Appendix – InfiniBand Router
IB router provides the ability to send traffic between two or more IB subnets thereby potentially expanding the size of the network to over 40k end-ports, enabling separation and fault resilience between islands and IB subnets, and enabling connection to different topologies used by different subnets.
The forwarding between the IB subnets is performed using GRH lookup. The IB router’s basic functionality includes:
Removal of current L2 LRH (local routing header)
Routing table lookup – using GID from GRH
Building new LRH according to the destination according to the routing table
The DLID in the new LRH is built using simplified GID-to-LID mapping (where LID = 16 LSB bits of GID) thereby not requiring to send for ARP query/lookup.
Site-Local Unicast GID Format
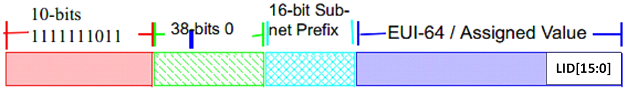
For this to work, the SM allocates an alias GID for each host in the fabric where the alias GID = {subnet prefix[127:64], reserved[63:16], LID[15:0}. Hosts should use alias GIDs in order to transmit traffic to peers on remote subnets.
Host-to-Host IB Router Unicast Flow
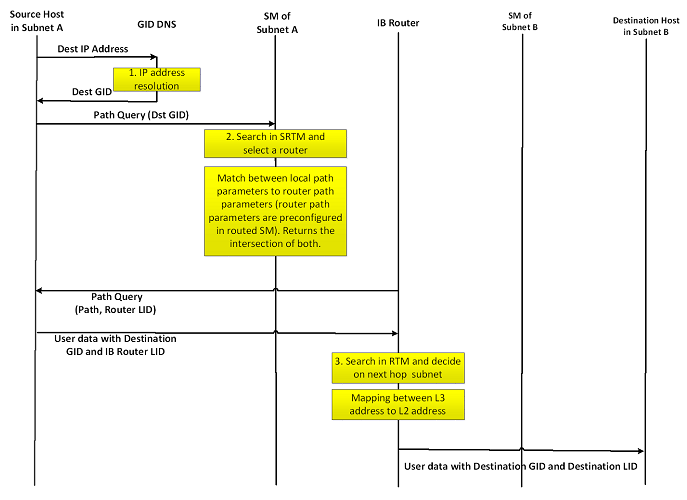
Please refer to UFM-SDN Appliance Command Reference Guide document for the IB router commands’ details
Configure multi-switch. Run:
ufmapl [ mgmt-sa ] (config) # ib router set-num-of-subnets --hostname 10.6.204.12 --username admin --password admin --num-of-subnets 6
Map interface to a subnet. Run:
ufmapl [ mgmt-sa ] (config) # ib router add-interfaces-to-subnet --hostname 10.6.204.12 --username admin --password admin --interface 1/1 --subnet infiniband-default
Create routing on IB subnet interface. Run:
ufmapl [ mgmt-sa ] (config) # ib router add-subnet-to-router --hostname 10.6.204.12 -–username admin --password admin --subnet infiniband-default