Puppet Agent
Puppet is a software that allows network administrators to automate repetitive tasks. NVIDIA Onyx includes a built-in agent for the open-source “Puppet” configuration change management system. The Puppet agent enables configuring switches in accordance with the standard “puppet-netdev-stdlib” type library and with the “Mellanox-netdev-stdlib-mlnxos” and “Mellanox-netdev-ospf-stdlib” type libraries provided to the Puppet community.For more information, please refer to the CLI commands, to the NetDev documentation and to Puppet modules GitHub page.
To set the puppet server:
Define the Puppet server (the name has to be a DNS and not IP).
switch(config) # puppet-agent master-hostname <please_type_your_hostname_DNS_here>Enable the Puppet agent.
switch(config) # puppet-agent enable(Optional) Verify there are no errors in the Puppet agent log.
switch(config) # show puppet-agent log continuous
This is to be performed on the first run only.
Using CLI Commands
Verify the certificate request.
# puppet cert list
"<switch>"(F4:B4:20:3B:2B:11:76:37:14:34:D0:D1:03:ED:3D:B5)Sign the certificate request if the cert_name parameter (e.g. switch1.domain) is in the list.
# puppet cert sign <full_domain_name>
Verify the request is removed from the Puppet certification list.
# puppet cert list
Accepting Certificate Requests in Puppet Server Console
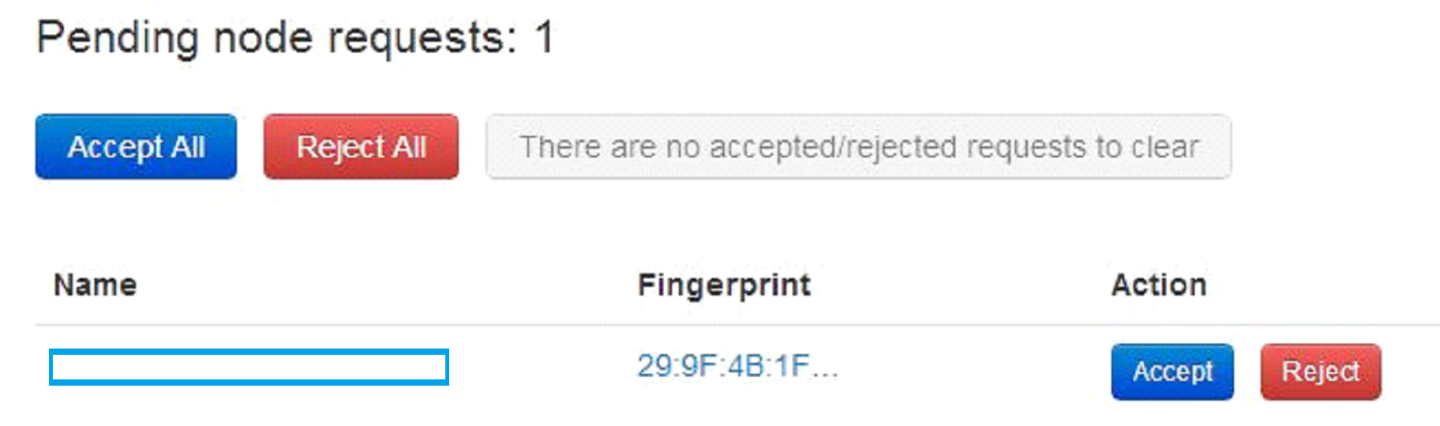
Go to the “nodes requests” page (the button is at the top right), and wait for a certificate request for the switch and then accept it.
For those types which have to be installed at the Puppet server prior to the first Puppet configuration run (before configuring resources on the switch), netdev-stdlib types and a package of providers is provided.
To install those modules, run the following commands in the Puppet server:
# puppet module install netdevops-netdev_stdlib
# puppet module install mellanox-netdev_ospf_stdlib
# puppet module install mellanox-netdev_stdlib_mlnxos
If a module is already installed, please use the command “puppet module upgrade <module_name>” or “puppet module install <module_name> --force” instead of “puppet module install <module_name>” to reinstall the modules.
For more information please refer to the Network Automation Tools page community page.
Assign configuration classes to a node.
Configuration files can be written and changed in the puppet server machine in the directory “/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/manifests/” (or “/etc/puppet/manifests” in case of an open source puppet server).
The file “/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/manifests/site.pp” is the main file for Puppet-classes-to-nodes association. To associate a configuration to a Puppet agent node, just append association lines as below:import"netdev_vlan_example"import"netdev_l2_vlan_example"import"netdev_lag_example"node'switch-6375dc.mtr.labs.mlnx'{ netdev_device { $hostname: } include vlan_example # Asserts aclassvlan_example in one of the files include l2_interface_example include lag_example }WarningIf you have a puppet console, you may assign classes of configuration in the following way:
•Add the relevant classes (using the console add class button on the “nodes” page).
•Assign the classes to the relevant nodes/groups in the puppet server console (in the console node/group page -> edit -> Classes).
Update VLAN.
Manifest example (located in “/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/manifests/netdev_vlan_example.pp”).classvlan_example{ $vlans = {'Vlan244'=> {vlan_id =>244, ensure => present},'Vlan245'=> {vlan_id =>245, ensure => present}, } create_resources( netdev_vlan, $vlans ) }Update Layer 2 Interface.
Manifest example (located in “/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/manifests/netdev_l2_interface_example.pp”).classvlans_ensure_example{ $vlans = {'Vlan347'=> {vlan_id =>347, ensure => present},'Vlan348'=> {vlan_id =>348, ensure => present},'Vlan349'=> {vlan_id =>349, ensure => present}, } create_resources( netdev_vlan, $vlans ) }classl2_interface_example{ include vlans_ensure_example #classto Ensure VLANs before assigning $l2_interfaces = {'ethernet 1/3'=> {ensure => absent, vlan_tagging => disable}, #default'ethernet 1/4'=> {ensure => present, vlan_tagging => enable, tagged_vlans => [Vlan348,Vlan347], untagged_vlan => Vlan349} #hybrid } create_resources( netdev_l2_interface, $l2_interfaces ) }Update LAG.
Manifest example (located in “/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/manifests/netdev_lag_example.pp”).classlag_example{ $lags = {'port-channel 101'=> {ensure => present, links => ['ethernet 1/12','ethernet 1/13'], lacp => active},'port-channel 102'=> {ensure => present, links => ['ethernet 1/6','ethernet 1/5'], lacp => disabled}, } create_resources( netdev_lag, $lags ) }WarningYou may add classes to ensure that all assigned links are with the same layer 1 and layer 2 configurations (similarly to the way we did in update l2_interface section with vlans_ensure_example class).
Ethernet and Port-Channel
Interface Capabilities
Field | Description | Values | Example |
ensure | Sets the given values or restores the interface to default | absent, present | ensure => present |
speed | Sets the speed of the interface. | auto*|10m|100m|1g|10g|40g|56g | speed => 1g |
admin | Disables/enables interface admin state. | up, down | admin => up |
mtu | Configures the maximum transmission unit frame size for the interface. | 1518-9216 | mtu => 1520 |
description | Sets the Ethernet and LAG description. | Text | description => “changed_by_puppet” |
VLAN Capabilities
Field | Description | Values | Example |
ensure | Creates or destroys the VLAN given as a resource ID | absent, present | ensure => present |
vlan_id | The VLAN ID | 1-4094 (integer) | vlan_id => 245 |
Layer 2 Ethernet Interface Capabilities
Field | Description | Values | Example |
ensure | Sets the given values or restores the Layer 2 interface to default. | absent, present | ensure => present |
vlan_tagging | VLAN tagging mode | enable,disable | vlan_tagging => enable |
tagged_vlans | List of tagged (trunked) VLANs | 2-4994 (range) | tagged_vlans => [Vlan348,Vlan347] |
untagged_vlan | Untag (access) VLAN | <VLAN name> | untagged_vlan => Vlan349 |
LAG Capabilities
Field | Description | Values | Example |
ensure | creates or destroys the port-channel given as a resource ID | absent, present | ensure => present |
lacp | The LACP mode of the LAG | passive | active | on | lacp => on |
links | List of ports assigned to the LAG | List of link names | links => ['ethernet 1/6','ethernet 1/5'] |
Layer 3 Interface Capabilities
Field | Description | Values | Example |
ensure | Creates or destroys the interface VLAN specified in the resource ID. | present, absent | ensure => present |
ipaddress | Sets IP address on the Layer 3 interface (requires netmask). | A valid IP address | ipaddress => ‘192.168.4.2’ |
netmask | Sets netmask for the IP address. | A valid netmask (of the form X.1X2.X3.X4), which creates a valid combination with the given IP address | netmask => ‘255.255.255.0’ |
method | Configures the method of the L3 interface (currently supports only static method). | static | method => static |
OSPF Interface Capabilities
Field | Description | Values | Example |
ensure | Creates or destroys the OSPF interface of the associated interface of the VLAN specified in the resource ID | present, absent | ensure => present |
area_id | The associated area ID | Integer representing an IP | area_id => ‘7200’ |
Type | The network type | broadcast, point_to_point | type => ‘point_to_point’ |
OSPF Area Capabilities
Field | Description | Values | Example |
ensure | Creates or destroys the OSPF area specified in the resource ID | present, absent | ensure => present |
router_id | The OSPF area associated router ID (currently supports only default router) | default | router_id => 'default' |
ospf_area_mode | The OSPF area mode | normal, stub, nssa | ospf_area_mode => 'stub' |
subnets | A list of associated subnets | List of subnets | ["192.168.4.0/24", "192.168.5.0/24"] |
Router OSPF Capabilities
Field | Description | Values | Example |
ensure | Enables/disables the router ID specified in the resource ID | present, absent | ensure => present |
SNMP, LLDP, IP Routing, and Spanning Tree Capabilities
Field | Description | Values | Example |
ensure | Enables/disables the protocol specified in the resource ID | present, absent | ensure => present |
Fetched Image Capabilities
Field | Description | Values | Example |
ensure | Enables/disables the protocol specified in the resource ID | present, absent | ensure => present |
protocol | Specifies the protocol for fetch method | http, https, ftp, tftp, scp, sftp | protocol => scp |
host | The host where the filename located | DNS/IP | host => my_DNS |
user | The username for fetching the image | Username | user => my_username |
password | The password for fetching the image | Password | password => my_pass |
location | The location of the file name in the host file system | Directory full path | location => '/tmp' |
force_delete | Remove all the images or only the ones which are not installed on any partition, before fetching | yes, no | force_delete => no |
Installed Image Capabilities
Field | Description | Values | Example |
ensure | Specifies if the image version given in as resource ID is ensured to be installed or not | present, absent | ensure => present |
is_next_boot | Ensures that the installed image is the next boot partition | yes, no | is_next_boot => yes |
configuration_write | Writes configurations to database. | yes, no | configuration_write => yes |
force_reload | Reload if image is in other partition. | yes, no | force_reload => no |
Resource Type | Puppet Type Name | Supported Resource IDS | Example |
Network device | netdev_device | $hostname | netdev_device { $hostname: } |
Layer 1 interface | netdev_interface | 'ethernet <#ID>', 'port-channel <#id>' | netdev_interface{'ethernet 1/3': ensure => absent} |
Layer 2 interface | netdev_l2_interface | 'ethernet <#ID>', 'port-channel <#id>' | netdev_l2_interface{'ethernet 1/3': ensure => absent} |
VLAN | netdev_vlan | VLAN name string | netdev_vlan {'Vlan244': vlan_id => 244, ensure => present } |
LAG | netdev_lag | 'port-channel <#id>' | netdev_lag {'port-channel 101': ensure => present } |
Layer 3 interface | netdev_l3_interface | 'vlan <#ID>' | netdev_l3_interface{ 'vlan 4': ipaddress => '192.168.4.2', netmask => '255.255.255.0'} |
OSPF interface | netdev_ospf_interface | 'vlan <#ID>' | netdev_ospf _interface{ 'vlan 4': ensure => present, area_id => '10' } |
OSPF area | netdev_ospf_area | Valid area ID (representing an IP) | netdev_ospf _area{ '10': ensure => present, ospf_area_mode=>'stub'} |
OSPF router | netdev_router_ospf | Currently only supports 'default' | netdev_router_ospf {'default': ensure => present } |
Protocol | mlnx_protocol | ip_routing, lldp, snmp, spanning_tree | mlnx_protocol { 'ip_routing': ensure => present} |
Fetched image | mlnx_fetched_img | The image file name | mlnx_fetched_image { 'onyx-X86_64-3.6.8008.img': ensure => present} |
Installed image | mlnx_installed_img | The image version name | mlnx_installed_img { '3.3.4300': ensure => present} |
This section presents common issues that may prevent the switch from connecting to the puppet server.
Switch and Server Clocks are not Synchronized
This can be fixed by using NTP to synchronize the clocks at the switch (using the command “ntp”) and at the server (e.g. using ”ntpdate”).
Outdated or Invalid SSL Certificates Either on the Switch or the Server
This can be fixed on the switch using the CLI command “puppet-agent clear-certificates” (requires “puppet-agent restart” to take effect).
On the server it can be fixed by running “puppet cert clean <switch_fqdn>” (FQDN is the Fully Qualified Domain Name which consists of a hostname and a domain suffix).
Communications Issue
Make sure it is possible to ping the puppet server hostname from the switch (using the command “ping”).
If the hostname is not reachable (e.g. no DNS server) it can be statically added to the switch local hosts lookup (using the command “ip host”).
Make sure that port 8140 is open (using the command “tracepath {<hostname> | <ip>}/8140”).
puppet-agent
puppet-agent Enters puppet agent configuration mode. | ||
Syntax Description | N/A | |
Default | N/A | |
Configuration Mode | config | |
History | 3.3.4200 | |
Example | switch (config) # puppet-agent | |
Related Commands | ||
Notes | ||
puppet-agent enable
puppet-agent [vrf <vrf-name>] enable [force] Enables PUPPET in VRF. | ||
Syntax Description | vrf-name | VRF name |
force | Enables PUPPETin the specified VRF and sets all relevan t PUPPET option to default | |
Default | PUPPET is enabled by default | |
Configuration Mode | config | |
History | 3.9.2000 | |
Example | switch (config) # puppet-agent vrf mgmt enable | |
Related Commands | ||
Notes | If VRF management exists, PUPPET will be enabled on VRF management. If VRF management not does not exist, PUPPET will be enabled on VRF default. | |
master-hostname
master-hostname <hostname> Sets the puppet server hostname. | ||
Syntax Description | hostname | Puppet server hostname |
Default | puppet | |
Configuration Mode | config puppet | |
History | 3.3.4200 | |
Example | switch (config puppet-agent) # master-hostname my_puppet_server_hostname | |
Related Commands | ||
Notes | ||
enable
enable Enables the puppet server on the switch. | ||
Syntax Description | N/A | |
Default | Disabled | |
Configuration Mode | config puppet | |
History | 3.3.4200 | |
Example | switch (config puppet-agent) # enable | |
Related Commands | ||
Notes | ||
run-interval
run-interval <time> Configures the time interval in which the puppet agent reports to the puppet server. | ||
Syntax Description | time | Can be in seconds (“30” or “30s”), minutes (“30m”), hours (“6h”), days (“2d”), or years (“5y”) |
Default | 30m | |
Configuration Mode | config puppet | |
History | 3.3.4302 | |
Example | switch (config puppet-agent) # run-interval 40m | |
Related Commands | show puppet-agent | |
Notes | ||
restart
puppet-agent restart Restarts the puppet agent. | ||
Syntax Description | time | Can be in seconds (“30” or “30s”), minutes (“30m”), hours (“6h”), days (“2d”), or years (“5y”) |
Default | N/A | |
Configuration Mode | config puppet | |
History | 3.3.4200 | |
Example | switch (config puppet-agent) # restart | |
Related Commands | ||
Notes | ||
show puppet-agent
show puppet-agent Displays Puppet agent status and configuration. | ||
Syntax Description | N/A | |
Default | N/A | |
Configuration Mode | Any command mode | |
History | 3.3.4200 3.9.2000—Updated example, adding "VRF name" field | |
Example |
| |
Related Commands | ||
Notes | ||
show puppet-agent log
show puppet-agent log [[not] [matching | continuous] <string> | files [[not] matching] <string>] Displays the Puppet agent’s log file. | ||
Syntax Description | continuous | Puppet agent log messages as they arrive |
files | Displays archived Puppet agent log files | |
matching | Displays Puppet agent log that match a given string | |
not | Displays Puppet agent log that do not meet a certain string | |
string | Free string | |
Default | N/A | |
Configuration Mode | Any command mode | |
History | 3.3.4200 | |
Example | ||
switch (config puppet-agent) # show puppet-agent log Mon Nov 04 11:52:42 +0000 2013 Puppet (notice): Starting Puppet client version 3.2.3 | ||
Related Commands | ||
Notes | ||