NVIDIA DOCA Switch Application Guide
This guide provides an example of switch implementation on top of NVIDIA® BlueField® DPU.
DOCA Switch is a network application that leverages the DPU's hardware capability for internal switching between representor ports on the DPU.
DOCA Switch is based on the DOCA Flow library. As such, it exposes a command line interface which receives DOCA Flow like commands to allow adding rules in real time.
DOCA Switch is designed to run on the DPU as a standalone application (all network traffic goes directly through it).
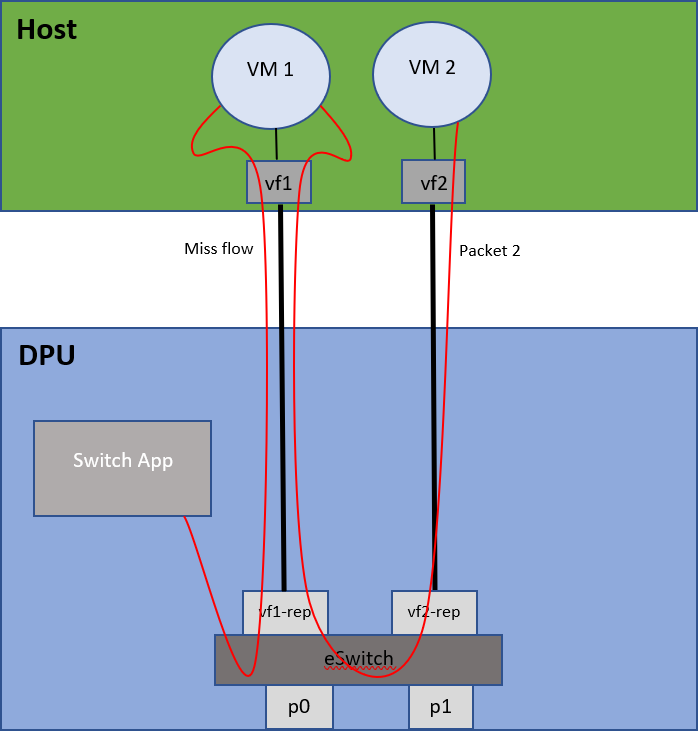
Traffic flows between two VMs on the host:
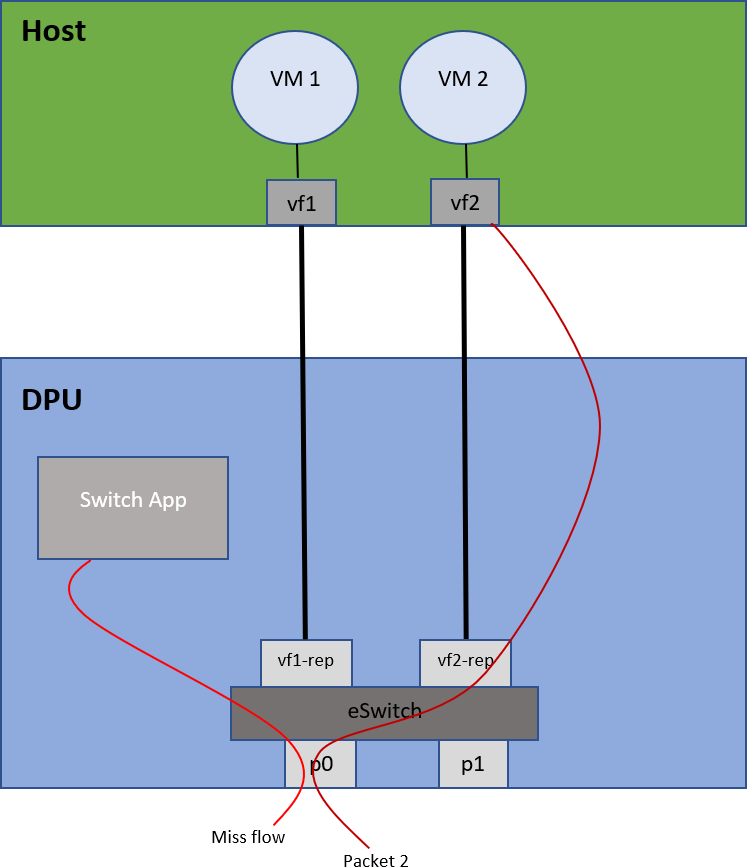
Traffic flow from a physical port to a VM on the host:
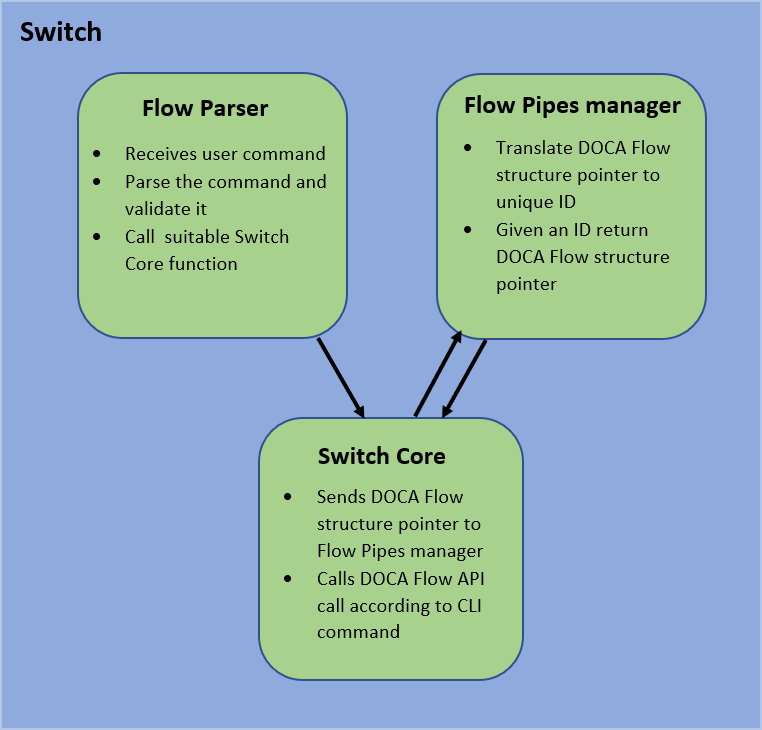
DOCA Switch is based on 3 modules:
Command line interface – receives pre-defined DOCA Flow-like commands and parses them
Flow pipes manger – generates a unique identification number for each DOCA Flow structure created
Switch core – combines all modules together and calls necessary DOCA Flow API
Port initialization cannot be made dynamically. All ports must be defined when running the application with standard DPDK flags.
When adding a pipe or an entry, the user must run commands to create the relevant structs beforehand
Optional parameters must be specified by the user in the command line; otherwise, NULL is used
After a pipe or an entry is created successfully, the relevant ID is printed for future use
This application leverages the following DOCA libraries:
Refer to its respective programming guide for more information.
Installation
Refer to the NVIDIA DOCA Installation Guide for Linux for details on how to install BlueField-related software.
Prerequisites
The switch application is based on DOCA Flow. Therefore, the user is required to allocate huge pages.
echo '2048' | sudo tee -a /sys/kernel/mm/hugepages/hugepages-2048kB/nr_hugepages
On some operating systems (RockyLinux, OpenEuler, CentOS 8.2) the default huge page size on the DPU (and Arm hosts) is larger than 2MB, and is often 512MB instead. Once can find out the sige of the huge pages using the following command:
$ grep -i huge /proc/meminfo
AnonHugePages: 0 kB
ShmemHugePages: 0 kB
FileHugePages: 0 kB
HugePages_Total: 4
HugePages_Free: 4
HugePages_Rsvd: 0
HugePages_Surp: 0
Hugepagesize: 524288 kB
Hugetlb: 6291456 kB
Given that the guiding principal is to allocate 4GB of RAM, in such cases instead of allocating 2048 pages, one should allocate the matching amount (8 pages):
echo '8' | sudo tee -a /sys/kernel/mm/hugepages/hugepages-524288kB/nr_hugepages
Application Execution
The switch application is provided in both source and binary forms, and the binary is located under /opt/mellanox/doca/applications/switch/bin/doca_switch.
Application usage instructions:
Usage: doca_switch [DPDK Flags] -- [DOCA Flags] DOCA Flags: -h, --help Print a help synopsis -v, --version Print program version information -l, --log-level Set the (numeric) log level
forthe program <10=DISABLE,20=CRITICAL,30=ERROR,40=WARNING,50=INFO,60=DEBUG,70=TRACE> --sdk-log-level Set the SDK (numeric) log levelforthe program <10=DISABLE,20=CRITICAL,30=ERROR,40=WARNING,50=INFO,60=DEBUG,70=TRACE> -j, --json <path> Parse all command flags from an input json fileInfoThis usage printout can be printed to the command line using the -h (or --help) options:
/opt/mellanox/doca/applications/
switch/bin/doca_switch -- -hInfoFor additional information, refer to section "Command Line Flags".
CLI example for running the application on the BlueField:
/opt/mellanox/doca/applications/
switch/bin/doca_switch -a03:00.0,representor=[0-2],dv_flow_en=2-- -l60Notedv_flow_en=2 is necessary to run the application with hardware steering.
NoteThe PCIe address (03:00.0) should match the address of the desired PCIe device.
Command Line Flags
|
Flag Type |
Short Flag |
Long Flag |
Description |
JSON Content |
|
General flags |
h |
help |
Prints a help synopsis |
N/A |
|
v |
version |
Prints program version information |
N/A |
|
|
l |
log-level |
Set the log level for the application:
|
|
|
|
N/A |
sdk-log-level |
Sets the log level for the program:
|
|
|
|
j |
json |
Parse all command flags from an input JSON file |
N/A |
Refer to DOCA Arg Parser for more information regarding the supported flags and execution modes.
Supported Commands
create pipe port_id=[port_id][,<optional_parameters>]Available optional parameters:
name=<pipe-name>
root_enable=[1|0]
monitor=[1|0]
match_mask=[1|0]
fwd=[1|0]
fwd_miss=[1|0]
type=[basic|control]
add entry pipe_id=<pipe_id>,pipe_queue=<pipe_queue>[,<optional_parameters>]Available optional parameters:
monitor=[1|0]
fwd=[1|0]
add control_pipe entry priority=<priority>,pipe_id=<pipe_id>,pipe_queue=<pipe_queue>[,<optional_parameters>]Available optional parameters:
match_mask=[1|0]
fwd=[1|0]
destroy pipe pipe_id=<pipe_id>
rm entry pipe_queue=<pipe_queue>,entry_id=[entry_id]
port pipes flush port_id=[port_id]
port pipes dump port_id=[port_id],file=[file_name]
query entry_id=[entry_id]
create [struct] [field=value,…]
Struct options: pipe_match, entry_match, match_mask, actions, monitor, fwd, fwd_missMatch struct fields:
Fields
Field Options
flags
port_meta
outer.eth.src_mac
outer.eth.dst_mac
outer.eth.type
outer.vlan_tci
outer.l3_type
ipv4, ipv6
outer.src_ip_addr
outer.dst_ip_addr
outer.l4_type_ext
tcp, udp , gre
outer.tcp.flags
FIN, SYN, RST, PSH, ACK, URG, ECE, CWR
outer.tcp_src_port
outer.tcp_dst_port
outer.udp_src_port
outer.udp_dst_port
tun_type
vxlan_tun_id
gre_key
gtp_teid
inner.eth.src_mac
inner.eth.dst_mac
inner.eth.type
inner.vlan_tci
inner.l3_type
ipv4, ipv6
inner.src_ip_addr
inner.dst_ip_addr
inner.l4_type_ext
tcp, udp
inner.tcp.flags
FIN, SYN, RST, PSH, ACK, URG, ECE, CWR
inner.tcp_src_port
inner.tcp_dst_port
inner.udp_src_port
inner.udp_dst_port
Actions struct fields:
Fields
Field Options
decap
true, false
mod_src_mac
mod_dst_mac
mod_src_ip_type
ipv4, ipv6
mod_src_ip_addr
mod_dst_ip_type
ipv4, ipv6
mod_dst_ip_addr
mod_src_port
mod_dst_port
ttl
has_encap
true, false
encap_src_mac
encap_dst_mac
encap_src_ip_type
ipv4, ipv6
encap_src_ip_addr
encap_dst_ip_type
ipv4, ipv6
encap_dst_ip_addr
encap_tup_type
vxlan, gtpu, gre
encap_vxlan-tun_id
encap_gre_key
encap_gtp_teid
FWD struct fields:
Fields
Field Options
type
rss, port, pipe, drop
rss_flags
rss_queues
num_of_queues
port_id
next_pipe_id
Monitor struct fields:
flags
cir
cbs
aging
The physical port number (only one physical port is supported) will always be 0 and all representor ports are numbered from 1 to N where N is the number of representors being used. For example:
Physical port ID: 0
VF0 representor port ID: 1
VF1 representor port ID: 2
VF2 representor port ID: 3
The following is an example of creating a pipe and adding one entry into it:
create fwd type=port,port_id=0xffff
create pipe port_id=0,name=p0_to_vf1,root_enable=1,fwd=1
create fwd type=port,port_id=1
add entry pipe_queue=0,fwd=1,pipe_id=1012
....
rm entry pipe_queue=0,entry_id=447
Pipe is configured on port ID 0 (physical port).
Entry is configured to forward all traffic directly into port ID 1 (VF0).
When the forwarding rule is no longer needed, the entry is deleted.
Ultimately, both entries are deleted, each according to the unique random ID it was given:
Troubleshooting
Refer to the NVIDIA DOCA Troubleshooting Guide for any issue encountered with the installation or execution of the DOCA applications.
In addition to providing the application in binary form, the installation also includes all of the application sources and compilation instructions so as to allow modifying the sources and recompiling the application. For more information about the applications, as well as development and compilation tips, refer to the DOCA Applications main guide.
The sources of the application can be found under the /opt/mellanox/doca/applications/switch/src directory.
Recompiling All Applications
The applications are all defined under a single meson project, so the default compilation recompiles all the DOCA applications.
To build all the applications together, run:
cd /opt/mellanox/doca/applications/
meson /tmp/build
ninja -C /tmp/build
doca_switch is created under /tmp/build/switch/src/.
Recompiling Only the Current Application
To directly build only the switch application:
cd /opt/mellanox/doca/applications/
meson /tmp/build -Denable_all_applications=false -Denable_switch=true
ninja -C /tmp/build
doca_switch is created under /tmp/build/switch/src/.
Alternatively, one can set the desired flags in the meson_options.txt file instead of providing them in the compilation command line:
Edit the following flags in /opt/mellanox/doca/applications/meson_options.txt:
Set enable_all_applications to false
Set enable_switch to true
Run the following compilation commands :
cd /opt/mellanox/doca/applications/ meson /tmp/build ninja -C /tmp/build
Infodoca_switch is created under /tmp/build/switch/src/.
Troubleshooting
Refer to the NVIDIA DOCA Troubleshooting Guide for any issue encountered with the compilation of the application .
Parse application argument.
Initialize the arg parser resources and register DOCA general parameters.
doca_argp_init();
Register application parameters.
register_switch_params();
Parse app parameters.
doca_argp_start();
Count total number of ports.
switch_ports_count();
Check how many ports are entered when running the application.
Initialize DPDK ports and queues.
dpdk_queues_and_ports_init();
Initialize DOCA Switch.
switch_init();
Initialize DOCA Flow.
Create port pairs.
Create Flow Pipes Manger module.
Register an action for each relevant CLI command.
Initialize Flow Parser.
flow_parser_init();
Reset all internal Flow Parser structures.
Start the command line interface.
Receive user commands, parse them, and call the required DOCA Flow API command.
Close the interactive shell once a "quit" command is entered.
Clean Flow Parser resources.
flow_parser_cleanup();
Destroy Switch resources.
switch_destroy();
Destroy Flow Pipes Manager resources.
Destroy DOCA Flow.
switch_destroy();
Destroy DPDK ports and queues.
dpdk_queues_and_ports_fini();
DPDK finish.
dpdk_fini();
Call rte_eal_destroy() to destroy initialized EAL resources.
Arg parser destroy.
doca_argp_destroy();
/opt/mellanox/doca/applications/switch/src