somatic
Run a somatic variant pipeline workflow.
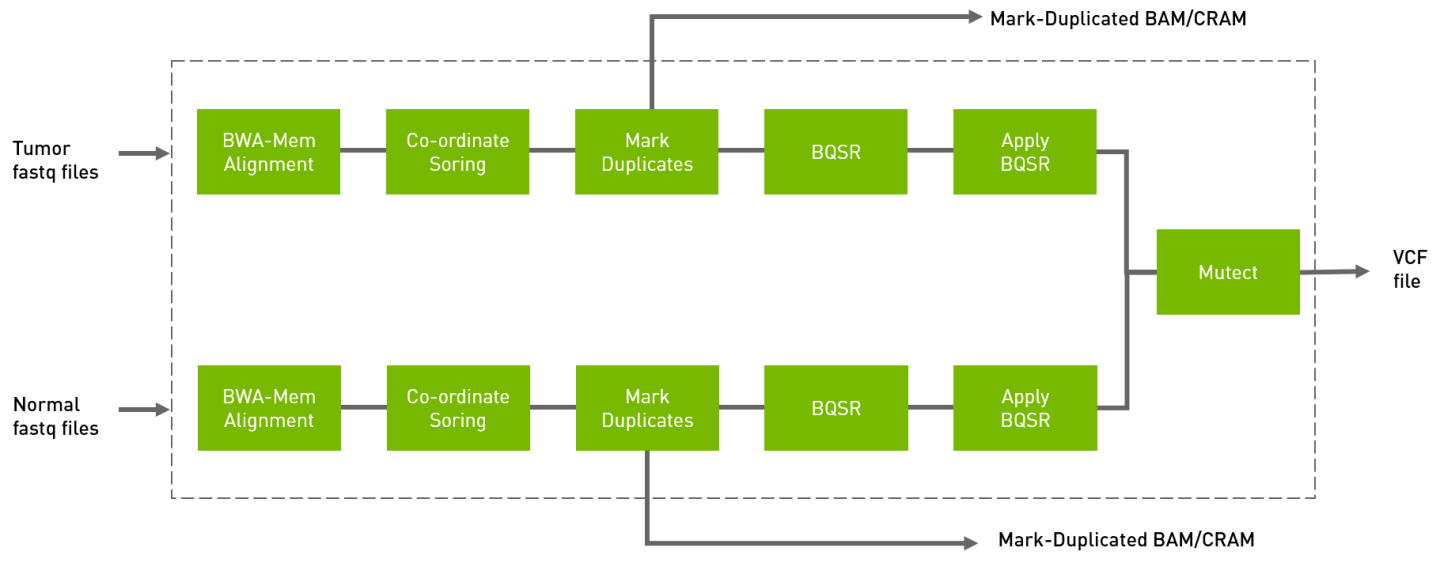
The somatic pipeline processes the tumor FASTQ files, and optionally normal FASTQ files and knownSites files, and generates tumor or tumor/normal analysis. The output is in VCF format.
# The command line below will run tumor-only analysis.
$ pbrun somatic \
--ref Ref/Homo_sapiens_assembly38.fasta \
--in-tumor-fq Data/sample_1.fq.gz Data/sample_2.fq.gz \
--out-vcf output.vcf \
--out-tumor-bam tumor.bam
# The command line below will run tumor-normal analysis.
$ pbrun somatic \
--ref Ref/Homo_sapiens_assembly38.fasta \
--knownSites Ref/Homo_sapiens_assembly38.known_indels.vcf.gz \
--in-tumor-fq Data/sample_1.fq.gz Data/sample_2.fq.gz "@RG\tID:sm_tumor_rg1\tLB:lib1\tPL:bar\tSM:sm_tumor\tPU:sm_tumor_rg1" \
--out-vcf output.vcf \
--out-tumor-bam tumor.bam \
--out-tumor-recal-file recal.txt \
--in-normal-fq normal0.fq.gz normal1.fq.gz "@RG\tID:sm_normal_rg1\tLB:lib1\tPL:bar\tSM:sm_normal\tPU:sm_normal_rg1" \
--out-normal-bam normal.bam
Run the tumor normal somatic pipeline from FASTQ to VCF.
Input/Output file options
- --ref REF
- --in-tumor-fq [IN_TUMOR_FQ [IN_TUMOR_FQ ...]]
- --in-se-tumor-fq [IN_SE_TUMOR_FQ [IN_SE_TUMOR_FQ ...]]
- --in-normal-fq [IN_NORMAL_FQ [IN_NORMAL_FQ ...]]
- --in-se-normal-fq [IN_SE_NORMAL_FQ [IN_SE_NORMAL_FQ ...]]
- --knownSites KNOWNSITES
- --interval-file INTERVAL_FILE
- --out-vcf OUT_VCF
- --out-tumor-bam OUT_TUMOR_BAM
- --out-normal-bam OUT_NORMAL_BAM
- --out-tumor-recal-file OUT_TUMOR_RECAL_FILE
- --out-normal-recal-file OUT_NORMAL_RECAL_FILE
Path to the reference file. (default: None)
Option is required.
Path to the pair-ended FASTQ files followed by optional read group with quotes (Example: "@RGtID:footLB:lib1tPL:bartSM:20"). The files can be in fastq or fastq.gz format. Either all sets of inputs have read group or none should have it and will be automatically added by the pipeline. This option can be repeated multiple times. Example 1: --in-tumor-fq sampleX_1_1.fastq.gz sampleX_1_2.fastq.gz --in-tumor-fq sampleX_2_1.fastq.gz sampleX_2_2.fastq.gz. Example 2: --in-tumor-fq sampleX_1_1.fastq.gz sampleX_1_2.fastq.gz "@RG ID:footLB:lib1tPL:bartSM:sm_tumortPU:unit1" --in-tumor-fq sampleX_2_1.fastq.gz sampleX_2_2.fastq.gz "@RG ID:foo2tLB:lib1tPL:bartSM:sm_tumortPU:unit2". For the same sample, Read Groups should have the same sample name (SM) and a different ID and PU. (default: None)
Path to the single-ended FASTQ file followed by an optional read group with quotes (Example: "@RGtID:footLB:lib1tPL:bartSM:sampletPU:foo"). The file must be in fastq or fastq.gz format. Either all sets of inputs must have a read group or none should have it; if no read group is provided one will be added automatically by the pipeline. This option can be repeated multiple times. Example 1: --in-se-tumor-fq sampleX_1.fastq.gz --in-se-tumor-fq sampleX_2.fastq.gz . Example 2: --in-se-tumor-fq sampleX_1.fastq.gz "@RGtID:footLB:lib1tPL:bartSM:tumortPU:unit1" --in-se-tumor-fq sampleX_2.fastq.gz "@RGtID:foo2tLB:lib1tPL:bartSM:tumortPU:unit2" . For the same sample, Read Groups should have the same sample name (SM) and a different ID and PU. (default: None)
Path to the pair-ended FASTQ files followed by an optional read group with quotes (Example: "@RGtID:footLB:lib1tPL:bartSM:20"). The files must be in fastq or fastq.gz format. Either all sets of inputs must have a read group or none should have it; if no rad group is provided one will be automatically added by the pipeline. This option can be repeated multiple times. Example 1: --in-normal-fq sampleX_1_1.fastq.gz sampleX_1_2.fastq.gz --in-fq sampleX_2_1.fastq.gz sampleX_2_2.fastq.gz . Example 2: --in-normal-fq sampleX_1_1.fastq.gz sampleX_1_2.fastq.gz "@RG ID:footLB:lib1tPL:bartSM:sm_normaltPU:unit1" --in-normal-fq sampleX_2_1.fastq.gz sampleX_2_2.fastq.gz "@RG ID:foo2tLB:lib1tPL:bartSM:sm_normaltPU:unit2". For the same sample, Read Groups should have the same sample name (SM) and a different ID and PU. (default: None)
Path to the single-ended FASTQ file followed by optional read group with quotes (Example: "@RGtID:footLB:lib1tPL:bartSM:sampletPU:foo"). The file must be in fastq or fastq.gz format. Either all sets of inputs must have a read group or none should have it; if absent it will be added automatically by the pipeline. This option can be repeated multiple times. Example 1: --in-se-normal-fq sampleX_1.fastq.gz --in-se-normal-fq sampleX_2.fastq.gz . Example 2: --in-se-normal-fq sampleX_1.fastq.gz "@RGtID:footLB:lib1tPL:bartSM:normaltPU:unit1" --in-se-normal-fq sampleX_2.fastq.gz "@RGtID:foo2tLB:lib1tPL:bartSM:normaltPU:unit2" . For the same sample, Read Groups should have the same sample name (SM) and a different ID and PU. (default: None)
Path to a known indels file. The file must be in vcf.gz format. This option can be used multiple times. (default: None)
Path to an interval file in one of these formats: Picard-style (.interval_list or .picard), GATK-style (.list or .intervals), or BED file (.bed). This option can be used multiple times. (default: None)
Path of VCF file after Variant Calling. (default: None)
Option is required.
Path of BAM file for tumor reads. (default: None)
Option is required.
Path of BAM file for normal reads. (default: None)
Path of the report file after Base Quality Score Recalibration for tumor sample. (default: None)
Path of the report file after Base Quality Score Recalibration for normal sample. (default: None)
Tool Options:
- -L INTERVAL, --interval INTERVAL
- --bwa-options BWA_OPTIONS
- --no-warnings
- --no-markdups
- --fix-mate
- --markdups-assume-sortorder-queryname
- --markdups-picard-version-2182
- --optical-duplicate-pixel-distance OPTICAL_DUPLICATE_PIXEL_DISTANCE
- -ip INTERVAL_PADDING, --interval-padding INTERVAL_PADDING
- --ploidy PLOIDY
- --max-mnp-distance MAX_MNP_DISTANCE
- --mutectcaller-options MUTECTCALLER_OPTIONS
- --tumor-read-group-sm TUMOR_READ_GROUP_SM
- --tumor-read-group-lb TUMOR_READ_GROUP_LB
- --tumor-read-group-pl TUMOR_READ_GROUP_PL
- --tumor-read-group-id-prefix TUMOR_READ_GROUP_ID_PREFIX
- --normal-read-group-sm NORMAL_READ_GROUP_SM
- --normal-read-group-lb NORMAL_READ_GROUP_LB
- --normal-read-group-pl NORMAL_READ_GROUP_PL
- --normal-read-group-id-prefix NORMAL_READ_GROUP_ID_PREFIX
Interval within which to call bqsr from the input reads. All intervals will have a padding of 100 to get read records, and overlapping intervals will be combined. Interval files should be passed using the --interval-file option. This option can be used multiple times (e.g. "-L chr1 -L chr2:10000 -L chr3:20000+ -L chr4:10000-20000") (default: None)
Pass supported bwa mem options as one string. The current original bwa mem supported options are -M, -Y, -T (e.g. --bwa-options="-M -Y") (default: None)
Suppress warning messages about system thread and memory usage. (default: None)
Do not perform the Mark Duplicates step. Return BAM after sorting. (default: None)
Add mate cigar (MC) and mate quality (MQ) tags to the output file. (default: None)
Assume the reads are sorted by queryname for Marking Duplicates. This will mark secondary, supplementary, and unmapped reads as duplicates as well. This flag will not impact variant calling while increasing processing times. (default: None)
Assume marking duplicates to be similar to Picard version 2.18.2. (default: None)
The maximum offset between two duplicate clusters in order to consider them optical duplicates. Ignored if --out-duplicate-metrics is not passed. (default: None)
Amount of padding (in base pairs) to add to each interval you are including. (default: None)
Ploidy assumed for the BAM file. Currently only haploid (ploidy 1) and diploid (ploidy 2) are supported. (default: 2)
Two or more phased substitutions separated by this distance or less are merged into MNPs. (default: 1)
Pass supported mutectcaller options as one string. Currently supported original mutectcaller options: -pcr-indel-model <NONE, HOSTILE, AGGRESSIVE, CONSERVATIVE> (e.g. --mutectcaller-options="-pcr-indel-model HOSTILE"). (default: None)
SM tag for read groups for tumor sample. (default: None)
LB tag for read groups for tumor sample. (default: None)
PL tag for read groups for tumor sample. (default: None)
Prefix for ID and PU tag for read groups for tumor sample. This prefix will be used for all pair of tumor FASTQ files in this run. The ID and PU tag will consist of this prefix and an identifier which will be unique for a pair of FASTQ files. (default: None)
SM tag for read groups for normal sample. (default: None)
LB tag for read groups for normal sample. (default: None)
PL tag for read groups for normal sample. (default: None)
Prefix for ID and PU tag for read groups for normal sample. This prefix will be used for all pair of normal FASTQ files in this run. The ID and PU tag will consist of this prefix and an identifier which will be unique for a pair of FASTQ files. (default: None)
Common options:
- --logfile LOGFILE
- --tmp-dir TMP_DIR
- --with-petagene-dir WITH_PETAGENE_DIR
- --keep-tmp
- --license-file LICENSE_FILE
- --no-seccomp-override
- --version
Path to the log file. If not specified, messages will only be written to the standard error output. (default: None)
Full path to the directory where temporary files will be stored.
Full path to the PetaGene installation directory. By default, this should have been installed at /opt/petagene. Use of this option also requires that the PetaLink library has been preloaded by setting the LD_PRELOAD environment variable. Optionally set the PETASUITE_REFPATH and PGCLOUD_CREDPATH environment variables that are used for data and credentials (default: None)
Do not delete the directory storing temporary files after completion.
Path to license file license.bin if not in the installation directory.
Do not override seccomp options for docker (default: None).
View compatible software versions.
GPU options:
- --num-gpus NUM_GPUS
- --gpu-devices GPU_DEVICES
Number of GPUs to use for a run. GPUs 0..(NUM_GPUS-1) will be used.
GPU devices to use for a run. By default, all GPU devices will be used.
To use specific GPU devices, enter a comma-separated list of GPU device
numbers. Possible device numbers can be found by examining the output of
the nvidia-smi command. For example, using --gpu-devices 0,1
would only use the first two GPUs.