OpenvSwitch Offload
Open vSwitch (OVS) is a software-based network technology that enhances virtual machine (VM) communication within internal and external networks. Typically deployed in the hypervisor, OVS employs a software-based approach for packet switching, which can strain CPU resources, impacting system performance and network bandwidth utilization. Addressing this, NVIDIA's Accelerated Switching and Packet Processing (ASAP2) technology offloads OVS data-plane tasks to specialized hardware, like the embedded switch (eSwitch) within the NIC subsystem, while maintaining an unmodified OVS control-plane. This results in notably improved OVS performance without burdening the CPU.
NVIDIA's OVS architecture extends the traditional OVS-DPDK and OVS-Kernel data-path offload interfaces, introducing OVS-DOCA as an additional implementation. OVS-DOCA, built upon NVIDIA's networking API, preserves the same interfaces as OVS-DPDK and OVS-Kernel while utilizing the DOCA Flow library. Unlike the other modes, OVS-DOCA exploits unique hardware offload mechanisms and application techniques, maximizing performance and features for NVIDA NICs and DPUs. This mode is especially efficient due to its architecture and DOCA library integration, enhancing e-switch configuration and accelerating hardware offloads beyond what the other modes can achieve.
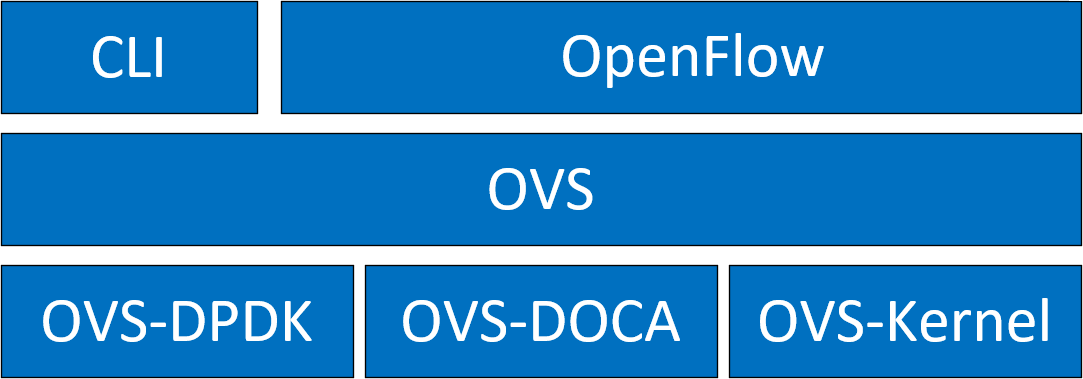
NVIDIA OVS installation contains all three OVS flavors. The following subsections describe the three flavors (default is OVS-Kernel) and how to configure each of them.
OVS and Virtualized Devices
When OVS is combined with NICs and DPUs (such as NVIDIA® ConnectX®-6 Lx/Dx and NVIDIA® BlueField®-2 and later), it utilizes the hardware data plane of ASAP2. This data plane can establish connections to VMs using either SR-IOV virtual functions (VFs) or virtual host data path acceleration (vDPA) with virtio.
In both scenarios, an accelerator engine within the NIC accelerates forwarding and offloads the OVS rules. This integrated solution accelerates both the infrastructure (via VFs through SR-IOV or virtio) and the data plane. For DPUs (which include a NIC subsystem), an alternate virtualization technology implements full virtio emulation within the DPU, enabling the host server to communicate with the DPU as a software virtio device.
When using ASAP2 data plane over SR-IOV virtual functions (VFs), the VF is directly passed through to the VM, with the NVIDIA driver running within the VM.
When using vDPA, the vDPA driver allows VMs to establish their connections through VirtIO. As a result, the data plane is established between the SR-IOV VF and the standard virtio driver within the VM, while the control plane is managed on the host by the vDPA application.
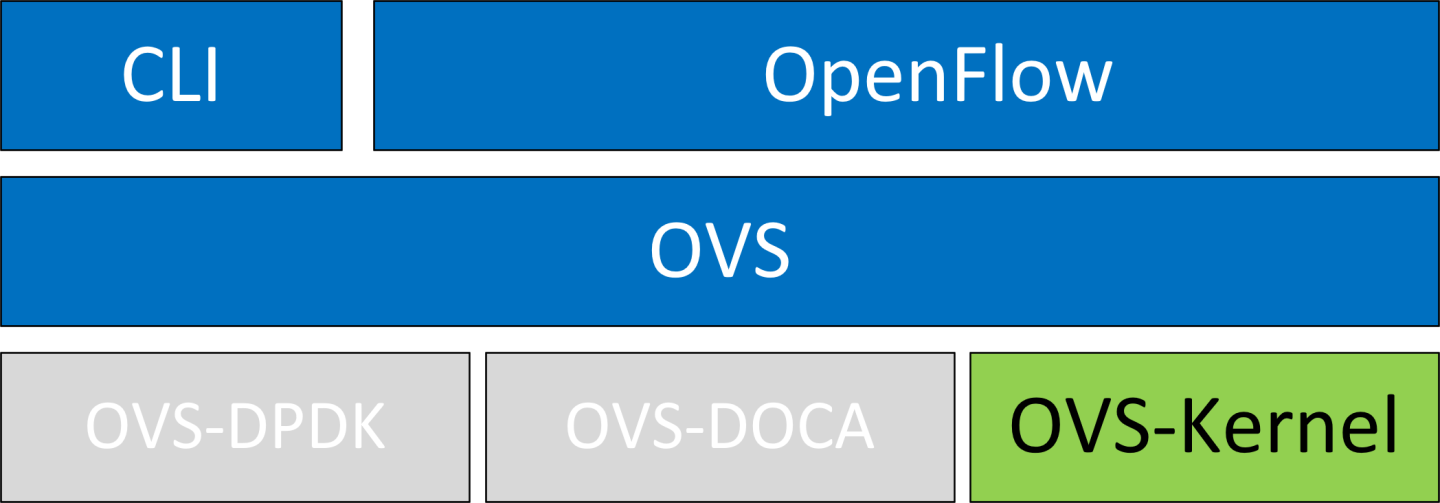
OVS-Kernel Hardware Offloads
OVS-Kernel is the default OVS flavor enabled on your NVIDIA device.
Switchdev Configuration
Unbind the VFs:
echo
0000:04:00.2> /sys/bus/pci/drivers/mlx5_core/unbind echo0000:04:00.3> /sys/bus/pci/drivers/mlx5_core/unbindNoteVMs with attached VFs must be powered off to be able to unbind the VFs.
Change the eSwitch mode from legacy to switchdev on the PF device:
# devlink dev eswitch set pci/
0000:3b:00.0mode switchdevThis also creates the VF representor netdevices in the host OS.
NoteBefore changing the mode, make sure that all VFs are unbound.
InfoTo return to SR-IOV legacy mode, run:
# devlink dev eswitch set pci/
0000:3b:00.0mode legacyThis also removes the VF representor netdevices.
On OSes or kernels that do not support devlink, moving to switchdev mode can be done using sysfs:
# echo switchdev > /sys/
class/net/enp4s0f0/compat/devlink/modeAt this stage, VF representors have been created. To map a representor to its VF, make sure to obtain the representor's switchid and portname by running:
# ip -d link show eth4
41: enp0s8f0_1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu1500qdisc mq state UP mode DEFAULT groupdefaultqlen1000link/ether ba:e6:21:37:bc:d4 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff promiscuity0addrgenmode eui64 numtxqueues10numrxqueues10gso_max_size65536gso_max_segs65535portname pf0vf1 switchid f4ab580003a1420cWhere:
switchid – used to map representor to device, both device PFs have the same switchid
portname – used to map representor to PF and VF. Value returned is pf<X>vf<Y>, where X is the PF number and Y is the number of VF.
Bind the VFs:
echo
0000:04:00.2> /sys/bus/pci/drivers/mlx5_core/bind echo0000:04:00.3> /sys/bus/pci/drivers/mlx5_core/bind
Switchdev Performance Tuning
Switchdev tuning improves its performance.
Steering Mode
OVS-kernel supports two steering modes for rule insertion into hardware:
SMFS (software-managed flow steering) – default mode; rules are inserted directly to the hardware by the software (driver). This mode is optimized for rule insertion.
DMFS (device-managed flow steering) – rule insertion is done using firmware commands. This mode is optimized for throughput with a small amount of rules in the system.
The steering mode can be configured via sysfs or devlink API in kernels that support it:
For sysfs:
echo <smfs|dmfs> > /sys/
class/net/<pf-netdev>/compat/devlink/steering_modeFor devlink:
devlink dev param set pci/
0000:00:08.0name flow_steering_mode value"<smfs|dmfs>"cmode runtime
Notes:
The mode should be set prior to moving to switchdev, by echoing to the sysfs or invoking the devlink command.
Only when moving to switchdev will the driver use the mode configured.
Mode cannot be changed after moving to switchdev.
The steering mode is applicable for switchdev mode only (i.e., it does not affect legacy SR-IOV or other configurations).
Troubleshooting SMFS
mlx5 debugfs supports presenting Software Steering resources. dr_domain including its tables, matchers and rules. The interface is read-only.
New steering rules cannot be inserted/deleted w hile the dump is being created,
The steering information is dumped in the CSV form in the following format: <object_type>,<object_ID>, <object_info>,...,<object_info> .
This data can be read at the following path: /sys/kernel/debug/mlx5/<BDF>/steering/fdb/<domain_handle> .
Example:
# cat /sys/kernel/debug/mlx5/0000:82:00.0/steering/fdb/dmn_000018644
3100,0x55caa4621c50,0xee802,4,65533
3101,0x55caa4621c50,0xe0100008
You can then use the steering dump parser to make the output more human-readable.
The parser can be found in this GitHub repository.
vPort Match Mode
OVS-kernel support two modes that define how the rules match on vport.
|
Mode |
Description |
|
Metadata |
Rules match on metadata instead of vport number (default mode). This mode is needed to support SR-IOV live migration and dual-port RoCE. Note
Matching on Metadata can have a performance impact.
|
|
Legacy |
Rules match on vport number. In this mode, performance can be higher in comparison to Metadata. It can be used only if SR-IOV live migration or dual port RoCE are enabled/used. |
vPort match mode can be controlled via sysfs:
Set legacy:
echo legacy > /sys/
class/net/<PF netdev>/compat/devlink/vport_match_modeSet metadata:
echo metadata > /sys/
class/net/<PF netdev>/compat/devlink/vport_match_mode
This mode must be set prior to moving to switchdev.
Flow Table Large Group Number
Offloaded flows, including connection tracking (CT), are added to the virtual switch forwarding data base (FDB) flow tables. FDB tables have a set of flow groups, where each flow group saves the same traffic pattern flows. For example, for CT offloaded flow, TCP and UDP are different traffic patterns which end up in two different flow groups.
A flow group has a limited size to save flow entries. By default, the driver has 15 big FDB flow groups. Each of these big flow groups can save 4M/(15+1)=256k different 5-tuple flow entries at most. For scenarios with more than 15 traffic patterns, the driver provides a module parameter (num_of_groups) to allow customization and performance tuning.
The mode can be controlled via module param or devlink API for kernels that support it:
Module param:
echo <num_of_groups> > /sys/module/mlx5_core/parameters/num_of_groups
Devlink:
devlink dev param set pci/
0000:82:00.0name fdb_large_groups cmode driverinit value20
The change takes effect immediately if no flows are inside the FDB table (no traffic running and all offloaded flows are aged out). And it can be dynamically changed without reloading the driver. If there are still offloaded flows when changing this parameter, it takes effect after all flows have aged out.
Open vSwitch Configuration
OVS configuration is a simple OVS bridge configuration with switchdev.
Run the OVS service:
systemctl start openvswitch
Create an OVS bridge (named ovs-sriov here):
ovs-vsctl add-br ovs-sriov
Enable hardware offload (disabled by default):
ovs-vsctl set Open_vSwitch . other_config:hw-offload=
trueRestart the OVS service:
systemctl restart openvswitch
This step is required for hardware offload changes to take effect.
Add the PF and the VF representor netdevices as OVS ports:
ovs-vsctl add-port ovs-sriov enp4s0f0 ovs-vsctl add-port ovs-sriov enp4s0f0_0 ovs-vsctl add-port ovs-sriov enp4s0f0_1
Make sure to bring up the PF and representor netdevices:
ip link set dev enp4s0f0 up ip link set dev enp4s0f0_0 up ip link set dev enp4s0f0_1 up
The PF represents the uplink (wire):
# ovs-dpctl show system
@ovs-system: lookups: hit:0missed:192lost:1flows:2masks: hit:384total:2hit/pkt:2.00port0: ovs-system (internal) port1: ovs-sriov (internal) port2: enp4s0f0 port3: enp4s0f0_0 port4: enp4s0f0_1Run traffic from the VFs and observe the rules added to the OVS data-path:
# ovs-dpctl dump-flows recirc_id(
0),in_port(3),eth(src=e4:11:22:33:44:50,dst=e4:1d:2d:a5:f3:9d), eth_type(0x0800),ipv4(frag=no), packets:33, bytes:3234, used:1.196s, actions:2recirc_id(0),in_port(2),eth(src=e4:1d:2d:a5:f3:9d,dst=e4:11:22:33:44:50), eth_type(0x0800),ipv4(frag=no), packets:34, bytes:3332, used:1.196s, actions:3In this example, the ping is initiated from VF0 (OVS port 3) to the outer node (OVS port 2), where the VF MAC is e4:11:22:33:44:50 and the outer node MAC is e4:1d:2d:a5:f3:9d. As previously shown, two OVS rules are added, one in each direction.
NoteUsers can also verify offloaded packets by adding type=offloaded to the command. For example:
ovs-appctl dpctl/dump-flows type=offloaded
OVS Performance Tuning
Flow Aging
The aging timeout of OVS is given in milliseconds and can be controlled by running:
ovs-vsctl set Open_vSwitch . other_config:max-idle=30000
TC Policy
Specifies the policy used with hardware offloading:
none – adds a TC rule to both the software and the hardware (default)
skip_sw – adds a TC rule only to the hardware
skip_hw – adds a TC rule only to the software
Example:
ovs-vsctl set Open_vSwitch . other_config:tc-policy=skip_sw
TC policy should only be used for debugging purposes.
max-revalidator
Specifies the maximum time (in milliseconds) for the revalidator threads to wait for kernel statistics before executing flow revalidation.
ovs-vsctl set Open_vSwitch . other_config:max-revalidator=10000
n-handler-threads
Specifies the number of threads for software datapaths to use to handle new flows.
ovs-vsctl set Open_vSwitch . other_config:n-handler-threads=4
The default value is the number of online CPU cores minus the number of revalidators.
n-revalidator-threads
Specifies the number of threads for software datapaths to use to revalidate flows in the datapath.
ovs-vsctl set Open_vSwitch . other_config:n-revalidator-threads=4
vlan-limit
Limits the number of VLAN headers that can be matched to the specified number.
ovs-vsctl set Open_vSwitch . other_config:vlan-limit=2
Basic TC Rules Configuration
Offloading rules can also be added directly, and not only through OVS, using the tc utility.
To create an offloading rule using TC:
Create an ingress qdisc (queueing discipline) for each interface that you wish to add rules into:
tc qdisc add dev enp4s0f0 ingress tc qdisc add dev enp4s0f0_0 ingress tc qdisc add dev enp4s0f0_1 ingress
Add TC rules using flower classifier in the following format:
tc filter add dev NETDEVICE ingress protocol PROTOCOL prio PRIORITY [chain CHAIN] flower [MATCH_LIST] [action ACTION_SPEC]
NoteA list of supported matches (specifications) and actions can be found in section "Classification Fields (Matches)".
Dump the existing tc rules using flower classifier in the following format:
tc [-s] filter show dev NETDEVICE ingress
SR-IOV VF LAG
SR-IOV VF LAG allows the NIC's physical functions (PFs) to get the rules that the OVS tries to offload to the bond net-device, and to offload them to the hardware e-switch.
The supported bond modes are as follows:
Active-backup
XOR
LACP
SR-IOV VF LAG enables complete offload of the LAG functionality to the hardware. The bonding creates a single bonded PF port. Packets from the up-link can arrive from any of the physical ports and are forwarded to the bond device.
When hardware offload is used, packets from both ports can be forwarded to any of the VFs. Traffic from the VF can be forwarded to both ports according to the bonding state. This means that when in active-backup mode, only one PF is up, and traffic from any VF goes through this PF. When in XOR or LACP mode, if both PFs are up, traffic from any VF is split between these two PFs.
SR-IOV VF LAG Configuration on ASAP2
To enable SR-IOV VF LAG, both physical functions of the NIC must first be configured to SR-IOV switchdev mode, and only afterwards bond the up-link representors.
The following example shows the creation of a bond interface over two PFs:
Load the bonding device and subordinate the up-link representor (currently PF) net-device devices:
modprobe bonding mode=
802.3ad Ifup bond0 (make sure ifcfg file is present with desired bond configuration) ip link set enp4s0f0 master bond0 ip link set enp4s0f1 master bond0Add the VF representor net-devices as OVS ports. If tunneling is not used, add the bond device as well.
ovs-vsctl add-port ovs-sriov bond0 ovs-vsctl add-port ovs-sriov enp4s0f0_0 ovs-vsctl add-port ovs-sriov enp4s0f1_0
Bring up the PF and the representor netdevices:
ip link set dev bond0 up ip link set dev enp4s0f0_0 up ip link set dev enp4s0f1_0 up
Once the SR-IOV VF LAG is configured, all VFs of the two PFs become part of the bond and behave as described above.
Using TC with VF LAG
Both rules can be added either with or without shared block:
With shared block (supported from kernel 4.16 and RHEL/CentOS 7.7 and above):
tc qdisc add dev bond0 ingress_block
22ingress tc qdisc add dev ens4p0 ingress_block22ingress tc qdisc add dev ens4p1 ingress_block22ingressAdd drop rule:
# tc filter add block
22protocol arp parent ffff: prio3\ flower \ dst_mac e4:11:22:11:4a:51\ action dropAdd redirect rule from bond to representor:
# tc filter add block
22protocol arp parent ffff: prio3\ flower \ dst_mac e4:11:22:11:4a:50\ action mirred egress redirect dev ens4f0_0Add redirect rule from representor to bond:
# tc filter add dev ens4f0_0 protocol arp parent ffff: prio
3\ flower \ dst_mac ec:0d:9a:8a:28:42\ action mirred egress redirect dev bond0
Without shared block (supported from kernel 4.15 and below):
Add redirect rule from bond to representor:
# tc filter add dev bond0 protocol arp parent ffff: prio
1\ flower \ dst_mac e4:11:22:11:4a:50\ action mirred egress redirect dev ens4f0_0Add redirect rule from representor to bond:
# tc filter add dev ens4f0_0 protocol arp parent ffff: prio
3\ flower \ dst_mac ec:0d:9a:8a:28:42\ action mirred egress redirect dev bond0
Classification Fields (Matches)
OVS-Kernel supports multiple classification fields which packets can fully or partially match.
Ethernet Layer 2
Destination MAC
Source MAC
Ethertype
Supported on all kernels.
In OVS dump flows:
skb_priority(0/0),skb_mark(0/0),in_port(eth6),eth(src=00:02:10:40:10:0d,dst=68:54:ed:00:af:de),eth_type(0x8100), packets:1981, bytes:206024, used:0.440s, dp:tc, actions:eth7
Using TC rules:
tc filter add dev $rep parent ffff: protocol arp pref 1 \
flower \
dst_mac e4:1d:2d:5d:25:35 \
src_mac e4:1d:2d:5d:25:34 \
action mirred egress redirect dev $NIC
IPv4/IPv6
Source address
Destination address
Protocol
TCP/UDP/ICMP/ICMPv6
TOS
TTL (HLIMIT)
Supported on all kernels.
In OVS dump flows:
Ipv4:
ipv4(src=0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0,dst=0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0,proto=17,tos=0/0,ttl=0/0,frag=no)
Ipv6:
ipv6(src=::/::,dst=1:1:1::3:1040:1008,label=0/0,proto=58,tclass=0/0x3,hlimit=64),
Using TC rules:
IPv4:
tc filter add dev $rep parent ffff: protocol ip pref 1 \
flower \
dst_ip 1.1.1.1 \
src_ip 1.1.1.2 \
ip_proto TCP \
ip_tos 0x3 \
ip_ttl 63 \
action mirred egress redirect dev $NIC
IPv6:
tc filter add dev $rep parent ffff: protocol ipv6 pref 1 \
flower \
dst_ip 1:1:1::3:1040:1009 \
src_ip 1:1:1::3:1040:1008 \
ip_proto TCP \
ip_tos 0x3 \
ip_ttl 63\
action mirred egress redirect dev $NIC
TCP/UDP Source and Destination Ports and TCP Flags
TCP/UDP source and destinations ports
TCP flags
Supported on kernel >4.13 and RHEL >7.5.
In OVS dump flows:
TCP: tcp(src=0/0,dst=32768/0x8000),
UDP: udp(src=0/0,dst=32768/0x8000),
TCP flags: tcp_flags(0/0)
Using TC rules:
tc filter add dev $rep parent ffff: protocol ip pref 1 \
flower \
ip_proto TCP \
dst_port 100 \
src_port 500 \
tcp_flags 0x4/0x7 \
action mirred egress redirect dev $NIC
VLAN
ID
Priority
Inner vlan ID and Priority
Supported kernels: All (QinQ: kernel 4.19 and higher, and RHEL 7.7 and higher).
In OVS dump flows:
eth_type(0x8100),vlan(vid=2347,pcp=0),
Using TC rules:
tc filter add dev $rep parent ffff: protocol 802.1Q pref 1 \
flower \
vlan_ethtype 0x800 \
vlan_id 100 \
vlan_prio 0 \
action mirred egress redirect dev $NIC
QinQ:
tc filter add dev $rep parent ffff: protocol 802.1Q pref 1 \
flower \
vlan_ethtype 0x8100 \
vlan_id 100 \
vlan_prio 0 \
cvlan_id 20 \
cvlan_prio 0 \
cvlan_ethtype 0x800 \
action mirred egress redirect dev $NIC
Tunnel
ID (Key)
Source IP address
Destination IP address
Destination port
TOS (supported from kernel 4.19 and above & RHEL 7.7 and above)
TTL (support from kernel 4.19 and above & RHEL 7.7 and above)
Tunnel options (Geneve)
Supported kernels:
VXLAN: All
GRE: Kernel >5.0, RHEL 7.7 and above
Geneve: Kernel >5.0, RHEL 7.7 and above
In OVS dump flows:
tunnel(tun_id=0x5,src=121.9.1.1,dst=131.10.1.1,ttl=0/0,tp_dst=4789,flags(+key))
Using TC rules:
# tc filter add dev $rep protocol 802.1Q parent ffff: pref 1
flower \
vlan_ethtype 0x800 \
vlan_id 100 \
vlan_prio 0 \
action mirred egress redirect dev $NIC
QinQ:
# tc filter add dev vxlan100 protocol ip parent ffff: \
flower \
skip_sw \
dst_mac e4:11:22:11:4a:51 \
src_mac e4+:11:22:11:4a:50 \
enc_src_ip 20.1.11.1 \
enc_dst_ip 20.1.12.1 \
enc_key_id 100 \
enc_dst_port 4789 \
action tunnel_key unset \
action mirred egress redirect dev ens4f0_0
Supported Actions
Forward
Forward action allows for packet redirection:
From VF to wire
Wire to VF
VF to VF
Supported on all kernels.
In OVS dump flows:
skb_priority(0/0),skb_mark(0/0),in_port(eth6),eth(src=00:02:10:40:10:0d,dst=68:54:ed:00:af:de),eth_type(0x8100), packets:1981, bytes:206024, used:0.440s, dp:tc, actions:eth7
Using TC rules:
tc filter add dev $rep parent ffff: protocol arp pref 1 \
flower \
dst_mac e4:1d:2d:5d:25:35 \
src_mac e4:1d:2d:5d:25:34 \
action mirred egress redirect dev $NIC
Drop
Drop action allows to drop incoming packets.
Supported on all kernels.
In OVS dump flows:
skb_priority(0/0),skb_mark(0/0),in_port(eth6),eth(src=00:02:10:40:10:0d,dst=68:54:ed:00:af:de),eth_type(0x8100), packets:1981, bytes:206024, used:0.440s, dp:tc, actions:drop
Using TC rules:
tc filter add dev $rep parent ffff: protocol arp pref 1 \
flower \
dst_mac e4:1d:2d:5d:25:35 \
src_mac e4:1d:2d:5d:25:34 \
action drop
Statistics
By default, each flow collects the following statistics:
Packets – number of packets which hit the flow
Bytes – total number of bytes which hit the flow
Last used – the amount of time passed since last packet hit the flow
Supported on all kernels.
In OVS dump flows:
skb_priority(0/0),skb_mark(0/0),in_port(eth6),eth(src=00:02:10:40:10:0d,dst=68:54:ed:00:af:de),eth_type(0x8100), packets:1981, bytes:206024, used:0.440s, dp:tc, actions:drop
Using TC rules:
#tc -s filter show dev $rep ingress
filter protocol ip pref 2 flower chain 0
filter protocol ip pref 2 flower chain 0 handle 0x2
eth_type ipv4
ip_proto tcp
src_ip 192.168.140.100
src_port 80
skip_sw
in_hw
action order 1: mirred (Egress Redirect to device p0v11_r) stolen
index 34 ref 1 bind 1 installed 144 sec used 0 sec
Action statistics:
Sent 388344 bytes 2942 pkt (dropped 0, overlimits 0 requeues 0)
backlog 0b 0p requeues 0
Tunnels: Encapsulation/Decapsulation
OVS-kernel supports offload of tunnels using encapsulation and decapsulation actions.
Encapsulation – pushing of tunnel header is supported on Tx
Decapsulation – popping of tunnel header is supported on Rx
Supported Tunnels:
VXLAN (IPv4/IPv6) – supported on all Kernels
GRE (IPv4/IPv6) – supported on kernel 5.0 and above & RHEL 7.6 and above
Geneve (IPv4/IPv6) – supported on kernel 5.0 and above & RHEL 7.6 and above
OVS configuration:
In case of offloading tunnel, the PF/bond should not be added as a port in the OVS datapath. It should rather be assigned with the IP address to be used for encapsulation.
The following example shows two hosts (PFs) with IPs 1.1.1.177 and 1.1.1.75, where the PF device on both hosts is enp4s0f0, and the VXLAN tunnel is set with VNID 98:
On the first host:
# ip addr add
1.1.1.177/24dev enp4s0f1 # ovs-vsctl add-port ovs-sriov vxlan0 -- setinterfacevxlan0 type=vxlan options:local_ip=1.1.1.177options:remote_ip=1.1.1.75options:key=98On the second host:
# ip addr add
1.1.1.75/24dev enp4s0f1 # ovs-vsctl add-port ovs-sriov vxlan0 -- setinterfacevxlan0 type=vxlan options:local_ip=1.1.1.75options:remote_ip=1.1.1.177options:key=98InfoFor a GRE IPv4 tunnel, use type=gre. For a GRE IPv6 tunnel, use type=ip6gre. For a Geneve tunnel, use type=geneve.
When encapsulating guest traffic, the VF's device MTU must be reduced to allow the host/hardware to add the encap headers without fragmenting the resulted packet. As such, the VF's MTU must be lowered by 50 bytes from the uplink MTU for IPv4 and 70 bytes for IPv6.
Tunnel offload using TC rules:
Encapsulation:
# tc filter add dev ens4f0_0 protocol 0x806 parent ffff: \
flower \
skip_sw \
dst_mac e4:11:22:11:4a:51 \
src_mac e4:11:22:11:4a:50 \
action tunnel_key set \
src_ip 20.1.12.1 \
dst_ip 20.1.11.1 \
id 100 \
action mirred egress redirect dev vxlan100
Decapsulation:
# tc filter add dev vxlan100 protocol 0x806 parent ffff: \
flower \
skip_sw \
dst_mac e4:11:22:11:4a:51 \
src_mac e4:11:22:11:4a:50 \
enc_src_ip 20.1.11.1 \
enc_dst_ip 20.1.12.1 \
enc_key_id 100 \
enc_dst_port 4789 \
action tunnel_key unset \
action mirred egress redirect dev ens4f0_0
VLAN Push/Pop
OVS-kernel supports offload of VLAN header push/pop actions:
Push – pushing of VLAN header is supported on Tx
Pop – popping of tunnel header is supported on Rx
OVS Configuration
Add a tag=$TAG section for the OVS command line that adds the representor ports. For example, VLAN ID 52 is being used here.
# ovs-vsctl add-port ovs-sriov enp4s0f0
# ovs-vsctl add-port ovs-sriov enp4s0f0_0 tag=52
# ovs-vsctl add-port ovs-sriov enp4s0f0_1 tag=52
The PF port should not have a VLAN attached. This will cause OVS to add VLAN push/pop actions when managing traffic for these VFs.
Dump Flow Example
recirc_id(0),in_port(3),eth(src=e4:11:22:33:44:50,dst=00:02:c9:e9:bb:b2),eth_type(0x0800),ipv4(frag=no), \
packets:0, bytes:0, used:never, actions:push_vlan(vid=52,pcp=0),2
recirc_id(0),in_port(2),eth(src=00:02:c9:e9:bb:b2,dst=e4:11:22:33:44:50),eth_type(0x8100), \
vlan(vid=52,pcp=0),encap(eth_type(0x0800),ipv4(frag=no)), packets:0, bytes:0, used:never, actions:pop_vlan,3
VLAN Offload Using TC Rules Example
# tc filter add dev ens4f0_0 protocol ip parent ffff: \
flower \
skip_sw \
dst_mac e4:11:22:11:4a:51 \
src_mac e4:11:22:11:4a:50 \
action vlan push id 100 \
action mirred egress redirect dev ens4f0
# tc filter add dev ens4f0 protocol 802.1Q parent ffff: \
flower \
skip_sw \
dst_mac e4:11:22:11:4a:51 \
src_mac e4:11:22:11:4a:50 \
vlan_ethtype 0x800 \
vlan_id 100 \
vlan_prio 0 \
action vlan pop \
action mirred egress redirect dev ens4f0_0
TC Configuration
Example of VLAN Offloading with popping header on Tx and pushing on Rx using TC rules:
# tc filter add dev ens4f0_0 ingress protocol 802.1Q parent ffff: \
flower \
vlan_id 100 \
action vlan pop \
action tunnel_key set \
src_ip 4.4.4.1 \
dst_ip 4.4.4.2 \
dst_port 4789 \
id 42 \
action mirred egress redirect dev vxlan0
# tc filter add dev vxlan0 ingress protocol all parent ffff: \
flower \
enc_dst_ip 4.4.4.1 \
enc_src_ip 4.4.4.2 \
enc_dst_port 4789 \
enc_key_id 42 \
action tunnel_key unset \
action vlan push id 100 \
action mirred egress redirect dev ens4f0_0
Header Rewrite
This action allows for modifying packet fields.
Ethernet Layer 2
Destination MAC
Source MAC
Supported kernels:
Kernel 4.14 and above
RHEL 7.5 and above
In OVS dump flows:
skb_priority(0/0),skb_mark(0/0),in_port(eth6),eth(src=00:02:10:40:10:0d,dst=68:54:ed:00:af:de),eth_type(0x8100), packets:1981, bytes:206024, used:0.440s, dp:tc, actions: set(eth(src=68:54:ed:00:f4:ab,dst=fa:16:3e:dd:69:c4)),eth7
Using TC rules:
tc filter add dev $rep parent ffff: protocol arp pref 1 \
flower \
dst_mac e4:1d:2d:5d:25:35 \
src_mac e4:1d:2d:5d:25:34 \
action pedit ex \
munge eth dst set 20:22:33:44:55:66 \
munge eth src set aa:ba:cc:dd:ee:fe \
action mirred egress redirect dev $NIC
IPv4/IPv6
Source address
Destination address
Protocol
TOS
TTL (HLIMIT)
Supported kernels:
Kernel 4.14 and above
RHEL 7.5 and above
In OVS dump flows:
Ipv4:
set(eth(src=de:e8:ef:27:5e:45,dst=00:00:01:01:01:01)),
set(ipv4(src=10.10.0.111,dst=10.20.0.122,ttl=63))
Ipv6:
set(ipv6(dst=2001:1:6::92eb:fcbe:f1c8,hlimit=63)),
Using TC rules:
IPv4:
tc filter add dev $rep parent ffff: protocol ip pref 1 \
flower \
dst_ip 1.1.1.1 \
src_ip 1.1.1.2 \
ip_proto TCP \
ip_tos 0x3 \
ip_ttl 63 \
pedit ex \
munge ip src set 2.2.2.1 \
munge ip dst set 2.2.2.2 \
munge ip tos set 0 \
munge ip ttl dec \
action mirred egress redirect dev $NIC
IPv6:
tc filter add dev $rep parent ffff: protocol ipv6 pref 1 \
flower \
dst_ip 1:1:1::3:1040:1009 \
src_ip 1:1:1::3:1040:1008 \
ip_proto tcp \
ip_tos 0x3 \
ip_ttl 63\
pedit ex \
munge ipv6 src set 2:2:2::3:1040:1009 \
munge ipv6 dst set 2:2:2::3:1040:1008 \
munge ipv6 hlimit dec \
action mirred egress redirect dev $NIC
IPv4 and IPv6 header rewrite is only supported with match on UDP/TCP/ICMP protocols.
TCP/UDP Source and Destination Ports
TCP/UDP source and destinations ports
Supported kernels:
Kernel 4.16 and above
RHEL 7.6 and above
In OVS dump flows:
TCP:
set(tcp(src= 32768/0xffff,dst=32768/0xffff)),
UDP:
set(udp(src= 32768/0xffff,dst=32768/0xffff)),
Using TC rules:
TCP:
tc filter add dev $rep parent ffff: protocol ip pref 1 \
flower \
dst_ip 1.1.1.1 \
src_ip 1.1.1.2 \
ip_proto tcp \
ip_tos 0x3 \
ip_ttl 63 \
pedit ex \
pedit ex munge ip tcp sport set 200
pedit ex munge ip tcp dport set 200
action mirred egress redirect dev $NIC
UDP:
tc filter add dev $rep parent ffff: protocol ip pref 1 \
flower \
dst_ip 1.1.1.1 \
src_ip 1.1.1.2 \
ip_proto udp \
ip_tos 0x3 \
ip_ttl 63 \
pedit ex \
pedit ex munge ip udp sport set 200
pedit ex munge ip udp dport set 200
action mirred egress redirect dev $NIC
VLAN
ID
Supported on all kernels.
In OVS dump flows:
Set(vlan(vid=2347,pcp=0/0)),
Using TC rules:
tc filter add dev $rep parent ffff: protocol 802.1Q pref 1 \
flower \
vlan_ethtype 0x800 \
vlan_id 100 \
vlan_prio 0 \
action vlan modify id 11 pipe
action mirred egress redirect dev $NIC
Connection Tracking
The TC connection tracking (CT) action performs CT lookup by sending the packet to netfilter conntrack module. Newly added connections may be associated, via the ct commit action, with a 32 bit mark, 128 bit label, and source/destination NAT values.
The following example allows ingress TCP traffic from the uplink representor to vf1_rep, while assuring that egress traffic from vf1_rep is only allowed on established connections. In addition, mark and source IP NAT is applied.
In OVS dump flows:
ct(zone=2,nat)
ct_state(+est+trk)
actions:ct(commit,zone=2,mark=0x4/0xffffffff,nat(src=5.5.5.5))
Using TC rules:
# tc filter add dev $uplink_rep ingress chain 0 prio 1 proto ip \
flower \
ip_proto tcp \
ct_state -trk \
action ct zone 2 nat pipe
action goto chain 2
# tc filter add dev $uplink_rep ingress chain 2 prio 1 proto ip \
flower \
ct_state +trk+new \
action ct zone 2 commit mark 0xbb nat src addr 5.5.5.7 pipe \
action mirred egress redirect dev $vf1_rep
# tc filter add dev $uplink_rep ingress chain 2 prio 1 proto ip \
flower \
ct_zone 2 \
ct_mark 0xbb \
ct_state +trk+est \
action mirred egress redirect dev $vf1_rep
// Setup filters on $vf1_rep, allowing only established connections of zone 2 through, and reverse nat (dst nat in this case)
# tc filter add dev $vf1_rep ingress chain 0 prio 1 proto ip \
flower \
ip_proto tcp \
ct_state -trk \
action ct zone 2 nat pipe \
action goto chain 1
# tc filter add dev $vf1_rep ingress chain 1 prio 1 proto ip \
flower \
ct_zone 2 \
ct_mark 0xbb \
ct_state +trk+est \
action mirred egress redirect dev eth0
CT Performance Tuning
Max offloaded connections – specifies the limit on the number of offloaded connections. Example:
devlink dev param set pci/${pci_dev} name ct_max_offloaded_conns value $max cmode runtime
Allow mixed NAT/non-NAT CT – allows offloading of the following scenario:
• cookie=
0x0, duration=21.843s, table=0, n_packets=4838718, n_bytes=241958846, ct_state=-trk,ip,in_port=enp8s0f0 actions=ct(table=1,zone=2) • cookie=0x0, duration=21.823s, table=1, n_packets=15363, n_bytes=773526, ct_state=+new+trk,ip,in_port=enp8s0f0 actions=ct(commit,zone=2,nat(dst=11.11.11.11)),output:"enp8s0f0_1"• cookie=0x0, duration=21.806s, table=1, n_packets=4767594, n_bytes=238401190, ct_state=+est+trk,ip,in_port=enp8s0f0 actions=ct(zone=2,nat),output:"enp8s0f0_1"Example:
echo enable > /sys/
class/net/<device>/compat/devlink/ct_action_on_nat_conns
Forward to Chain (TC Only)
TC interface supports adding flows on different chains. Only chain 0 is accessed by default. Access to the other chains requires using the goto action.
In this example, a flow is created on chain 1 without any match and redirect to wire.
The second flow is created on chain 0 and match on source MAC and action goto chain 1.
This example simulates simple MAC spoofing:
#tc filter add dev $rep parent ffff: protocol all chain 1 pref 1 \
flower \
action mirred egress redirect dev $NIC
#tc filter add dev $rep parent ffff: protocol all chain 1 pref 1 \
flower \
src_mac aa:bb:cc:aa:bb:cc \
action goto chain 1
Port Mirroring: Flow-based VF Traffic Mirroring for ASAP²
Unlike para-virtual configurations, when the VM traffic is offloaded to hardware via SR-IOV VF, the host-side admin cannot snoop the traffic (e.g., for monitoring).
ASAP² uses the existing mirroring support in OVS and TC along with the enhancement to the offloading logic in the driver to allow mirroring the VF traffic to another VF.
The mirrored VF can be used to run traffic analyzer (e.g., tcpdump, wireshark, etc.) and observe the traffic of the VF being mirrored.
The following example shows the creation of port mirror on the following configuration:
# ovs-vsctl show
09d8a574-9c39-465c-9f16-47d81c12f88a
Bridge br-vxlan
Port "enp4s0f0_1"
Interface "enp4s0f0_1"
Port "vxlan0"
Interface "vxlan0"
type: vxlan
options: {key="100", remote_ip="192.168.1.14"}
Port "enp4s0f0_0"
Interface "enp4s0f0_0"
Port "enp4s0f0_2"
Interface "enp4s0f0_2"
Port br-vxlan
Interface br-vxlan
type: internal
ovs_version: "2.14.1"
To set enp4s0f0_0 as the mirror port and mirror all the traffic:
# ovs-vsctl -- --id=
@pget port enp4s0f0_0 \ -- --id=@mcreate mirror name=m0 select-all=trueoutput-port=@p\ -- set bridge br-vxlan mirrors=@m
To set enp4s0f0_0 as the mirror port, only mirror the traffic, and set enp4s0f0_1 as the destination port:
# ovs-vsctl -- --id=
@p1get port enp4s0f0_0 \ -- --id=@p2get port enp4s0f0_1 \ -- --id=@mcreate mirror name=m0 select-dst-port=@p2output-port=@p1\ -- set bridge br-vxlan mirrors=@m
To set enp4s0f0_0 as the mirror port, only mirror the traffic, and set enp4s0f0_1 as the source port:
# ovs-vsctl -- --id=
@p1get port enp4s0f0_0 \ -- --id=@p2get port enp4s0f0_1 \ -- --id=@mcreate mirror name=m0 select-src-port=@p2output-port=@p1\ -- set bridge br-vxlan mirrors=@m
To set enp4s0f0_0 as the mirror port and mirror all the traffic on enp4s0f0_1:
# ovs-vsctl -- --id=
@p1get port enp4s0f0_0 \ -- --id=@p2get port enp4s0f0_1 \ -- --id=@mcreate mirror name=m0 select-dst-port=@p2select-src-port=@p2output-port=@p1\ -- set bridge br-vxlan mirrors=@m
To clear the mirror port:
ovs-vsctl clear bridge br-vxlan mirrors
Mirroring using TC:
Mirror to VF:
tc filter add dev $rep parent ffff: protocol arp pref
1\ flower \ dst_mac e4:1d:2d:5d:25:35\ src_mac e4:1d:2d:5d:25:34\ action mirred egress mirror dev $mirror_rep pipe \ action mirred egress redirect dev $NICMirror to tunnel:
tc filter add dev $rep parent ffff: protocol arp pref
1\ flower \ dst_mac e4:1d:2d:5d:25:35\ src_mac e4:1d:2d:5d:25:34\ action tunnel_key set \ src_ip1.1.1.1\ dst_ip1.1.1.2\ dst_port4789\ id768\ pipe \ action mirred egress mirror dev vxlan100 pipe \ action mirred egress redirect dev $NIC
Forward to Multiple Destinations
Forwarding to up 32 destinations (representors and tunnels) is supported using TC:
Example 1 – forwarding to 32 VFs:
tc filter add dev $NIC parent ffff: protocol arp pref
1\ flower \ dst_mac e4:1d:2d:5d:25:35\ src_mac e4:1d:2d:5d:25:34\ action mirred egress mirror dev $rep0 pipe \ action mirred egress mirror dev $rep1 pipe \ ... action mirred egress mirror dev $rep30 pipe \ action mirred egress redirect dev $rep31Example 2 – forwarding to 16 tunnels:
tc filter add dev $rep parent ffff: protocol arp pref
1\ flower \ dst_mac e4:1d:2d:5d:25:35\ src_mac e4:1d:2d:5d:25:34\ action tunnel_key set src_ip $ip_src dst_ip $ip_dst \ dst_port4789id0nocsum \ pipe action mirred egress mirror dev vxlan0 pipe \ action tunnel_key set src_ip $ip_src dst_ip $ip_dst \ dst_port4789id1nocsum \ pipe action mirred egress mirror dev vxlan0 pipe \ ... action tunnel_key set src_ip $ip_src dst_ip $ip_dst \ dst_port4789id15nocsum \ pipe action mirred egress redirect dev vxlan0
TC supports up to 32 actions.
If header rewrite is used, then all destinations should have the same header rewrite.
If VLAN push/pop is used, then all destinations should have the same VLAN ID and actions.
sFlow
sFlow allows for monitoring traffic sent between two VMs on the same host using an sFlow collector.
The following example assumes the environment is configured as described later.
# ovs-vsctl show
09d8a574-9c39-465c-9f16-47d81c12f88a
Bridge br-vxlan
Port "enp4s0f0_1"
Interface "enp4s0f0_1"
Port "vxlan0"
Interface "vxlan0"
type: vxlan
options: {key="100", remote_ip="192.168.1.14"}
Port "enp4s0f0_0"
Interface "enp4s0f0_0"
Port "enp4s0f0_2"
Interface "enp4s0f0_2"
Port br-vxlan
Interface br-vxlan
type: internal
ovs_version: "2.14.1"
To sample all traffic over the OVS bridge:
# ovs-vsctl -- --id=@sflow create sflow agent=\"$SFLOW_AGENT\" \
target=\"$SFLOW_TARGET:$SFLOW_PORT\" \
header=$SFLOW_HEADER \
sampling=$SFLOW_SAMPLING polling=10 \
-- set bridge br-vxlan sflow=@sflow
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
SFLOW_AGENT |
Indicates that the sFlow agent should send traffic from SFLOW_AGENT's IP address |
|
SFLOW_TARGET |
Remote IP address of the sFlow collector |
|
SFLOW_HEADER |
Size of packet header to sample (in bytes) |
|
SFLOW_SAMPLING |
Sample rate |
To clear the sFlow configuration:
# ovs-vsctl clear bridge br-vxlan sflow
To list the sFlow configuration:
# ovs-vsctl list sflow
sFlow using TC:
Sample to VF
tc filter add dev $rep parent ffff: protocol arp pref 1 \
flower \
dst_mac e4:1d:2d:5d:25:35 \
src_mac e4:1d:2d:5d:25:34 \
action sample rate 10 group 5 trunc 96 \
action mirred egress redirect dev $NIC
A userspace application is needed to process the sampled packet from the kernel. An example is available on Github.
Rate Limit
OVS-kernel supports offload of VF rate limit using OVS configuration and TC.
The following example sets the rate limit to the VF related to representor eth0 to 10Mb/s:
OVS:
ovs-vsctl set
interfaceeth0 ingress_policing_rate=10000TC:
tc_filter add dev eth0 root prio
1protocol ip matchall skip_sw action police rate 10mbit burst 20k
Kernel Requirements
This kernel config should be enabled to support switchdev offload.
CONFIG_NET_ACT_CSUM – needed for action csum
CONFIG_NET_ACT_PEDIT – needed for header rewrite
CONFIG_NET_ACT_MIRRED – needed for basic forward
CONFIG_NET_ACT_CT – needed for CT (supported from kernel 5.6)
CONFIG_NET_ACT_VLAN – needed for action vlan push/pop
CONFIG_NET_ACT_GACT
CONFIG_NET_CLS_FLOWER
CONFIG_NET_CLS_ACT
CONFIG_NET_SWITCHDEV
CONFIG_NET_TC_SKB_EXT – needed for CT (supported from kernel 5.6)
CONFIG_NET_ACT_CT – needed for CT (supported from kernel 5.6)
CONFIG_NFT_FLOW_OFFLOAD
CONFIG_NET_ACT_TUNNEL_KEY
CONFIG_NF_FLOW_TABLE – needed for CT (supported from kernel 5.6)
CONFIG_SKB_EXTENSIONS – needed for CT (supported from kernel 5.6)
CONFIG_NET_CLS_MATCHALL
CONFIG_NET_ACT_POLICE
CONFIG_MLX5_ESWITCH
VF Metering
OVS-kernel supports offloading of VF metering (TX and RX) using sysfs. Metering of number of packets per second (PPS) and bytes per second (BPS) is supported.
The following example sets Rx meter on VF 0 with value 10Mb/s BPS:
echo 10000000 > /sys/class/net/enp4s0f0/device/sriov/0/meters/rx/bps/rate
echo 65536 > /sys/class/net/enp4s0f0/device/sriov/0/meters/rx/bps/burst
The following example sets Tx meter on VF 0 with value 1000 PPS:
echo 1000 > /sys/class/net/enp4s0f0/device/sriov/0/meters/tx/pps/rate
echo 100 > /sys/class/net/enp4s0f0/device/sriov/0/meters/tx/pps/burst
Both rate and burst must not be zero and burst may need to be adjusted according to the requirements.
The following counters can be used to query the number dropped packet/bytes:
cat /sys/class/net/enp8s0f0/device/sriov/0/meters/rx/pps/packets_dropped
cat /sys/class/net/enp8s0f0/device/sriov/0/meters/rx/pps/bytes_dropped
cat /sys/class/net/enp8s0f0/device/sriov/0/meters/rx/bps/packets_dropped
cat /sys/class/net/enp8s0f0/device/sriov/0/meters/rx/bps/bytes_dropped
cat /sys/class/net/enp8s0f0/device/sriov/0/meters/tx/pps/packets_dropped
cat /sys/class/net/enp8s0f0/device/sriov/0/meters/tx/pps/bytes_dropped
cat /sys/class/net/enp8s0f0/device/sriov/0/meters/tx/bps/packets_dropped
cat /sys/class/net/enp8s0f0/device/sriov/0/meters/tx/bps/bytes_dropped
Representor Metering
Metering for uplink and VF representors traffic is supported.
Traffic going to a representor device can be a result of a miss in the embedded switch (eSwitch) FDB tables. This means that a packet which arrives from that representor into the eSwitch has not matched against the existing rules in the hardware FDB tables and must be forwarded to software to be handled there and is, therefore, forwarded to the originating representor device driver.
The meter allows to configure the max rate [packets per second] and max burst [packets] for traffic going to the representor driver. Any traffic exceeding values provided by the user are dropped in hardware. There are statistics that show the number of dropped packets.
The configuration of representor metering is done via miss_rl_cfg.
Full path of the miss_rl_cfg parameter: /sys/class/net//rep_config/miss_rl_cfg
Usage: echo "<rate> <burst>" > /sys/class/net//rep_config/miss_rl_cfg.
rate is the max rate of packets allowed for this representor (in packets/sec units)
burst is the max burst size allowed for this representor (in packets units)
Both values must be specified. Both of their default values is 0, signifying unlimited rate and burst.
To view the amount of packets and bytes dropped due to traffic exceeding the user-provided rate and burst, two read-only sysfs for statistics are available:
/sys/class/net//rep_config/miss_rl_dropped_bytes – counts how many FDB-miss bytes are dropped due to reaching the miss limits
/sys/class/net//rep_config/miss_rl_dropped_packets – counts how many FDB-miss packets are dropped due to reaching the miss limits
OVS Metering
There are two types of meters, kpps (kilobits per second) and pktps (packets per second). OVS-Kernel supports offloading both of them.
The following example is to offload a kpps meter.
Create OVS meter with a target rate:
ovs-ofctl -O OpenFlow13 add-meter ovs-sriov meter=
1,kbps,band=type=drop,rate=204800Delete the default rule:
ovs-ofctl del-flows ovs-sriov
Configure OpenFlow rules:
ovs-ofctl -O OpenFlow13 add-flow ovs-sriov
'ip,dl_dst=e4:11:22:33:44:50,actions= meter:1,output:enp4s0f0_0'ovs-ofctl -O OpenFlow13 add-flow ovs-sriov'ip,dl_src=e4:11:22:33:44:50,actions= output:enp4s0f0'ovs-ofctl -O OpenFlow13 add-flow ovs-sriov'arp,actions=normal'Here, the VF bandwidth on the receiving side is limited by the rate configured in step 1.
Run iperf server and be ready to receive UDP traffic. On the outer node, run iperf client to send UDP traffic to this VF. After traffic starts, check the offloaded meter rule:
ovs-appctl dpctl/dump-flows --names type=offloaded recirc_id(
0),in_port(enp4s0f0),eth(dst=e4:11:22:33:44:50),eth_type(0x0800),ipv4(frag=no), packets:11626587, bytes:17625889188, used:0.470s, actions:meter(0),enp4s0f0_0
To verify metering, iperf client should set the target bandwidth with a number which is larger than the meter rate configured. Then it should apparent that packets are received with the limited rate on the server side and the extra packets are dropped by hardware.
Multiport eSwitch Mode
The multiport eswitch mode allows adding rules on a VF representor with an action forwarding the packet to the physical port of the physical function. This can be used to implement failover or forward packets based on external information such as the cost of the route.
To configure multiport eswitch mode , the nvconig parameter LAG_RESOURCE_ALLOCATION must be set.
After the driver loads, configure multiport eSwitch for each PF where enp8s0f0 and enp8s0f1 represent the netdevices for the PFs:
echo multiport_esw > /sys/
class/net/enp8s0f0/compat/devlink/lag_port_select_mode echo multiport_esw > /sys/class/net/enp8s0f1/compat/devlink/lag_port_select_modeThe mode becomes operational after entering switchdev mode on both PFs.
Rule example:
tc filter add dev enp8s0f0_0 prot ip root flower dst_ip 7.7.7.7 action mirred egress redirect dev enp8s0f1
OVS-DPDK Hardware Offloads
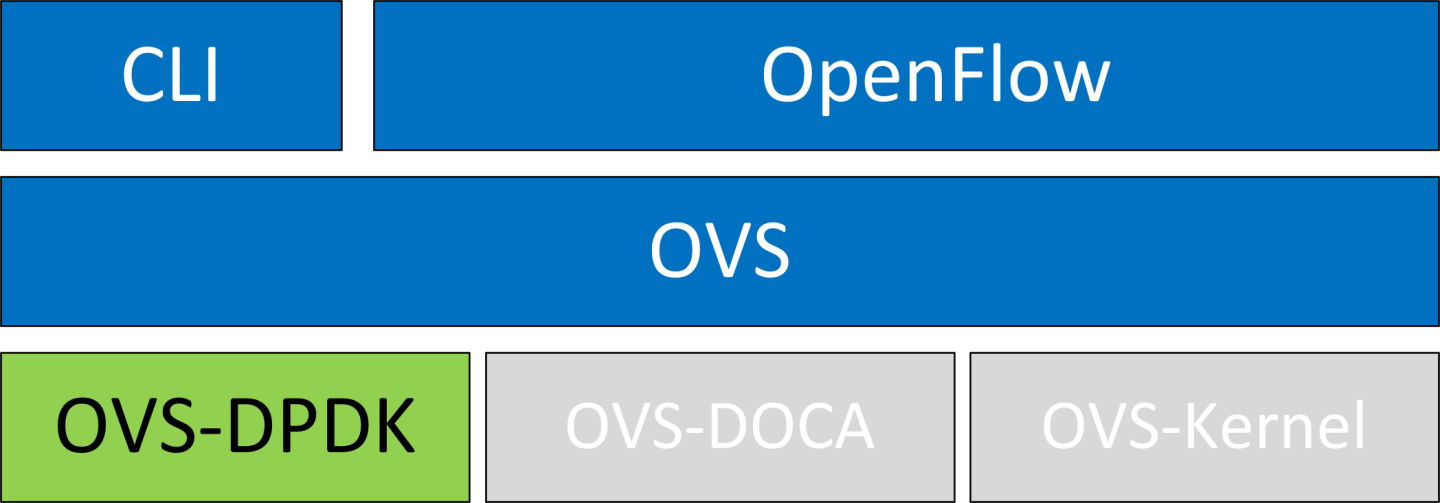
OVS-DPDK Hardware Offloads Configuration
To configure OVS-DPDK HW offloads:
Unbind the VFs:
echo
0000:04:00.2> /sys/bus/pci/drivers/mlx5_core/unbind echo0000:04:00.3> /sys/bus/pci/drivers/mlx5_core/unbindNoteVMs with attached VFs must be powered off to be able to unbind the VFs.
Change the e-switch mode from legacy to switchdev on the PF device (make sure all VFs are unbound). This also creates the VF representor netdevices in the host OS.
echo switchdev > /sys/
class/net/enp4s0f0/compat/devlink/modeTo revert to SR-IOV legacy mode:
echo legacy > /sys/
class/net/enp4s0f0/compat/devlink/modeNoteThis command removes the VF representor netdevices.
Bind the VFs:
echo
0000:04:00.2> /sys/bus/pci/drivers/mlx5_core/bind echo0000:04:00.3> /sys/bus/pci/drivers/mlx5_core/bindRun the OVS service:
systemctl start openvswitch
Enable hardware offload (disabled by default):
ovs-vsctl --no-wait set Open_vSwitch . other_config:dpdk-init=
trueovs-vsctl set Open_vSwitch . other_config:hw-offload=trueConfigure the DPDK whitelist:
ovs-vsctl --no-wait set Open_vSwitch . other_config:dpdk-extra=
"-a 0000:01:00.0,representor=[0],dv_flow_en=1,dv_esw_en=1,dv_xmeta_en=1"Where representor=[0-N].
Restart the OVS service:
systemctl restart openvswitch
InfoThis step is required for the hardware offload changes to take effect.
Create OVS-DPDK bridge:
ovs-vsctl --no-wait add-br br0-ovs -- set bridge br0-ovs datapath_type=netdev
Add PF to OVS:
ovs-vsctl add-port br0-ovs pf -- set Interface pf type=dpdk options:dpdk-devargs=
0000:88:00.0Add representor to OVS:
ovs-vsctl add-port br0-ovs representor -- set Interface representor type=dpdk options:dpdk-devargs=
0000:88:00.0,representor=[0]Where representor=[0-N].
Offloading VXLAN Encapsulation/Decapsulation Actions
vSwitch in userspace requires an additional bridge. The purpose of this bridge is to allow use of the kernel network stack for routing and ARP resolution.
The datapath must look up the routing table and ARP table to prepare the tunnel header and transmit data to the output port.
Configuring VXLAN Encap/Decap Offloads
The configuration is done with:
PF on 0000:03:00.0 PCIe and MAC 98:03:9b:cc:21:e8
Local IP 56.56.67.1 – br-phy interface is configured to this IP
Remote IP 56.56.68.1
To configure OVS-DPDK VXLAN:
Create a br-phy bridge:
ovs-vsctl add-br br-phy -- set Bridge br-phy datapath_type=netdev -- br-set-external-id br-phy bridge-id br-phy -- set bridge br-phy fail-mode=standalone other_config:hwaddr=
98:03:9b:cc:21:e8Attach PF interface to br-phy bridge:
ovs-vsctl add-port br-phy p0 -- set Interface p0 type=dpdk options:dpdk-devargs=
0000:03:00.0Configure IP to the bridge:
ip addr add
56.56.67.1/24dev br-phyCreate a br-ovs bridge:
ovs-vsctl add-br br-ovs -- set Bridge br-ovs datapath_type=netdev -- br-set-external-id br-ovs bridge-id br-ovs -- set bridge br-ovs fail-mode=standalone
Attach representor to br-ovs:
ovs-vsctl add-port br-ovs pf0vf0 -- set Interface pf0vf0 type=dpdk options:dpdk-devargs=
0000:03:00.0,representor=[0]Add a port for the VXLAN tunnel:
ovs-vsctl add-port ovs-sriov vxlan0 -- set
interfacevxlan0 type=vxlan options:local_ip=56.56.67.1options:remote_ip=56.56.68.1options:key=45options:dst_port=4789
CT Offload
CT enables stateful packet processing by keeping a record of currently open connections. OVS flows using CT can be accelerated using advanced NICs by offloading established connections.
To view offloaded connections, run:
ovs-appctl dpctl/offload-stats-show
SR-IOV VF LAG
To configure OVS-DPDK SR-IOV VF LAG:
Enable SR-IOV on the NICs:
mlxconfig -d <PCI> set SRIOV_EN=
1Allocate the desired number of VFs per port:
echo $n > /sys/
class/net/<net name>/device/sriov_numvfsUnbind all VFs:
echo <VF PCI> >/sys/bus/pci/drivers/mlx5_core/unbind
Change both devices' mode to switchdev:
devlink dev eswitch set pci/<PCI> mode switchdev
Create Linux bonding using kernel modules:
modprobe bonding mode=<desired mode>
InfoOther bonding parameters can be added here. The supported bond modes are: Active-backup, XOR and LACP.
Bring all PFs and VFs down:
ip link set <PF/VF> down
Attach both PFs to the bond:
ip link set <PF> master bond0
To use VF-LAG with OVS-DPDK, add the bond master (PF) to the bridge:
ovs-vsctl add-port br-phy p0 -- set Interface p0 type=dpdk options:dpdk-devargs=
0000:03:00.0options:dpdk-lsc-interrupt=trueAdd representor $N of PF0 or PF1 to a bridge:
ovs-vsctl add-port br-phy rep$N -- set Interface rep$N type=dpdk options:dpdk-devargs=<PF0 PCI>,representor=pf0vf$N
Or:
ovs-vsctl add-port br-phy rep$N -- set Interface rep$N type=dpdk options:dpdk-devargs=<PF0 PCI>,representor=pf1vf$N
VirtIO Acceleration Through VF Relay: Software and Hardware vDPA
Hardware vDPA is enabled by default. In case your hardware does not support vDPA, the driver will fall back to Software vDPA.
To check which vDPA mode is activated on your driver, run: ovs-ofctl -O OpenFlow14 dump-ports br0-ovs and look for hw-mode flag.
This feature has not been accepted to the OVS-DPDK upstream yet, making its API subject to change.
In user space, there are two main approaches for communicating with a guest (VM), either through SR-IOV or virtio.
PHY ports (SR-IOV) allow working with port representor, which is attached to the OVS and a matching VF is given with pass-through to the guest. HW rules can process packets from up-link and direct them to the VF without going through SW (OVS). Therefore, using SR-IOV achieves the best performance.
However, SR-IOV architecture requires the guest to use a driver specific to the underlying HW. Specific HW driver has two main drawbacks:
Breaks virtualization in some sense (guest is aware of the HW). It can also limit the type of images supported.
Gives less natural support for live migration.
Using a virtio port solves both problems, however, it reduces performance and causes loss of some functionalities, such as, for some HW offloads, working directly with virtio. The netdev type dpdkvdpa solves this conflict as it is similar to the regular DPDK netdev yet introduces several additional functionalities.
dpdkvdpa translates between the PHY port to the virtio port. It takes packets from the Rx queue and sends them to the suitable Tx queue, and allows transfer of packets from the virtio guest (VM) to a VF and vice-versa, benefitting from both SR-IOV and virtio.
To add a vDPA port:
ovs-vsctl add-port br0 vdpa0 -- set Interface vdpa0 type=dpdkvdpa \
options:vdpa-socket-path=<sock path> \
options:vdpa-accelerator-devargs=<vf pci id> \
options:dpdk-devargs=<pf pci id>,representor=[id] \
options: vdpa-max-queues =<num queues> \
options: vdpa-sw=<true/false>
vdpa-max-queues is an optional field. When the user wants to configure 32 vDPA ports, the maximum queues number is limited to 8.
vDPA Configuration in OVS-DPDK Mode
Prior to configuring vDPA in OVS-DPDK mode, perform the following:
Generate the VF:
echo
0> /sys/class/net/enp175s0f0/device/sriov_numvfs echo4> /sys/class/net/enp175s0f0/device/sriov_numvfsUnbind each VF:
echo <pci> > /sys/bus/pci/drivers/mlx5_core/unbind
Switch to switchdev mode:
echo switchdev >> /sys/
class/net/enp175s0f0/compat/devlink/modeBind each VF:
echo <pci> > /sys/bus/pci/drivers/mlx5_core/bind
Initialize OVS:
ovs-vsctl --no-wait set Open_vSwitch . other_config:dpdk-init=
trueovs-vsctl --no-wait set Open_vSwitch . other_config:hw-offload=true
To configure vDPA in OVS-DPDK mode:
OVS configuration:
ovs-vsctl --no-wait set Open_vSwitch . other_config:dpdk-extra=
"-a 0000:01:00.0,representor=[0],dv_flow_en=1,dv_esw_en=1,dv_xmeta_en=1"/usr/share/openvswitch/scripts/ovs-ctl restartCreate OVS-DPDK bridge:
ovs-vsctl add-br br0-ovs -- set bridge br0-ovs datapath_type=netdev ovs-vsctl add-port br0-ovs pf -- set Interface pf type=dpdk options:dpdk-devargs=
0000:01:00.0Create vDPA port as part of the OVS-DPDK bridge:
ovs-vsctl add-port br0-ovs vdpa0 -- set Interface vdpa0 type=dpdkvdpa options:vdpa-socket-path=/var/run/virtio-forwarder/sock0 options:vdpa-accelerator-devargs=
0000:01:00.2options:dpdk-devargs=0000:01:00.0,representor=[0] options: vdpa-max-queues=8
To configure vDPA in OVS-DPDK mode on BlueField DPUs, set the bridge with the software or hardware vDPA port:
To create the OVS-DPDK bridge on the Arm side:
ovs-vsctl add-br br0-ovs -- set bridge br0-ovs datapath_type=netdev ovs-vsctl add-port br0-ovs pf -- set Interface pf type=dpdk options:dpdk-devargs=
0000:af:00.0ovs-vsctl add-port br0-ovs rep-- set Interface rep type=dpdk options:dpdk-devargs=0000:af:00.0,representor=[0]To create the OVS-DPDK bridge on the host side:
ovs-vsctl add-br br1-ovs -- set bridge br1-ovs datapath_type=netdev protocols=OpenFlow14 ovs-vsctl add-port br0-ovs vdpa0 -- set Interface vdpa0 type=dpdkvdpa options:vdpa-socket-path=/var/run/virtio-forwarder/sock0 options:vdpa-accelerator-devargs=
0000:af:00.2NoteTo configure SW vDPA, add options:vdpa-sw=true to the command.
Software vDPA Configuration in OVS-Kernel Mode
Software vDPA can also be used in configurations where hardware offload is done through TC and not DPDK.
OVS configuration:
ovs-vsctl set Open_vSwitch . other_config:dpdk-extra=
"-a 0000:01:00.0,representor=[0],dv_flow_en=1,dv_esw_en=0,idv_xmeta_en=0,isolated_mode=1"/usr/share/openvswitch/scripts/ovs-ctl restartCreate OVS-DPDK bridge:
ovs-vsctl add-br br0-ovs -- set bridge br0-ovs datapath_type=netdev
Create vDPA port as part of the OVS-DPDK bridge:
ovs-vsctl add-port br0-ovs vdpa0 -- set Interface vdpa0 type=dpdkvdpa options:vdpa-socket-path=/var/run/virtio-forwarder/sock0 options:vdpa-accelerator-devargs=
0000:01:00.2options:dpdk-devargs=0000:01:00.0,representor=[0] options: vdpa-max-queues=8Create Kernel bridge:
ovs-vsctl add-br br-kernel
Add representors to Kernel bridge:
ovs-vsctl add-port br-kernel enp1s0f0_0 ovs-vsctl add-port br-kernel enp1s0f0
Large MTU/Jumbo Frame Configuration
To configure MTU/jumbo frames:
Verify that the Kernel version on the VM is 4.14 or above:
cat /etc/redhat-release
Set the MTU on both physical interfaces in the host:
ifconfig ens4f0 mtu
9216Send a large size packet and verify that it is sent and received correctly:
tcpdump -i ens4f0 -nev icmp & ping
11.100.126.1-s9188-Mdo-c1Enable host_mtu in XML and add the following values:
host_mtu=
9216,csum=on,guest_csum=on,host_tso4=on,host_tso6=onExample:
<qemu:commandline> <qemu:arg value=
'-chardev'/> <qemu:arg value='socket,id=charnet1,path=/tmp/sock0,server'/> <qemu:arg value='-netdev'/> <qemu:arg value='vhost-user,chardev=charnet1,queues=16,id=hostnet1'/> <qemu:arg value='-device'/> <qemu:arg value='virtio-net-pci,mq=on,vectors=34,netdev=hostnet1,id=net1,mac=00:21:21:24:02:01,bus=pci.0,addr=0xC,page-per-vq=on,rx_queue_size=1024,tx_queue_size=1024,host_mtu=9216,csum=on,guest_csum=on,host_tso4=on,host_tso6=on'/> </qemu:commandline>Add the mtu_request=9216 option to the OVS ports inside the container and restart the OVS:
ovs-vsctl add-port br0-ovs pf -- set Interface pf type=dpdk options:dpdk-devargs=
0000:c4:00.0mtu_request=9216Or:
ovs-vsctl add-port br0-ovs vdpa0 -- set Interface vdpa0 type=dpdkvdpa options:vdpa-socket-path=/tmp/sock0 options:vdpa-accelerator-devargs=
0000:c4:00.2options:dpdk-devargs=0000:c4:00.0,representor=[0] mtu_request=9216/usr/share/openvswitch/scripts/ovs-ctl restartStart the VM and configure the MTU on the VM:
ifconfig eth0
11.100.124.2/16up ifconfig eth0 mtu9216ping11.100.126.1-s9188-Mdo-c1
E2E Cache
This feature is supported at beta level.
OVS offload rules are based on a multi-table architecture. E2E cache enables merging the multi-table flow matches and actions into one joint flow.
This improves CT performance by using a single-table when an exact match is detected.
To set the E2E cache size (default is 4k):
ovs-vsctl set open_vswitch . other_config:e2e-size=<size>
systemctl restart openvswitch
To enable E2E cache (disabled by default):
ovs-vsctl set open_vswitch . other_config:e2e-enable=true
systemctl restart openvswitch
To run E2E cache statistics:
ovs-appctl dpctl/dump-e2e-stats
To run E2E cache flows:
ovs-appctl dpctl/dump-e2e-flows
Geneve Encapsulation/Decapsulation
Geneve tunneling offload support includes matching on extension header.
To configure OVS-DPDK Geneve encap/decap:
Create a br-phy bridge:
ovs-vsctl --may-exist add-br br-phy -- set Bridge br-phy datapath_type=netdev -- br-set-external-id br-phy bridge-id br-phy -- set bridge br-phy fail-mode=standalone
Attach PF interface to br-phy bridge:
ovs-vsctl add-port br-phy pf -- set Interface pf type=dpdk options:dpdk-devargs=<PF PCI>
Configure IP to the bridge:
ifconfig br-phy <$local_ip_1> up
Create a br-int bridge:
ovs-vsctl --may-exist add-br br-
int-- set Bridge br-intdatapath_type=netdev -- br-set-external-id br-intbridge-id br-int-- set bridge br-intfail-mode=standaloneAttach representor to br-int:
ovs-vsctl add-port br-
intrep$x -- set Interface rep$x type=dpdk options:dpdk-devargs=<PF PCI>,representor=[$x]Add a port for the Geneve tunnel:
ovs-vsctl add-port br-
intgeneve0 -- setinterfacegeneve0 type=geneve options:key=<VNI> options:remote_ip=<$remote_ip_1> options:local_ip=<$local_ip_1>
Parallel Offloads
OVS-DPDK supports parallel insertion and deletion of offloads (flow and CT). While multiple threads are supported (only one is used by default).
To configure multiple threads:
ovs-vsctl set Open_vSwitch . other_config:n-offload-threads=3
systemctl restart openvswitch
Refer to the OVS user manual for more information.
sFlow
sFlow allows monitoring traffic sent between two VMs on the same host using an sFlow collector.
To sample all traffic over the OVS bridge, run the following:
# ovs-vsctl -- --id=@sflow create sflow agent=\"$SFLOW_AGENT\" \
target=\"$SFLOW_TARGET:$SFLOW_HEADER\" \
header=$SFLOW_HEADER \
sampling=$SFLOW_SAMPLING polling=10 \
-- set bridge sflow=@sflow
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
SFLOW_AGENT |
Indicates that the sFlow agent should send traffic from SFLOW_AGENT's IP address |
|
SFLOW_TARGET |
Remote IP address of the sFlow collector |
|
SFLOW_PORT |
Remote IP destination port of the sFlow collector |
|
SFLOW_HEADER |
Size of packet header to sample (in bytes) |
|
SFLOW_SAMPLING |
Sample rate |
To clear the sFlow configuration, run:
# ovs-vsctl clear bridge br-vxlan mirrors
Currently sFlow for OVS-DPDK is supported without CT.
CT CT NAT
To enable ct-ct-nat offloads in OVS-DPDK (disabled by default), run:
ovs-vsctl set open_vswitch . other_config:ct-action-on-nat-conns=true
If disabled, ct-ct-nat configurations are not fully offloaded, improving connection offloading rate for other cases (ct and ct-nat).
If enabled, ct-ct-nat configurations are fully offloaded but ct and ct-nat offloading would be slower to create.
OpenFlow Meters (OpenFlow13+)
OpenFlow meters in OVS are implemented according to RFC 2697 (Single Rate Three Color Marker—srTCM).
The srTCM meters an IP packet stream and marks its packets either green, yellow, or red. The color is decided on a Committed Information Rate (CIR) and two associated burst sizes, Committed Burst Size (CBS), and Excess Burst Size (EBS).
A packet is marked green if it does not exceed the CBS, yellow if it exceeds the CBS but not the EBS, and red otherwise.
The volume of green packets should never be smaller than the CIR.
To configure a meter in OVS:
Create a meter over a certain bridge, run:
ovs-ofctl -O openflow13 add-meter $bridge meter=$id,$pktps/$kbps,band=type=drop,rate=$rate,[burst,burst_size=$burst_size]
Parameters:
Parameter
Description
bridge
Name of the bridge on which the meter should be applied.
id
Unique meter ID (32 bits) to be used as an identifier for the meter.
pktps/kbps
Indication if the meter should work according to packets or kilobits per second.
rate
Rate of pktps/kbps of allowed data transmission.
burst
If set, enables burst support for meter bands through the burst_size parameter.
burst_size
If burst is specified for the meter entry, configures the maximum burst allowed for the band in kilobits/packets, depending on whether kbps or pktps has been specified. If unspecified, the switch is free to select some reasonable value depending on its configuration. Currently, if burst is not specified, the burst_size parameter is set the same as rate.
Add the meter to a certain OpenFlow rule. For example:
ovs-ofctl -O openflow13 add-flow $bridge
"table=0,actions=meter:$id,normal"View the meter statistics:
ovs-ofctl -O openflow13 meter-stats $bridge meter=$id
For more information, refer to official OVS documentation.
OVS-DOCA Hardware Offloads
OVS-DOCA is designed on top of NVIDIA's networking API to preserve the same OpenFlow, CLI, and data interfaces (e.g., vdpa, VF passthrough), and northbound API as OVS-DPDK and OVS-Kernel. While all OVS flavors make use of flow offloads for hardware acceleration, due to its architecture and use of DOCA libraries, the OVS-DOCA mode provides the most efficient performance and feature set among them, making the most out of NVIDA NICs and DPUs.
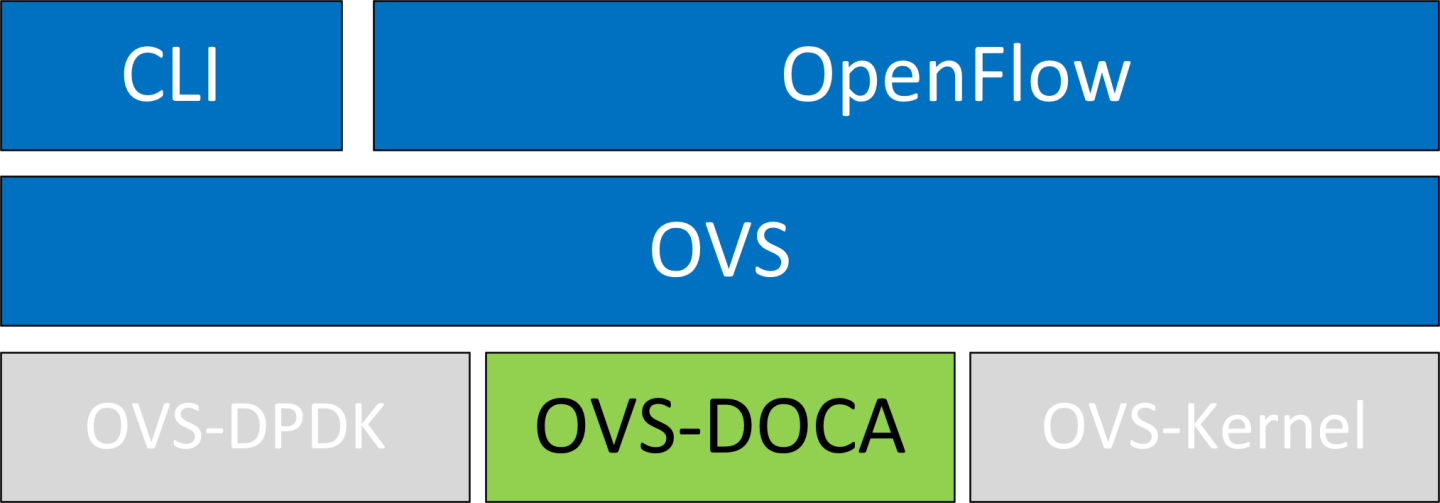
The following subsections provide the necessary steps to launch/deploy OVS DOCA.
Configuring OVS-DOCA
To configure OVS DOCA HW offloads:
Unbind the VFs:
echo 0000:04:00.2 > /sys/bus/pci/drivers/mlx5_core/unbind echo 0000:04:00.3 > /sys/bus/pci/drivers/mlx5_core/unbind
NoteVMs with attached VFs must be powered off to be able to unbind the VFs.
Change the e-switch mode from legacy to switchdev on the PF device (make sure all VFs are unbound):
echo switchdev > /sys/class/net/enp4s0f0/compat/devlink/mode
NoteThis command also creates the VF representor netdevices in the host OS.
To revert to SR-IOV legacy mode:
echo legacy > /sys/class/net/enp4s0f0/compat/devlink/mode
Bind the VFs:
echo 0000:04:00.2 > /sys/bus/pci/drivers/mlx5_core/bind echo 0000:04:00.3 > /sys/bus/pci/drivers/mlx5_core/bind
Configure huge pages:
mkdir -p /hugepages mount -t hugetlbfs hugetlbfs /hugepages echo 4096 > /sys/devices/system/node/node0/hugepages/hugepages-2048kB/nr_hugepages
Run the Open vSwitch service:
systemctl start openvswitch
Enable DOCA mode and hardware offload (disabled by default):
ovs-vsctl --no-wait set Open_vSwitch . other_config:doca-init=true ovs-vsctl set Open_vSwitch . other_config:hw-offload=true
Restart the Open vSwitch service.
systemctl restart openvswitch
InfoThis step is required for HW offload changes to take effect.
Create OVS-DOCA bridge:
ovs-vsctl --no-wait add-br br0-ovs -- set bridge br0-ovs datapath_type=netdev
Add PF to OVS:
ovs-vsctl add-port br0-ovs pf -- set Interface pf type=dpdk options:dpdk-devargs=0000:88:00.0,dv_flow_en=2,dv_xmeta_en=4
InfoOVS-DOCA uses DPDK ports and configuration. Note the different dpdk-devargs parameters.
Add representor to OVS:
ovs-vsctl add-port br0-ovs representor -- set Interface representor type=dpdk options:dpdk-devargs=0000:88:00.0,representor=[<vf-number>],dv_flow_en=2,dv_xmeta_en=4
NoteNote that <vf-number> must be replaced by the number of the VF.
Optional configuration:
To set port MTU, run:
ovs-vsctl set interface pf mtu_request=9000
NoteOVS restart is required for changes to take effect.
To set VF/SF MAC, run:
ovs-vsctl add-port br0-ovs representor -- set Interface representor type=dpdk options:dpdk-devargs=0000:88:00.0,representor=[<vf-number>],dv_flow_en=2,dv_xmeta_en=4 options:dpdk-vf-mac=00:11:22:33:44:55
NoteUnbinding and rebinding the VFs/SFs is required for the change to take effect.
Notable Differences Between OVS-DPDK and OVS-DOCA
OVS-DOCA shares most of its structure with OVS-DPDK. To benefit from the DOCA offload design, some of the behavior of userland datapath and ports are however modified.
Eswitch Dependency
Configured in switchdev mode, the physical port and all supported functions share a single general domain to execute the offloaded flows, the eswitch.
All ports on the same eswitch are dependent on its physical function. If this main physical function is deactivated (e.g., removed from OVS or its link set down), dependent ports are disabled as well.
Pre-allocated Offload Tables
To offer the highest insertion speed, DOCA offloads pre-allocate offload structures (entries and containers).
When starting the vSwitch daemon, offloads are thus configured with sensible defaults. If different numbers of offloads are required, configuration entries specific to OVS-DOCA are available and are described in the next section.
Unsupported CT-CT-NAT
The special ct-ct-nat mode that can be configured in OVS-kernel and OVS-DPDK is not supported by OVS-DOCA.
OVS-DOCA Specific vSwitch Configuration
The following configuration is particularly useful or specific to OVS-DOCA mode.
The full list of OVS vSwitch configuration is documented in man ovs-vswitchd.conf.db.
other_config
The following table provides other_config configurations which are global to the vSwitch (non-exhaustive list, check manpage for more):
|
Configuration |
Description |
|
other_config:doca-init |
|
|
other_config:hw-offload-ct-size |
|
|
other_config:hw-offload-ct-ipv6-enabled |
|
|
other_config:doca-congestion-threshold |
|
|
other_config:ctl-pipe-size |
|
|
other_config:ctl-pipe-infra-size |
|
|
other_config:pmd-quiet-idle |
|
|
other_config:pmd-maxsleep |
|
|
other_config:dpdk-max-memzones |
|
netdev-dpdk
The following table provides netdev-dpdk configurations which only userland (DOCA or DPDK) netdevs support (non-exhaustive list, check manpage for more):
|
Configuration |
Description |
|
options:iface-name |
|
Offloading VXLAN Encapsulation/Decapsulation Actions
vSwitch in userspace rather than kernel-based Open vSwitch requires an additional bridge. The purpose of this bridge is to allow use of the kernel network stack for routing and ARP resolution.
The datapath must look up the routing table and ARP table to prepare the tunnel header and transmit data to the output port.
VXLAN encapsulation/decapsulation offload configuration is done with:
PF on 0000:03:00.0 PCIe and MAC 98:03:9b:cc:21:e8
Local IP 56.56.67.1 – the br-phy interface is configured to this IP
Remote IP 56.56.68.1
To configure OVS DOCA VXLAN:
Create a br-phy bridge:
ovs-vsctl add-br br-phy -- set Bridge br-phy datapath_type=netdev -- br-set-external-id br-phy bridge-id br-phy -- set bridge br-phy fail-mode=standalone other_config:hwaddr=98:03:9b:cc:21:e8
Attach PF interface to br-phy bridge:
ovs-vsctl add-port br-phy p0 -- set Interface p0 type=dpdk options:dpdk-devargs=0000:03:00.0,dv_flow_en=2,dv_xmeta_en=4
Configure IP to the bridge:
ip addr add 56.56.67.1/24 dev br-phy
Create a br-ovs bridge:
ovs-vsctl add-br br-ovs -- set Bridge br-ovs datapath_type=netdev -- br-set-external-id br-ovs bridge-id br-ovs -- set bridge br-ovs fail-mode=standalone
Attach representor to br-ovs:
ovs-vsctl add-port br-ovs pf0vf0 -- set Interface pf0vf0 type=dpdk options:dpdk-devargs=0000:03:00.0,representor=[0],dv_flow_en=2,dv_xmeta_en=4
Add a port for the VXLAN tunnel:
ovs-vsctl add-port ovs-sriov vxlan0 -- set interface vxlan0 type=vxlan options:local_ip=56.56.67.1 options:remote_ip=56.56.68.1 options:key=45 options:dst_port=4789
Offloading Connection Tracking
Connection tracking enables stateful packet processing by keeping a record of currently open connections.
OVS flows utilizing connection tracking can be accelerated using advanced NICs by offloading established connections.
To view offload statistics, run:
ovs-appctl dpctl/offload-stats-show
SR-IOV VF LAG
To configure OVS-DOCA SR-IOV VF LAG:
Enable SR-IOV on the NICs:
mlxconfig -d <PCI> set SRIOV_EN=1
Allocate the desired number of VFs per port:
echo $n > /sys/class/net/<net name>/device/sriov_numvfs
Unbind all VFs:
echo <VF PCI> >/sys/bus/pci/drivers/mlx5_core/unbind
Change both NICs' mode to SwitchDev:
devlink dev eswitch set pci/<PCI> mode switchdev
Create Linux bonding using kernel modules:
modprobe bonding mode=<desired mode>
NoteOther bonding parameters can be added here. The supported bond modes are Active-Backup, XOR, and LACP.
Bring all PFs and VFs down:
ip link set <PF/VF> down
Attach both PFs to the bond:
ip link set <PF> master bond0
Bring PFs and bond link up:
ip link set <PF0> up ip link set <PF1> up ip link set bond0 up
To work with VF-LAG with OVS-DPDK, add the bond master (PF) to the bridge:
ovs-vsctl add-port br-phy p0 -- set Interface p0 type=dpdk options:dpdk-devargs=0000:03:00.0,dv_flow_en=2,dv_xmeta_en=4 options:dpdk-lsc-interrupt=true
Add representor $N of PF0 or PF1 to a bridge:
ovs-vsctl add-port br-phy rep$N -- set Interface rep$N type=dpdk options:dpdk-devargs=<PF0-PCI>,representor=pf0vf$N,dv_flow_en=2,dv_xmeta_en=4
Or:
ovs-vsctl add-port br-phy rep$N -- set Interface rep$N type=dpdk options:dpdk-devargs=<PF0-PCI>,representor=pf1vf$N,dv_flow_en=2,dv_xmeta_en=4
Multiport eSwitch Mode
Multiport eswitch mode allows adding rules on a VF representor with an action, forwarding the packet to the physical port of the physical function. This can be used to implement failover or to forward packets based on external information such as the cost of the route.
To configure multiport eswitch mode , the nvconig parameter LAG_RESOURCE_ALLOCATION=1 must be set.
After the driver loads, and before moving to switchdev mode, configure multiport eswitch for each PF where p0 and p1 represent the netdevices for the PFs:
devlink dev param set pci/
0000:03:00.0name esw_multiport value1cmode runtime devlink dev param set pci/0000:03:00.1name esw_multiport value1cmode runtimeInfoThe mode becomes operational after entering switchdev mode on both PFs.
This mode can be activated by default in BlueField by adding the following line into /etc/mellanox/mlnx-bf.conf:
ENABLE_ESWITCH_MULTIPORT=
"yes"
While in this mode, the second port is not an eswitch manager, and should be add to OVS using this command:
ovs-vsctl add-port br-phy p1 -- set interface p1 type=dpdk options:dpdk-devargs="0000:08:00.0,dv_xmeta_en=4,dv_flow_en=2,representor=pf1
VFs for the second port can be added using this command:
ovs-vsctl add-port br-phy p1vf0 -- set interface p1 type=dpdk options:dpdk-devargs="0000:08:00.0,dv_xmeta_en=4,dv_flow_en=2,representor=pf1vf0
Offloading Geneve Encapsulation/Decapsulation
Geneve tunneling offload support includes matching on extension header.
OVS-DOCA Geneve option limitations:
Only 1 Geneve option is supported
Max option len is 7
To change the Geneve option currently being matched and encapsulated, users must remove all ports or restart OVS and configure the new option
Users must change firmware configuration to enable the flex parser by running the following commands:
mst start mlxconfig -d <mst device> s FLEX_PARSER_PROFILE_ENABLE=8 mlxfwreset -d <mst device> r -y
To configure OVS-DOCA Geneve encapsulation/decapsulation:
Create a br-phy bridge:
ovs-vsctl --may-exist add-br br-phy -- set Bridge br-phy datapath_type=netdev -- br-set-external-id br-phy bridge-id br-phy -- set bridge br-phy fail-mode=standalone
Attach a PF interface to br-phy bridge:
ovs-vsctl add-port br-phy pf -- set Interface pf type=dpdk options:dpdk-devargs=<PF PCI>,dv_flow_en=2,dv_xmeta_en=4
Configure an IP to the bridge:
ifconfig br-phy <$local_ip_1> up
Create a br-int bridge:
ovs-vsctl --may-exist add-br br-int -- set Bridge br-int datapath_type=netdev -- br-set-external-id br-int bridge-id br-int -- set bridge br-int fail-mode=standalone
Attach a representor to br-int:
ovs-vsctl add-port br-int rep$x -- set Interface rep$x type=dpdk options:dpdk-devargs=<PF PCI>,representor=[$x],dv_flow_en=2,dv_xmeta_en=4
Add a port for the Geneve tunnel:
ovs-vsctl add-port br-int geneve0 -- set interface geneve0 type=geneve options:key=<VNI> options:remote_ip=<$remote_ip_1> options:local_ip=<$local_ip_1>
GRE Tunnel Offloads
To configure OVS-DOCA GRE encapsulation/decapsulation:
Create a br-phy bridge:
ovs-vsctl --may-exist add-br br-phy -- set Bridge br-phy datapath_type=netdev -- br-set-external-id br-phy bridge-id br-phy -- set bridge br-phy fail-mode=standalone
Attach a PF interface to br-phy bridge:
ovs-vsctl add-port br-phy pf -- set Interface pf type=dpdk options:dpdk-devargs=<PF PCI>,dv_flow_en=2,dv_xmeta_en=4
Configure an IP to the bridge:
ifconfig br-phy <$local_ip_1> up
Create a br-int bridge:
ovs-vsctl --may-exist add-br br-int -- set Bridge br-int datapath_type=netdev -- br-set-external-id br-int bridge-id br-int -- set bridge br-int fail-mode=standalone
Attach a representor to br-int:
ovs-vsctl add-port br-int rep$x -- set Interface rep$x type=dpdk options:dpdk-devargs=<PF PCI>,representor=[$x],dv_flow_en=2,dv_xmeta_en=4
Add a port for the Geneve tunnel:
ovs-vsctl add-port br-int gre0 -- set interface gre0 type=gre options:key=<VNI> options:remote_ip=<$remote_ip_1> options:local_ip=<$local_ip_1>
DP-HASH Offloads
OVS supports group configuration. The "select" type executes one bucket in the group, balancing across the buckets according to their weights. To select a bucket, for each live bucket, OVS hashes flow data with the bucket ID and multiplies that by the bucket weight to obtain a "score". The bucket with the highest score is selected.
For more details, refer to the ovs-ofctl man.
For example:
ovs-ofctl add-group br-int 'group_id=1,type=select,bucket=<port1>'
ovs-ofctl add-flow br-int in_port=<port0>,actions=group=1
Limitations:
Offloads are supported on IP traffic only (IPv4 or IPv6)
The hash calculation may be different for packets going into software vs. ones that are offloaded
Does not work concurrently with CT (i.e., configure hw-offload-ct-size="0" beforehand)
OVS-DOCA Known Limitations
Only one insertion thread is supported (n-offload-threads=1)
Only 250K connection are offloadable by default (can be configured)
Only 8 CT zones are supported by CT offload
Offload of IPv6 tunnels are not supported
OVS-DOCA Debugging
Additional debugging information can be enabled in the vSwitch log file using the dbg log level:
(
topics='netdev|ofproto|ofp|odp|doca'
IFS=$'\n'; for topic in $(ovs-appctl vlog/list | grep -E "$topics" | cut -d' ' -f1)
do
printf "$topic:file:dbg "
done
) | xargs ovs-appctl vlog/set
The listed topics are relevant to DOCA offload operations.
Coverage counters specific to the DOCA offload provider have been added. The following command should be used to check them:
ovs-appctl coverage/show # Print the current non-zero coverage counters
The following table provides the meaning behind these DOCA-specific counters:
|
Counter |
Description |
|
doca_async_queue_full |
The asynchronous offload insertion queue was full while the daemon attempted to insert a new offload. The queue will have been flushed and insertion attempted again. This is not a fatal error but is the sign of a slowed down hardware. |
|
doca_async_queue_blocked |
The asynchronous offload insertion queue has remained full even after several attempts to flush its currently enqueued requests. While not a fatal error, it should never happen during normal offload operations and should be considered a bug. |
|
doca_async_add_failed |
An asynchronous insertion failed specifically due to its asynchronous nature. This is not expected to happen and should be considered a bug. |
|
doca_pipe_resize |
The number of time a DOCA pipe has been resized. This is normal and expected as DOCA pipes receives more entries. |
|
doca_pipe_resize_over_10_ms |
A DOCA pipe resize took longer than 10ms to complete. It can happen infrequently. If a sudden drop in insertion rate is measured, this counter could help identify the root cause. |
OVS Metrics
OVS exposes Prometheus metrics through its control socket (experimental feature). These metrics can be accessed using the command:
ovs-appctl metrics/show
A terminal dashboard is also installed with OVS, ovs-metrics. This script is dependent on the OVS Python API (package python3-openvswitch). Its default mode currently watches over a set of offload-related metrics.
Verifying Host Connection on Linux
When the DPU is connected to another DPU on another machine, manually assign IP addresses with the same subnet to both ends of the connection.
Assuming the link is connected to p3p1 on the other host, run:
$ ifconfig p3p1 192.168.200.1/24 up
On the host which the DPU is connected to, run:
$ ifconfig p4p2 192.168.200.2/24 up
Have one ping the other. This is an example of the DPU pinging the host:
$ ping 192.168.200.1
Verifying Connection from Host to BlueField
There are two SFs configured on the BlueFIeld-2 device, enp3s0f0s0 and enp3s0f1s0, and their representors are part of the built-in bridge. These interfaces will get IP addresses from the DHCP server if it is present. Otherwise it is possible to configure IP address from the host. It is possible to access BlueField via the SF netdev interfaces.
For example:
Verify the default OVS configuration. Run:
# ovs-vsctl show 5668f9a6-6b93-49cf-a72a-14fd64b4c82b Bridge ovsbr1 Port pf0hpf Interface pf0hpf Port ovsbr1 Interface ovsbr1 type: internal Port p0 Interface p0 Port en3f0pf0sf0 Interface en3f0pf0sf0 Bridge ovsbr2 Port en3f1pf1sf0 Interface en3f1pf1sf0 Port ovsbr2 Interface ovsbr2 type: internal Port pf1hpf Interface pf1hpf Port p1 Interface p1 ovs_version: "2.14.1"
Verify whether the SF netdev received an IP address from the DHCP server. If not, assign a static IP. Run:
# ifconfig enp3s0f0s0 enp3s0f0s0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 inet 192.168.200.125 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.200.255 inet6 fe80::8e:bcff:fe36:19bc prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link> ether 02:8e:bc:36:19:bc txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet) RX packets 3730 bytes 1217558 (1.1 MiB) RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0 TX packets 22 bytes 2220 (2.1 KiB) TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
Verify the connection of the configured IP address. Run:
# ping 192.168.200.25 -c 5 PING 192.168.200.25 (192.168.200.25) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 192.168.200.25: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.228 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.200.25: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.175 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.200.25: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.232 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.200.25: icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=0.174 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.200.25: icmp_seq=5 ttl=64 time=0.168 ms --- 192.168.200.25 ping statistics --- 5 packets transmitted, 5 received, 0% packet loss, time 91ms rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.168/0.195/0.232/0.031 ms
Verifying Host Connection on Windows
Set IP address on the Windows side for the RShim or Physical network adapter, please run the following command in Command Prompt:
PS C:\Users\Administrator> New-NetIPAddress -InterfaceAlias "Ethernet 16" -IPAddress "192.168.100.1" -PrefixLength 22
To get the interface name, please run the following command in Command Prompt:
PS C:\Users\Administrator> Get-NetAdapter
Output should give us the interface name that matches the description (e.g. NVIDIA BlueField Management Network Adapter).
Ethernet 2 NVIDIA ConnectX-4 Lx Ethernet Adapter 6 Not Present 24-8A-07-0D-E8-1D
Ethernet 6 NVIDIA ConnectX-4 Lx Ethernet Ad...#2 23 Not Present 24-8A-07-0D-E8-1C
Ethernet 16 NVIDIA BlueField Management Netw...#2 15 Up CA-FE-01-CA-FE-02
Once IP address is set, Have one ping the other.
C:\Windows\system32>ping 192.168.100.2
Pinging 192.168.100.2 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.100.2: bytes=32 time=148ms TTL=64
Reply from 192.168.100.2: bytes=32 time=152ms TTL=64
Reply from 192.168.100.2: bytes=32 time=158ms TTL=64
Reply from 192.168.100.2: bytes=32 time=158ms TTL=64