DPUServiceChain
This document describes how to use DPUServiceChain in DPF.
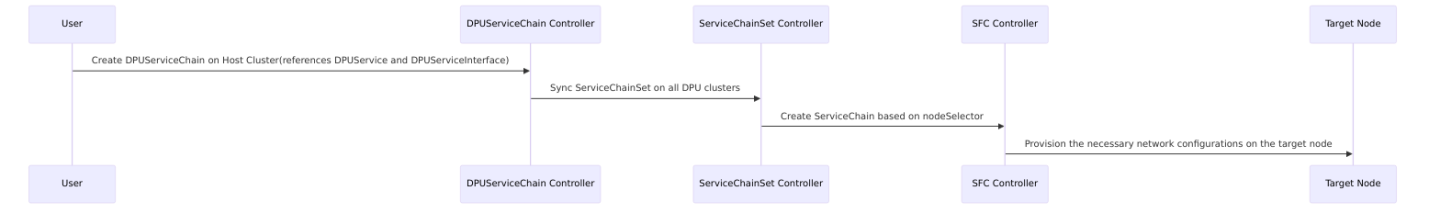
The purpose of DPUServiceChain is to allow user to define how to steer traffic on DPU through DPUServiceInterfaces. The following controllers are used internally to achieve this.
1) User creates DPUServiceChain, servicechaincontroller consumes it on the host cluster.
2) ServiceChainSet is created on DPU clusters
3) ServiceChain is created for individual nodes based on nodeSelector.
4) SFC controller provisions the necessary network configurations on DPU.
DPUServiceChain example:
The following YAML manifest defines a DPUServiceChain named example-chain and refers to one DPUService named example-service and 4 DPUServiceInterfaces. DPUServiceChain will define how the traffic will flow through those DPUServiceInterfaces.
DPUServiceInterfaces
apiVersion: svc.dpu.nvidia.com/v1alpha1
kind: DPUServiceInterface
metadata:
name: p0
namespace: dpf-operator-system
spec:
template:
spec:
template:
metadata:
labels:
uplink: "p0"
spec:
interfaceType: physical
physical:
interfaceName: p0
apiVersion: svc.dpu.nvidia.com/v1alpha1
kind: DPUServiceInterface
metadata:
name: pf0hpf
namespace: dpf-operator-system
spec:
template:
spec:
nodeSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: kubernetes.io/os
operator: In
values:
- "linux"
template:
metadata:
labels:
uplink: "pf0hpf"
spec:
interfaceType: pf
pf:
pfID: 0
apiVersion: svc.dpu.nvidia.com/v1alpha1
kind: DPUServiceInterface
metadata:
name: eth1
namespace: dpf-operator-system
spec:
template:
spec:
template:
metadata:
labels:
svc.dpu.nvidia.com/interface: "eth1"
svc.dpu.nvidia.com/service: example-service
spec:
interfaceType: service
service:
serviceID: example-service
network: mybrsfc
interfaceName: eth1
apiVersion: svc.dpu.nvidia.com/v1alpha1
kind: DPUServiceInterface
metadata:
name: eth2
namespace: dpf-operator-system
spec:
template:
spec:
template:
metadata:
labels:
svc.dpu.nvidia.com/interface: "eth2"
svc.dpu.nvidia.com/service: example-service
spec:
interfaceType: service
service:
serviceID: example-service
network: mybrsfc
interfaceName: eht2
DPUService
apiVersion: svc.dpu.nvidia.com/v1alpha1
kind: DPUService
metadata:
name: example-service
namespace: dpf-operator-system
spec:
serviceID: example-service
interfaces:
- eth1
- eth2
helmChart:
source:
repoURL: https://helm.ngc.nvidia.com/nvidia/doca
version: 1.0.1
chart: example-service
values:
resources:
memory: 6Gi
DPUServiceChain
apiVersion: svc.dpu.nvidia.com/v1alpha1
kind: DPUServiceChain
metadata:
name: example-chain
namespace: dpf-operator-system
spec:
template:
spec:
template:
spec:
switches:
- ports:
- serviceInterface:
matchLabels:
uplink: p0
- serviceInterface:
matchLabels:
svc.dpu.nvidia.com/service: example-service
svc.dpu.nvidia.com/interface: eth1
- ports:
- serviceInterface:
matchLabels:
svc.dpu.nvidia.com/service: example-service
svc.dpu.nvidia.com/interface: eth2
- serviceInterface:
matchLabels:
uplink: pf0hpf
Let's break it down step by step.
1) There are 4 DPUServiceInterfaces 1) uplink port p0 2) uplink port pf0hpf on host 3) service interface eth1 4) service interface eth2 2) There is one DPUService 1) example-service which has two interfaces eth1 and eth2 3) There is one DPUServiceChain 1) example-chain
p0 --> eth1 --> eth2 --> pf0hpf
In the above example, traffic will flow from uplink port p0 to example DPU service's eth1 iface. From eth1 iface, it will go to eth2 iface(eth1->eth2 is handled by the service itself and not by the chain) and then to uplink port pf0hpf on the host.