Introduction
This manual is intended for system administrators responsible for the installation, configuration, management and maintenance of the software and hardware of VPI (InfiniBand, Ethernet) adapter cards. It is also intended for application developers.
This document provides instructions on how to install the driver on NVIDIA ConnectX® network adapter solutions supporting the following uplinks to servers.
Uplink/NICs | Driver Name | Uplink Speed |
ConnectX®-3/ConnectX-3 Pro | mlx4 |
|
ConnectX-4 | mlx5 |
|
ConnectX-4 Lx |
| |
ConnectX-5/ConnectX-5 Ex |
| |
ConnectX-6 |
| |
ConnectX-6 Dx |
| |
Innova™ IPsec EN |
| |
Connect-IB® |
|
56GbE is a NVIDIA propriety link speed can be achieved while connecting a NVIDIA adapter card to
NVIDIA SX10XX switch series, or connecting a NVIDIA adapter card to another NVIDIA adapter card.Supports both NRZ and PAM4 modes.
All Mellanox network adapter cards are compatible with OpenFabrics-based RDMA protocols and software and are supported by major operating system distributions.
Mellanox OFED is certified with the following products:
Mellanox Messaging Accelerator (VMA™) software: Socket acceleration library that performs OS bypass for standard socket-based applications.
Please note, VMA support is provided separately from Mellanox OFED support. For further information, please refer to the VMA documentation (https://docs.nvidia.com/networking/category/vma).Mellanox Unified Fabric Manager (UFM®) software: Powerful platform for managing demanding scale-out computing fabric environments, built on top of the OpenSM industry standard routing engine.
Fabric Collective Accelerator (FCA) - FCA is a Mellanox MPI-integrated software package that utilizes CORE-Direct technology for implementing the MPI collectives communications.
The figure below shows a diagram of the Mellanox OFED stack, and how upper layer protocols (ULPs) interface with the hardware and with the kernel and userspace. The application level also shows the versatility of markets that Mellanox OFED applies to.
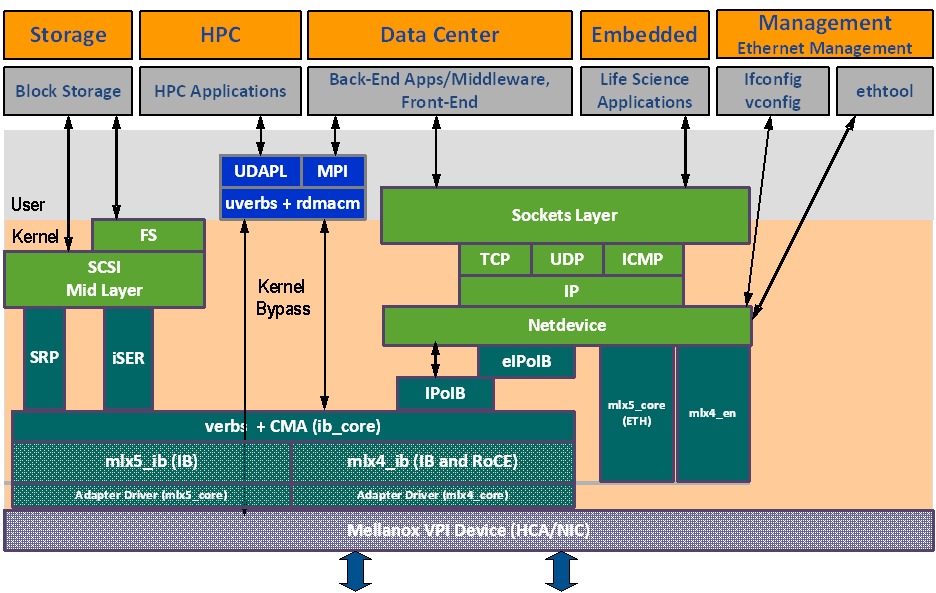
The following subsections briefly describe the various components of the Mellanox OFED stack.
mlx4 VPI Driver
mlx4 is the low-level driver implementation for the ConnectX® family adapters designed by Mellanox Technologies. ConnectX®-3 adapters can operate as an InfiniBand adapter, or as an Ethernet NIC. The OFED driver supports InfiniBand and Ethernet NIC configurations. To accommodate the supported configurations, the driver is split into the following modules:
mlx4_core
Handles low-level functions like device initialization and firmware commands processing. Also controls resource allocation so that the InfiniBand and Ethernet functions can share the device without interfering with each other.
mlx4_ib
Handles InfiniBand-specific functions and plugs into the InfiniBand mid layer.
mlx4_en
A 10/40GigE driver under drivers/net/ethernet/mellanox/mlx4 that handles Ethernet specific functions and plugs into the netdev mid layer.
mlx5 Driver
mlx5 is the low-level driver implementation for the Connect-IB® and ConnectX®-4 adapters designed by Mellanox Technologies. Connect-IB® operates as an InfiniBand adapter whereas and ConnectX®-4 operates as a VPI adapter (Infiniband and Ethernet). The mlx5 driver is comprised of the following kernel modules:
mlx5_core
Acts as a library of common functions (e.g. initializing the device after reset) required by Connect-IB® and ConnectX®-4 adapter cards. mlx5_core driver also implements the Ethernet interfaces for ConnectX®-4. Unlike mlx4_en/core, mlx5 drivers do not require the mlx5_en module as the Ethernet functionalities are built-in in the mlx5_core module.
mlx5_ib
Handles InfiniBand-specific functions and plugs into the InfiniBand mid layer.
libmlx5
libmlx5 is the provider library that implements hardware specific user-space functionality. If there is no compatibility between the firmware and the driver, the driver will not load and a message will be printed in the dmesg.
The following are the libmlx5 environment variables:
MLX5_FREEZE_ON_ERROR_CQE
Causes the process to hang in a loop of completion with error, which is not flushed with error or retry exceeded occurs/
Otherwise disabled
MLX5_POST_SEND_PREFER_BF
Configures every work request that can use blue flame will use blue flame
Otherwise - blue flame depends on the size of the message and inline indication in the packet
MLX5_SHUT_UP_BF
Disables blue flame feature
Otherwise - do not disable
MLX5_SINGLE_THREADED
All spinlocks are disabled
Otherwise - spinlocks enabled
Used by applications that are single threaded and would like to save the overhead of taking spinlocks.
MLX5_CQE_SIZE
64 - completion queue entry size is 64 bytes (default)
128 - completion queue entry size is 128 bytes
MLX5_SCATTER_TO_CQE
Small buffers are scattered to the completion queue entry and manipulated by the driver. Valid for RC transport.
Default is 1, otherwise disabled
MLX5_ENABLE_CQE_COMPRESSION
Saves PCIe bandwidth by compressing a few CQEs into a smaller amount of bytes on PCIe. Setting this variable 1enables CQE compression.
Default value 0 (disabled)
MLX5_RELAXED_PACKET_ORDERING_ON
See “Out-of-Order (OOO) Data Placement Experimental Verbs” section.
Mid-layer Core
Core services include management interface (MAD), connection manager (CM) interface, and Subnet Administrator (SA) interface. The stack includes components for both user-mode and kernel applications. The core services run in the kernel and expose an interface to user-mode for verbs, CM and management.
Upper Layer Protocols (ULPs)
IP over IB (IPoIB)
The IP over IB (IPoIB) driver is a network interface implementation over InfiniBand. IPoIB encapsulates IP datagrams over an InfiniBand connected or datagram transport service. IPoIB pre-appends the IP datagrams with an encapsulation header and sends the outcome over the InfiniBand transport service. The transport service is Unreliable Datagram (UD) by default, but it may also be configured to be Reliable Connected (RC), in case RC is supported. The interface supports unicast, multicast and broadcast. For details, see “IP over InfiniBand (IPoIB)” section.
iSCSI Extensions for RDMA (iSER)
iSCSI Extensions for RDMA (iSER) extends the iSCSI protocol to RDMA. It permits data to be transferred directly into and out of SCSI buffers without intermediate data copies. For further information, please refer to “iSCSI Extensions for RDMA (iSER)” section.
SCSI RDMA Protocol (SRP)
SCSI RDMA Protocol (SRP) is designed to take full advantage of the protocol offload and RDMA features provided by the InfiniBand architecture. SRP allows a large body of SCSI software to be readily used on InfiniBand architecture. The SRP driver—known as the SRP Initiator—differs from traditional low-level SCSI drivers in Linux. The SRP Initiator does not control a local HBA; instead, it controls a connection to an I/O controller—known as the SRP Target—to provide access to remote storage devices across an InfiniBand fabric. The SRP Target resides in an I/O unit and provides storage services. See “SRP - SCSI RDMA Protocol” section.
User Direct Access Programming Library (uDAPL)
User Direct Access Programming Library (uDAPL) is a standard API that promotes data center application data messaging performance, scalability, and reliability over RDMA interconnects InfiniBand and RoCE. The uDAPL interface is defined by the DAT collaborative. This release of the uDAPL reference implementation package for both DAT 1.2 and 2.0 specification is timed to coincide with OFED release of the Open Fabrics (www.openfabrics.org) software stack.
MPI
Message Passing Interface (MPI) is a library specification that enables the development of parallel software libraries to utilize parallel computers, clusters, and heterogeneous networks. Mellanox OFED includes the following MPI implementation over InfiniBand:
Open MPI – an open source MPI-2 implementation by the Open MPI Project
Mellanox OFED also includes MPI benchmark tests such as OSU BW/LAT, Intel MPI BeBenchmarkand Presta.
InfiniBand Subnet Manager
All InfiniBand-compliant ULPs require a proper operation of a Subnet Manager (SM) running on the InfiniBand fabric, at all times. An SM can run on any node or on an IB switch. OpenSM is an InfiniBand-compliant Subnet Manager, and it is installed as part of Mellanox OFED1.
1. OpenSM is disabled by default. See “OpenSM” section for details on enabling it.
Diagnostic Utilities
Mellanox OFED includes the following two diagnostic packages for use by network and data center managers:
ibutils – Mellanox Technologies diagnostic utilities
infiniband-diags – OpenFabrics Alliance InfiniBand diagnostic tools
Mellanox Firmware Tools
The Mellanox Firmware Tools (MFT) package is a set of firmware management tools for a single InfiniBand node. MFT can be used for:
Generating a standard or customized Mellanox firmware image
Burning a firmware image to a single InfiniBand node
MFT includes a set of tools used for performing firmware update and configuration, as well as debug and diagnostics, and provides MST service. For the full list of available tools within MFT, please refer to MFT documentation (https://docs.mellanox.com/category/mft).
ISO Image
Mellanox OFED for Linux (MLNX_OFED_LINUX) is provided as ISO images or as a tarball, one per supported Linux distribution and CPU architecture, that includes source code and binary RPMs, firmware, utilities, and documentation. The ISO image contains an installation script (called mlnxofedinstall) that performs the necessary steps to accomplish the following:
Discover the currently installed kernel
Uninstall any InfiniBand stacks that are part of the standard operating system distribution or another vendor's commercial stack
Install the MLNX_OFED_LINUX binary RPMs (if they are available for the current kernel)
Identify the currently installed InfiniBand HCAs and perform the required firmware updates
Software Components
MLNX_OFED_LINUX contains the following software components:
Mellanox Host Channel Adapter Drivers
mlx5, mlx4 (VPI), which is split into multiple modules:
mlx4_core (low-level helper)
mlx4_ib (IB)
mlx5_ib
mlx5_core (includes Ethernet)
mlx4_en (Ethernet)
Mid-layer core
Verbs, MADs, SA, CM, CMA, uVerbs, uMADs
Upper Layer Protocols (ULPs)
IPoIB, SRP Initiator and SRP
MPI
Open MPI stack supporting the InfiniBand, RoCE and Ethernet interfaces
MPI benchmark tests (OSU BW/LAT, Intel MPI Benchmark, Presta)
OpenSM: InfiniBand Subnet Manager
Utilities
Diagnostic tools
Performance tests
Sysinfo (see Sysinfo User Manual)
Firmware tools (MFT)
Source code for all the OFED software modules (for use under the conditions mentioned in the modules' LICENSE files)
Documentation
Firmware
The ISO image includes the following firmware item:
mlnx-fw-updater RPM/DEB package, which contains firmware binaries for supported devices (using mlxfwmanager tool).
Directory Structure
The ISO image of MLNX_OFED_LINUX contains the following files and directories:
mlnxofedinstall - This is the MLNX_OFED_LINUX installation script.
ofed_uninstall.sh - This is the MLNX_OFED_LINUX un-installation script.
<RPMS folders> - Directory of binary RPMs for a specific CPU architecture.
src/ - Directory of the OFED source tarball.
MLNX_OFED includes the OFED source RPM packages used as a build platform for kernel code but does not include the sources of Mellanox proprietary packages.
mlnx_add_kernel_support.sh - Script required to rebuild MLNX_OFED_LINUX for customized kernel version on supported Linux Distribution
RPM based - A script required to rebuild MLNX_OFED_LINUX for customized kernel version on supported RPM-based Linux Distribution
docs/ - Directory of Mellanox OFED related documentation
mlx4 Module Parameters
In order to set mlx4 parameters, add the following line(s) to /etc/modprobe.d/mlx4.conf:
options mlx4_core parameter=<value>
and/or
options mlx4_ib parameter=<value>
and/or
options mlx4_en parameter=<value>
The following sections list the available mlx4 parameters.
mlx4_ib Parameters
sm_guid_assign: | Enable SM alias_GUID assignment if sm_guid_assign > 0 (Default: 0) (int) |
dev_assign_str:1 | Map device function numbers to IB device numbers (e.g.'0000:04:00.0-0,002b:1c:0b.a-1,...'). Hexadecimal digits for the device function (e.g. 002b:1c:0b.a) and decimal for IB device numbers (e.g. 1). Max supported devices - 32 (string) |
en_ecn | Enable q/ecn [enable = 1, disable = 0 (default)] (bool) |
In the current version, this parameter is using a decimal number to describe the InfiniBand device, and not a hexadecimal number as in previous versions.
The purpose is to uniform the mapping of device function numbers with InfiniBand device numbers, as defined for other module parameters (e.g. num_vfs
and probe_vf). For example, to map mlx4_15 to device function number 04:00.0 in the current version, we use “options mlx4_ib dev_assign_str=04:00.0-15”,
as opposed to the previous version where we used “options mlx4_ib dev_assign_str=04:00.0-f”
mlx4_core Parameters
debug_level | Enable debug tracing if > 0 (int) |
msi_x | 0 - don't use MSI-X, 1 - use MSI-X, >1 - limit number of MSI-X irqs to msi_x (non-SRIOV only) (int) |
enable_sys_tune | Tune the cpu's for better performance (default 0) (int) |
block_loopback | Block multicast loopback packets if > 0 (default: 1) (int) |
num_vfs | Either a single value (e.g. '5') to define uniform num_vfs value for all devices functions or a string to map device function numbers to their num_vfs values (e.g. '0000:04:00.0-5,002b:1c:0b.a-15'). Hexadecimal digits for the device function (e.g. 002b:1c:0b.a) and decimal for num_vfs value (e.g. 15). (string) |
probe_vf | Either a single value (e.g. '3') to indicate that the Hypervisor driver itself should activate this number of VFs for each HCA on the host, or a string to map device function numbers to their probe_vf values (e.g. '0000:04:00.0-3,002b:1c:0b.a-13'). Hexadecimal digits for the device function (e.g. 002b:1c:0b.a) and decimal for probe_vf value (e.g. 13). (string) |
log_num_mgm_entry_size | log mgm size, that defines the num of qp per mcg, for example: 10 gives 248.range: 7 <= log_num_mgm_entry_size <= 12. To activate device managed flow steering when available, set to -1 (int) |
high_rate_steer | Enable steering mode for higher packet rate (obsolete, set "Enable optimized steering" option in log_num_mgm_entry_size to use this mode). (int) |
fast_drop | Enable fast packet drop when no recieve WQEs are posted (int) |
enable_64b_cqe_eqe | Enable 64 byte CQEs/EQEs when the FW supports this if non-zero (default: 1) (int) |
log_num_mac | Log2 max number of MACs per ETH port (1-7) (int) |
log_num_vlan | (Obsolete) Log2 max number of VLANs per ETH port (0-7) (int) |
log_mtts_per_seg | Log2 number of MTT entries per segment (0-7) (default: 0) (int) |
port_type_array | Either pair of values (e.g. '1,2') to define uniform port1/port2 types configuration for all devices functions or a string to map device function numbers to their pair of port types values (e.g. '0000:04:00.0-1;2,002b:1c:0b.a-1;1'). Valid port types: 1-ib, 2-eth, 3-auto, 4-N/A If only a single port is available, use the N/A port type for port2 (e.g '1,4'). |
log_num_qp | log maximum number of QPs per HCA (default: 19) (int) |
log_num_srq | log maximum number of SRQs per HCA (default: 16) (int) |
log_rdmarc_per_qp | log number of RDMARC buffers per QP (default: 4) (int) |
log_num_cq | log maximum number of CQs per HCA (default: 16) (int) |
log_num_mcg | log maximum number of multicast groups per HCA (default: 13) (int) |
log_num_mpt | log maximum number of memory protection table entries per HCA (default: 19) (int) |
log_num_mtt | log maximum number of memory translation table segments per HCA (default: max(20, 2*MTTs for register all of the host memory limited to 30)) (int) |
enable_qos | Enable Quality of Service support in the HCA (default: off) (bool) |
internal_err_reset | Reset device on internal errors if non-zero (default is 1) (int) |
ingress_parser_mode | Mode of ingress parser for ConnectX3-Pro. 0 - standard. 1 - checksum for non TCP/UDP. (default: standard) (int) |
roce_mode | Set RoCE modes supported by the port |
ud_gid_type | Set gid type for UD QPs |
log_num_mgm_entry_size | log mgm size, that defines the num of qp per mcg, for example: 10 gives 248.range: 7 <= log_num_mgm_entry_size <= 12 (default = -10). |
use_prio | Enable steering by VLAN priority on ETH ports (deprecated) (bool) |
enable_vfs_qos | Enable Virtual VFs QoS (default: off) (bool) |
mlx4_en_only_mode | Load in Ethernet only mode (int) |
enable_4k_uar | Enable using 4K UAR. Should not be enabled if have VFs which do not support 4K UARs (default: true) (bool) |
mlx4_en_only_mode | Load in Ethernet only mode (int) |
rr_proto | IP next protocol for RoCEv1.5 or destination port for RoCEv2. Setting 0 means using driver default values (deprecated) (int) |
mlx4_en Parameters
inline_thold | The threshold for using inline data (int) Default and max value is 104 bytes. Saves PCI read operation transaction, packet less then threshold size will be copied to hw buffer directly. (range: 17-104) |
udp_rss: | Enable RSS for incoming UDP traffic (uint) On by default. Once disabled no RSS for incoming UDP traffic will be done. |
pfctx | Priority-based Flow Control policy on TX[7:0]. Per priority bit mask (uint) |
pfcrx | Priority-based Flow Control policy on RX[7:0]. Per priority bit mask (uint) |
udev_dev_port_dev_id | Work with dev_id or dev_port when supported by the kernel. Range: 0 <= udev_dev_port_dev_id <= 2 (default = 0). |
udev_dev_port_dev_id: | Work with dev_id or dev_port when supported by the kernel. Range: 0 <= udev_dev_port_dev_id <= 2 (default = 0). • 0: Work with dev_port if supported by the kernel, otherwise work with dev_id. • 1: Work only with dev_id regardless of dev_port support. • 2: Work with both of dev_id and dev_port (if dev_port is supported by the kernel). (int) |
mlx5_core Module Parameters
The mlx5_core module supports a single parameter used to select the profile which defines the number of resources supported.
prof_sel | The parameter name for selecting the profile. The supported values for profiles are:
|
guids | charp |
node_guid | guids configuration. This module parameter will be obsolete! |
debug_mask | debug_mask: 1 = dump cmd data, 2 = dump cmd exec time, 3 = both. Default=0 (uint) |
probe_vf | probe VFs or not, 0 = not probe, 1 = probe. Default = 1 (bool) |
num_of_groups | Controls the number of large groups in the FDB flow table. Default=4; Range=1-1024 |
ib_core Parameters
send_queue_size | Size of send queue in number of work requests (int) |
recv_queue_size | Size of receive queue in number of work requests (int) |
force_mr | Force usage of MRs for RDMA READ/WRITE operations (bool) |
roce_v1_noncompat_gid | Default GID auto configuration (Default: yes) (bool) |
ib_ipoib Parameters
max_nonsrq_conn_qp | Max number of connected-mode QPs per interface (applied only if shared receive queue is not available) (int) |
mcast_debug_level | Enable multicast debug tracing if > 0 (int) |
send_queue_size | Number of descriptors in send queue (int) |
recv_queue_size | Number of descriptors in receive queue (int) |
debug_level | Enable debug tracing if > 0 (int) |
ipoib_enhanced | Enable IPoIB enhanced for capable devices (default = 1) (0-1) (int) |
The following parameters, supported in mlx4 driver only, can be changed using the Devlink user interface:
Parameter | Description | Parameter Type |
internal_error_reset | Enables resetting the device on internal errors | Generic |
max_macs | Max number of MACs per ETH port | Generic |
region_snapshot_enable | Enables capturing region snapshots | Generic |
enable_64b_cqe_eqe | Enables 64 byte CQEs/EQEs when supported by FW | Driver-specific |
enable_4k_uar | Enables using 4K UAR | Driver-specific |
Device Capabilities
Normally, an application needs to query the device capabilities before attempting to create a resource. It is essential for the application to be able to operate over different devices with different capabilities.
Specifically, when creating a QP, the user needs to specify the maximum number of outstanding work requests that the QP supports. This value should not exceed the queried capabilities. However, even when you specify a number that does not exceed the queried capability, the verbs can still fail since some other factors such as the number of scatter/gather entries requested, or the size of the inline data required, affect the maximum possible work requests. Hence an application should try to decrease this size (halving is a good new value) and retry until it succeeds.