SALT
Salt is a different approach to infrastructure management, founded on the idea that high-speed communication with large numbers of systems can open new capabilities. This approach makes Salt a powerful multitasking system that can solve many specific problems in an infrastructure.
The backbone of Salt is the remote execution engine, which creates a high-speed, secure and bi-directional communication net for groups of systems. On top of this communication system, Salt provides an extremely fast, flexible, and easy-to-use configuration management system called Salt States.
For a list of Salt’s Napalm supported modules, please refer to the NAPALM-Onyx github repository.
Install Salt packages:
curl -L https:
//bootstrap.saltstack.com -o install_salt.shsudo sh install_salt.sh -P -M yum install -y salt-master salt-minion salt-ssh salt-syndic salt-cloud salt-apiInstall the Napalm library.
yum install epel-release yum install -y python-pip yum install libxml2-devel libxslt-devel zlib-devel gcc openssl-devel libffi-devel python-devel pip install pyzmq --install-option=
"--zmq=bundled"pip install napalm
Open the /etc/salt/master file.
Replace #interface: 0.0.0.0 with interface: <machine_ip>.
Replace #hash_type: md5 with hash_type: sha256.
Find file_roots and pillar_rootsand and add the following lines below them:
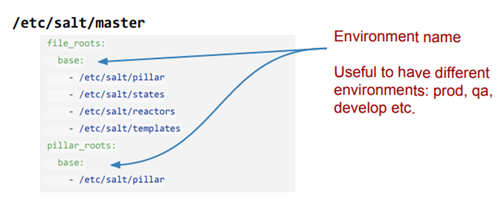
Save and quit by entering: wq
Restart the Salt-master file:
sudo systemctl start salt-master.service sudo systemctl enable salt-master.service
After the installation, modify the /etc/salt/minion configuration file as below:
Open the /etc/salt/minion file.
Replace #master: salt with master: 10.99.0.10.
Replace #hash_type: md5 with: hash_type: sha256.
Save and quit by entering: wq
Restart and enable Salt-minion.
sudo systemctl start salt-minion.service
Run /etc/salt/proxy.
Find the below attributes and fill them out as shown below:
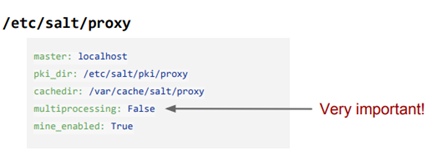
Create a pillar directory under /etc/salt.
mkdir -r /etc/salt/pillar
Go to the /etc/salt/pillar directory
Create the top.sls file inside this directory.
Per each switch, insert the following information:
• DEVICE_ID
• DEVICE_SLS_FILENAME
Create a new file: [DEVICE_SLS_FILENAME].sls
Insert the following information into the above file:proxy: proxytype: napalm driver: [DRIVER] host: [HOSTNAME] username: [USERNAME] passwd: [PASSWORD]
Example:
proxy: proxytype: napalm driver: onyx_ssh host:
10.209.37.247username: admin passwd: admin propt_name: switch20 ssh_args:‘-0PubkeyAuthentication=no’Restart Salt on the server in order to use the new configuration
systemctl stop salt-minion systemctl stop salt-master systemctl stop salt-proxy@<switch_name> systemctl start salt-master systemctl start salt-minion systemctl start salt-proxy@<switch_name>
The following Salt command can be used:
Check if the switch is connected to the server running the Salt master:
salt onyx1 net.connected
Run any command on the switch using net.cli (example: using “show version”):
salt onyx1 net.cli
'show version'Get the switch mac address:
salt onyx1 net.mac
Get the switch arp table:
salt onyx1 net.arp
Get switch information (uptime, vendor, os-version, etc):
salt onyx1 net.facts
Get the switch interfaces details:
salt onyx1 net.interfaces