NVIDIA DOCA PCC Application Guide
This document provides a DOCA PCC implementation on top of NVIDIA® BlueField® DPU.
Programmable Congestion Control (PCC) allows users to design and implement their own congestion control (CC) algorithm, giving them the flexibility to work out an optimal solution to handle congestion in their clusters. On BlueField-3, PCC is provided as a component of DOCA.
The application leverages the DOCA PCC API to provide users the flexibility to manage allocation of DPA resources according to their requirements.
Typical DOCA application includes App running on host/Arm and App running on DPA. Developers are advised to use the host/Arm application with minimal changes and focus on developing their algorithm and integrating it into the DPA application.
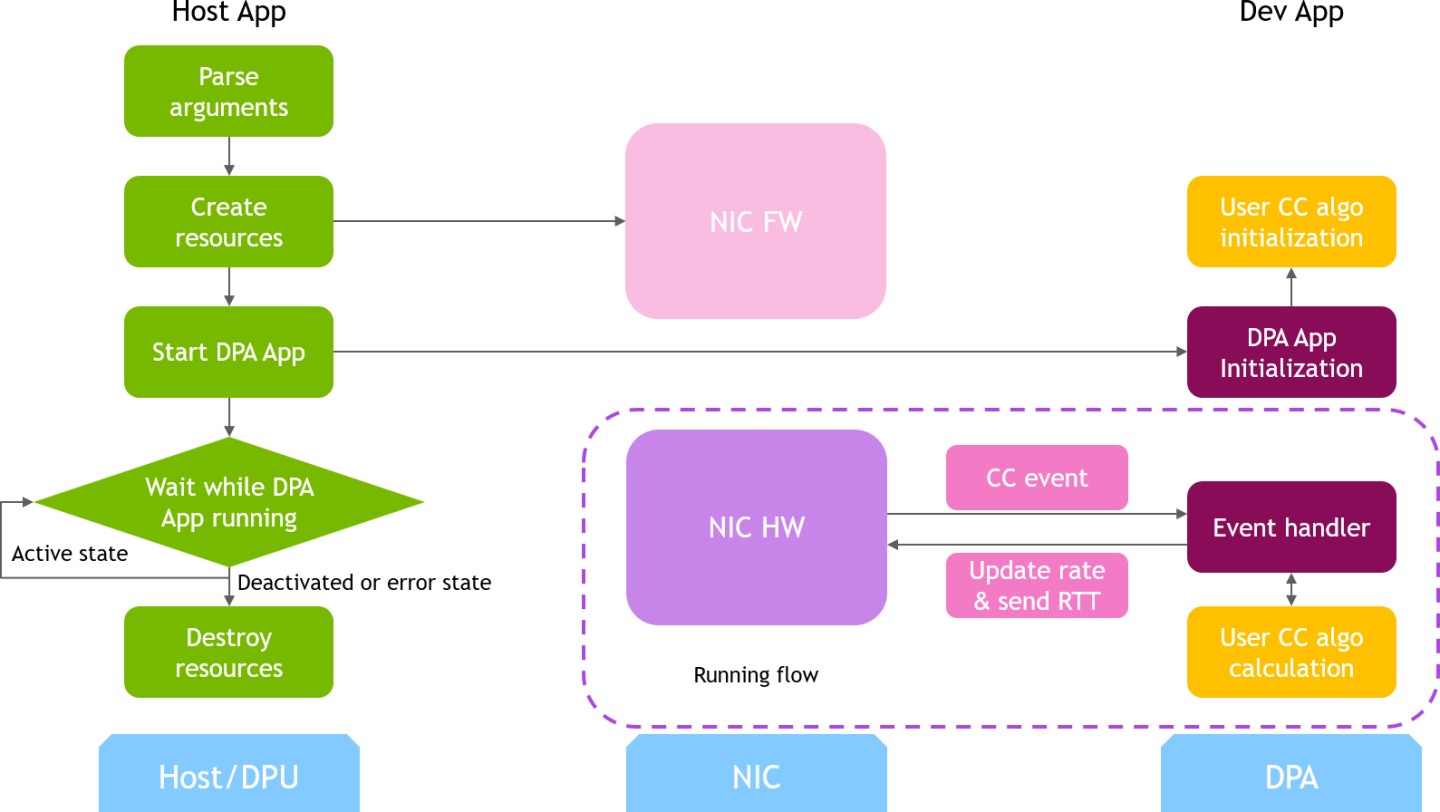
DOCA PCC application consists of two parts:
Host/Arm app is the control plane. It is responsible for allocating all resources and handover to the DPA app initially, then destroying everything when the DPA app finishes its operation. The host app must always be alive to stay in control while the device app is working.
Device/DPA app is the data plane. It is mainly for CC event handler. When the first thread is activated, DPA App initialization is done in the DOCA PCC library by calling the algorithm initialization function implemented by the user in the app. Moreover, the user algorithm execution function is called when a CC event arrives. The user algorithm takes event data as input and performs a calculation using per-flow context and replies with updated rate value and a flag to sent RTT request.
The host/Arm application sends command to NIC firmware when allocating or destroying resources. CC events are generated by NIC hardware automatically when sending data or receiving ACK/NACK/CNP/RTT packets, then the device application handles these events by calling the user algorithm. After the DPA application replies to hardware, handling of current event is done and the next event can arrive.
/opt/mellanox/doca/applications/pcc/src
├── host
│ ├── pcc.c
│ ├── pcc_core.c
│ └── pcc_core.h
└── device
├── algo
│ ├── rtt_template.h
│ ├── rtt_template_algo_params.h
│ ├── rtt_template_ctxt.h
│ └── rtt_template.c
└── pcc_dev_main.c
The main content of the reference DOCA PCC application files are the following:
host/pcc.c – entry point to entire application
host/pcc_core.c – host functions to initialize and destroy the PCC application resources, parsers for PCC command line parameters
device/pcc_dev_main.c – callbacks for user CC algorithm initialization, user CC algorithm calculation, algorithm parameter change notification
device/algo/* – user CC algorithm reference template. Put user algorithm code here.
This application leverages the following DOCA library:
Refer to its respective programming guide for more information.
NVIDIA BlueField-3 DPU is required
Firmware 32.38.1000 and higher
MFT 4.25 and higher
Installation
Refer to the NVIDIA DOCA Installation Guide for Linux for details on how to install BlueField-related software.
Prerequisites
Enable USER_PROGRAMMABLE_CC in mlxconfig:
mlxconfig -y -d /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf0 set USER_PROGRAMMABLE_CC=1
R eset firmware or power cycle the host to apply the configuration change.
Make sure to perform graceful shutdown before power cycling the host.
Application Execution
The PCC application is provided in both source and binary forms. The binary is located under /opt/mellanox/doca/applications/pcc/bin/doca_pcc.
Application usage instructions:
Usage: doca_pcc [DOCA Flags] [Program Flags] DOCA Flags: -h, --help Print a help synopsis -v, --version Print program version information -l, --log-level Set the (numeric) log level
forthe program <10=DISABLE,20=CRITICAL,30=ERROR,40=WARNING,50=INFO,60=DEBUG,70=TRACE> --sdk-log-level Set the SDK (numeric) log levelforthe program <10=DISABLE,20=CRITICAL,30=ERROR,40=WARNING,50=INFO,60=DEBUG,70=TRACE> -j, --json <path> Parse all command flags from an input json file Program Flags: -d, --device <IB device names> IB device name that supports PCC (mandatory). -w, --wait-time <PCC wait time> The duration of the DOCA PCC wait (optional), can provide negative values which means infinity. If not provided then -1will be chosen. -p, --pcc-threads <pcc-threads-list> A list of the PCC threads numbers to be chosenforthe DOCA PCC context to run on (optional). Must be provided as a string, such that the number are separated by a space.NoteThis usage printout can be printed to the command line using the -h (or --help) options:
/opt/mellanox/doca/applications/pcc/bin/doca_pcc -h
NoteFor additional information, refer to section "Command Line Flags".
CLI example for running the application on the BlueField or the host:
/opt/mellanox/doca/applications/pcc/bin/doca_pcc -d mlx5_0
WarningThe IB device identifier (mlx5_0) should match the identifier of the desired IB device.
The application also supports a JSON-based deployment mode, in which all command-line arguments are provided through a JSON file:
doca_pcc --json [json_file]
For example:
cd /opt/mellanox/doca/applications/pcc/bin ./doca_pcc --json ./pcc_params.json
WarningBefore execution, ensure that the used JSON file contains the correct configuration parameters, and especially the PCIe addresses necessary for the deployment.
Command Line Flags
|
Flag Type |
Short Flag |
Long Flag/JSON Key |
Description |
JSON Content |
|
General flags |
h |
help |
Prints a help synopsis |
N/A |
|
v |
version |
Prints program version information |
N/A |
|
|
l |
log-level |
Sets the log level for the program:
|
N/A |
|
|
N/A |
sdk-log-level |
Sets the log level for the program:
|
N/A |
|
|
j |
json |
Parse all command flags from an input JSON file |
N/A |
|
|
Program flags |
d |
device |
IB device name that supports PCC |
|
|
w |
wait-time |
(Optional) In seconds, the duration of the DOCA PCC wait. Negative values mean infinity. |
|
|
|
p |
pcc-threads |
(Optional) A list of the PCC EU indexes to be chosen for the DOCA PCC event handler threads to run on. Must be provided as a string, such that the numbers are separated by a space. The placement of the PCC threads per core can be controlled using the EU indexes. Utilizing a large number of EUs, while limiting the number of threads per core, gives the best event handling rate and lowest event latency. The last EU is used for communication with the NIC while all others are for data path CC event handling. |
|
Refer to DOCA Arg Parser for more information regarding the supported flags and execution modes.
Troubleshooting
Refer to the NVIDIA DOCA Troubleshooting Guide for any issue encountered with the installation or execution of the DOCA applications.
In addition to providing the application in binary form, the installation also includes all of the application sources and compilation instructions so as to allow modifying the sources and recompiling the application. For more information about the applications, as well as development and compilation tips, refer to the DOCA Applications page.
The sources of the application can be found under the /opt/mellanox/doca/applications/pcc/src directory.
Recompiling All Applications
The applications are all defined under a single meson project, so the default compilation recompiles all the DOCA applications.
To build all the applications together, run:
cd /opt/mellanox/doca/applications/
meson /tmp/build
ninja -C /tmp/build
doca_pcc is created under /tmp/build/pcc/src/.
Recompiling PCC Application Only
To directly build only the PCC application:
cd /opt/mellanox/doca/applications/
meson /tmp/build -Denable_all_applications=false -Denable_pcc=true
ninja -C /tmp/build
doca_pcc is created under /tmp/build/pcc/src/.
Alternatively, one can set the desired flags in the meson_options.txt file instead of providing them in the compilation command line:
Edit the following flags in /opt/mellanox/doca/applications/meson_options.txt:
Set enable_all_applications to false
Set enable_pcc to true
Run the following compilation commands :
cd /opt/mellanox/doca/applications/ meson /tmp/build ninja -C /tmp/build
Notedoca_pcc is created under /tmp/build/pcc/src/.
Troubleshooting
Refer to the NVIDIA DOCA Troubleshooting Guide for any issue encountered with the compilation of the application.
This section lists the application's configuration flow, explaining the different DOCA function calls and wrappers.
Parse application argument.
Initialize arg parser resources and register DOCA general parameters.
doca_argp_init();
Register PCC application parameters.
register_pcc_params();
Parse the arguments.
doca_argp_start();
Parse DOCA flags.
Parse DOCA PCC parameters.
PCC initialization.
pcc_init();
Open DOCA device that supports PCC.
Create DOCA PCC context.
Configure affinity of threads handling CC events.
Start DOCA PCC.
doca_pcc_start();
Create PCC process and other resources.
Trigger initialization of PCC on device.
Register the PCC in the NIC hardware so CC events can be generated and an event handler can be triggered.
Process state monitor loop.
doca_pcc_get_process_state(); doca_pcc_wait();
Get the state of the process:
State
Description
DOCA_PCC_PS_ACTIVE = 0
The process handles CC events (only one process is active at a given time)
DOCA_PCC_PS_STANDBY = 1
The process is in standby mode (another process is already ACTIVE)
DOCA_PCC_PS_DEACTIVATED = 2
The process has been deactivated by NIC firmware and should be destroyed
DOCA_PCC_PS_ERROR = 3
The process is in error state and should be destroyed
Wait on process events from the device.
PCC destroy.
doca_pcc_destroy();
Destroy PCC resources. The process stops handling PCC events.
Close DOCA device.
Arg parser destroy.
doca_argp_destroy()
The Port Programmable Congestion Control (PPCC) register allows the user to configure and read PCC algorithms and their parameters/counters.
It supports the following functionalities:
Enabling different algorithms on different ports
Querying information of both algorithms and tunable parameters/counters
Changing algorithm parameters without compiling and reburning user image
Querying or clearing programmable counters
Usage
The PPCC register can be accessed using a string similar to the following:
sudo mlxreg -d /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf0 -y --get --op "cmd_type=0" --reg_name PPCC --indexes "local_port=1,pnat=0,lp_msb=0,algo_slot=0,algo_param_index=0"
sudo mlxreg -d /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf0 -y --set "cmd_type=1" --reg_name PPCC --indexes "local_port=1,pnat=0,lp_msb=0,algo_slot=0,algo_param_index=0"
Where you must:
Set the cmd_type and the indexes
Give values for algo_slot, algo_param_index
Keep local_port=1, pnat=0, lp_msb=0
Keep doca_pcc application running
|
cmd_type |
Description |
Method |
Index |
Input (in --set) |
Output |
|
0x0 |
Get algorithm info |
Get |
algo_slot |
N/A |
|
|
0x1 |
Enable algorithm |
Set |
sl_bitmask trace_en counter_en |
N/A |
|
|
0x2 |
Disable algorithm |
Set |
N/A |
N/A |
|
|
0x3 |
Get algorithm enabling status |
Get |
N/A |
|
|
|
0x4 |
Get number of parameters |
Get |
N/A |
|
|
|
0x5 |
Get parameter information |
Get |
algo_slot algo_param_index |
N/A |
|
|
0x6 |
Get parameter value |
Get |
N/A |
|
|
|
0x7 |
Get and clear parameter |
Get |
N/A |
|
|
|
0x8 |
Set parameter value |
Set |
Parameter value |
N/A |
|
|
0xA |
Bulk get parameters |
Get |
algo_slot |
N/A |
|
|
0xB |
Bulk set parameters |
Set |
text_length - param num x 4 text[0]…text[n] - param values |
N/A |
|
|
0xC |
Bulk get counters |
Get |
N/A |
|
|
|
0xD |
Bulk get and clear counters |
Get |
N/A |
|
|
|
0xE |
Get number of counters |
Get |
N/A |
|
|
|
0xF |
Get counter information |
Get |
algo_slot algo_param_index |
N/A |
|
|
0x10 |
Get algorithm info array |
Get |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Internal Default Algorithm
The internal default algorithm is used when enhanced connection establishment (ECE) negotiation fails. It is mainly used for backward compatibility and can be disabled using "force mode". Otherwise, users may change doca_pcc_dev_user_algo() in the device app to run a specific algorithm without considering the algorithm negotiation.
The force mode command is per port:
sudo mlxreg -d /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf0 -y --get --op "cmd_type=2" --reg_name PPCC --indexes "local_port=1,pnat=0,lp_msb=0,algo_slot=15,algo_param_index=0"
sudo mlxreg -d /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf0.1 -y --get --op "cmd_type=2" --reg_name PPCC --indexes "local_port=1,pnat=0,lp_msb=0,algo_slot=15,algo_param_index=0"
Counters
Counters are shared on the port and are only enabled on one algo_slot per port. The following command enables the counters while enabling the algorithm according to the algo_slot:
sudo mlxreg -d /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf0 -y --set "cmd_type=1,counter_en=1" --reg_name PPCC --indexes "local_port=1,pnat=0,lp_msb=0,algo_slot=0,algo_param_index=0"
After counters are enabled on the algo_slot, they can be queried using cmd_type 0xC or 0xD.
sudo mlxreg -d /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf0 -y --get --op "cmd_type=12" --reg_name PPCC --indexes "local_port=1,pnat=0,lp_msb=0,algo_slot=0,algo_param_index=0"
sudo mlxreg -d /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf0 -y --get --op "cmd_type=13" --reg_name PPCC --indexes "local_port=1,pnat=0,lp_msb=0,algo_slot=0,algo_param_index=0"
/opt/mellanox/doca/applications/pcc/src
/opt/mellanox/doca/applications/pcc/bin/pcc_params.json