Installation for DPU Mode
Contents:
DPU mode is the default mode for BlueField DPUs, while BlueField SuperNICs are shipped with NIC mode as their default. To switch between the modes, see NVIDIA BlueField Modes of Operation. To check which mode your BlueField is currently running:
Using RedFish on the 1GbE interface, refer to NVIDIA BlueField BMC Software Documentation
From the host server, refer to "Enabling NIC Mode on BlueField-3 from Linux"
From the host server's UEFI BIOS menu, refer to "Configuring NIC Mode on BlueField-3 from Host BIOS HII UEFI Menu"
In the out-of-box state of the BlueField the host is assumed to be trusted. Later in this procedure, after performing BFB Bundle update, a step is provided to disable the host RShim which the user must perform to protect the BlueField from potential security threats from the host.
The following diagram illustrates the sequence of events and actions from first time power-up of the NVIDIA® BlueField® networking platform (DPU or SuperNIC) in the data center environment through provisioning and maintenance.
The numbers indicated in the sequence diagram correspond to the steps that follow it.
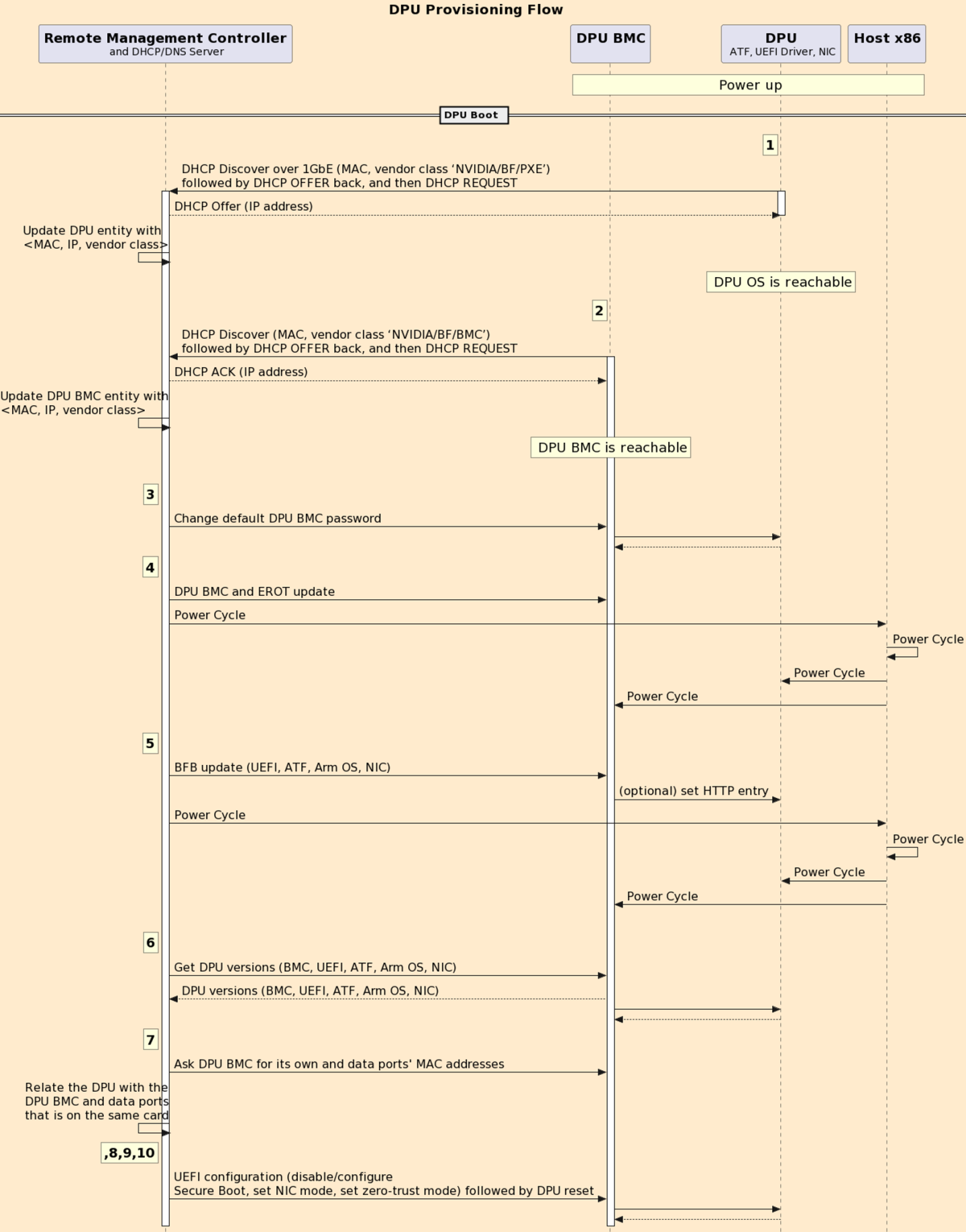
At the end of this procedure, the BlueField should be configured with an IP address, all required settings, has up-to-date software component versions, and is ready to use.
The BlueField SoC boots to the UEFI BIOS and DHCP DISCOVER is sent
BlueField SoC runs UEFI/PXE which sends a DHCP DISCOVER over the 1GbE OOB interface, including vendor class (
"NVIDIA/BF/PXE") for BlueField SoC (to allow customer's server to differentiate between BlueField SoC and BlueField BMC), and MAC for identification and discovery. See Appendix B for more information.A customer's DHCP server inspects the MAC address and the vendor class, allocates IP, and continues the standard DHCP.
DHCP server updates RMC of the new BlueField discovered with detailed information (e.g., MAC, IP address, vendor class).
BlueField BMC issues DHCP DISCOVER over the 1GbE OOB interface, including vendor class ("NVIDIA/BF/BMC") for BlueField-BMC, and MAC for identification and discovery. Example of BlueField BMC DHCP DISCOVER packet structure (note "NVIDIA/BF/BMC" in line 13):
root@bf-bmc:~# 18:18:10.563269 IP (tos 0xc0, ttl 64, id 0, offset 0, flags [none], proto UDP (17), length 320)
0.0.0.0.bootpc > 255.255.255.255.bootps: [udp sum ok] BOOTP/DHCP, Request from b8:3f:d2:ca:4b:26 (oui Unknown), length 292, xid 0xfc2acdec, secs 1, Flags [none] (0x0000)
Client-Ethernet-Address b8:3f:d2:ab:cd:ef (oui Unknown)
Vendor-rfc1048 Extensions
Magic Cookie 0x63825363
DHCP-Message (53), length 1: Discover
Client-ID (61), length 7: ether b8:3f:d2:ab:cd:ef
Parameter-Request (55), length 9:
Subnet-Mask (1), Default-Gateway (3), Domain-Name-Server (6), Hostname (12)
Domain-Name (15), Static-Route (33), NTP (42), Unknown (120)
Classless-Static-Route (121)
MSZ (57), length 2: 576
Hostname (12), length 7: "bf-bmc" Vendor-Class (60), length 13: "NVIDIA/BF/BMC" END (255), length 0
18:18:10.565261 IP (tos 0x0, ttl 63, id 0, offset 0, flags [DF], proto UDP (17), length 353)
(example) dhcp01.XX.YY > ldev-platform-13-043-bmc.bootpc: [no cksum] BOOTP/DHCP, Reply, length 325, hops 1, xid 0xfc2acdec, secs 1, Flags [none] (0x0000)
(example) Your-IP ldev-platform-13-043-bmc.XX.YY
(example) Server-IP l-pxe02.XX.YY
Gateway-IP 10.237.0.255
Client-Ethernet-Address b8:3f:d2:ab:cd:ef (oui Unknown)
file "pxelinux.0" Vendor-rfc1048 Extensions
Magic Cookie 0x63825363
DHCP-Message (53), length 1: Offer
Server-ID (54), length 4: (example) dhcp01.XX.YY
Lease-Time (51), length 4: 43200
Subnet-Mask (1), length 4: 255.255.0.0
Default-Gateway (3), length 4
(example) GW.XX.YY
Hostname (12), length 24: "ldev-platform-13-043-bmc" Domain-Name (15), length 13: "<local domain name>" NTP (42), length 4: (example) NTP.XX.YY
END (255), length 0
18:18:10.565261 IP (tos 0x0, ttl 62, id 0, offset 0, flags [DF], proto UDP (17), length 353)
dhcp01.XX.YY > ldev-platform-13-043-bmc.<local domain name>: [no cksum] BOOTP/DH
DHCP server inspects the MAC address and the vendor class, allocates IP and continues the standard DHCP flow.
DHCP server updates RMC of the new BlueField BMC discovered with detailed information: MAC, IP address, vendor classes, etc.
To communicate with the BlueField BMC, change the default password (0penBmc) by sending the following Redfish schema to the BlueField BMC:
curl -k -u root:0penBmc -H "Content-Type: application/json" -X PATCH https://<BF-BMC-IP>/redfish/v1/AccountService/Accounts/root -d '{"Password" : "<user-password>"}'
Where <BF-BMC-IP> is the IP address for the BlueField BMC (e.g., 10.10.1.2), and <user-password> is the chosen password to log into the BlueField BMC with root privileges.
The BMC password must comply with the following policy parameters:
Using ASCII and Unicode characters is permitted
Minimum length: 12
Maximum length: 20
Maximum number of consecutive character pairs: 4
InfoTwo characters are consecutive if
|hex(char_1)-hex(char_2)|=1.Examples of passwords with 5 consecutive character pairs (invalid):
DcBa123456AbCd!;ab1XbcYcdZdeGef!;Testing_123abcgh!.
The following is a valid example password:
HelloNvidia3D!
A user account is locked for 10 minutes after 10 consecutive failed attempts.
For example:
[redfish_scripts] $ curl -k -u root:0penBmc -H "Content-Type: application/json" -X PATCH https://<BF-BMC-IP>/redfish/v1/AccountService/Accounts/root -d '{"Password" : "HelloNvidia3D!"}'
Response:
{
"@Message.ExtendedInfo": [
{
"@odata.type": "#Message.v1_1_1.Message",
"Message": "The request completed successfully.",
"MessageArgs": [],
"MessageId": "Base.1.15.0.Success",
"MessageSeverity": "OK",
"Resolution": "None"
}
]
}
Upgrade BlueField BMC firmware via the Redfish "update service schema" through the 1GbE OOB.
If a BlueField-2 is in your possession and it is the first time you are upgrading BlueField BMC, follow Appendix A.
If a BlueField-3 is in your possession, follow the instructions in the following subsections
Make sure to download the latest BlueField BMC image available from the BlueField Runtime and Driver Downloader.
Update BMC Firmware
Run the following Redfish command over the 1GbE out-of-band interface on the BlueField BMC to trigger a secure BlueField BMC firmware update:
curl -k -u root:'<password>' -H "Content-Type: application/octet-stream" -X POST -T <package_path> https://<BF-BMC-IP>/redfish/v1/UpdateService/update
Where:
<password>– BlueField BMC password<package_path>– BMC firmware update package path pointing to BMC*.fwpkgbinary (e.g.,bf3-bmc-23.09-6_opn.fwpkg)<BF-BMC-IP>– BMC IP addressAfter pushing the image to the BlueField BMC, a new task is created. Example:
{ "@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/TaskService/Tasks/0", "@odata.type": "#Task.v1_4_3.Task", "Id": "0", "TaskState": "Running" }
InfoBMC firmware update takes ~12 minutes.
To track the progress of the update, use the task
Idreceived in the response above (i.e., 0) in your query and monitor the value of the task’sPercentCompletefield:curl -k -u root:'<password>' -X GET https://<BF-BMC-IP>/redfish/v1/TaskService/Tasks/<task_id> | jq -r ' .PercentComplete'
Where:
<password>– BlueField BMC password<BF-BMC-IP>– BMC IP address<task_id>– task ID of the update process as received in the response under theIdvalueExample output:
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed 100 2123 100 2123 0 0 38600 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 37910 20
See
PercentCompleteis at 20 percent.
Proceed to the next step when the process reaches 100%.
Update eROT Firmware
Trigger a secure firmware update:
curl -k -u root:'<password>' -H "Content-Type: application/octet-stream" -X POST -T <package_path> https://<BF-BMC-IP>/redfish/v1/UpdateService/update
Where:
<password>– BlueField BMC password<package_path>– eROT firmware update package path pointing to eROT*.fwpkgbinary (e.g.cec1736-ecfw-00.02.0127.0000-n02-rel-prod.fwpkg)<BF-BMC-IP>– BMC IP addressAfter initiating the eROT secure update, a new task is created. Example:
{ "@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/TaskService/Tasks/0", "@odata.type": "#Task.v1_4_3.Task", "Id": "0", "TaskState": "Running" }
InfoeROT firmware update takes ~20 seconds.
To track the progress of the update, use the task
Idreceived in the response above (i.e., 0) in your query and monitor the value of the task’sPercentCompletefield:curl -k -u root:'<password>' -X GET https://<BF-BMC-IP>/redfish/v1/TaskService/Tasks/<task_id> | jq -r ' .PercentComplete'
NoteRun this command several times until
PercentCompleteshows 100 before proceeding to other operations.Where:
<password>– BlueField BMC password<BF-BMC-IP>– BMC IP address<task_id>– task ID of the update process as received in the response under theIdvalue
For the firmware of the BMC and CEC to apply and to allow new Redfish APIs which are required for the following steps, a power cycle of the BlueField is required. The BlueField-3 is installed in the host's PCIe slot. To initiate the power cycle sequence for the BlueField, the entire server on which it is installed must be power cycled.
Possible Error Codes During BMC/eROT Upgrade
Fault | Diagnosis and Possible Solution |
Connection to BMC breaks during firmware package transfer |
A new firmware update can be attempted by the Redfish client. |
Connection to BMC breaks during firmware update |
A new firmware update can be attempted by the Redfish client. |
Two firmware update requests are initiated | The Redfish server blocks the second firmware update request and returns the following:
Check the status of the ongoing firmware update by looking at the TaskCollection resource. |
Redfish task hangs |
A new firmware update can be attempted by the Redfish client. |
BMC-EROT communication failure during image transfer | The Redfish task monitoring the firmware update indicates a failure:
The Redfish client may retry the firmware update. |
Firmware update fails | The Redfish task monitoring the firmware update indicates a failure:
The Redfish client may retry the firmware update. |
ERoT failure (not responding) | The Redfish task monitoring the firmware update indicates a failure:
The Redfish client may retry the firmware update. |
Firmware image validation failure | The Redfish task monitoring the firmware update indicates a failure:
The Redfish client might retry the firmware update. |
Power loss before activation command is sent |
A new firmware update can be attempted by the Redfish client. |
Firmware activation failure | The Redfish task monitoring the firmware update indicates a failure:
The Redfish client may retry the firmware update. |
Push to BMC firmware package greater than 200 MB |
|
Upgrade the BlueField firmware components (i.e., ATF, UEFI, NIC-firmware) and the BSP using the BFB image.
Make sure to download the latest DOCA image (BFB file) available from the BlueField Runtime and Driver Downloader.
The included page could not be found.
Verify BlueField BSP, BlueField BMC and BlueField NIC firmware versions are up to date according to the NVIDIA BlueField BMC Software User Manual and NVIDIA BlueField BSP Release Notes.
Use the Redfish
FirmwareInventoryschema over the 1GbE OOB interface to the BlueField's BMC:[redfish_scripts] $ curl -k -u root:<password> -H "Content-Type: application/octet-stream" -X GET https://<BF-BMC-IP>/redfish/v1/UpdateService/FirmwareInventory { "@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/UpdateService/FirmwareInventory", "@odata.type": "#SoftwareInventoryCollection.SoftwareInventoryCollection", "Members": [ { "@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/UpdateService/FirmwareInventory/9f7ec75a_BMC_Firmware" }, { "@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/UpdateService/FirmwareInventory/Bluefield_FW_ERoT" }, { "@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/UpdateService/FirmwareInventory/DPU_ATF" }, { "@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/UpdateService/FirmwareInventory/DPU_BOARD" }, { "@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/UpdateService/FirmwareInventory/DPU_BSP" }, { "@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/UpdateService/FirmwareInventory/DPU_NIC" }, { "@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/UpdateService/FirmwareInventory/DPU_NODE" }, { "@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/UpdateService/FirmwareInventory/DPU_OFED" }, { "@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/UpdateService/FirmwareInventory/DPU_OS" }, { "@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/UpdateService/FirmwareInventory/DPU_SYS_IMAGE" }, { "@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/UpdateService/FirmwareInventory/DPU_UEFI" } ], "Members@odata.count": 11, "Name": "Software Inventory Collection" }
Response example for
DPU_ATF:> curl -k -u root:<password> -H "Content-Type: application/octet-stream" -X GET https://<BF-BMC-IP>/redfish/v1/UpdateService/FirmwareInventory/DPU_ATF { "@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/UpdateService/FirmwareInventory/DPU_ATF", "@odata.type": "#SoftwareInventory.v1_4_0.SoftwareInventory", "Description": "Host image", "Id": "DPU_ATF", "Members@odata.count": 1, "Name": " "Software Inventory", "RelatedItem": [ { "@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/Systems/Bluefield/Bios" } ], "SoftwareId": "", "Status": { "Health": "OK", "HealthRollup": "OK", "State": "OK", }, "Updateable": true, "Version": "v2.2(release):4.0.2-33-gd9f4ad5"
InfoThis request may also be used to query some of the other previously mentioned components (e.g.,
9f7ec75a_BMC_Firmware,Bluefield_FW_ERoT).If the versions are not as expected, upgrade as needed:
Download the latest DOCA (BFB file) versions from the downloader at the bottom of the DOCA product page.
DOCA (BFB) upgrade options (upgrading UEFI, ATF, Arm OS, NIC firmware components):
Recommended—BFB upgrade from remote management controller using Redfish
UpdateServiceschema over 1GbE to BlueField BMC:export token=`curl -k -H
"Content-Type: application/json"-X POST https://<bmc_ip>/login -d '{"username":"root", "password":"<password>"}' | grep token | awk '{print $2;}' | tr -d '"'`For more information on deploying BlueField software from the BMC, refer to the "Deploying BlueField Software Using BFB from BMC" page of the NVIDIA BlueField BSP document.
Get the BlueField's BMC MAC address using the following Redfish command over the 1GbE OOB port to the BlueField BMC:
curl -k -u root:<password> -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -X GET https://<BF-BMC-IP>/redfish/v1/Managers/Bluefield_BMC/EthernetInterfaces/eth0 { "@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/Managers/Bluefield_BMC/EthernetInterfaces/eth0", "@odata.type": "#EthernetInterface.v1_6_0.EthernetInterface", "DHCPv4": { "DHCPEnabled": true, "UseDNSServers": true, "UseDomainName": true, "UseNTPServers": true }, "DHCPv6": { "OperatingMode": "Stateful", "UseDNSServers": true, "UseDomainName": true, "UseNTPServers": true }, "Description": "Management Network Interface", "FQDN": "dpu-bmc", "HostName": "BlueField-bmc", "IPv4Addresses": [ { "Address": "10.237.40.179", "AddressOrigin": "DHCP", "Gateway": "0.0.0.0", "SubnetMask": "255.255.0.0" } ], "IPv4StaticAddresses": [], "IPv6AddressPolicyTable": [], "IPv6Addresses": [ { "Address": "fdfd:fdfd:10:237:966d:aeff:fe17:9f5f", "AddressOrigin": "DHCPv6", "AddressState": null, "PrefixLength": 64 }, { "Address": "fe80::966d:aeff:fe17:9f5f", "AddressOrigin": "LinkLocal", "AddressState": null, "PrefixLength": 64 } ], "IPv6DefaultGateway": "fe80::445b:ed80:5f97:8900", "IPv6StaticAddresses": [], "Id": "eth0", "InterfaceEnabled": true, "LinkStatus": "LinkUp", "MACAddress": "94:6d:ae:17:9f:5f", "MTUSize": 1500, "Name": "Manager Ethernet Interface", "NameServers": [ "fdfd:fdfd:7:77:250:56ff:fe8b:e4f9" ], "SpeedMbps": 0, "StaticNameServers": [], "Status": { "Health": "OK", "HealthRollup": "OK", "State": "Enabled" }, "VLANs": { "@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/Managers/Bluefield_BMC/EthernetInterfaces/eth0/VLANs" } }
Get the BlueField's high-speed port's MAC addresses using the following Redfish command over the 1GbE OOB port to the BlueField BMC:
curl -k -u root:<password> -H "Content-Type: application/octet-stream" -X GET https://<bmc_ip>/redfish/v1/Chassis/Card1/NetworkAdapters/NvidiaNetworkAdapter/NetworkDeviceFunctions/eth0f0 { "@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/Chassis/Card1/NetworkAdapters/NvidiaNetworkAdapter/NetworkDeviceFunctions/eth0f0", "@odata.type": "#NetworkDeviceFunction.v1_9_0.NetworkDeviceFunction", "Ethernet": { "MACAddress": "02:b1:b6:12:39:05", "MTUSize": 1500 }, "Id": "eth0f0", "Links": { "OffloadSystem": { "@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/Systems/Bluefield" }, "PhysicalPortAssignment": { "@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/Chassis/Card1/NetworkAdapters/NvidiaNetworkAdapter/Ports/eth0" } }, "Name": "NetworkDeviceFunction", "NetDevFuncCapabilities": [ "Ethernet" ], "NetDevFuncType": "Ethernet" }
Unless it is explicitly desired for the host to be trusted, make sure to disable the host PCIe RShim to protect the BlueField from potential security threats from the host:
Use Redfish BIOS settings schema over the 1GbE OOB to the BlueField BMC:
curl -k -X PATCH -d '{"Attributes":{"Internal CPU Model": "Restricted"}}' -u root:<password> https://<BF-BMC-IP>/redfish/v1/Systems/<SystemID>/Bios/Settings | python3 -m json.tool
The available BlueField host privilege levels are
RestrictedandPrivileged. The default isPrivileged, where the host has access to BlueField.Change the privilege level to
Restricted.
Changing host privilege level requires BlueField reset for the change to take effect.
For more information on BlueField modes of operation, refer to this page.
To change from DPU mode to NIC mode (or vice versa):
To enable NIC mode:
curl -k -u root:<password> -H 'content-type: application/json' -d '{ "Attributes": { "NicMode": "NicMode" } }' -X PATCH https://<BF-BMC-IP>/redfish/v1/Systems/Bluefield/Bios/Settings
To disable NIC mode:
curl -k -u root:<password> -H 'content-type: application/json' -d '{ "Attributes": { "NicMode": "DpuMode" } }' -X PATCH https://<BF-BMC-IP>/redfish/v1/Systems/Bluefield/Bios/Settings
To check that the BMC recorded the change for the next UEFI reboot to apply it:
curl -k -u root:<password> -H 'content-type: application/json' -X GET https://<BF-BMC-IP>/redfish/v1/Systems/Bluefield/Bios/Settings
NoteReset the BlueField (Arm and NIC) for the mode change to take effect.
To verify that the NIC mode has updated accordingly:
curl -k -u root:<password> -H 'content-type: application/json' -X GET https://<BF-BMC-IP>/redfish/v1/Systems/Bluefield/Bios/
As part of the default settings of the BlueField, UEFI Secure Boot is enabled and requires no special configuration to use it with the bundled Ubuntu OS shipped with the BlueField device. Disabling UEFI Secure Boot may be necessary when running an unsigned Arm OS image, such as a customer OS. Using Redfish Secure Boot schema over 1GbE to BlueField BMC, run:
curl -k -u root:<password> -H "Content-Type: application/octet-stream" -X GET https://<BF-BMC-IP>/redfish/v1/Systems/Bluefield/SecureBoot
{
"@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/Systems/Bluefield/SecureBoot",
"@odata.type": "#SecureBoot.v1_1_0.SecureBoot",
"Description": "The UEFI Secure Boot associated with this system.",
"Id": "SecureBoot",
"Name": "UEFI Secure Boot",
"SecureBootCurrentBoot": "Enabled",
"SecureBootEnable": true,
"SecureBootMode": "SetupMode"
}
curl -k -u root:<BF-BMC-PASSWORD> -X PATCH https://<BF-BMC-IP>/redfish/v1/Systems/Bluefield/SecureBoot -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{"SecureBootEnable": false}'
After running this command, the BlueField Arm OS must be rebooted twice. The first reboot is for the UEFI redfish client to read the request from the BMC and apply it; the second reboot is for the setting to take effect.
From the BlueField BMC using Redfish:
curl -k -u root:<BF-BMC-PASSWORD> -X POST https://<BF-BMC-IP>/redfish/v1/Systems/Bluefield/Actions/ComputerSystem.Reset -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{"ResetType":"ForceRestart"}'
From RShim:
echo 'SW_RESET 1' > /dev/rshim0/misc
From the BlueField Arm OS:
reboot
For more information on user management, review this page.