GRID Software for Citrix XenServer Release Notes
GRID Software for Citrix XenServer Release Notes Version 367.132/370.39
Release information for all users of NVIDIA GRID software and hardware on Citrix XenServer.
These Release Notes summarize current status, information on validated platforms, and known issues with NVIDIA GRID™ software and hardware on Citrix XenServer.
This release includes the following software:
- NVIDIA GRID Virtual GPU Manager version 367.132 for the Citrix XenServer releases listed in Hypervisor Software Releases
- NVIDIA Windows drivers for vGPU version 370.39
- NVIDIA Linux drivers for vGPU version 367.133
If you install the wrong package for the version of Citrix XenServer you are using, GRID vGPU Manager will fail to load.
The GRID vGPU Manager and Windows guest VM drivers must be installed together. Older VM drivers will not function correctly with this release of GRID vGPU Manager. Similarly, older GRID vGPU Managers will not function correctly with this release of Windows guest drivers. See VM running older NVIDIA vGPU drivers fails to initialize vGPU when booted.
Updates in this release:
- Miscellaneous bug fixes
- Security updates
This release of NVIDIA GRID software provides support for several NVIDIA GPUs on validated server hardware platforms, Citrix XenServer hypervisor software versions, and guest operating systems.
2.1. Supported NVIDIA GPUs and Validated Server Platforms
This release of NVIDIA GRID software provides support for the following NVIDIA GPUs on Citrix XenServer, running on validated server hardware platforms:
- GRID K1
- GRID K2
- Tesla M6
- Tesla M10
- Tesla M60
For a list of validated server platforms, refer to NVIDIA GRID Certified Servers.
Tesla M60 and M6 GPUs support compute mode and graphics mode. GRID vGPU requires GPUs that support both modes to operate in graphics mode.
Recent Tesla M60 GPUs and M6 GPUs are supplied in graphics mode. However, your GPU might be in compute mode if it is an older Tesla M60 GPU or M6 GPU, or if its mode has previously been changed.
To configure the mode of Tesla M60 and M6 GPUs, use the gpumodeswitch tool provided with GRID software releases.
2.2. Hypervisor Software Releases
This release supports only the hypervisor software releases listed in the table.If a specific release, even an update release, is not listed, it’s not supported.
| Software | Release Supported |
|---|---|
| Citrix XenServer 7.1 |
RTM build is supported. |
| Citrix XenServer 7.0 |
RTM build 125380 is supported. |
| Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops (formerly known as "Citrix XenDesktop") |
Version 7 1909 Version 7 1808 Version 7.18 GA Version 7.15 CU3 (LTSR) Version 7.15 (LTSR) |
2.3. Guest OS Support
NVIDIA GRID software supports several Windows releases and Linux distributions as a guest OS.
Use only a guest OS release that is listed as supported by NVIDIA GRID software with your virtualization software. To be listed as supported, a guest OS release must be supported not only by NVIDIA GRID software, but also by your virtualization software. NVIDIA cannot support guest OS releases that your virtualization software does not support.
Windows Guest OS Support
NVIDIA GRID software supports only the following Windows releases as a guest OS on Citrix XenServer:
If a specific release, even an update release, is not listed, it’s not supported.
- Windows Server 2016 1607, 1709
- Windows Server 2012 R2
- Windows Server 2008 R2
- Windows 10 RTM (1507), November Update (1511), Anniversary Update (1607), Creators Update (1703) (32/64-bit)
- Windows 8.1 (32/64-bit)
- Windows 8 (32/64-bit)
- Windows 7 (32/64-bit)
2.3.2. Linux Guest OS Support
NVIDIA GRID software supports only the following Linux distributions as a guest OS only on supported Tesla GPUs on Citrix XenServer:
If a specific release, even an update release, is not listed, it’s not supported.
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.0-7.4
- CentOS 7.0-7.4
- Ubuntu 16.04 LTS
- Ubuntu 14.04 LTS
GRID K1 and GRID K2 do not support vGPU on a Linux guest OS.
Known product limitations for this release of NVIDIA GRID are described in the following sections.
3.1. vGPU profiles with 512 Mbytes or less of frame buffer support only 1 virtual display head on Windows 10
Description
To reduce the possibility of memory exhaustion, vGPU profiles with 512 Mbytes or less of frame buffer support only 1 virtual display head on a Windows 10 guest OS.
The following vGPU profiles have 512 Mbytes or less of frame buffer:
- Tesla M6-0B, M6-0Q
- Tesla M10-0B, M10-0Q
- Tesla M60-0B, M60-0Q
- GRID K100, K120Q
- GRID K200, K220Q
Workaround
Use a profile that supports more than 1 virtual display head and has at least 1 Gbyte of frame buffer.
3.2. NVENC requires at least 1 Gbyte of frame buffer
Description
Using the frame buffer for the NVIDIA hardware-based H.264/HEVC video encoder (NVENC) may cause memory exhaustion with vGPU profiles that have 512 Mbytes or less of frame buffer. To reduce the possibility of memory exhaustion, NVENC is disabled on profiles that have 512 Mbytes or less of frame buffer. Application GPU acceleration remains fully supported and available for all profiles, including profiles with 512 MBytes or less of frame buffer. NVENC support from both Citrix and VMware is a recent feature and, if you are using an older version, you should experience no change in functionality.
The following vGPU profiles have 512 Mbytes or less of frame buffer:
- Tesla M6-0B, M6-0Q
- Tesla M10-0B, M10-0Q
- Tesla M60-0B, M60-0Q
- GRID K100, K120Q
- GRID K200, K220Q
Workaround
If you require NVENC to be enabled, use a profile that has at least 1 Gbyte of frame buffer.
3.3. VM running older NVIDIA vGPU drivers fails to initialize vGPU when booted
Description
A VM running older NVIDIA drivers, such as those from a previous vGPU release, will fail to initialize vGPU when booted on a Citrix XenServer platform running the current release of GRID Virtual GPU Manager.
In this scenario, the VM boots in standard VGA mode with reduced resolution and color depth. The NVIDIA GRID GPU is present in Windows Device Manager but displays a warning sign, and the following device status:
Windows has stopped this device because it has reported problems. (Code 43)
Depending on the versions of drivers in use, the Citrix XenServer VM’s /var/log/messages log file reports one of the following errors:
- An error message:
vmiop_log: error: Unable to fetch Guest NVIDIA driver information
- A version mismatch between guest and host drivers:
vmiop_log: error: Guest VGX version(1.1) and Host VGX version(1.2) do not match
- A signature mismatch:
vmiop_log: error: VGPU message signature mismatch.
Resolution
Install the latest NVIDIA vGPU release drivers in the VM.
3.4. Virtual GPU fails to start if ECC is enabled
Description
Tesla M60 and Tesla M6 GPUs support error correcting code (ECC) memory for improved data integrity. Tesla M60 and M6 GPUs in graphics mode are supplied with ECC memory disabled by default, but it may subsequently be enabled using nvidia-smi.
However, NVIDIA GRID vGPU does not support ECC memory. If ECC memory is enabled, NVIDIA GRID vGPU fails to start. The following error is logged in the Citrix XenServer VM’s /var/log/messages log file:
vmiop_log: error: Initialization: VGX not supported with ECC Enabled.
Resolution
Ensure that ECC is disabled on all GPUs.
- Use nvidia-smi to list the status of all GPUs, and check for ECC noted as enabled on GPUs.
- Change the ECC status to off on each GPU for which ECC is enabled by executing the following command:
nvidia-smi -i id -e 0
id is the index of the GPU as reported by nvidia-smi.
- Reboot the host.
3.5. Single vGPU benchmark scores are lower than passthrough GPU
Description
A single vGPU configured on a physical GPU produces lower benchmark scores than the physical GPU run in passthrough mode.
Aside from performance differences that may be attributed to a vGPU’s smaller framebuffer size, vGPU incorporates a performance balancing feature known as Frame Rate Limiter (FRL), which is enabled on all vGPUs. FRL is used to ensure balanced performance across multiple vGPUs that are resident on the same physical GPU. The FRL setting is designed to give good interactive remote graphics experience but may reduce scores in benchmarks that depend on measuring frame rendering rates, as compared to the same benchmarks running on a passthrough GPU.
Resolution
FRL is controlled by an internal vGPU setting. NVIDIA does not validate vGPU with FRL disabled, but for validation of benchmark performance, FRL can be temporarily disabled by specifying frame_rate_limiter=0 in the VM’s platform:vgpu_extra_args parameter:
[root@xenserver ~]# xe vm-param-set uuid=e71afda4-53f4-3a1b-6c92-a364a7f619c2 platform:vgpu_extra_args="frame_rate_limiter=0"
[root@xenserver ~]#
The setting takes effect the next time the VM is started or rebooted.
With this setting in place, the VM’s vGPU will run without any frame rate limit. The FRL can be reverted back to its default setting in one of the following ways:
- Removing the
vgpu_extra_argskey from theplatformparameter - Removing
frame_rate_limiter=0from thevgpu_extra_argskey - Setting
frame_rate_limiter=1. For example:[root@xenserver ~]# xe vm-param-set uuid=e71afda4-53f4-3a1b-6c92-a364a7f619c2 platform:vgpu_extra_args="frame_rate_limiter=1" [root@xenserver ~]#
3.6. Virtual GPU fails to start when GPUs are mapped above 4G
Version
XenServer 6.2
Status
Fixed in XenServer 6.5
Description
GRID vGPU on Citrix XenServer 6.2 does not support operation with GPUs mapped above the 4 gigabyte (4G) boundary in the system’s physical address space.
If GPUs are mapped above 4G, the GRID vGPU Manager rpm will warn at the time of installation:
Warning: vGPU does not support GPUs mapped in 64-bit address space. Please disable 64-bit MMIO from the system's BIOS. Refer to vGPU release notes for details.
Also, the NVIDIA kernel driver will fail to load in XenServer’s dom0, so the nvidia module won’t appear in the module listing produced by lsmod. Additionally, the following warning messages will be present in the output of dmesg:
NVRM: This PCI I/O region assigned to your NVIDIA device is invalid:
NVRM: BAR1 is 128M @ 0xf800000000000000 (PCI:03ff:00:07.0)
NVRM: This is a 64-bit BAR mapped above 4GB by the system
NVRM: BIOS or the Linux kernel. The NVIDIA Linux/x86
NVRM: graphics driver and other system software components
NVRM: do not support this configuration.
Resolution
Ensure that GPUs are mapped below the 4G boundary by disabling your server’s SBIOS option that controls 64-bit memory-mapped I/O support. This option may be labeled Enable4G>Decode or Enable 64-bit MMIO.
3.7. nvidia-smi fails to operate when all GPUs are assigned to GPU passthrough mode
Description
If all GPUs in the platform are assigned to VMs in passthrough mode, nvidia-smi will return an error:
[root@xenserver-vgx-test ~]# nvidia-smi
Failed to initialize NVML: Unknown Error
This is because GPUs operating in passthrough mode are not visible to nvidia-smi and the NVIDIA kernel driver operating in the Citrix XenServer dom0.
To confirm that all GPUs are operating in passthrough, use XenCenter’s GPU tab to review current GPU assignment:
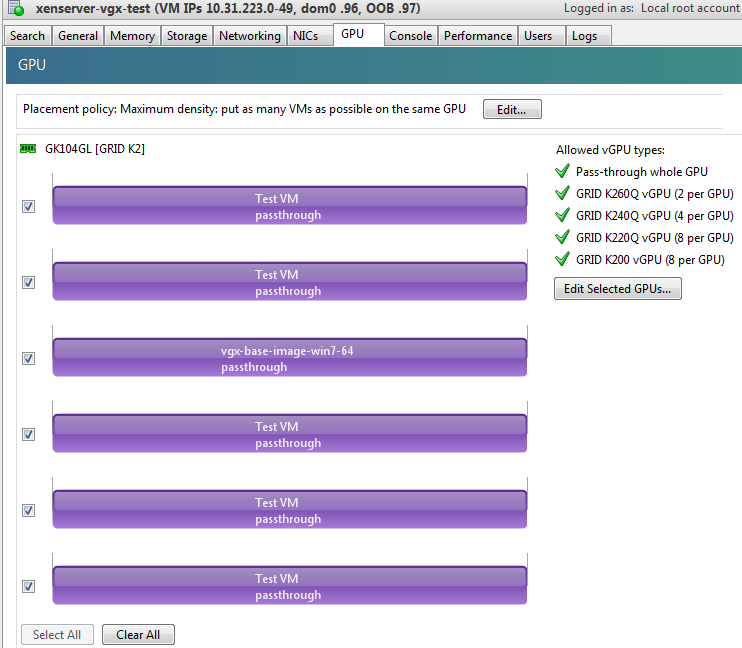
Resolution
N/A
3.8. GRID K1 and GRID K2 cards do not support monitoring of vGPU engine usage
Description
GRID K1 and GRID K2 cards do not support monitoring of vGPU engine usage. All tools and APIs for any vGPU running on GRID K1 or GRID K2 cards report 0 for the following usage statistics:
- 3D/Compute
- Memory controller bandwidth
- Video encoder
- Video decoder
3.9. Windows Aero is disabled on XenDesktop session using 3 or 4 monitors in 2560×1600 resolution
Description
Windows Aero may be disabled when XenDesktop is connected to a VM with a vGPU or passthrough GPU, with 3 or 4 monitors at 2560×1600 resolution.
This limitation is a limitation of Windows 7. For details, see the Microsoft knowledge base article Desktop background disappears with very large extended desktop on Windows 7.
3.10. VMs configured with large memory fail to initialize vGPU when booted
Description
When starting multiple VMs configured with large amounts of RAM (typically more than 32GB per VM), a VM may fail to initialize vGPU. In this scenario, the VM boots in standard VGA mode with reduced resolution and color depth. The NVIDIA GRID GPU is present in Windows Device Manager but displays a warning sign, and the following device status:
Windows has stopped this device because it has reported problems. (Code 43)
The Citrix XenServer VM’s /var/log/messages log file contains these error messages:
vmiop_log: error: NVOS status 0x29
vmiop_log: error: Assertion Failed at 0x7620fd4b:179
vmiop_log: error: 8 frames returned by backtrace
...
vmiop_log: error: VGPU message 12 failed, result code: 0x29
...
vmiop_log: error: NVOS status 0x8
vmiop_log: error: Assertion Failed at 0x7620c8df:280
vmiop_log: error: 8 frames returned by backtrace
...
vmiop_log: error: VGPU message 26 failed, result code: 0x8
Resolution
vGPU reserves a portion of the VM’s framebuffer for use in GPU mapping of VM system memory. The reservation is sufficient to support up to 32GB of system memory, and may be increased to accommodate up to 64GB by specifying enable_large_sys_mem=1 in the VM’s platform:vgpu_extra_args parameter:
[root@xenserver ~]# xe vm-param-set uuid=e71afda4-53f4-3a1b-6c92-a364a7f619c2 platform:vgpu_extra_args="enable_large_sys_mem=1"
The setting takes effect the next time the VM is started or rebooted. With this setting in place, less GPU FB is available to applications running in the VM. To accommodate system memory larger than 64GB, the reservation can be further increased by specifying extra_fb_reservation in the VM’s platform:vgpu_extra_args parameter, and setting its value to the desired reservation size in megabytes. The default value of 64M is sufficient to support 64GB of RAM. We recommend adding 2M of reservation for each additional 1GB of system memory. For example, to support 96GB of RAM, set extra_fb_reservation to 128:
platform:vgpu_extra_args="enable_large_sys_mem=1, extra_fb_reservation=128"
The reservation can be reverted back to its default setting in one of the following ways:
- Removing the
vgpu_extra_argskey from theplatformparameter - Removing
enable_large_sys_memfrom thevgpu_extra_argskey - Setting
enable_large_sys_mem=0
3.11. vGPU host driver RPM upgrade fails
Description
Upgrading vGPU host driver RPM fails with the following message on the console:
[root@xenserver ~]# rpm –U NVIDIA-vGPU-xenserver-6.5-352.46.x86_64.rpm
error: Failed dependencies:
NVIDIA-vgx-xenserver conflicts with NVIDIA-vGPU-xenserver-6.5-352.46.x86_64
[root@xenserver ~]#
Resolution
Uninstall the older vGPU RPM before installing the latest driver.
Use the following command to uninstall the older vGPU RPM:
[root@xenserver ~]# rpm –e NVIDIA-vgx-xenserver
5.1. Restricting Access to GPU Performance Counters
The NVIDIA graphics driver contains a vulnerability (CVE-2018-6260) that may allow access to application data processed on the GPU through a side channel exposed by the GPU performance counters. To address this vulnerability, update the driver and restrict access to GPU performance counters to allow access only by administrator users and users who need to use CUDA profiling tools.
The GPU performance counters that are affected by this vulnerability are the hardware performance monitors used by the CUDA profiling tools such as CUPTI, Nsight Graphics, and Nsight Compute. These performance counters are exposed on the hypervisor host and in guest VMs only as follows:
- On the hypervisor host, they are always exposed. However, the Virtual GPU Manager does not access these performance counters and, therefore, is not affected.
- In Windows and Linux guest VMs, they are exposed only in VMs configured for GPU pass through. They are not exposed in VMs configured for NVIDIA vGPU.
5.1.1. Windows: Restricting Access to GPU Performance Counters for One User by Using NVIDIA Control Panel
Perform this task from the guest VM to which the GPU is passed through.
Ensure that you are running NVIDIA Control Panel version 8.1.950.
- Open NVIDIA Control Panel:
- Right-click on the Windows desktop and select NVIDIA Control Panel from the menu.
- Open Windows Control Panel and double-click the NVIDIA Control Panel icon.
- In NVIDIA Control Panel, select the Manage GPU Performance Counters task in the Developer section of the navigation pane.
- Complete the task by following the instructions in the Manage GPU Performance Counters > Developer topic in the NVIDIA Control Panel help.
5.1.2. Windows: Restricting Access to GPU Performance Counters Across an Enterprise by Using a Registry Key
You can use a registry key to restrict access to GPU Performance Counters for all users who log in to a Windows guest VM. By incorporating the registry key information into a script, you can automate the setting of this registry for all Windows guest VMs across your enterprise.
Perform this task from the guest VM to which the GPU is passed through.
Only enterprise administrators should perform this task. Changes to the Windows registry must be made with care and system instability can result if registry keys are incorrectly set.
- Set the RmProfilingAdminOnly Windows registry key to 1.
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\NVIDIA Corporation\Global\NVTweak] Value: "RmProfilingAdminOnly" Type: DWORD Data: 00000001
The data value 1 restricts access, and the data value 0 allows access, to application data processed on the GPU through a side channel exposed by the GPU performance counters.
- Restart the VM.
5.1.3. Linux Guest VMs and Hypervisor Host: Restricting Access to GPU Performance Counters
On systems where unprivileged users don't need to use GPU performance counters, restrict access to these counters to system administrators, namely users with the CAP_SYS_ADMIN capability set. By default, the GPU performance counters are not restricted to users with the CAP_SYS_ADMIN capability.
Perform this task from the guest VM to which the GPU is passed through or from your hypervisor host machine.
In Linux guest VMs, this task requires sudo privileges. On your hypervisor host machine, this task must be performed as the root user on the machine.
- Log in to the guest VM or open a command shell on your hypervisor host machine.
- Set the kernel module parameter NVreg_RestrictProfilingToAdminUsers to 1 by adding this parameter to the /etc/modprobe.d/nvidia.conf file.
-
If you are setting only this parameter, add an entry for it to the /etc/modprobe.d/nvidia.conf file as follows:
options nvidia NVreg_RegistryDwords="NVreg_RestrictProfilingToAdminUsers=1"
-
If you are setting multiple parameters, set them in a single entry as in the following example:
options nvidia NVreg_RegistryDwords="RmPVMRL=0x0" "NVreg_RestrictProfilingToAdminUsers=1"
If the /etc/modprobe.d/nvidia.conf file does not already exist, create it.
-
- Restart the VM or reboot your hypervisor host machine.
6.1. NVOS errors might be logged when the NvFBC state is changed
Description
When the NvFBC state is changed in the VM, the following error messages might be written to the log files:
NVOS status 0x56
Failed to reset guest's license info in host
If you see these errors in the log files, ignore them.
Workaround
None required.
Status
Open
Ref. #
200494421
6.2. vGPU guest VM driver not properly loaded on servers with more than 512 GB of system memory
Description
Support for vGPU is limited to servers with a maximum of 512 GB of system memory. On servers with more than 512 GB of system memory, the guest VM driver is not properly loaded. Device Manager marks the vGPU with a yellow exclamation point.
Resolution
Disable PV IOMMU to limit the amount of system memory on the server to a maximum of 512 GB.
[root@xenserver ~]# /opt/xensource/libexec/xen-cmdline --set-xen iommu=dom0-passhthrough
Status
Not an NVIDIA bug
Ref. #
1799582
6.3. Memory exhaustion can occur with vGPU profiles that have 512 Mbytes or less of frame buffer
Description
Memory exhaustion can occur with vGPU profiles that have 512 Mbytes or less of frame buffer.
This issue typically occurs in the following situations:
- Full screen 1080p video content is playing in a browser. In this situation, the session hangs and session reconnection fails.
- Multiple display heads are used with Citrix XenDesktop or VMware Horizon on a Windows 10 guest VM.
- Higher resolution monitors are used.
- Applications that are frame-buffer intensive are used.
- NVENC is in use.
To reduce the possibility of memory exhaustion, NVENC is disabled on profiles that have 512 Mbytes or less of frame buffer.
When memory exhaustion occurs, the NVIDIA host driver reports Xid error 31 and Xid error 43 in XenServer’s /var/log/messages file.
The following vGPU profiles have 512 Mbytes or less of frame buffer:
- Tesla M6-0B, M6-0Q
- Tesla M10-0B, M10-0Q
- Tesla M60-0B, M60-0Q
- GRID K100, K120Q
- GRID K200, K220Q
The root cause is a known issue associated with changes to the way that recent Microsoft operating systems handle and allow access to overprovisioning messages and errors. If your systems are provisioned with enough frame buffer to support your use cases, you should not encounter these issues.
Workaround
- Use an appropriately sized vGPU to ensure that the frame buffer supplied to a VM through the vGPU is adequate for your workloads.
- Monitor your frame buffer usage.
- If you are using Windows 10, consider these workarounds and solutions:
-
Use a profile that has 1 Gbyte of frame buffer.
-
Optimize your Windows 10 resource usage.
To obtain information about best practices for improved user experience using Windows 10 in virtual environments, complete the NVIDIA GRID vGPU Profile Sizing Guide for Windows 10 download request form.
For more information, see also Windows 10 Optimization for XenDesktop on the Citrix blog.
-
Status
Open
Ref. #
- 200130864
- 1803861
6.4. VM bug checks after the guest VM driver for Windows 10 RS2 is installed
Description
When the VM is rebooted after the guest VM driver for Windows 10 RS2 is installed, the VM bug checks. When Windows boots, it selects one of the standard supported video modes. If Windows is booted directly with a display that is driven by an NVIDIA driver, for example a vGPU on Citrix XenServer, a blue screen crash occurs.
This issue occurs when the screen resolution is switched from VGA mode to a resolution that is higher than 1920×1200.
Fix
Download and install Microsoft Windows Update KB4020102 from the Microsoft Update Catalog.
Workaround
If you have applied the fix, ignore this workaround.
Otherwise, you can work around this issue until you are able to apply the fix by not using resolutions higher than 1920×1200.
- Choose a GPU profile in Citrix XenCenter that does not allow resolutions higher than 1920×1200.
- Before rebooting the VM, set the display resolution to 1920×1200 or lower.
Status
Not an NVIDIA bug
Ref. #
200310861
6.5. On XenServer 7.0, VMs unexpectedly reboot and XenServer crashes or freezes
Description
On XenServer 7.0, VMs to which a vGPU is attached unexpectedly reboot and XenServer crashes or freezes.
The event log in XenServer’s /var/log/crash/xen.log file lists the following errors:
- A fatal bus error on a component at the slot where the GPU card is installed
- A fatal error on a component at bus 0, device 2, function 0
This issue occurs when page-modification logging (PML) is enabled on Intel Broadwell CPUs running XenServer 7.0. Citrix is aware of this issue and is working on a permanent fix.
Workaround
Disable page-modification logging (PML) as explained in XenServer 7 host crash while starting multiple virtual machines in the Citrix Support Knowledge Center.
Status
Not an NVIDIA bug
Ref. #
1853248
6.6. With no NVIDIA driver installed, XenServer misidentifies Tesla M10 cards
Description
An erroneous entry in the pci.ids database causes Citrix XenServer to identify Tesla M10 cards as GRID M40 when no NVIDIA driver is installed.
Version
Citrix XenServer 6.5 and 7.0
Workaround
None
Status
Not an NVIDIA bug
Ref. #
NVIDIA-420/1792341
6.7. GNOME Display Manager (GDM) fails to start on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.2 and CentOS 7.0
Description
GDM fails to start on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.2 and CentOS 7.0 with the following error:
Oh no! Something has gone wrong!
Workaround
Permanently enable permissive mode for Security Enhanced Linux (SELinux).
- As root, edit the /etc/selinux/config file to set
SELINUXtopermissive.SELINUX=permissive
- Reboot the system.
~]# reboot
For more information, see Permissive Mode in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 SELinux User's and Administrator's Guide.
Status
Not an NVIDIA bug
Ref. #
200167868
6.8. Video goes blank when run in loop in Windows Media Player
Description
When connected to a vGPU-enabled VM using Citrix XenDesktop, a video played back in looping mode on Windows Media Player goes blank or freezes after a few iterations.
Workaround
None
Status
Not an NVIDIA bug
Ref. #
1306623
6.9. Local VGA console is momentarily unblanked when XenDesktop changes resolution of the VM desktop
Description
When XenDesktop establishes a remote connection to a VM using vGPU, the VM’s local VGA console display in XenCenter is blanked (assuming the VM local console has not been disabled by setting platform:vgpu_extra_args="disable_vnc=1"). If the XenDesktop session changes resolution of the VM’s desktop, the local VGA console momentarily unblanks, allowing a XenCenter user to briefly view the desktop.
Workaround
Disable the VM’s local VGA console
xe vm-param-set uuid=vm-uuid platform:vgpu_extra_args="disable_vnc=1"
Status
Open
Ref. #
NVIDIA-145/1375164
6.10. VM bugchecks on shutdown/restart when XenDesktop is installed and NVIDIA driver is uninstalled or upgraded.
Description
If the XenDesktop agent is installed in a VM before any NVIDIA GPU driver is installed, the VM will bugcheck (bluescreen) when the NVIDIA driver is subsequently upgraded or uninstalled. The bugcheck code is 0x7E, SYSTEM_THREAD_EXCEPTION_NOT_HANDLED.
Workaround
Use one of the following workarounds:
- Do a force shutdown of the VM and restart it.
- Install the NVIDIA driver in guest VMs before installing XenDesktop.
Status
Open
Ref. #
NVIDIA-295/200018125
6.11. Application frame rate may drop when running XenDesktop at 2560×1600 resolution.
Description
An application’s rendering frame rate may drop when running XenDesktop at 2560×1600 resolution, relative to the frame rate obtained at lower resolutions.
Fix
Using the Windows regedit utility within the VM, open the HKLM\SOFTWARE\Citrix\Graphics registry key and create a new DWORD value, EncodeSpeed, with a value of 2. Reboot the VM. This setting may improve the delivered frame rate at the expense of a reduction in image quality.
Status
Open
Ref. #
NVIDIA-190/1416336
6.12. Windows VM BSOD
Description
Windows VM bugchecks on XenServer when running a large number of vGPU based VMs.
XenServer’s /var/log/messages file contains these error messages:
NVRM: Xid (PCI:0000:08:00): 31, Ch 0000001e, engmask 00000111, intr 10000000
NVRM: Xid (PCI:0000:08:00): 31, Ch 00000016, engmask 00000111, intr 10000000
...
vmiop_log: error: Assertion Failed at 0xb5b898d8:4184
vmiop_log: error: 8 frames returned by backtrace
vmiop_log: error: /usr/lib/libnvidia-vgx.so(_nv000793vgx+0x69d) [0xb5b8064d]
vmiop_log: error: /usr/lib/libnvidia-vgx.so(_nv000479vgx+0x118) [0xb5b898d8]
vmiop_log: error: /usr/lib/libnvidia-vgx.so(_nv000782vgx+0x59) [0xb5b85f49]
vmiop_log: error: /usr/lib/libnvidia-vgx.so(_nv000347vgx+0x3db) [0xb5b932db]
vmiop_log: error: /usr/lib/libnvidia-vgx.so [0xb5b78e4a]
vmiop_log: error: /usr/lib/xen/bin/vgpu [0x80554be]
vmiop_log: error: /lib/libpthread.so.0 [0xb7612912]
vmiop_log: error: /lib/libc.so.6(clone+0x5e) [0xb76fc5ee]
vmiop_log: error: failed to initialize guest PTE entries
vmiop_log: error: failed to fill up guest PTE entries 3
vmiop_log: error: VGPU message 27 failed, result code: 0xff000003
vmiop_log: error: 0xc1d00001, 0xff010000, 0x1a77ba000, 0x0, 0x1,
vmiop_log: error: 0x1, 0x1000, 0x10202, 0xc1d00001, 0xff010000,
vmiop_log: error: 0xcaf00004, 0x0
vmiop_log: error: Timeout occurred, reset initiated.
Version
XenServer 6.2
Fix
Ensure that you are running the latest OEM firmware for your GRID boards.
Status
Closed
Ref. #
NVIDIA-327/1632120
6.13. Windows VM BSOD when upgrading NVIDIA drivers over a XenDesktop session
Description
Windows VM bugchecks when NVIDIA guest drivers are upgraded over a XenDesktop session.
If the VM is restarted after the bugcheck, the upgraded driver loads correctly and full functionality is available.
Fix
Upgrade XenDesktop to 7.6 Feature Pack 3
Status
Closed
Ref. #
NVIDIA-370/200130780
6.14. XenCenter does not allow vGPUs to be selected as a GPU type for Linux VMs
Description
When creating a new Linux VM or editing the properties of an existing Linux VM, XenCenter does not allow vGPUs to be selected as a GPU type.
vGPU on Linux VMs is supported as a technical preview on XenServer 6.5, and does include XenCenter integration.
Version
Affects the XenCenter integration with XenServer 6.5 only.
Resolved in the XenCenter integration with XenServer 7.0.
Workaround
Refer to XenServer vGPU Management in GRID Software User Guide for how to configure vGPU by using the xe CLI.
Status
Closed
Ref. #
NVIDIA-360
6.15. If X server is killed on a RHEL7 VM running vGPU, XenCenter console may not automatically switch to text console
Description
If X server is killed on a RHEL7 VM running vGPU, XenCenter console may display a corrupted image and fail to switchover to text console.
The failure to switchover to text console is due to a bug in RHEL7, which causes X server to not start correctly under certain configurations.
Workaround
Use CTRL+ALT+F1, F2, or F3 to switch between Linux terminals.
Status
Closed
Ref. #
NVIDIA-350/200123378
6.16. Multiple WebGL tabs in Microsoft Internet Explorer may trigger TDR on Windows VMs
Description
Running intensive WebGL applications in multiple IE tabs may trigger a TDR on Windows VMs.
Workaround
Disable hardware acceleration in IE.
To enable software rendering in IE, refer to the Microsoft knowledge base article How to enable or disable software rendering in Internet Explorer.
Status
Open
Ref. #
200148377
6.17. XenDesktop shows only a black screen when connected to a vGPU VM
Description
XenDesktop sometimes displays only a black screen when it is connected to an NVIDIA vGPU VM. The probable cause is that the display that is connected to the NVIDIA vGPU is entering a lower power state.
Fix
Disable all display-related power management settings.
For detailed instructions, visit Microsoft power plans frequently asked questions and from the list, select your OS version.
Status
Not an NVIDIA bug
Ref. #
1719877
Notice
ALL NVIDIA DESIGN SPECIFICATIONS, REFERENCE BOARDS, FILES, DRAWINGS, DIAGNOSTICS, LISTS, AND OTHER DOCUMENTS (TOGETHER AND SEPARATELY, "MATERIALS") ARE BEING PROVIDED "AS IS." NVIDIA MAKES NO WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED, IMPLIED, STATUTORY, OR OTHERWISE WITH RESPECT TO THE MATERIALS, AND EXPRESSLY DISCLAIMS ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF NONINFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY, AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
Information furnished is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, NVIDIA Corporation assumes no responsibility for the consequences of use of such information or for any infringement of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from its use. No license is granted by implication of otherwise under any patent rights of NVIDIA Corporation. Specifications mentioned in this publication are subject to change without notice. This publication supersedes and replaces all other information previously supplied. NVIDIA Corporation products are not authorized as critical components in life support devices or systems without express written approval of NVIDIA Corporation.
HDMI
HDMI, the HDMI logo, and High-Definition Multimedia Interface are trademarks or registered trademarks of HDMI Licensing LLC.
OpenCL
OpenCL is a trademark of Apple Inc. used under license to the Khronos Group Inc.
Trademarks
NVIDIA, the NVIDIA logo, NVIDIA GRID, vGPU, and Tesla are trademarks or registered trademarks of NVIDIA Corporation in the U.S. and other countries. Other company and product names may be trademarks of the respective companies with which they are associated.