Overview
These pages are intended for network administrators who are responsible for configuring and managing NVIDIA’s switch platforms.
The following table lists the documents referenced in this User Manual.
Document Name | Description |
System Hardware User Manual | This document contains hardware descriptions, LED assignments, and hardware specifications, among other things |
Switch Product Release Notes | Please look up the relevant switch system/series Release Notes file |
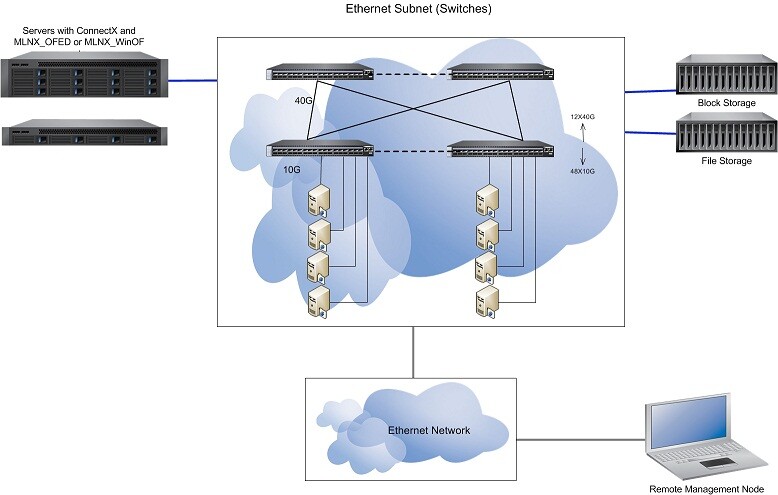
This reference architecture provides general information concerning NVIDIA L2 and L3 Virtual Modular Switch (VMS) configuration and design | |
Community | Provides Ethernet Switch Solutions |
Term | Description |
AAA | Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting:
|
ARP | Address Resolution Protocol. A protocol that translates IP addresses into MAC addresses for communication over a local area network (LAN). |
CLI | Command Line Interface. A user interface in which you type commands at the prompt. |
DCB | Data Center Bridging |
DCBX | Should be Data Center Bridging eXchange—an extension of Link Layer Data Protocol to discover DCB compliant peers and exchange configuration information |
DHCP | The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is an automatic configuration protocol used on IP networks. |
DNS | Domain Name System. A hierarchical naming system for devices in a computer network. |
ECN | Explicit Congestion Notification |
ETS | Enhanced Transmission Selection provides a common management framework for assignment of bandwidth to traffic classes. |
FTP/TFTP/sFTP | File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a standard network protocol used to transfer files from one host to another over a TCP-based network, such as the Internet. |
Gateway | A network node that interfaces with both InfiniBand and Ethernet, using different network protocols. |
HA | High Availability. A system design protocol that provides redundancy of system components, thus enables overcoming single or multiple failures in minimal downtime. |
Host | A computer platform executing an Operating System which may control one or more network adapters |
LACP | Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) provides a method to control the bundling of several physical ports together to form a single logical channel. LACP allows a network device to negotiate an automatic bundling of links by sending LACP packets to the peer (directly connected device that also implements LACP). |
LDAP | The Lightweight Directory Access Protocol is an industry standard application protocol for accessing and maintaining distributed directory information services over an IP network. |
LLDP | Link Layer Discovery Protocol. A vendor neutral link layer protocol used by network devices to advertise their identify, capabilities and for neighbor discovery. |
MAC | A Media Access Control address (MAC address) is a unique identifier assigned to network interfaces for communications on the physical network segment. MAC addresses are used for numerous network technologies and most IEEE 802 network technologies including Ethernet. |
MTU | Maximum Transfer Unit. The maximum size of a packet payload (not including headers) that can be sent /received from a port. |
Network Adapter | A hardware device that allows for communication between computers in a network. |
NTP | Network Time Protocol. A protocol for synchronizing computer clocks in a network. |
PFC/FC | Priority Based Flow Control applies pause functionality to traffic classes OR classes of service on the Ethernet link. |
PTP IEEE-1588 | Precision Time Protocol. A high-accuracy time transfer protocol for synchronizing computer clocks in a network. |
RADIUS | Remote Authentication Dial In User Service. A networking protocol that enables AAA centralized management for computers to connect and use a network service. |
RDMA | Remote Direct Memory Access. Accessing memory in a remote side without involvement of the remote CPU. |
RoCE | RDMA over Converged Ethernet. A network protocol that leverages Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) capabilities to accelerate communications between applications hosted on clusters of servers and storage arrays. |
RSTP | Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol. A spanning-tree protocol used to prevent loops in bridge configurations. RSTP is not aware of VLANs and blocks ports at the physical level. |
SCP | Secure Copy or SCP is a means of securely transferring computer files between a local and a remote host or between two remote hosts. It is based on the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol. |
SNMP | Simple Network Management Protocol. A network protocol for the management of a network and the monitoring of network devices and their functions. |
SSH | Secure Shell. A protocol (program) for securely logging in to and running programs on remote machines across a network. The program authenticates access to the remote machine and encrypts the transferred information through the connection. |
syslog | A standard for forwarding log messages in an IP network. |
TACACS+ | Terminal Access Controller Access-Control System Plus. A networking protocol that enables access to a network of devices via one or more centralized servers. TACACS+ provides separate AAA services. |
Feature | Detail |
Software management |
|
File management |
|
Logging |
|
Management interface |
|
Chassis management |
|
Network management interfaces |
|
Security |
|
Date and time |
|
Cables & transceivers |
|
Feature | Detail |
Layer 2 Feature Set |
|
Layer 3 Feature Set |
|
Synchronization |
|
Quality of Service |
|
Management & Automation |
|
Network Virtualization |
|
Software Defined Network (SDN) |
|
Docker Container |
|
Monitoring & Telemetry |
|
Security |
|