Deploying BlueField Software Using BFB from BMC
It is recommended to upgrade your NVIDIA® BlueField® networking platform (DPU or SuperNIC) to the latest software and firmware versions available to benefit from new features and latest bug fixes.
This section assumes that a BlueField has already been installed in a server according to the instructions detailed in the BlueField's hardware user guide.
The following table lists an overview of the steps required to install Ubuntu BFB on your BlueField:
|
Step |
Procedure |
Direct Link |
|
1 |
Verify that RShim is already running on BMC |
|
|
2 |
Change the default credentials using bf.cfg file (optional) |
|
|
3 |
Install the Ubuntu BFB image |
|
|
4 |
Verify installation completed successfully |
|
|
5 |
Upgrade the firmware on your BlueField |
It is important to learn your BlueField's device-id to perform some of the software installations or upgrades in this guide.
To determine the device ID of the BlueField Platform on your setup, run:
host# mst start
host# mst status -v
Example output:
MST modules:
------------
MST PCI module is not loaded
MST PCI configuration module loaded
PCI devices:
------------
DEVICE_TYPE MST PCI RDMA NET NUMA
BlueField2(rev:1) /dev/mst/mt41686_pciconf0.1 3b:00.1 mlx5_1 net-ens1f1 0
BlueField2(rev:1) /dev/mst/mt41686_pciconf0 3b:00.0 mlx5_0 net-ens1f0 0
BlueField3(rev:1) /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf0.1 e2:00.1 mlx5_1 net-ens7f1np1 4
BlueField3(rev:1) /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf0 e2:00.0 mlx5_0 net-ens7f0np0 4
The device IDs for the BlueField-2 and BlueField-3 networking platforms in this example are /dev/mst/mt41686_pciconf0 and /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf0 respectively.
Display the current setting. Run:
# cat /dev/rshim<N>/misc | grep DEV_NAME
DEV_NAME usb-1.0
This output indicates that the RShim service is ready to use. If you do not receive this output:
Restart RShim service:
sudo systemctl restart rshim
Verify the current setting again. Run:
# cat /dev/rshim<N>/misc | grep DEV_NAME
If DEV_NAME does not appear, then proceed to "RShim driver not loading on BlueField with integrated BMC".
To update the software on the NVIDIA® BlueField® device, the BlueField must be booted up without mounting the eMMC flash device. This requires an external boot flow where a BFB (which includes ATF, UEFI, Arm OS, NIC firmware, and initramfs) is pushed from an external host via USB or PCIe. On BlueField devices with an integrated BMC, the USB interface is internally connected to the BMC and is enabled by default. Therefore, you must verify that the RShim driver is running on the BMC. This provides the ability to push a bootstream over the USB interface to perform an external boot.
To update the software on the NVIDIA® BlueField® device, the BlueField must be booted up without mounting the eMMC flash device. This requires an external boot flow where a BFB (which includes ATF, UEFI, Arm OS, NIC firmware, and initramfs) is pushed from an external host via USB or PCIe. On BlueField devices with an integrated BMC, the USB interface is internally connected to the BMC and is enabled by default. Therefore, you must verify that the RShim driver is running on the BMC. This provides the ability to push a bootstream over the USB interface to perform an external boot.
Changing Default Credentials Using bf.cfg
Ubuntu users are prompted to change the default password (ubuntu) for the default user (ubuntu) upon first login. Logging in will not be possible even if the login prompt appears until all services are up ("DPU is ready" message appears in /dev/rshim0/misc).
Attempting to log in before all services are up prints the following message: Permission denied, please try again.
Alternatively, Ubuntu users can provide a unique password that will be applied at the end of the BFB installation. This password must be defined in a bf.cfg configuration file. To set the password for the ubuntu user:
Create password hash. Run:
# openssl passwd -1 Password: Verifying - Password: $1$3B0RIrfX$TlHry93NFUJzg3Nya00rE1
Add the password hash in quotes to the bf.cfg file:
# vim bf.cfg ubuntu_PASSWORD='$1$3B0RIrfX$TlHry93NFUJzg3Nya00rE1'
The bf.cfg file is used with the bfb-install script in the steps that follow.
Installing BFB
The BFB installation procedure consists of the following main stages:
Disabling RShim on the server.
Initiating the BFB update procedure by transferring the BFB image using one of the following options:
Redfish interface – SimpleUpdate with SCP, HTTP, or HTTPS
Confirming the identity of the host and BMC—required only for SCP, during first-time setup or after BMC factory reset.
Sending a SimpleUpdate request.
While the BlueField Bundle (BFB) contains NIC firmware images, it does not automatically install them. To automatically install the NIC firmware during BFB upgrade, generate the configuration file bf.cfg and combine it with the BFB file:
# echo WITH_NIC_FW_UPDATE=yes > bf.cfg
# cat <path_to_bfb> bf.cfg > new.bfb
Transferring BFB File
Since the BFB is too large to store on the BMC flash or tmpfs, the image must be written to the RShim device. This can be done by either running SCP directly or using the Redfish interface.
Redfish Interface
Installing BFB File Using SCP Protocol
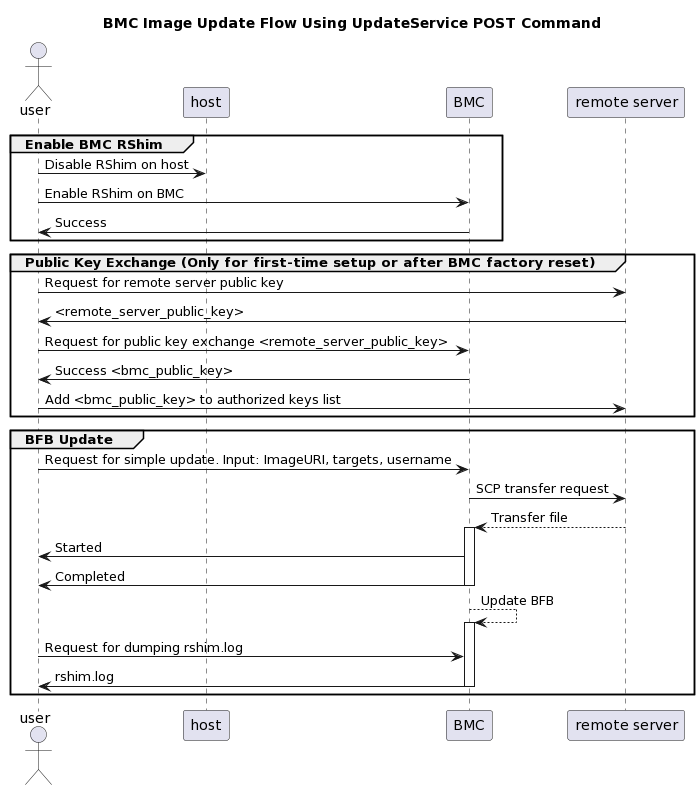
The following are the detailed instructions outlining each step in the diagram above:
Prepare secure file transfer of BFB:
Gather the public SSH host keys of the server holding the new.bfb file. Run the following against the server holding the new.bfb file ("Remote Server"):
InfoOpenSSH is required for this step.
ssh-keyscan -t <key_type> <remote_server_ip>
Where:
key_type – the type of key associated with the server storing the BFB file (e.g., ed25519)
remote_server_ip – the IP address of the server hosting the BFB file
Retrieve the remote server's public key from the response, and send the following Redfish command to the BlueField BMC:
curl -k -u root:'<password>' -H "Content-Type: application/json" -X POST -d '{"RemoteServerIP":"<remote_server_ip>", "RemoteServerKeyString":"<remote_server_public_key>"}' https://<bmc_ip>/redfish/v1/UpdateService/Actions/Oem/NvidiaUpdateService.PublicKeyExchange
Where:
password – BlueField BMC password
remote_server_ip – the IP address of the server hosting the BFB file
remote_server_public_key – remote server's public key from the ssh-keyscan response, which contains both the type and the public key with one space between the two fields (i.e., "<type> <public_key>")
bmc_ip – BMC IP address
Extract the BMC public key information (i.e., "<type> <bmc_public_key> <username>@<hostname>") from the PublicKeyExchange response and append it to the authorized_keys file on the remote server holding the BFB file. This enables password-less key-based authentication for users.
{ "@Message.ExtendedInfo": [ { "@odata.type": "#Message.v1_1_1.Message", "Message": "Please add the following public key info to ~/.ssh/authorized_keys on the remote server", "MessageArgs": [ "<type> <bmc_public_key> root@dpu-bmc" ] }, { "@odata.type": "#Message.v1_1_1.Message", "Message": "The request completed successfully.", "MessageArgs": [], "MessageId": "Base.1.15.0.Success", "MessageSeverity": "OK", "Resolution": "None" } ] }
Initiate image transfer. Run the following Redfish command:
curl -k -u root:'<password>' -H "Content-Type: application/json" -X POST -d '{"TransferProtocol":"SCP", "ImageURI":"<image_uri>","Targets":["redfish/v1/UpdateService/FirmwareInventory/DPU_OS"], "Username":"<username>"}' https://<bmc_ip>/redfish/v1/UpdateService/Actions/UpdateService.SimpleUpdate
NoteThis command uses SCP for the image transfer, initiates a soft reset on the BlueField, and then pushes the boot stream. For NVIDIA-supplied BFBs, the eMMC is flashed automatically once the boot stream is pushed. Upon success, a running message is received.
InfoAfter the BMC boots, it may take a few seconds (6-8 seconds for NVIDIA® BlueField®-2, and 2 seconds for BlueField-3) until the BlueField BSP (DPU_OS) is up.
Where:
image_uri – contains both the remote server IP address and the full path to the .bfb file on the remote server, with one slash between the two fields (i.e., <remote_server_ip>/<full_path_of_bfb> ).
InfoFor example, if <remote_server_ip> is 10.10.10.10 and <full_path_of_bfb> is /tmp/file.bfb then "ImageURI":"10.10.10.10//tmp/file.bfb".
username – username on the remote server
bmc_ip – BMC IP address
Response/error messages:
If RShim is disabled:
{ "error": { "@Message.ExtendedInfo": [ { "@odata.type": "#Message.v1_1_1.Message", "Message": "The requested resource of type Target named '/dev/rshim0/boot' was not found.", "MessageArgs": [ "Target", "/dev/rshim0/boot" ], "MessageId": "Base.1.15.0.ResourceNotFound", "MessageSeverity": "Critical", "Resolution": "Provide a valid resource identifier and resubmit the request." } ], "code": "Base.1.15.0.ResourceNotFound", "message": "The requested resource of type Target named '/dev/rshim0/boot' was not found." }
If a username or any other required field is missing:
{ "Username@Message.ExtendedInfo": [ { "@odata.type": "#Message.v1_1_1.Message", "Message": "The create operation failed because the required property Username was missing from the request.", "MessageArgs": [ "Username" ], "MessageId": "Base.1.15.0.CreateFailedMissingReqProperties", "MessageSeverity": "Critical", "Resolution": "Correct the body to include the required property with a valid value and resubmit the request if the operation failed." } ] }
Success message if the request is valid and a task is created:
{ "@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/TaskService/Tasks/<task_id>", "@odata.type": "#Task.v1_4_3.Task", "Id": "<task_id>", "TaskState": "Running", "TaskStatus": "OK" }
Run the following Redfish command to track the SCP image's transfer status (percentage is not updated until it reaches 100%):
curl -k -u root:
'<password>'-X GET https://<bmc_ip>/redfish/v1/TaskService/Tasks/<task_id>NoteDuring the transfer, the PercentComplete value remains at 0. If no errors occur, the TaskState is set to Running, and a keep-alive message is generated every 5 minutes with the content "Transfer is still in progress (X minutes elapsed). Please wait". Once the transfer is completed, the PercentComplete is set to 100, and the TaskState is updated to Completed.
Upon failure, a message is generated with the relevant resolution.
Where:
bmc_ip – BMC IP address
task_id – task ID received by the UpdateService command response
Examples:
Response/error messages:
If host identity is not confirmed or the provided host key is wrong:
{ "@odata.type": "#MessageRegistry.v1_4_1.MessageRegistry", "Message": "Transfer of image '<file_name>' to '/dev/rshim0/boot' failed.", "MessageArgs": [ "<file_name>, "/dev/rshim0/boot" ], "MessageId": "Update.1.0.TransferFailed", "Resolution": " Unknown Host: Please provide server's public key using PublicKeyExchange ", "Severity": "Critical" } … "PercentComplete": 0, "StartTime": "<start_time>", "TaskMonitor": "/redfish/v1/TaskService/Tasks/<task_id>/Monitor", "TaskState": "Exception", "TaskStatus": "Critical"
InfoIn this case, revoke the remote server key using the following Redfish command:
curl -k -u root:'<password>' -H "Content-Type: application/json" -X POST -d '{"RemoteServerIP":"<remote_server_ip>"}' https://<bmc_ip>/redfish/v1/UpdateService/Actions/Oem/NvidiaUpdateService.RevokeAllRemoteServerPublicKeys
Where:
remote_server_ip – remote server's IP address
bmc_ip – BMC IP address
Then repeat steps 1 and 2.
If the BMC identity is not confirmed:
{ "@odata.type": "#MessageRegistry.v1_4_1.MessageRegistry", "Message": "Transfer of image '<file_name>' to '/dev/rshim0/boot' failed.", "MessageArgs": [ "<file_name>", "/dev/rshim0/boot" ], "MessageId": "Update.1.0.TransferFailed", "Resolution": "Unauthorized Client: Please use the PublicKeyExchange action to receive the system's public key and add it as an authorized key on the remote server", "Severity": "Critical" } … "PercentComplete": 0, "StartTime": "<start_time>", "TaskMonitor": "/redfish/v1/TaskService/Tasks/<task_id>/Monitor", "TaskState": "Exception", "TaskStatus": "Critical"
InfoIn this case, verify that the BMC key has been added correctly to the authorized_key file on the remote server.
If SCP fails:
{ "@odata.type": "#MessageRegistry.v1_4_1.MessageRegistry", "Message": "Transfer of image '<file_name>' to '/dev/rshim0/boot' failed.", "MessageArgs": [ "<file_name>", "/dev/rshim0/boot" ], "MessageId": "Update.1.0.TransferFailed", "Resolution": "Failed to launch SCP", "Severity": "Critical" } … "PercentComplete": 0, "StartTime": "<start_time>", "TaskMonitor": "/redfish/v1/TaskService/Tasks/<task_id>/Monitor", "TaskState": "Exception", "TaskStatus": "Critical"
Success/status messages:
The keep-alive message:
{ "@odata.type": "#MessageRegistry.v1_4_1.MessageRegistry", "Message": " <file_name>' is being transferred to '/dev/rshim0/boot'.", "MessageArgs": [ " <file_name>", "/dev/rshim0/boot" ], "MessageId": "Update.1.0.TransferringToComponent", "Resolution": "Transfer is still in progress (5 minutes elapsed): Please wait", "Severity": "OK" } … "PercentComplete": 0, "StartTime": "<start_time>", "TaskMonitor": "/redfish/v1/TaskService/Tasks/<task_id>/Monitor", "TaskState": "Running", "TaskStatus": "OK"
Upon successful completion of SCP BFB transfer:
{ "@odata.type": "#MessageRegistry.v1_4_1.MessageRegistry", "Message": "Device 'DPU' successfully updated with image '<file_name>'.", "MessageArgs": [ "DPU", "<file_name>" ], "MessageId": "Update.1.0.UpdateSuccessful", "Resolution": "None", "Severity": "OK" }, … "PercentComplete": 100, "StartTime": "<start_time>", "TaskMonitor": "/redfish/v1/TaskService/Tasks/<task_id>/Monitor", "TaskState": "Completed", "TaskStatus": "OK"
Installing BFB File with HTTP Protocol
Make sure the BFB file, new.bfb, is available on HTTP server
Initiate image transfer. Run the following Redfish command:
curl -k -u root:'<password>' -H "Content-Type: application/json" -X POST -d '{"TransferProtocol":"HTTP", "ImageURI":"<image_uri>","Targets":["redfish/v1/UpdateService/FirmwareInventory/DPU_OS"]}' https://<bmc_ip>/redfish/v1/UpdateService/Actions/UpdateService.SimpleUpdate
NoteThis command uses HTTP to download the image, initiates a soft reset on the BlueField, and pushes the boot stream. For NVIDIA-supplied BFBs, the eMMC is flashed automatically once the boot stream is pushed. Upon success, a running message is received.
InfoAfter the BMC boots, it may take a few seconds (6-8 seconds in BlueField-2 and 2 seconds in BlueField-3) until the BlueField BSP (DPU_OS) is up.
Where:
image_uri – contains both the HTTP server address and the exported path to the .bfb file on the server, with one slash between the two fields (i.e., <http_server>/<exported_path_of_bfb> ).
InfoFor example, if <http_server> is 10.10.10.10 and <exported_path_of_bfb> is /tmp/new.bfb then "ImageURI":"10.10.10.10//tmp/new.bfb".
bmc_ip – BMC IP address
Response/error messages:
If RShim is disabled:
{ "error": { "@Message.ExtendedInfo": [ { "@odata.type": "#Message.v1_1_1.Message", "Message": "The requested resource of type Target named '/dev/rshim0/boot' was not found.", "MessageArgs": [ "Target", "/dev/rshim0/boot" ], "MessageId": "Base.1.15.0.ResourceNotFound", "MessageSeverity": "Critical", "Resolution": "Provide a valid resource identifier and resubmit the request." } ], "code": "Base.1.15.0.ResourceNotFound", "message": "The requested resource of type Target named '/dev/rshim0/boot' was not found." }
If the HTTPS server address is wrong or the HTTPS service is not stated, an "Unknown Host" error is expected:
{ "@odata.type": "#MessageRegistry.v1_4_1.MessageRegistry", "Message": "Transfer of image 'new.bfb' to '/dev/rshim0/boot' failed.", "MessageArgs": [ "new.bfb", "/dev/rshim0/boot" ], "MessageId": "Update.1.0.TransferFailed", "Resolution": "Unknown Host: Please provide server's public key using PublicKeyExchange (for SCP download) or Check and restart server's web service (for HTTP/HTTPS download)", "Severity": "Critical" },
If TransferProtocol or any other required field are wrong:
{ "@Message.ExtendedInfo": [ { "@odata.type": "#Message.v1_1_1.Message", "Message": "The parameter TransferProtocol for the action UpdateService.SimpleUpdate is not supported on the target resource.", "MessageArgs": [ "TransferProtocol", "UpdateService.SimpleUpdate" ], "MessageId": "Base.1.16.0.ActionParameterNotSupported", "MessageSeverity": "Warning", "Resolution": "Remove the parameter supplied and resubmit the request if the operation failed." } ] }
If Targets or any other required field are missing:
{ "Targets@Message.ExtendedInfo": [ { "@odata.type": "#Message.v1_1_1.Message", "Message": "The create operation failed because the required property Targets was missing from the request.", "MessageArgs": [ "Targets" ], "MessageId": "Base.1.16.0.CreateFailedMissingReqProperties", "MessageSeverity": "Critical", "Resolution": "Correct the body to include the required property with a valid value and resubmit the request if the operation failed." } ] }
Success message if the request is valid and a task is created:
{ "@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/TaskService/Tasks/<task_id>", "@odata.type": "#Task.v1_4_3.Task", "Id": "<task_id>", "TaskState": "Running", "TaskStatus": "OK" }
Installing BFB File with HTTPS Protocol
Make sure the BFB file, new.bfb, is available on HTTPS server
Make sure the BMC has certificate to authenticate the HTTPS server. Or install a valid certificate to authenticate:
curl -c cjar -b cjar -k -u root:'<password>' -X POST https://$bmc/redfish/v1/Managers/Bluefield_BMC/Truststore/Certificates -d @CAcert.json
Initiate image transfer. Run the following Redfish command:
curl -k -u root:'<password>' -H "Content-Type: application/json" -X POST -d '{"TransferProtocol":"HTTPS", "ImageURI":"<image_uri>","Targets":["redfish/v1/UpdateService/FirmwareInventory/DPU_OS"]}' https://<bmc_ip>/redfish/v1/UpdateService/Actions/UpdateService.SimpleUpdate
NoteThis command uses HTTPS for the image download, initiates a soft reset on the BlueField, and then pushes the boot stream. For NVIDIA-supplied BFBs, the eMMC is flashed automatically once the boot stream is pushed. Upon success, a running message is received.
InfoAfter the BMC boots, it may take a few seconds (6-8 seconds in BlueField-2 and 2 seconds in BlueField-3) until the BlueField BSP (DPU_OS) is up.
Where:
image_uri – contains both the HTTPS server address and the exported path to the .bfb file on the server, with one slash between the two fields (i.e., <https_server>/<exported_path_of_bfb> ).
InfoFor example, if <https_server> is urm.nvidia.com and <exported_path_of_bfb> is artifactory/sw-mlnx-bluefield-generic/Ubuntu22.04/new.bfb then "ImageURI":"10.126.206.42/artifactory/sw-mlnx-bluefield-generic/Ubuntu22.04/new.bfb".
bmc_ip – BMC IP address
Response / error messages:
If RShim is disabled:
{ "error": { "@Message.ExtendedInfo": [ { "@odata.type": "#Message.v1_1_1.Message", "Message": "The requested resource of type Target named '/dev/rshim0/boot' was not found.", "MessageArgs": [ "Target", "/dev/rshim0/boot" ], "MessageId": "Base.1.15.0.ResourceNotFound", "MessageSeverity": "Critical", "Resolution": "Provide a valid resource identifier and resubmit the request." } ], "code": "Base.1.15.0.ResourceNotFound", "message": "The requested resource of type Target named '/dev/rshim0/boot' was not found." }
If the HTTPS server address is wrong or the HTTPS service is not stated, an "Unknown Host" error is expected:
{ "@odata.type": "#MessageRegistry.v1_4_1.MessageRegistry", "Message": "Transfer of image 'new.bfb' to '/dev/rshim0/boot' failed.", "MessageArgs": [ "new.bfb", "/dev/rshim0/boot" ], "MessageId": "Update.1.0.TransferFailed", "Resolution": "Unknown Host: Please provide server's public key using PublicKeyExchange (for SCP download) or Check and restart server's web service (for HTTP/HTTPS download)", "Severity": "Critical" },
If TransferProtocol or any other required field are wrong:
{ "@Message.ExtendedInfo": [ { "@odata.type": "#Message.v1_1_1.Message", "Message": "The parameter TransferProtocol for the action UpdateService.SimpleUpdate is not supported on the target resource.", "MessageArgs": [ "TransferProtocol", "UpdateService.SimpleUpdate" ], "MessageId": "Base.1.16.0.ActionParameterNotSupported", "MessageSeverity": "Warning", "Resolution": "Remove the parameter supplied and resubmit the request if the operation failed." } ] }
If Targets or any other required field are missing:
{ "Targets@Message.ExtendedInfo": [ { "@odata.type": "#Message.v1_1_1.Message", "Message": "The create operation failed because the required property Targets was missing from the request.", "MessageArgs": [ "Targets" ], "MessageId": "Base.1.16.0.CreateFailedMissingReqProperties", "MessageSeverity": "Critical", "Resolution": "Correct the body to include the required property with a valid value and resubmit the request if the operation failed." } ] }
If the HTTPS server fails to authenticate the current installed certificate:
{ "@odata.type": "#MessageRegistry.v1_4_1.MessageRegistry", "Message": "Transfer of image 'new.bfb' to '/dev/rshim0/boot' failed.", "MessageArgs": [ "new.bfb", "/dev/rshim0/boot" ], "MessageId": "Update.1.0.TransferFailed", "Resolution": "Bad Certificate: Please check the remote server certification, correct and replace the current installed one", "Severity": "Critical" },
Success message if the request is valid and a task is created:
{ "@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/TaskService/Tasks/<task_id>", "@odata.type": "#Task.v1_4_3.Task", "Id": "<task_id>", "TaskState": "Running", "TaskStatus": "OK" }
Tracking Image Transfer Status and Progress for HTTP/HTTPS Protocols
The following section is relevant for HTTP/HTTPS protocols which received a success message of a valid SimpleUpdate request and a running task state.
Run the following Redfish command to track image transfer status and progress:
curl -k -u root:'<password>' -X GET https://<bmc_ip>/redfish/v1/TaskService/Tasks/<task_id>
Example:
{
"@odata.type": "#MessageRegistry.v1_4_1.MessageRegistry",
"Message": "Image 'new.bfb' is being transferred to '/dev/rshim0/boot'.",
"MessageArgs": [
"new.bfb",
"/dev/rshim0/boot"
],
"MessageId": "Update.1.0.TransferringToComponent",
"Resolution": "Transfer started",
"Severity": "OK"
},
…
"PercentComplete": 60,
"StartTime": "2024-06-10T19:39:03+00:00",
"TaskMonitor": "/redfish/v1/TaskService/Tasks/1/Monitor",
"TaskState": "Running",
"TaskStatus": "OK"
Direct SCP
scp <path_to_bfb> root@<bmc_ip>:/dev/rshim0/boot
If bf.cfg is required as part of the boot process, run:
cat <path_to_bfb> bf.cfg > new.bfb
scp <path to new.bfb> root@<bmc_ip>:/dev/rshim0/boot
Tracking Installation Progress and Status
After image transfer is complete, users may follow the installation progress and status with the help of a dump of current the RShim miscellaneous messages log.
Initiate request for dump download:
sudo curl -k -u root:'<password>' -d '{"DiagnosticDataType": "Manager"}' -X POST https://<ip_address>/redfish/v1/Managers/Bluefield_BMC/LogServices/Dump/Actions/LogService.CollectDiagnosticData
Where:
<ip-address> – BMC IP address
<password> – BMC password
Use the received task ID to poll for dump completion:
sudo curl -k -u root:'<password>' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -X GET https://<ip_address>/redfish/v1/TaskService/Tasks/<task_id>
Where:
<ip-address> – BMC IP address
<password> – BMC password
<task_id> – Task ID received from the first command
Once dump is complete, download and review the dump:
sudo curl -k -u root:'<password>' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -X GET https://<ip_address>/redfish/v1/Managers/Bluefield_BMC/LogServices/Dump/Entries/<entry_id>/attachment --output </path/to/tar/log_dump.tar.xz>
Where:
<ip-address> – BMC IP address
<password> – BMC password
<entry_id> – The entry ID of the dump in redfish/v1/Managers/Bluefield_BMC/LogServices/Dump/Entries
</path/to/tar/log_dump.tar.xz> – path to download the log dump log_dump.tar.xz
Untar the file to review the logs. For example:
tar xvfJ log_dump.tar.xz
The log is contained in the rshim.log file. The log displays Reboot, finished, DPU is ready, or In Enhanced NIC mode when BFB installation completes.
NoteIf the downloaded log file does not contain any of these strings, keep downloading the log file until they appear.
When installation is complete, you may crosscheck the new BFB version against the version provided to verify a successful upgrade:
curl -k -u root:"<PASSWORD>" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -X GET https://<bmc_ip>/redfish/v1/UpdateService/FirmwareInventory/DPU_OS
Example response:
"@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/UpdateService/FirmwareInventory/DPU_OS", "@odata.type": "#SoftwareInventory.v1_4_0.SoftwareInventory", "Description": "Host image", "Id": "DPU_OS", "Members@odata.count": 1, "Name": "Software Inventory", "RelatedItem": [ { "@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/Systems/Bluefield/Bios" } ], "SoftwareId": "", "Status": { "Conditions": [], "Health": "OK", "HealthRollup": "OK", "State": "Enabled" }, "Updateable": true, "Version": "DOCA_2.2.0_BSP_4.2.1_Ubuntu_22.04-8.23-07"
For comprehensive list of the supported parameters to customize bf.cfg during BFB installation, refer to section "bf.cfg Parameters".
After installation of the Ubuntu OS is complete, the following note appears in /dev/rshim0/misc on first boot:
...
INFO[MISC]: Linux up
INFO[MISC]: DPU is ready
"DPU is ready" indicates that all the relevant services are up and users can login the system.
After the installation of the Ubuntu 20.04 BFB, the configuration detailed in the following sections is generated.
Make sure all the services (including cloud-init) are started on BlueField and to perform a graceful shutdown before power cycling the host server.
BlueField OS image version is stored under /etc/mlnx-release in the BlueField:
# cat /etc/mlnx-release
bf-bundle-2.7.0-<version>_ubuntu-22.04_prod
To upgrade firmware:
Access the BlueField using one of the available interfaces (RShim console, BMC console, SSH via oob_net0 or tmfifo_net0 interfaces).
Upgrade the firmware on BlueField. Run:
sudo /opt/mellanox/mlnx-fw-updater/mlnx_fw_updater.pl --force-fw-update
Example output:
Device #1: ---------- Device Type: BlueField-2 [...] Versions: Current Available FW <Old_FW> <New_FW>
NoteImportant! To apply NVConfig changes, stop here and follow the steps in section "Updating NVConfig Params". In this case, the following step #3 is redundant.
Perform a BlueField system reboot for the upgrade to take effect.
Optional. To reset the BlueField NIC firmware configuration (aka Nvconfig params) to their factory default values, run the following from the BlueField ARM OS or from the host OS:
# sudo mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/<MST device> -y reset Reset configuration for device /dev/mst/<MST device>? (y/n) [n] : y Applying... Done! -I- Please reboot machine to load new configurations.
NoteFor now, please ignore tool's instruction to reboot
NoteTo learn what MST device the BlueField has on your setup, run:
mst start mst status
Example output taken on a multiple BlueField host:
// The MST device corresponds with PCI Bus address. MST modules: ------------ MST PCI module is not loaded MST PCI configuration module loaded MST devices: ------------ /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf0 - PCI configuration cycles access. domain:bus:dev.fn=0000:03:00.0 addr.reg=88 data.reg=92 cr_bar.gw_offset=-1 Chip revision is: 01 /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf1 - PCI configuration cycles access. domain:bus:dev.fn=0000:83:00.0 addr.reg=88 data.reg=92 cr_bar.gw_offset=-1 Chip revision is: 01 /dev/mst/mt41686_pciconf0 - PCI configuration cycles access. domain:bus:dev.fn=0000:a3:00.0 addr.reg=88 data.reg=92 cr_bar.gw_offset=-1 Chip revision is: 01
The MST device IDs for the BlueField-2 and BlueField-3 devices in this example are /dev/mst/mt41686_pciconf0 and /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf0 respectively.
(Optional) Enable NVMe emulation. Run:
sudo mlxconfig -d <MST device> -y s NVME_EMULATION_ENABLE=1
Skip this step if your BlueField is Ethernet only. Please refer to section "Supported Platforms and Interoperability" under the Release Notes to learn your BlueField type.
If you have an InfiniBand-and-Ethernet-capable BlueField, the default link type of the ports will be configured to IB. If you want to change the link type to Ethernet, please run the following configuration:
sudo mlxconfig -d <MST device> -y s LINK_TYPE_P1=2 LINK_TYPE_P2=2
Perform a BlueField system-level reset for the new settings to take effect.