Link Aggregation
Network bonding enables combining two or more network interfaces into a single interface. It increases the network throughput, bandwidth and provides redundancy if one of the interfaces fails.
NVIDIA ® BlueField ® networking platforms (DPUs or SuperNICs) have an option to configure network bonding on the Arm side in a manner transparent to the host. Under such configuration, the host would only see a single PF.
This functionality is supported when BlueField is set in embedded function ownership mode for both ports.
While LAG is being configured (starting with step 2 under section "LAG Configuration"), traffic cannot pass through the physical ports.
The following diagram describes this configuration:
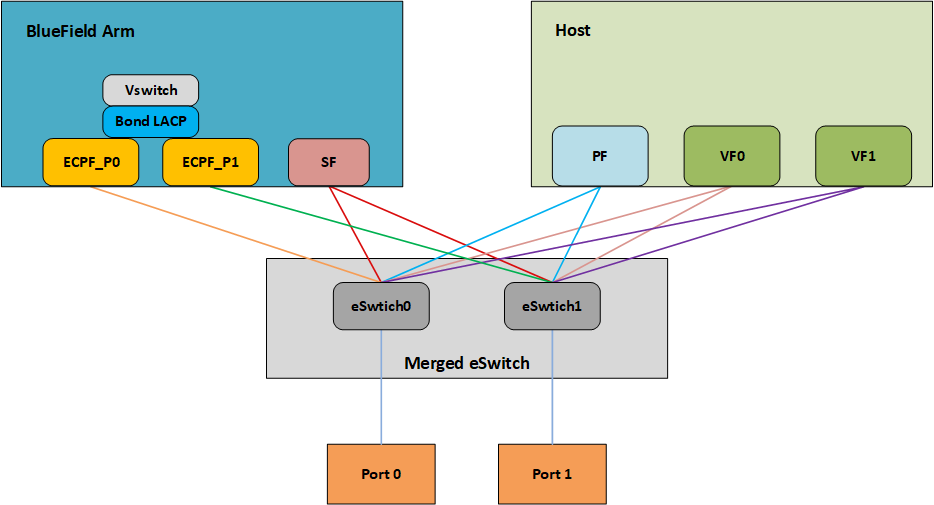
Two LAG modes are supported on BlueField:
Queue Affinity mode
Hash mode
Queue Affinity Mode
In this mode, packets are distributed according to the QPs.
To enable this mode, run:
$ mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/<device-name> s LAG_RESOURCE_ALLOCATION=0
Example device name: mt41686_pciconf0.
Add/edit the following field from /etc/mellanox/mlnx-bf.conf as follows:
LAG_HASH_MODE="no"
Perform BlueField system reboot for the mlxconfig settings to take effect.
Hash Mode
In this mode, packets are distributed to ports according to the hash on packet headers.
For this mode, prerequisite steps 3 and 4 are not required.
To enable this mode, run:
$ mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/<device-name> s LAG_RESOURCE_ALLOCATION=1
Example device name: mt41686_pciconf0.
Add/edit the following field from /etc/mellanox/mlnx-bf.conf as follows:
LAG_HASH_MODE="yes"
Perform BlueField system reboot for the mlxconfig settings to take effect.
Set the LAG mode to work with.
(Optional) Hide the second PF on the host. Run:
$ mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/<device-name> s HIDE_PORT2_PF=True NUM_OF_PF=1
Example device name: mt41686_pciconf0.
NotePerform BlueField system reboot for the mlxconfig settings to take effect.
Delete any installed Scalable Functions (SFs) on the Arm side.
Stop the driver on the host side. Run:
$ systemctl stop openibd
The uplink interfaces (p0 and p1) on the Arm side must be disconnected from any OVS bridge.
Create the bond interface. Run:
$ ip link add bond0 type bond $ ip link set bond0 down $ ip link set bond0 type bond miimon 100 mode 4 xmit_hash_policy layer3+4
NoteWhile LAG is being configured (starting with the next step), traffic cannot pass through the physical ports.
Subordinate both the uplink representors to the bond interface. Run:
$ ip link set p0 down $ ip link set p1 down $ ip link set p0 master bond0 $ ip link set p1 master bond0
Bring the interfaces up. Run:
$ ip link set p0 up $ ip link set p1 up $ ip link set bond0 up
The following is an example of LAG configuration in Ubuntu:
# cat /etc/network/interfaces # interfaces(
5) file used by ifup(8) and ifdown(8) # Include files from /etc/network/interfaces.d: source /etc/network/interfaces.d/* auto lo iface lo inet loopback #p0 auto p0 iface p0 inet manual bond-master bond1 # #p1 auto p1 iface p1 inet manual bond-master bond1 #bond1 auto bond1 iface bond1 inetstaticaddress192.168.1.1netmask255.255.0.0mtu1500bond-mode2bond-slaves p0 p1 bond-miimon100pre-up (sleep2&& ifup p0) & pre-up (sleep2&& ifup p1) &As a result, only the first PF of the BlueFields would be available to the host side for networking and SR-IOV.
WarningWhen in shared RQ mode (enabled by default), the uplink interfaces (p0 and p1) must always stay enabled. Disabling them will break LAG support and VF-to-VF communication on same host.
For OVS configuration, the bond interface is the one that needs to be added to the OVS bridge (interfaces p0 and p1 should not be added). The PF representor for the first port (pf0hpf) of the LAG must be added to the OVS bridge. The PF representor for the second port (pf1hpf) would still be visible, but it should not be added to OVS bridge. Consider the following examples:
ovs-vsctl add-br bf-lag
ovs-vsctl add-port bf-lag bond0
ovs-vsctl add-port bf-lag pf0hpf
Trying to change bonding configuration in Queue Affinity mode (including bringing the subordinated interface up/down) while the host driver is loaded would cause FW syndrome and failure of the operation. Make sure to unload the host driver before altering BlueField bonding configuration to avoid this.
When performing driver reload (openibd restart) or reboot, it is required to remove bond configuration and to reapply the configurations after the driver is fully up. Refer to steps 1-4 of "Removing LAG Configuration".
If Queue Affinity mode LAG is configured (i.e., LAG_RESOURCE_ALLOCATION=0):
Delete any installed Scalable Functions (SFs) on the Arm side.
Stop driver (openibd) on the host side. Run:
systemctl stop openibd
Delete the LAG OVS bridge on the Arm side. Run:
ovs-vsctl del-br bf-lag
This allows for later restoration of OVS configuration for non-LAG networking.
Stop OVS service. Run:
systemctl stop openvswitch-switch.service
Run:
ip link set bond0 down modprobe -rv bonding
As a result, both of the BlueField's network interfaces would be available to the host side for networking and SR-IOV.
For the host to be able to use BlueField's ports, make sure to attach the ECPF and host representor in an OVS bridge on the Arm side. Refer to "Virtual Switch on BlueField" for instructions on how to perform this.
Revert from HIDE_PORT2_PF, on the Arm side. Run:
mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/<device-name> s HIDE_PORT2_PF=False NUM_OF_PF=2
Restore default LAG settings in BlueField's firmware. Run:
mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/<device-name> s LAG_RESOURCE_ALLOCATION=DEVICE_DEFAULT
Delete the following line from /etc/mellanox/mlnx-bf.conf on the Arm side:
LAG_HASH_MODE=...
Perform BlueField system reboot for the mlxconfig settings to take effect.
Only LAG hash mode is supported with BlueField multi-host.
LAG Multi-host Prerequisites
Enable LAG hash mode.
Hide the second PF on the host. Run:
$ mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/<device-name> s HIDE_PORT2_PF=True NUM_OF_PF=1
Make sure NVME emulation is disabled:
$ mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/<device-name> s NVME_EMULATION_ENABLE=0
Example device name: mt41686_pciconf0.
The uplink interfaces (p0 and p4) on the Arm side, representing port0 and port1, must be disconnected from any OVS bridge. As a result, only the first PF of BlueField would be available to the host side for networking and SR-IOV.
LAG Configuration on Multi-host
Create the bond interface. Run:
$ ip link add bond0 type bond $ ip link set bond0 down $ ip link set bond0 type bond miimon 100 mode 4 xmit_hash_policy layer3+4
Subordinate both the uplink representors to the bond interface. Run:
$ ip link set p0 down $ ip link set p4 down $ ip link set p0 master bond0 $ ip link set p4 master bond0
Bring the interfaces up. Run:
$ ip link set p0 up $ ip link set p4 up $ ip link set bond0 up
For OVS configuration, the bond interface is the one that must be added to the OVS bridge (interfaces p0 and p4 should not be added). The PF representor, pf0hpf, must be added to the OVS bridge with the bond interface. The rest of the uplink representors must be added to another OVS bridge along with their PF representors. Consider the following examples:
ovs-vsctl add-br br-lag ovs-vsctl add-port br-lag bond0 ovs-vsctl add-port br-lag pf0hpf ovs-vsctl add-br br1 ovs-vsctl add-port br1 p1 ovs-vsctl add-port br1 pf1hpf ovs-vsctl add-br br2 ovs-vsctl add-port br2 p2 ovs-vsctl add-port br2 pf2hpf ovs-vsctl add-br br3 ovs-vsctl add-port br3 p3 ovs-vsctl add-port br3 pf3hpf
NoteWhen performing driver reload (openibd restart) or reboot, you must remove bond configuration from NetworkManager, and to reapply the configurations after the driver is fully up.
Removing LAG Configuration on Multi-host
Refer to section "Removing LAG Configuration".