Virtio-net
The guidelines are for Virtio-net users and customers. It is recommended to read the user manual first.
Command | Description |
| Check status of virtio-net-controller service |
| Version of virtio-net-controller |
| Lis virtnet command line help manual |
| List all virtnet device and general information |
| Query detailed information of device x |
To check controller log. Run from DPU side:
$ journalctl -u virtio-net-controller -f -n 400
This command shows 400 lines of the latest log, adjust the number of lines as needed.
BlueField-3 Jumbo MTU Does Not Work
Problem
Ping failed with packet size greater than 1500/4000 after configuring jumbo MTU.
Solution
Jumbo MTU is supported starting from the following kernel version:
Release | |
Upstream | VM kernel: 4.18.0-193.el8.x86_64 VM Linux version supports big MTU after 4.11. |
Ubuntu | DOCA_2.5.0_BSP_4.5.0_Ubuntu_22.04 |
Virtnet | v1.7 or v1.6.26 |
The following steps configure jumbo MTU:
Change the MTU of uplink representor (or bond) from the BlueField Arm OS:
# echo
9216> /sys/bus/pci/devices/0000:03:00.0/net/p0/mtuRestart virtio-net-controller from the BlueField Arm OS:
# systemctl restart virtio-net-controlle
Change the corresponding device MTU on BlueField Arm OS. For example, for the first VF on the first PF, run:
# virtnet modify -p
0-v0device -t9216Reload the virtio driver from the guest OS:
# modprobe -rv virtio-net && modprobe -v virtio-net
Verify the VQs' MTU configuration is correct on BlueField Arm OS:
# virtnet query -p
0-v0--dbg_stats | grep jumbo_mtu"jumbo_mtu":1"jumbo_mtu":1Change the MTU of the virtio-net interface from the guest OS:
# echo
9216> /sys/bus/pci/devices/0000:af:00.2/virtio0/net/enp175s0f2/mtu
Virtio-net-controller.service Fails to Start
Problem
The problem can be verified using the following commands:
# virtnet list
ERR: Can't connect to virtnet controller: [Errno 111] Connection refused
Check 'systemctl status virtio-net-controller'
Or controller is not ready to accept commands
# systemctl status virtio-net-controller
virtio-net-controller.service - Nvidia VirtIO Net Controller Daemon
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/virtio-net-controller.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: inactive (dead) since Fri 2023-10-27 17:46:59 CDT; 2min 26s ago
Docs: file:/opt/mellanox/mlnx_virtnet/README.md
Process: 29652 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/virtio_net_manager (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 29652 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Solution
The problem may happen due to the following reasons.
Virtio-net Not Enabled
Check if mlxconfig has
VIRTIO_NET_EMULATION_ENABLEenabled:# mlxconfig -d
03:00.0-e q | grep -i VIRTIO_NET_EMULATION_ENABLE * VIRTIO_NET_EMULATION_ENABLE False(0) True(1) True(1)Both 2 and 3 columns should appear as
true.If they are not, perform the following from the BlueField Arm side:
# mlxconfig -d
03:00.0s VIRTIO_NET_EMULATION_ENABLE=1Perform a BlueField system-level reset as documented in the BlueField software documentation.
Not Enough SFs Reserved
This can happen when more VIRTIO_NET_EMULATION_NUM_PF are reserved than PF_TOTAL_SF, as each virtio-net PF/VF requires a corresponding SF created:
# mlxconfig -d 03:00.0 -e q | grep -iE 'PF_TOTAL_SF|VIRTIO_NET_EMULATION_NUM_PF'
* VIRTIO_NET_EMULATION_NUM_PF 0 4 4
* PF_TOTAL_SF 0 8 8
By default, the BlueField creates an SF for each PF. Take this into consideration when reserving PF_TOTAL_SF.
Function Not Implemented Error when Creating VF
Problem
Creating a virtio-net VF returns an error from the command line:
# echo 3 > /sys/bus/pci/drivers/virtio-pci/0000:41:00.2/sriov_numvfs
write error: Function not implemented
The host-side dmesg shows the following:
[ 301.204661] virtio-pci 0000:41:00.2: Driver doesn't support SRIOV configuration via sysfs
Solution
Virtio SR-IOV is only supported starting from the following kernel version:
Release | |
Upstream | 4.18 with commit cfecc2918d2b3 |
Ubuntu | Ubuntu-hwe-4.18.0-9.10_18.04.1 |
CentOS | 3.10.0-957.el7 / 7.6.1810 |
Guest OS Stuck when Creating VF
Problem
The following command from the hypervisor hangs:
# echo 100 > /sys/bus/pci/drivers/virtio-pci/0000:89:00.4/sriov_numvfs
Solution
This can happen when more VIRTIO_NET_EMULATION_NUM_PF/VIRTIO_NET_EMULATION_NUM_VF are reserved than PF_TOTAL_SF (VIRTIO_NET_EMULATION_NUM_PF + VIRTIO_NET_EMULATION_NUM_VF > PF_TOTAL_SF) as each virtio-net PF/VF requires a corresponding SF created. Example:
# mlxconfig -d 03:00.0 -e q | grep -iE 'PF_TOTAL_SF|VIRTIO_NET_EMULATION_NUM_PF|VIRTIO_NET_EMULATION_NUM_VF'
* VIRTIO_NET_EMULATION_NUM_VF 0 126 126
* VIRTIO_NET_EMULATION_NUM_PF 0 4 4
* PF_TOTAL_SF 0 508 508
By default, BlueField creates an SF for each PF. Take this into consideration when reserving PF_TOTAL_SF.
BlueField supports a limited number of SFs. The SF reserved on the BlueField Arm side and host side are not shared. Make sure to remove the SFs reserved on the host side when reserving a large number on the BlueField Arm side.
Hotplug Device Does Not Show Correctly in Guest OS
Problem
After creating a hotplug device from the BlueField side, probing virtio drivers does not create the virtio-net device correctly.
Solution
The problem may happen due to the following reasons.
BAR 0
Possible failure on BAR 0. check dmesg from guest OS for corresponding hotplug BDF:
[10.874845] pci 0000:87:00.1: BAR 0: failed to assign [mem size 0x00100000]
In this example, the hotplug PCIe BDF is 87:00.1. This value can be retrieved using "lspci | grep -i virtio" from the guest OS.
This can be normally resolved by adding
"pci=realloc" in the Linux command line (grub).
BAR 14/15
Possible failure on other PCIe BAR. Check the dmesg from the guest OS for the corresponding hotplug BDF:
[ 2893.484281] pcieport 0000:10:01.0: bridge window [mem 0x00100000-0x000fffff] to [bus 12] add_size 200000 add_align 100000
[ 2893.484285] pcieport 0000:10:01.0: BAR 14: no space for [mem size 0x00200000]
[ 2893.484287] pcieport 0000:10:01.0: BAR 14: failed to assign [mem size 0x00200000]
[ 2893.484289] pcieport 0000:10:01.0: BAR 14: no space for [mem size 0x00200000]
[ 2893.484290] pcieport 0000:10:01.0: BAR 14: failed to assign [mem size 0x00200000]
In this example, the hotplug PCIe BDF is 10:01.0. This value can be retrieved using "lspci | grep -i virtio" from the guest OS.
This is mostly due to there being insufficient BAR resources. Try to reduce the PF BAR size by performing the following from the BlueField side:
# mlxconfig -d
03:00.0s PF_LOG_BAR_SIZE=0This can also be caused by the BIOS provider not reserving enough memory. Check the guest OS's dmesg for similar messages for the PCIe bus of the BlueField device:
[
3.979061] pci_bus0000:a0: root bus resource [mem0x41c0800000-0x41c10fffffwindow] (9M) [3.979062] pci_bus0000:a0: root bus resource [bus a0-bf] [4.017770] pci0000:a4:00.0: bridge window [mem0x41c0800000-0x41c0ffffff64bit pref] (8M) [4.018243] pci0000:a4:00.0: BAR15: no spacefor[mem size0x0580000064bit pref] (88M) [4.018245] pci0000:a4:00.0: BAR15: failed to assign [mem size0x0580000064bit pref]On the host, the prefetchable memory limit of the root bus (
a0) is only 9 M. This means that all the devices under this bus (including BlueField) can only be allocated 9M prefetchable memory in total.The BAR 15 is the total prefetchable memory limit on the bridge (
a4) of the device. The PCI bridge window of the BlueField for prefetchable memory is 8M, but the bridge requires 88M for its child device ( BlueField ). A fter several attempts, the PCIe bridge did not find sufficient IO memory to allocate for BlueField BARs. This can be solved by contacting the BIOS provider to provide enough memory to the PCI root.
Rescan
If the the hotplug operation from the BlueField Arm side is performed before the guest OS is up, and the virtio device is not found by the command "lspci | grep -i virtio". Try to rescan from guest OS:
# echo 1>/sys/bus/pci/rescan
No Hotplug from BIOS
The server BIOS may not support hotplug device. This can be confirmed by looking at guest OS dmesg:
[8.209406] acpi PNP0A08:03: _OSC: platform does not support [PCIeHotplug PME]
Try to enable hotplug from the BIOS:
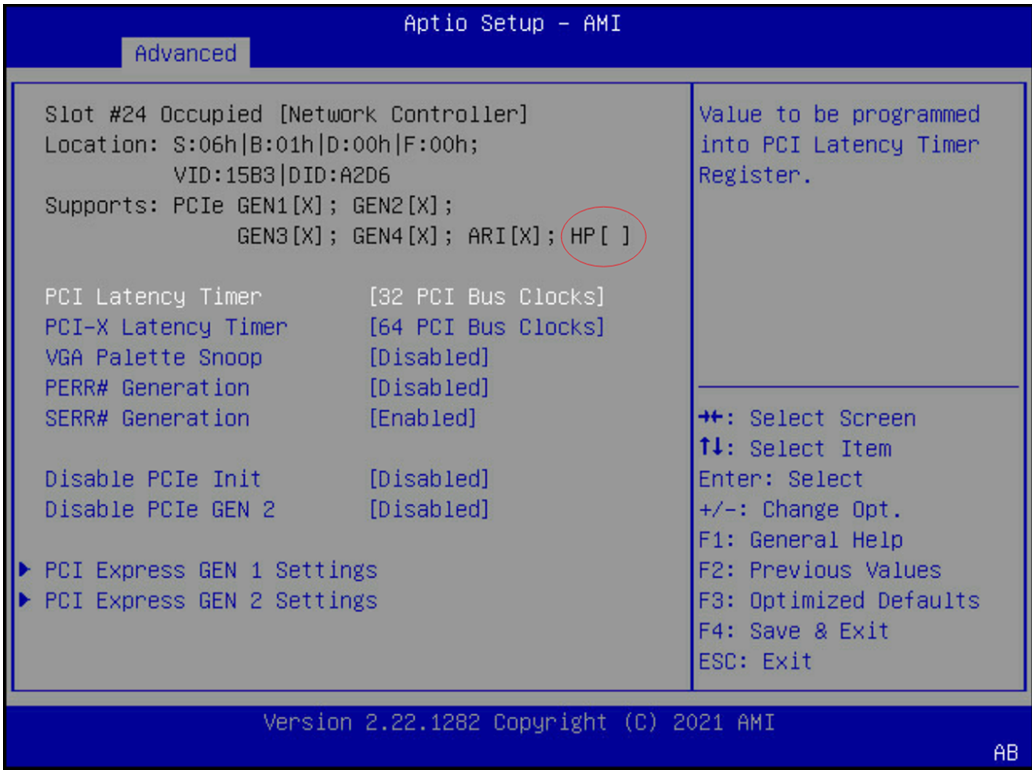
Force Hotplug
Guest OS may be running a kernel older than 4.19, the virtio device is not found by "lspci | grep -i virtio". Add the entry pciehp.pciehp_force=1 to the grub command line.
Hot-unplug Devices with Heavy Self-traffic, Guest OS Gets Call Trace
Problem
When the guest OS is running heavy traffic (e.g., iperf/iperf3) on a hotplug virtio-net device, unplugging those devices from BlueField side at the same time may results in the guest OS hanging.
The guest OS would print a call traffic similar like the following:
[ 203.886218] CPU: 35 PID: 3077 Comm: iperf3 Not tainted 6.6.0 #1
[ 203.886222] Hardware name: Dell Inc. PowerEdge R7525/0590KW, BIOS 2.2.5 04/08/2021
[ 203.886224] RIP: 0010:free_old_xmit_skbs+0x5d/0xf0 [virtio_net]
[ 203.886247] Code: 41 f6 c4 01 75 75 66 90 44 89 fe 4c 89 e7 45 03 6c 24 70 e8 65 1a 0a f0 83 c3 01 49 8b 3e 48 8d 75 cc e8 26 21 d1 ef 49 89 c4 <48> 85 c0 75 d1 85 db 74 0e 4d 01 ae 80 02 00 00 49 01 9e 78 02 00
[ 203.886249] RSP: 0018:ffffac62cb837678 EFLAGS: 00000246
[ 203.886253] RAX: 0000000000000000 RBX: 0000000000000000 RCX: ffff9a35e7dbc000
[ 203.886255] RDX: 0000000000000000 RSI: ffffac62cb83767c RDI: ffff9a2e5e7d8900
[ 203.886257] RBP: ffffac62cb8376b0 R08: 0000000000000000 R09: 000000000003b2f0
[ 203.886259] R10: ffff9a2e4a570b00 R11: 000000000000000c R12: 0000000000000000
[ 203.886261] R13: 0000000000000000 R14: ffff9a2e62a48800 R15: 0000000000000000
[ 203.886263] FS: 00007f8444643400(0000) GS:ffff9a359f2c0000(0000) knlGS:0000000000000000
[ 203.886266] CS: 0010 DS: 0000 ES: 0000 CR0: 0000000080050033
[ 203.886268] CR2: 000056277998d028 CR3: 0000000127976000 CR4: 0000000000350ee0
[ 203.886270] Call Trace:
[ 203.886274] <NMI>
[ 203.886277] ? show_regs+0x6e/0x80
[ 203.886289] ? nmi_cpu_backtrace+0xb1/0x120
[ 203.886298] ? nmi_cpu_backtrace_handler+0x15/0x20
[ 203.886305] ? nmi_handle+0x6b/0x180
[ 203.886310] ? default_do_nmi+0x45/0x120
[ 203.886316] ? exc_nmi+0x142/0x1c0
[ 203.886319] ? end_repeat_nmi+0x16/0x67
[ 203.886328] ? free_old_xmit_skbs+0x5d/0xf0 [virtio_net]
[ 203.886334] ? free_old_xmit_skbs+0x5d/0xf0 [virtio_net]
[ 203.886341] ? free_old_xmit_skbs+0x5d/0xf0 [virtio_net]
[ 203.886347] </NMI>
[ 203.886348] <TASK>
[ 203.886349] ? free_old_xmit_skbs+0x8c/0xf0 [virtio_net]
[ 203.886356] start_xmit+0x149/0x500 [virtio_net]
[ 203.886364] dev_hard_start_xmit+0x95/0x1e0
[ 203.886370] ? validate_xmit_skb_list+0x51/0x80
[ 203.886374] sch_direct_xmit+0x10c/0x3a0
[ 203.886381] __dev_queue_xmit+0xa47/0xda0
[ 203.886387] ip_finish_output2+0x2ef/0x5a0
[ 203.886393] ? srso_return_thunk+0x5/0x10
[ 203.886400] ? nf_conntrack_in+0xeb/0x6c0 [nf_conntrack]
[ 203.886428] __ip_finish_output+0xb7/0x190
[ 203.886433] ip_finish_output+0x32/0x100
[ 203.886437] ip_output+0x63/0xf0
[ 203.886441] ? __pfx_ip_finish_output+0x10/0x10
[ 203.886446] ip_local_out+0x62/0x70
[ 203.886449] __ip_queue_xmit+0x18e/0x4b0
[ 203.886454] ip_queue_xmit+0x19/0x20
[ 203.886456] __tcp_transmit_skb+0xb2d/0xcd0
[ 203.886462] ? srso_return_thunk+0x5/0x10
[ 203.886469] tcp_write_xmit+0x565/0x1620
[ 203.886474] tcp_push_one+0x40/0x50
[ 203.886476] tcp_sendmsg_locked+0x350/0xee0
[ 203.886481] ? tcp_current_mss+0x75/0xd0
[ 203.886488] tcp_sendmsg+0x31/0x50
[ 203.886491] inet_sendmsg+0x47/0x80
[ 203.886498] sock_write_iter+0x163/0x190
[ 203.886507] vfs_write+0x342/0x3f0
[ 203.886517] ksys_write+0xb9/0xf0
[ 203.886520] __x64_sys_write+0x1d/0x30
[ 203.886522] do_syscall_64+0x60/0x90
[ 203.886528] ? srso_return_thunk+0x5/0x10
[ 203.886531] ? ksys_write+0xb9/0xf0
[ 203.886532] ? srso_return_thunk+0x5/0x10
[ 203.886535] ? exit_to_user_mode_prepare+0x35/0x180
[ 203.886542] ? srso_return_thunk+0x5/0x10
[ 203.886544] ? syscall_exit_to_user_mode+0x38/0x50
[ 203.886549] ? __x64_sys_write+0x1d/0x30
[ 203.886551] ? srso_return_thunk+0x5/0x10
[ 203.886553] ? do_syscall_64+0x6d/0x90
[ 203.886556] ? srso_return_thunk+0x5/0x10
[ 203.886558] ? syscall_exit_to_user_mode+0x38/0x50
[ 203.886561] ? srso_return_thunk+0x5/0x10
[ 203.886564] ? do_syscall_64+0x6d/0x90
[ 203.886566] ? __x64_sys_write+0x1d/0x30
[ 203.886568] ? srso_return_thunk+0x5/0x10
[ 203.886570] ? do_syscall_64+0x6d/0x90
[ 203.886572] ? srso_return_thunk+0x5/0x10
[ 203.886575] ? sysvec_apic_timer_interrupt+0x52/0x90
[ 203.886578] entry_SYSCALL_64_after_hwframe+0x6e/0xd8
Root Cause
From kernel 5.14, the following patch introduced a while loop for the virtio-net TX path which may enter infinite when VQ is broken (e.g., device is removed) under heavy traffic:
commit a7766ef18b33674fa164e2e2916cef16d4e17f43
Author: Michael S. Tsirkin <mst@redhat.com>
Date: Tue Apr 13 01:30:45 2021 -0400
virtio_net: disable cb aggressively
There are currently two cases where we poll TX vq not in response to a
callback: start xmit and rx napi. We currently do this with callbacks
enabled which can cause extra interrupts from the card. Used not to be
a big issue as we run with interrupts disabled but that is no longer the
case, and in some cases the rate of spurious interrupts is so high
linux detects this and actually kills the interrupt.
Fix up by disabling the callbacks before polling the tx vq.
Signed-off-by: Michael S. Tsirkin <mst@redhat.com>
Solution
Currently, there is no official fix from the kernel side, some The following workarounds may be employed:
Use kernel without the offending kernel patches
Stop heavy traffic while performing unplug
Ubuntu Guest OS Stuck with Kernel 5.15.0-88/89-generic
Problem
When probing the virtio-pci and virtio-net kernel modules while running Ubuntu 22.04 with kernel 5.15.0-88/89-generic with any virtio function (i.e, PF or VF), the guest OS hangs and prints call traces as follows:
[ 2052.109566] CPU: 0 PID: 1183 Comm: systemd-udevd Tainted: P O L 5.15.0-88-generic #98-Ubuntu
[ 2052.109568] Hardware name: Red Hat KVM, BIOS 1.15.0-2.module+el8.6.0+14757+c25ee005 04/01/2014
[ 2052.109570] RIP: 0010:virtqueue_is_broken+0x9/0x20
[ 2052.109579] RSP: 0018:ffffc206423a79c0 EFLAGS: 00000246
[ 2052.109581] RAX: 0000000000000000 RBX: ffff9e8980bfa980 RCX: 0000000000000a20
[ 2052.109582] RDX: 0000000000000000 RSI: ffffc206423a79cc RDI: ffff9e89847b9000
[ 2052.109583] RBP: ffffc206423a7a60 R08: 0000000000000000 R09: 0000000000000003
[ 2052.109584] R10: 0000000000000003 R11: 0000000000000002 R12: ffffc206423a79f0
[ 2052.109585] R13: 0000000000000002 R14: 0000000000000004 R15: ffff9e8984667400
[ 2052.109586] FS: 00007f3e295388c0(0000) GS:ffff9e89bbc00000(0000) knlGS:0000000000000000
[ 2052.109588] CS: 0010 DS: 0000 ES: 0000 CR0: 0000000080050033
[ 2052.109590] CR2: 0000555613432be0 CR3: 0000000116af0002 CR4: 0000000000170ef0
[ 2052.109593] Call Trace:
[ 2052.109595] <IRQ>
[ 2052.109598] ? show_trace_log_lvl+0x1d6/0x2ea
[ 2052.109605] ? show_trace_log_lvl+0x1d6/0x2ea
[ 2052.109609] ? _virtnet_set_queues+0xbb/0x100 [virtio_net]
[ 2052.109615] ? show_regs.part.0+0x23/0x29
[ 2052.109618] ? show_regs.cold+0x8/0xd
[ 2052.109621] ? watchdog_timer_fn+0x1be/0x220
[ 2052.109625] ? lockup_detector_update_enable+0x60/0x60
[ 2052.109627] ? __hrtimer_run_queues+0x107/0x230
[ 2052.109631] ? kvm_clock_get_cycles+0x11/0x20
[ 2052.109637] ? hrtimer_interrupt+0x101/0x220
[ 2052.109640] ? __sysvec_apic_timer_interrupt+0x61/0xe0
[ 2052.109644] ? sysvec_apic_timer_interrupt+0x7b/0x90
[ 2052.109650] </IRQ>
[ 2052.109650] <TASK>
[ 2052.109651] ? asm_sysvec_apic_timer_interrupt+0x1b/0x20
[ 2052.109655] ? virtqueue_is_broken+0x9/0x20
[ 2052.109656] ? virtnet_send_command+0x105/0x170 [virtio_net]
[ 2052.109660] _virtnet_set_queues+0xbb/0x100 [virtio_net]
[ 2052.109670] virtnet_probe+0x4ca/0xa10 [virtio_net]
[ 2052.109674] virtio_dev_probe+0x1ae/0x260
[ 2052.109676] really_probe+0x222/0x420
[ 2052.109679] __driver_probe_device+0xe8/0x140
[ 2052.109681] driver_probe_device+0x23/0xc0
[ 2052.109683] __driver_attach+0xf7/0x1f0
[ 2052.109685] ? __device_attach_driver+0x140/0x140
[ 2052.109687] bus_for_each_dev+0x7f/0xd0
[ 2052.109691] driver_attach+0x1e/0x30
[ 2052.109693] bus_add_driver+0x148/0x220
[ 2052.109695] driver_register+0x95/0x100
[ 2052.109697] register_virtio_driver+0x20/0x40
[ 2052.109698] virtio_net_driver_init+0x74/0x1000 [virtio_net]
[ 2052.109702] ? 0xffffffffc0d6f000
[ 2052.109704] do_one_initcall+0x49/0x1e0
[ 2052.109709] ? kmem_cache_alloc_trace+0x19e/0x2e0
[ 2052.109713] do_init_module+0x52/0x260
[ 2052.109716] load_module+0xb2b/0xbc0
[ 2052.109718] __do_sys_finit_module+0xbf/0x120
[ 2052.109721] __x64_sys_finit_module+0x18/0x20
[ 2052.109722] do_syscall_64+0x5c/0xc0
[ 2052.109725] ? do_syscall_64+0x69/0xc0
[ 2052.109726] ? syscall_exit_to_user_mode+0x35/0x50
[ 2052.109729] ? __x64_sys_newfstatat+0x1c/0x30
[ 2052.109733] ? do_syscall_64+0x69/0xc0
[ 2052.109735] entry_SYSCALL_64_after_hwframe+0x62/0xcc
Solution
There is a bug in upstream version v6.5-rc4, which is fixed in v6.5-rc7. Canonical backported the problematic patch to Ubuntu 5.15.0-88/89.generic, which triggers this Virtio-net deadlock issue:
commit 51b813176f098ff61bd2833f627f5319ead098a5
Author: Jason Wang <jasowang@redhat.com>
Date: Wed Aug 9 23:12:56 2023 -0400
virtio-net: set queues after driver_ok
Commit 25266128fe16 ("virtio-net: fix race between set queues and
probe") tries to fix the race between set queues and probe by calling
_virtnet_set_queues() before DRIVER_OK is set. This violates virtio
spec. Fixing this by setting queues after virtio_device_ready().
Note that rtnl needs to be held for userspace requests to change the
number of queues. So we are serialized in this way.
Fixes: 25266128fe16 ("virtio-net: fix race between set queues and probe")
Reported-by: Dragos Tatulea <dtatulea@nvidia.com>
Acked-by: Michael S. Tsirkin <mst@redhat.com>
Signed-off-by: Jason Wang <jasowang@redhat.com>
Signed-off-by: David S. Miller <davem@davemloft.net>
Switch default kernel back to another version (e.g., 5.15.0-79-generic).
From 5.15.0-90-generic, the Ubuntu official kernel has the issue fixed.
There are multiple ways to switch the default kernel. The following is only one example:
Users must have root permission before proceeding.
Open
/etc/default/gruband changeGRUB_DEFAULTas follows:GRUB_DEFAULT=saved
Save file.
Run the following to get the number of the kernel you want
# grep
"menuentry 'Ubuntu,"/boot/grub/grub.cfgInfoNumbering starts from 0 (i.e., first entry is 0)
Run the following to set the default kernel:
# grub-set-
defaultnum_from_last_stepReboot.