when using ragged tensors. Used for workspace allocation. Defaults to \(B \times S_q\) if not provided.max_total_seq_len_kv(Optional[int]): Maximum total sequence tokens for KV when using ragged tensors. Used for workspace allocation. Defaults to \(B \times S_{kv}\) if not provided.diagonal_alignment(Optional[cudnn.diagonal_alignment]): Must match the forward pass.diagonal_band_left_bound(Optional[int]): Must match the forward pass.diagonal_band_right_bound(Optional[int]): Must match the forward pass.dropout(Optional[tuple]): Dropout configuration. Must match the forward pass to ensure the same dropout mask is applied.use_deterministic_algorithm(Optional[bool]): If True, forces deterministic gradient computation. This ensures bitwise-identical results across multiple runs but may be slower. Default is False.compute_data_type(Optional[cudnn.data_type]): Data type for internal computation.name(Optional[str]): Name for the operation.
Returns:
dQ(cudnn_tensor): The gradient with respect to the query tensor.dK(cudnn_tensor): The gradient with respect to the key tensor.dV(cudnn_tensor): The gradient with respect to the value tensor.
Important Notes:
The backward operation does NOT support paged attention. K and V must be contiguous tensors.
All masking and dropout configurations must exactly match the forward pass to ensure correct gradients.
When using ragged tensors, set
max_total_seq_len_qandmax_total_seq_len_kvto the maximum total tokens (sum of sequence lengths) for proper workspace allocation.Python sample: samples/python/51_sdpa_backward.ipynb
C++ sample: samples/cpp/sdpa
Python tests (v2 with randomized configurations): test/python/test_mhas_v2.py
Tensors#
Input Tensors#
Tensor Name |
Device |
Data Type |
Dimensions |
|---|---|---|---|
dO |
GPU |
FP16 or BF16 |
\((B, H_{q}, S_{q}, D_{v})\) |
Output Tensors#
Tensor Name |
Device |
Data Type |
Dimensions |
|---|---|---|---|
dQ |
GPU |
FP16 or BF16 |
\((B, H_{q}, S_{q}, D_{qk})\) |
dK |
GPU |
FP16 or BF16 |
\((B, H_{k}, S_{kv}, D_{qk})\) |
dV |
GPU |
FP16 or BF16 |
\((B, H_{v}, S_{kv}, D_{v})\) |
Example Usage:
# Backward pass graph
graph_backward = cudnn.pygraph(
io_data_type=cudnn.data_type.HALF,
intermediate_data_type=cudnn.data_type.FLOAT,
compute_data_type=cudnn.data_type.FLOAT,
)
q = graph_backward.tensor_like(q_gpu)
k = graph_backward.tensor_like(k_gpu)
v = graph_backward.tensor_like(v_gpu)
o = graph_backward.tensor_like(o_gpu)
dO = graph_backward.tensor_like(dO_gpu)
stats = graph_backward.tensor_like(stats_gpu)
dQ, dK, dV = graph_backward.sdpa_backward(
name="sdpa_backward",
q=q,
k=k,
v=v,
o=o,
dO=dO,
stats=stats,
attn_scale=attn_scale,
diagonal_band_right_bound=0, # Must match forward
diagonal_alignment=cudnn.diagonal_alignment.TOP_LEFT,
use_deterministic_algorithm=True, # For reproducible training
)
dQ.set_output(True).set_dim(q_gpu.shape).set_stride(q_gpu.stride())
dK.set_output(True).set_dim(k_gpu.shape).set_stride(k_gpu.stride())
dV.set_output(True).set_dim(v_gpu.shape).set_stride(v_gpu.stride())
SDPA FP8 Forward#
This operation computes the scaled dot product attention (SDPA) in the 8-bit floating point (FP8) datatype, using the FlashAttention-2 algorithm as described in the paper FlashAttention-2: Faster Attention with Better Parallelism and Work Partitioning. It is applicable for both training and inference phases, with an option to generate a stats tensor to be used for backwards training computation.
The FP8 datatype consists of two encodings:
FP8_E4M3(1 sign bit, 4 exponent bits, and 3 mantissa bits)FP8_E5M2(1 sign bit, 5 exponent bits, 2 mantissa bits).
Due to the limited numerical precision of FP8 data type, for practical use cases, you must scale values computed in FP32 format before storing them in FP8 format, and descale the values stored in FP8 format before performing computations on them. For more information, refer to the Transformer Engine FP8 Primer.
The suggested value for the scaling factor is computed as: (Max representable value in the fp8 format) / (Max absolute value seen in the tensor for the previous layer).
For E4M3, the suggested scaling factor is
448.f/ prev_layer_tensor_amax(rounded to the nearest lower power of two)For E5M2, the suggested scaling factor is
57344.f/ prev_layer_tensor_amax(rounded to the nearest lower power of two)
The suggested value for the descale factor is the reciprocal of the scale factor.
Since scaling and descaling are critical for convergence with FP8 datatype, you are required to pass scaling and descaling input tensors, as well as amax output tensors.
C++ API#
// returns [o, stats, amax_s, amax_o]
std::array<std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes>, 4>
Graph::sdpa_fp8(std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> q,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> k,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> v,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> descale_q,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> descale_k,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> descale_v,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> descale_s,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> scale_s,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> scale_o,
SDPA_fp8_attributes attributes);
The options parameter of type SDPA_fp8_attributes is used to control the attributes of the forward operation, as detailed below:
// Indicates that softmax_stats should be generated (useful during training).
// If false, the softmax_stats output will be nullptr.
SDPA_fp8_attributes&
set_generate_stats(bool const value);
SDPA_fp8_attributes&
set_logit_max(std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> value);
SDPA_fp8_attributes&
set_score_sum_exp(std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> value);
SDPA_fp8_attributes&
set_attn_scale(std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> value);
SDPA_fp8_attributes&
set_attn_scale(float const value);
SDPA_fp8_attributes&
set_causal_mask(bool const value);
SDPA_fp8_attributes&
set_bias(std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> value);
SDPA_fp8_attributes&
set_padding_mask(bool const value);
SDPA_fp8_attributes&
set_seq_len_q(std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> value);
SDPA_fp8_attributes&
set_seq_len_kv(std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> value);
SDPA_fp8_attributes&
set_dropout(float const probability,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> seed,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> offset);
SDPA_fp8_attributes&
set_dropout(std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> mask,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> scale);
// DEPRECATED
// Calls set_generate_stats(!value) (note the negation of `value`).
SDPA_fp8_attributes&
set_is_inference(bool const value);
Python API#
Args:
q (cudnn_tensor): The query data.
k (cudnn_tensor): The key data.
v (cudnn_tensor): The value data.
descale_q (cudnn_tensor): Descale factor for query.
descale_k (cudnn_tensor): Descale factor for key.
descale_v (cudnn_tensor): Descale factor for value.
descale_s (cudnn_tensor): Descale factor for S tensor.
scale_s (cudnn_tensor): Scale factor for S tensor.
scale_o (cudnn_tensor): Scale factor for output.
attn_scale (Optional[Union[float, cudnn_tensor]]): The scale factor for attention. Default is None.
use_causal_mask (Optional[bool]): Whether to use causal mask. Default is False.
compute_data_type (Optional[cudnn.data_type]): The data type for computation. Default is NOT_SET.
name (Optional[str]): The name of the operation.
generate_stats (Optional[bool]): If true, compute and output softmax stats (useful at training time). Default is None, but one of {generate_stats, is_inference} must be set.
Deprecated Args:
is_inference (Optional[bool]): If false, compute and output softmax stats. Prefer generate_stats instead (NOTE: generate_stats takes the negation of the argument to is_inference).
Returns:
o (cudnn_tensor): The output data.
stats (Optional[cudnn_tensor]): The softmax statistics, if generate_stats is true.
amax_s (cudnn_tensor): The absolute maximum of S tensor.
amax_o (cudnn_tensor): The absolute maximum of output tensor.
Configurable Options#
The current FP8 support is a subset of the options supported in FP16 and BF16 support.
Attention scale (
attn_scale): Applies a scaling factor to attention scores before the softmax, such as \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{\text{d}}}\). Set to 1.0 by default.Causal mask: Fills the upper triangular matrix of attention scores with negative infinity.
Limitations#
Requires Hopper (SM90) or newer architecture.
Head dimension must be a multiple of 16.
Limited masking options compared to FP16/BF16 (causal mask only).
Requires explicit scale/descale tensors for all FP8 inputs and outputs.
Tensors#
The tensors in forward operation are defined as the following:
\(P = QK^T\)
\(S = \text{softmax}(P)\)
\(O = SV\)
Input Tensors#
Tensor Name |
Device |
Data Type |
Dimensions |
|---|---|---|---|
Q |
GPU |
E4M3 or E5M2 |
\((B, H_{q}, S_{q}, D_{qk})\) |
K |
GPU |
E4M3 or E5M2 |
\((B, H_{k}, S_{kv}, D_{qk})\) |
V |
GPU |
E4M3 or E5M2 |
\((B, H_{v}, S_{kv}, D_{v})\) |
Descale Q |
GPU |
FP32 |
\((1, 1, 1, 1)\) |
Descale K |
GPU |
FP32 |
\((1, 1, 1, 1)\) |
Descale V |
GPU |
FP32 |
\((1, 1, 1, 1)\) |
(Bias mask) Bias Mask |
GPU |
E4M3 or E5M2 |
\((1, 1, S_{q}, S_{kv})\), \((1, H_{q}, S_{q}, S_{kv})\), \((B, 1, S_{q}, S_{kv})\), or \((B, H_{q}, S_{q}, S_{kv})\) |
(Padding mask) Sequence Length Q |
GPU |
INT32 |
\((B, 1, 1, 1)\) |
(Padding mask) Sequence Length KV |
GPU |
INT32 |
\((B, 1, 1, 1)\) |
(Philox RNG Dropout) Seed |
CPU or GPU |
INT32 or INT64 |
\((1, 1, 1, 1)\) |
(Philox RNG Dropout) Offset |
CPU or GPU |
INT32 or INT64 |
\((1, 1, 1, 1)\) |
(Custom Dropout Mask) Mask |
GPU |
E4M3 or E5M2 |
\((1, 1, S_{q}, S_{kv})\), \((1, H_{q}, S_{q}, S_{kv})\), \((B, 1, S_{q}, S_{kv})\), or \((B, H_{q}, S_{q}, S_{kv})\) |
(Custom Dropout Mask) Scale |
GPU |
FP32 |
\((1, 1, 1, 1)\) |
Descale S |
GPU |
FP32 |
\((1, 1, 1, 1)\) |
Scale S |
GPU |
FP32 |
\((1, 1, 1, 1)\) |
Output Tensors#
Tensor Name |
Device |
Data Type |
Dimensions |
|---|---|---|---|
O |
GPU |
E4M3 or E5M2 |
\((B, H_{q}, S_{q}, D_{v})\) |
Stats (training only) |
GPU |
FP32 |
\((B, H_{q}, S_{q}, 1)\) |
AMax S |
GPU |
FP32 |
\((1, 1, 1, 1)\) |
AMax O |
GPU |
FP32 |
\((1, 1, 1, 1)\) |
Where:
\(B\) is the batch size
\(H_{q}\) is the number of query heads
\(H_{k}\) is the number of key heads
\(H_{v}\) is the number of value heads
\(S_{q}\) is the sequence length of the query
\(S_{kv}\) is the sequence length of the key and value
\(D_{qk}\) is the embedding dimension per head of query and key
\(D_{v}\) is the embedding dimension per head of value
Samples and tests#
C++ sample: samples/cpp/sdpa
SDPA FP8 Backward#
This operation computes the gradients for scaled dot product attention (SDPA) 8-bit floating point (FP8) datatype, using the FlashAttention-2 algorithm as described in the paper FlashAttention-2: Faster Attention with Better Parallelism and Work Partitioning. You are required to pass the stats tensor from the forward operation to the backward operation as input.
C++ sample: samples/cpp/sdpa
C++ API#
// returns [dQ, dK, dV, amax_dQ, amax_dK, amax_dV, amax_dP]
std::array<std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes>, 7>
Graph::sdpa_fp8_backward(std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> q,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> k,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> v,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> o,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> dO,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> Stats,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> descale_q,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> descale_k,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> descale_v,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> descale_o,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> descale_do,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> descale_s,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> descale_dp,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> scale_s,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> scale_dq,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> scale_dk,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> scale_dv,
std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> scale_dp,
SDPA_fp8_backward_attributes attributes);
The options parameter of type SDPA_fp8_backward_attributes is used to control the attributes of the backward operation, as detailed below:
SDPA_fp8_backward_attributes&
set_attn_scale(std::shared_ptr<Tensor_attributes> value);
SDPA_fp8_backward_attributes&
set_attn_scale(float const value);
SDPA_fp8_backward_attributes&
set_causal_mask(bool const value);
Python API#
Args:
q (cudnn_tensor): The query data.
k (cudnn_tensor): The key data.
v (cudnn_tensor): The value data.
o (cudnn_tensor): The output data.
dO (cudnn_tensor): The output gradient data.
stats (cudnn_tensor): The softmax statistics in case the operation is in a training step.
descale_q (cudnn_tensor): Descale factor for query.
descale_k (cudnn_tensor): Descale factor for key.
descale_v (cudnn_tensor): Descale factor for value.
descale_o (cudnn_tensor): Descale factor for output.
descale_dO (cudnn_tensor): Descale factor for output gradient.
descale_s (cudnn_tensor): Descale factor for S tensor.
descale_dP (cudnn_tensor): Descale factor for P gradient tensor.
scale_s (cudnn_tensor): Scale factor for S tensor.
scale_dQ (cudnn_tensor): Scale factor for query gradient.
scale_dK (cudnn_tensor): Scale factor for key gradient.
scale_dV (cudnn_tensor): Scale factor for value gradient.
scale_dP (cudnn_tensor): Scale factor for dP gradient.
attn_scale (Optional[Union[float, cudnn_tensor]]): The scale factor for attention. Default is None.
use_causal_mask (Optional[bool]): Whether to use causal mask. Default is False.
compute_data_type (Optional[cudnn.data_type]): The data type for computation. Default is NOT_SET.
name (Optional[str]): The name of the operation.
Returns:
dQ (cudnn_tensor): The query gradient data.
dK (cudnn_tensor): The key gradient data.
dV (cudnn_tensor): The value gradient data.
amax_dQ (cudnn_tensor): The absolute maximum of query gradient tensor.
amax_dK (cudnn_tensor): The absolute maximum of key gradient tensor.
amax_dV (cudnn_tensor): The absolute maximum of value gradient tensor.
amax_dP (cudnn_tensor): The absolute maximum of dP tensor.
Limitations#
Requires Hopper (SM90) or newer architecture.
Dropout is not supported in FP8 backward pass.
Only causal masking is supported.
Requires explicit scale/descale tensors for all FP8 inputs and outputs.
Tensors#
The tensors in backward operation are defined as the following:
\(dV = S^TdO\)
\(dS = dOV^T\)
\(dP = \text{dSoftmax}(dS)\)
\(dQ = dPK\)
\(dK = QdP\)
Input Tensors#
Tensor Name |
Device |
Data Type |
Dimensions |
|---|---|---|---|
Q |
GPU |
E4M3 or E5M2 |
\((B, H_{q}, S_{q}, D_{qk})\) |
K |
GPU |
E4M3 or E5M2 |
\((B, H_{k}, S_{kv}, D_{qk})\) |
V |
GPU |
E4M3 or E5M2 |
\((B, H_{v}, S_{kv}, D_{v})\) |
O |
GPU |
E4M3 or E5M2 |
\((B, H_{q}, S_{q}, D_{v})\) |
dO |
GPU |
E4M3 or E5M2 |
\((B, H_{q}, S_{q}, D_{v})\) |
Stats |
GPU |
FP32 |
\((B, H_{q}, S_{q}, 1)\) |
Descale Q |
GPU |
FP32 |
\((1, 1, 1, 1)\) |
Descale K |
GPU |
FP32 |
\((1, 1, 1, 1)\) |
Descale V |
GPU |
FP32 |
\((1, 1, 1, 1)\) |
Descale O |
GPU |
FP32 |
\((1, 1, 1, 1)\) |
Descale dO |
GPU |
FP32 |
\((1, 1, 1, 1)\) |
Descale S |
GPU |
FP32 |
\((1, 1, 1, 1)\) |
Descale dP |
GPU |
FP32 |
\((1, 1, 1, 1)\) |
Scale S |
GPU |
FP32 |
\((1, 1, 1, 1)\) |
Scale dQ |
GPU |
FP32 |
\((1, 1, 1, 1)\) |
Scale dK |
GPU |
FP32 |
\((1, 1, 1, 1)\) |
Scale dV |
GPU |
FP32 |
\((1, 1, 1, 1)\) |
Scale dP |
GPU |
FP32 |
\((1, 1, 1, 1)\) |
Output Tensors#
Tensor Name |
Device |
Data Type |
Dimensions |
|---|---|---|---|
dQ |
GPU |
E4M3 or E5M2 |
\((B, H_{q}, S_{q}, D_{qk})\) |
dK |
GPU |
E4M3 or E5M2 |
\((B, H_{k}, S_{kv}, D_{qk})\) |
dV |
GPU |
E4M3 or E5M2 |
\((B, H_{v}, S_{kv}, D_{v})\) |
Amax dQ |
GPU |
FP32 |
\((1, 1, 1, 1)\) |
Amax dK |
GPU |
FP32 |
\((1, 1, 1, 1)\) |
Amax dV |
GPU |
FP32 |
\((1, 1, 1, 1)\) |
Amax dP |
GPU |
FP32 |
\((1, 1, 1, 1)\) |
Where:
\(B\) is the batch size
\(H_{q}\) is the number of query heads
\(H_{k}\) is the number of key heads
\(H_{v}\) is the number of value heads
\(S_{q}\) is the sequence length of the query
\(S_{kv}\) is the sequence length of the key and value
\(D_{qk}\) is the embedding dimension per head of query and key
\(D_{v}\) is the embedding dimension per head of value
FAQs#
Logical vs Physical Layout#
BHSD Layout (Batch-Head-Sequence-Dim)#
The default logical layout where dimensions are ordered as \((B, H, S, D)\).
Dimensions: \([B, H_q, S_q, D_{qk}]\)
Strides: \([H_q \times S_q \times D_{qk}, S_q \times D_{qk}, D_{qk}, 1]\)
This is the most common layout and matches PyTorch’s default attention tensor ordering.
BSHD Layout (Batch-Sequence-Head-Dim)#
A physical layout where sequence comes before heads in memory, while maintaining the logical \((B, H, S, D)\) dimension order.
Dimensions: \([B, H_q, S_q, D_{qk}]\) (logical order, unchanged)
Strides: \([S_q \times H_q \times D_{qk}, D_{qk}, H_q \times D_{qk}, 1]\)
Note: The dimension order remains \((B, H, S, D)\) but strides are reordered so that in memory, sequence varies faster than head.
cuDNN Flex Attention API#
SDPA and SDPA backward operations now accept the functions set_score_mod and set_score_mod_bprop, which allows modification of the attention score matrix. These functions can be used to program a sub-graph of pointwise operations that can subsequently be used to program the score modifier. Note that this function usage is mutually exclusive to the usage of ready made options. Also, note that the graph argument in the score_mod function is not the same as the sdpa graph. So, any tensor to be passed as input to the score-mod sub-graph must first be registered with main graph and subsequently passed as argument to the score_mod function. The SDPA operation also now accepts the function set_block_mask, which applies a block mask to the score matrix. The implementation assumes a 128 x 128 block size.