NVIDIA DOCA NAT Application Guide
This document provides a NAT implementation on top of NVIDIA® BlueField® DPU.
The Network Address Translation (NAT) reference application leverages the DPU's hardware capability to switch packets with local IP addresses to global ones and vise versa.
The NAT application is based on the DOCA Flow API used for the programming of the DPU's hardware.
NAT can operate in three modes:
Static mode – application gets pairs of local IP address and global IP address from the user using a JSON file
Dynamic mode – user provides pool of global IP addresses that can be used. The application should pick one address from the pool for new local area network (LAN) IP address and use it. Once the session closes, the addresses are returned to the pool.
PAT mode (DNS offload) – the user provides one global address to use. In addition, the user provides mapping between the local port address to the global port. For each packet, the local address is replaced with the global one and ports are replaced according to mapping table.
The NAT application is design to run on the DPU. The DPU intercepts ingress traffic from both wire and host, switches the relevant IP address and port according to data configured by the user, and forwards it to the egress port.
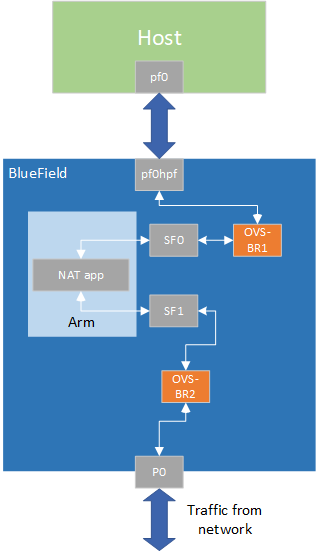
NAT runs on the DPU to classify packets.
The app should be configured using a JSON file which includes the operation mode.
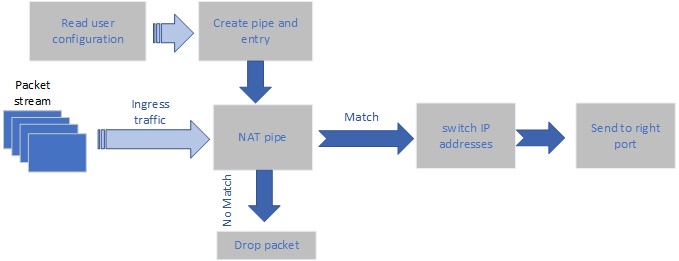
Static Mode
For static mode, the JSON file should include pairs of local and global IP addresses. No change for ports in this mode.
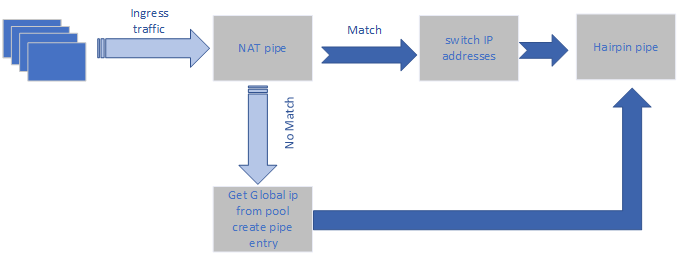
Dynamic Mode
The user must provide a pool of global IP addresses to use. The application allocates a global address to every miss in the pipe (new local address).
If no more global addresses are available in the pool, the user gets an error message and the packet is sent as is.
The application performs a callback to remove the matching of global and local IPs and returns the address to the pool.
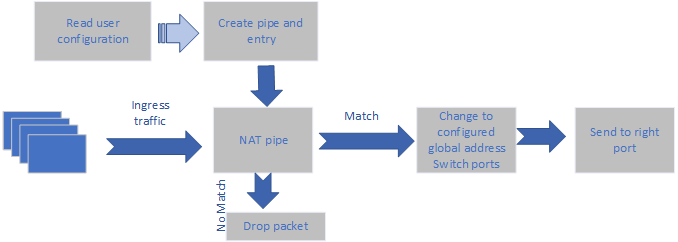
PAT (NAT Offload) Mode
The user provides a global address to replace all local addresses in the user LAN.
The user provides a matching of local IP and port to global port.
The application changes the local IP of every match to the global IP provided by the user and updates the port number according to user configuration.
This application leverages the following DOCA library:
Refer to its respective programming guide for more information.
Installation
Refer to the NVIDIA DOCA Installation Guide for Linux for details on how to install BlueField-related software .
Prerequisites
The NAT application is based on DOCA Flow. Therefore, the user is required to allocate huge pages.
echo '2048' | sudo tee -a /sys/kernel/mm/hugepages/hugepages-2048kB/nr_hugepages
On some operating systems (RockyLinux, OpenEuler, CentOS 8.2) the default huge page size on the DPU (and Arm hosts) is larger than 2MB, and is often 512MB instead. In such cases, the guiding principal is to allocate 4GB of RAM, and instead of allocating 2048 pages, one should allocate the matching amount (8 pages):
sudo echo 8 > /proc/sys/vm/nr_hugepages
Application Execution
The NAT application is provided in both source and binary forms, The binary is located under /opt/mellanox/doca/applications/nat/bin/doca_nat.
Application usage instructions:
Usage: doca_nat [DPDK Flags] -- [DOCA Flags] [Program Flags] DOCA Flags: -h, --help Print a help synopsis -v, --version Print program version information -l, --log-level Set the (numeric) log level
forthe program <10=DISABLE,20=CRITICAL,30=ERROR,40=WARNING,50=INFO,60=DEBUG,70=TRACE> --sdk-log-level Set the SDK (numeric) log levelforthe program <10=DISABLE,20=CRITICAL,30=ERROR,40=WARNING,50=INFO,60=DEBUG,70=TRACE> -j, --json <path> Parse all command flags from an input json file Program Flags: -m, --mode <mode> set NAT mode -r, --nat-rules <path> Path to the JSON file with NAT rules -lan, --lan-intf <lan intf> name of LANinterface-wan, --wan-intf <wan intf> name of waninterfaceNoteThis usage printout can be printed to the command line using the -h (or --help) options:
/opt/mellanox/doca/applications/nat/bin/doca_nat -- -h
NoteFor additional information, refer to section "Command Line Flags".
CLI example for running the application on the BlueField:
/opt/mellanox/doca/applications/nat/bin/doca_nat -a auxiliary:mlx5_core.sf.
4,dv_flow_en=2-a auxiliary:mlx5_core.sf.5,dv_flow_en=2-- -mstatic-r /opt/mellanox/doca/applications/nat/bin/nat_static_rules.json -lan sf3 -wan sf4WarningSFs must be enabled according to NVIDIA BlueField DPU Scalable Function User Guide.
WarningThe flag -a auxiliary:mlx5_core.sf.4,dv_flow_en=2 -a auxiliary:mlx5_core.sf.5,dv_flow_en=2 is mandatory for proper usage of the application. Modifying this flag results in unexpected behavior as only 2 ports are supported. The SF number is arbitrary and configurable.
WarningThe SF numbers must match the identifiers of the configured SFs.
The application also supports a JSON-based deployment mode, in which all command-line arguments are provided through a JSON file:
doca_nat --json [json_file]
For example:
cd /opt/mellanox/doca/applications/nat/bin ./doca_nat --json ./nat_params.json
WarningBefore execution, ensure that the used JSON file contains the correct configuration parameters, and especially the PCIe addresses necessary for the deployment.
Command Line Flags
|
Flag Type |
Short Flag |
Long Flag/JSON Key |
Description |
JSON Content |
|
DPDK Flags |
a |
devices |
Add a PCIe device into the list of devices to probe |
|
|
General flags |
h |
help |
Prints a help synopsis |
N/A |
|
v |
version |
Prints program version information |
N/A |
|
|
l |
log-level |
Set the log level for the application:
|
|
|
|
N/A |
sdk-log-level |
Sets the log level for the program:
|
|
|
|
j |
json |
Parse all command flags from an input json file |
N/A |
|
|
Program Flags |
m |
mode |
Set NAT mode |
|
|
r |
nat-rules |
Path to the JSON file with NAT rules |
|
|
|
lan |
Lan-intf |
Name of LAN interface |
|
|
|
wan |
Wan-intf |
Name of WAN interface |
|
Refer to DOCA Arg Parser for more information regarding the supported flags and execution modes.
Troubleshooting
Refer to the NVIDIA DOCA Troubleshooting Guide for any issue encountered with the installation or execution of the DOCA applications .
In addition to providing the application in binary form, the installation also includes all of the application sources and compilation instructions so as to allow modifying the sources and recompiling the application. For more information about the applications, as well as development and compilation tips, refer to the DOCA Applications page.
The sources of the application can be found under the /opt/mellanox/doca/applications/nat/src directory.
Recompiling All Applications
The applications are all defined under a single meson project, so the default compilation recompiles all the DOCA applications.
To build all the applications together, run:
cd /opt/mellanox/doca/applications/
meson /tmp/build
ninja -C /tmp/build
doca_nat is created under /tmp/build/nat/src/.
Recompiling NAT Application Only
To directly build only the NAT application:
cd /opt/mellanox/doca/applications/
meson /tmp/build -Denable_all_applications=false -Denable_nat=true
ninja -C /tmp/build
doca_nat is created under /tmp/build/nat/src/.
Alternatively, users can set the desired flags in the meson_options.txt file instead of providing them in the compilation command line:
Edit the following flags in /opt/mellanox/doca/applications/meson_options.txt:
Set enable_all_applications to false
Set enable_nat to true
Run the following compilation commands :
cd /opt/mellanox/doca/applications/ meson /tmp/build ninja -C /tmp/build
Notedoca_nat is created under /tmp/build/nat/src/
Troubleshooting
Refer to the NVIDIA DOCA Troubleshooting Guide for any issue encountered with the compilation of the application .
Parse application argument.
Initialize arg parser resources and register DOCA general parameters.
doca_argp_init();
Register NAT application.
register_nat_params()
Parse the arguments.
doca_argp_start();
Parse DPDK flags and invoke handler for calling the rte_eal_init() function.
Parse app parameters.
DPDK initialization.
dpdk_init();
Calls rte_eal_init() to initialize EAL resources with the provided EAL flags.
DPDK port initialization and start.
dpdk_queues_and_ports_init();
Initialize DPDK ports, including mempool allocation.
Initialize hairpin queues if needed.
Bind hairpin queues of each port to its peer port.
NAT initialization.
nat_init();
DOCA Flow and DOCA Flow port initialization.
Init user configuration rules into app structure.
parsing_nat_rules();
Init pipes and entry according to rules.
nat_pipes_init();
Wait for signal to end application.
NAT destroy.
nat_destroy();
DPDK ports and queues destruction.
dpdk_queues_and_ports_fini();
DPDK finish.
dpdk_fini();
Calls rte_eal_destroy() to destroy initialized EAL resources.
Arg parser destroy.
doca_argp_destroy();
/opt/mellanox/doca/applications/nat/src
/opt/mellanox/doca/applications/nat/bin/nat_params.json