Access Control List Configuration
Recent-list LimiterNVOS Linux provides the NVUE, an NVOS Linux-specific userspace tool to configure custom ACLs on mgmt interfaces including 'eth0' and 'loopback' interfaces.
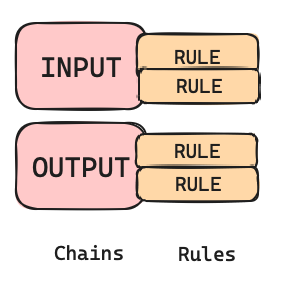
Chains
ACLs in NVOS Linux classify and control packets to and from the switch, asserting policies at layers 3 and 4 of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model by inspecting packet headers according to a list of rules.
The rules inspect or operate on packets at several points (chains) in the life of the packet through the system:
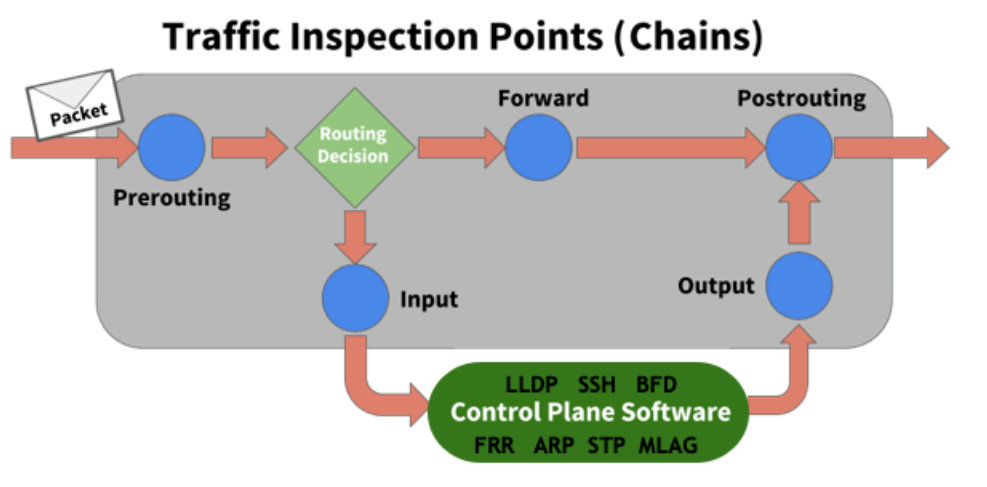
Supported chains are:
- PREROUTING touches packets before the switch routes them.
- INPUT touches packets after the switch determines that the packets are for the local system but before the control plane software receives them.
- OUTPUT touches packets from the control plane software before they leave the switch.
- POSTROUTING touches packets immediately before they leave the switch but after a routing decision.
Rules
Rules classify the traffic you want to control. You apply rules to chains.
NVOS provides a comfortable way to manage ACL rules configurations on the system using NVUE.
Consider the following example, where we want to accept packets matching the following criteria:
TCP packets.
Source IP address—
10.0.14.2/32Any source port.
Destination IP address—
10.0.15.8/32Any destination port.
The steps we need to perform are:
Set the rule type, the matching protocol, source IP address and port, destination IP address and port, and the action. You must provide a name for the rule (EXAMPLE1 in the commands below):
admin
@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE1 type ipv4 admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE1 rule10match ip protocol tcp admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE1 rule10match ip source-ip10.0.14.2/32admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE1 rule10match ip tcp source-port ANY admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE1 rule10match ip dest-ip10.0.15.8/32admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE1 rule10match ip tcp dest-port ANY admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE1 rule10action permitApply the rule to an inbound or outbound interface with the
nv set interface <interface> aclcommand.For rules affecting the PREROUTING or POSTROUNTING chain, apply the rule to an inbound or outbound interface accordingly: For example:
admin
@nvos:~$ nv setinterfaceeth0 acl EXAMPLE1 inbound admin@nvos:~$ nv config applyFor rules affecting the INPUT or OUPUT chain, apply the rule to inbound control plane or outbound control plane interface accordingly. For example:
admin
@nvos:~$ nv setinterfaceeth0 acl EXAMPLE1 inbound control-plane admin@nvos:~$ nv config apply
If an ACL is not applied to an interface it will not take any effect during the process of a packet.
To see the configured rule run the NVUE nv show acl <rule-name> rule <ID> command:
admin@nvos:~$ nv show acl EXAMPLE1 rule 10
operational applied
------------------- ------------ ------------
match
ip
source-ip 10.0.14.2/32 10.0.14.2/32
dest-ip 10.0.15.8/32 10.0.15.8/32
protocol tcp tcp
tcp
[source-port] ANY ANY
[dest-port] ANY ANY
To remove this rule, run the nv unset acl <acl-name> and nv unset interface <interface> acl <acl-name> commands.
admin@nvos:~$ nv unset acl EXAMPLE1
admin@nvos:~$ nv unset interface eth0 acl EXAMPLE1
admin@nvos:~$ nv config apply
To show ACL statistics per interface, such as the total number of bytes that match the ACL rule, run the nv show interface <interface-id> acl <acl-id> statistics or nv show interface <interface-id> acl <acl-id> statistics <rule-id> command, for example:
admin@nvos:~$ nv show interface eth0 acl EXAMPLE1 statistics
Rule In Packet In Byte Out Packet Out Byte Layer Remark Action Summary
---- --------- ------- ---------- -------- ----- ------ ------ --------------------------------
10 0 0 ip permit match.ip.dest-ip: 10.0.15.8/32
match.ip.protocol: tcp
match.ip.source-ip: 10.0.14.2/32
match.ip.tcp.dest-port: ANY
match.ip.tcp.source-port: ANY
To see the list of all NVUE ACL commands, run the nv list-commands acl command.
Rule Support
Rule Element | Supported |
Matches | Src/Dst, IP protocol In/out interface IPv4: ecn, icmp IPv6: icmpv6, routing-header, extension-header IP common: tcp (with flags), udp, multiport, frag, mss, connection-state |
Standard Actions | permit, deny, log (log with log prefix), empty (no action specified) |
Limiters | Recent-list Hashlimit |
The default action for each rule defined is no action. Packet matching such rules will not be affected and will continue to be processed by the proceeding rules in order.
Control Plane Limiters
NVUE allows you to configure rate limit on traffic, so incoming packets drop if they exceed certain thresholds. NVUE provides two limiters to achieve it: recent-list and hashlimit.
Recent-List Limiter
Allows you to dynamically create a list of IP addresses and then match against that list in a few different ways, for example:
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE2 type ipv4
admin@nvos:~$
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE2 rule 10 match ip tcp dest-port 22
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE2 rule 10 match ip protocol tcp
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE2 rule 10 match ip recent-list action set
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE2 rule 10 match ip recent-list name TCP-SSH-LIMIT
admin@nvos:~$
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE2 rule 20 match ip tcp dest-port 22
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE2 rule 20 match ip protocol tcp
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE2 rule 20 match ip recent-list action update
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE2 rule 20 match ip recent-list update-interval 60
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE2 rule 20 match ip recent-list hit-count 100
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE2 rule 20 match ip recent-list name TCP-SSH-LIMIT
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE2 rule 20 action deny
admin@nvos:~$
admin@nvos:~$ nv set interface eth0 acl EXAMPLE2 inbound control-plane
admin@nvos:~$ nv config apply
The above example, limits any source IP address sending more than 100 packets per 60-second interval to the switch, if it exceeds this rate all packets from this source IP address will be blocked.
Configuring the recent-list limiter consists of two consecutive rules, both rules should contain the same matching criteria (protocol tcp and dest-port 22 in the above example) and the name of the recent-list (TCP-SSH-LIMIT in the above example).
The first rule is set to action 'set'
The second rule is set to recent-list action 'update' and specified with the requested threshold using 'hit-count' and 'update-interval' (100 packets per 60-second interval in the above example)
The second rule action is set to deny
Hashlimit Limiter
Uses hash buckets to express a rate limiting match for a group of connections using a single rule. Grouping can be done per-hostgroup (source and/or destination address). It gives you the ability to express "Npackets per time quantum per group", for example:
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE3 type ipv4
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE3 rule 10 match ip tcp dest-port 22
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE3 rule 10 match ip protocol tcp
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE3 rule 10 match ip hashlimit name TCP-SSH-LIMIT
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE3 rule 10 match ip hashlimit rate-above 5/min
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE3 rule 10 match ip hashlimit burst 2
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE3 rule 10 match ip hashlimit expire 3000
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE3 rule 10 match ip hashlimit mode src-ip
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE3 rule 10 match ip hashlimit source-mask 32
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE3 rule 10 action deny
admin@nvos:~$ nv set interface eth0 acl EXAMPLE2 inbound control-plane
admin@nvos:~$ nv config apply
The above example, limits any source IP address sending more than 5 packets per minute to the switch with a burst of 2 packets, if it exceeds this rate all packets from this source IP address will be blocked for 3000 milliseconds as specified in the expire parameter and will be able to send again after this period.
Configuring the recent-list limiter can be configured in one single ACL rule. T he following parameters need to be configured for the hashlimit: name, rate-above, burst, expire and mode. The source-mask or destination-mask are optional.
Filter Specific TCP Flags
The example rule below drops ingress IPv4 TCP packets when you set the SYN bit and reset the RST, ACK, and FIN bits. The rule applies inbound on interface eth0. After configuring this rule, you cannot establish new TCP sessions that originate from ingress mgmt port eth0. You can establish TCP sessions that originate from any other port.
NVUE Commands
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE4 type ipv4
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE4 rule 20 match ip protocol tcp
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE4 rule 20 match ip tcp flags syn
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE4 rule 20 match ip tcp mask rst
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE4 rule 20 match ip tcp mask syn
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE4 rule 20 match ip tcp mask fin
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE4 rule 20 match ip tcp mask ack
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE4 rule 20 action deny
admin@nvos:~$ nv set interface eth0 acl EXAMPLE4 inbound
admin@nvos:~$ nv config apply
Control Who Can SSH into the Switch
Run the following commands to control who can SSH into the switch. In the following example, 10.10.10.1/32 is the interface IP address (or loopback IP address) of the switch and 10.255.4.0/24 can SSH into the switch.
NVUE Commands
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl example2 type ipv4
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl example2 rule 10 match ip source-ip 10.255.4.0/24
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl example2 rule 10 match ip dest-ip 10.10.10.1/32
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl example2 rule 10 action permit
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl example2 rule 20 match ip source-ip ANY
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl example2 rule 20 match ip dest-ip 10.10.10.1/32
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl example2 rule 20 action deny
admin@nvos:~$ nv set interface eth0 acl example2 inbound
admin@nvos:~$ nv config apply
Match on ECN Bits in the TCP IP Header
ECN allows end-to-end notification of network congestion without dropping packets. You can add ECN rules to match on the ECE, CWR, and ECT flags in the TCP IPv4 header.
By default, ECN rules match a packet with the bit set. You can reverse the match by using an explanation point (!).
Match on the ECE Bit
After an endpoint receives a packet with the CE bit set by a router, it sets the ECE bit in the returning ACK packet to notify the other endpoint that it needs to slow down.
To match on the ECE bit:
NVUE Commands
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl example2 type ipv4
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl example2 rule 10 match ip protocol tcp
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl example2 rule 10 match ip ecn flags tcp-ece
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl example2 rule 10 action permit
admin@nvos:~$ nv set interface eth0 acl example2 inbound
admin@nvos:~$ nv config apply
Match on the CWR Bit
The CWR bit notifies the other endpoint of the connection that it received and reacted to an ECE.
To match on the CWR bit:
NVUE Commands
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl example2 type ipv4
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl example2 rule 10 match ip protocol tcp
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl example2 rule 10 match ip ecn flags tcp-cwr
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl example2 rule 10 action permit
admin@nvos:~$ nv set interface eth0 acl example2 inbound
admin@nvos:~$ nv config apply
Match on the ECT Bit
The ECT codepoints negotiate if the connection is ECN capable by setting one of the two bits to 1. Routers also use the ECT bit to indicate that they are experiencing congestion by setting both the ECT codepoints to 1.
To match on the ECT bit:
NVUE Commands
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl example2 type ipv4
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl example2 rule 10 match ip protocol tcp
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl example2 rule 10 match ip ecn ip-ect 1
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl example2 rule 10 action permit
admin@nvos:~$ nv set interface eth0 acl example2 inbound
admin@nvos:~$ nv config apply
Set DSCP on Transit Traffic
The following examples use the mangle table to modify the packet as it transits the switch. DSCP is in decimal notation in the examples below.
To set SSH as high priority traffic:
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE1 type ipv4
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE1 rule 10 match ip protocol tcp
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE1 rule 10 match ip tcp dest-port 22
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE1 rule 10 action set dscp 46
admin@nvos:~$ nv set interface eth0 acl EXAMPLE1 inbound
admin@nvos:~$ nv config apply
To set everything coming in swp1 as AF13:
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE1 type ipv4
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE1 rule 10 action set dscp 14
admin@nvos:~$ nv set interface eth0 acl EXAMPLE1 inbound
admin@nvos:~$ nv config apply
To set Packets destined for 10.0.100.27 as best effort:
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE1 type ipv4
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE1 rule 10 match ip dest-ip 10.0.100.27/32
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE1 rule 10 action set dscp 0
admin@nvos:~$ nv set interface eth0 acl EXAMPLE1 inbound
admin@nvos:~$ nv config apply
To use a range of ports for TCP traffic:
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE1 type ipv4
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE1 rule 10 match ip protocol tcp
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE1 rule 10 match ip source-ip 10.0.0.17/32
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE1 rule 10 match ip tcp source-port 10000:20000
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE1 rule 10 match ip dest-ip 10.0.100.27/32
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE1 rule 10 match ip tcp dest-port 10000:20000
admin@nvos:~$ nv set acl EXAMPLE1 rule 10 action set dscp 34
admin@nvos:~$ nv set interface eth0 acl EXAMPLE1 inbound
admin@nvos:~$ nv config apply
To specify all ports on the switch in NVUE (swp+ in an iptables rule), you must set the range of interfaces on the switch as in the examples above (
nv set interface swp1-48
). This command creates as many rules in the
/etc/cumulus/acl/policy.d/50_nvue.rules
file as the number of interfaces in the range you specify.