Introduction
The NVIDIA® BlueField® DPU is a data center infrastructure on a chip that combines a high-speed networking interface with powerful, software-programmable Arm cores, enabling breakthrough networking, storage, and security performance. The BlueField DPU offloads, accelerates, and isolates a broad range of software-defined infrastructure services which traditionally ran on the host's CPU, overcoming performance and scalability bottlenecks, and eliminating security threats in modern data centers.
BlueField DPUs transform traditional computing environments to secure and accelerated data centers, allowing organizations to efficiently run data-driven, cloud-native applications alongside legacy applications. By decoupling the data center infrastructure from business applications, BlueField DPUs enhance data center security, streamline operations, and reduce total cost of ownership.
The BlueField DPU contains a programmable CPU based on Arm cores, a state-of-the-art NVIDIA® ConnectX®, and an enhanced set of security, storage, and networking accelerators that can be configured to perform multiple software-defined, hardware-accelerated functions. With a BlueField DPU, a software-defined network, and/or software-defined storage solution can be deployed and offloaded from the main host CPU in the server. Similarly, other dedicated services (e.g., distributed firewall, deep packet inspection, malware detection) can run on the BlueField DPU and can be accelerated with zero CPU overheads.
The BlueField DPU resembles a server embedded within the server itself, creating a secure environment where an infrastructure stack can operate independently from the primary (i.e., host) CPU, effectively isolating it from the untrusted tenant applications.
This is the recommended mode for utilizing the DPU in which software running on the host CPU has no direct access to the DPU. For instance, in a scenario where a cloud service provider is responsible for managing both networking and storage in a cloud infrastructure stack, it can establish an isolated environment within the DPU.
The NVIDIA® BlueField® SuperNIC is the world’s most advanced network accelerator, designed for supercharging hyperscale generative AI workloads. It delivers deterministic, isolated performance, with secure cloud multi-tenancy. Featured on the Spectrum-X networking platform, NVIDIA integrates BlueField-3 SuperNICs across its accelerated systems to enable peak AI workload efficiency. Powered by the NVIDIA DOCA software, the SuperNIC offers up to 400Gb/s connectivity between GPU servers, with features like RoCE adaptive routing, direct data placement (DDP), and programmable congestion control. With its unique HHHL form factor and low-power platform, the BlueField-3 SuperNIC fits most enterprise-class servers.
To read more about the BlueField-3 features and benefits, refer to this page.
To read more about the BlueField-2 features and benefits, refer to this page.
The following subsections detail the available modes of operation.
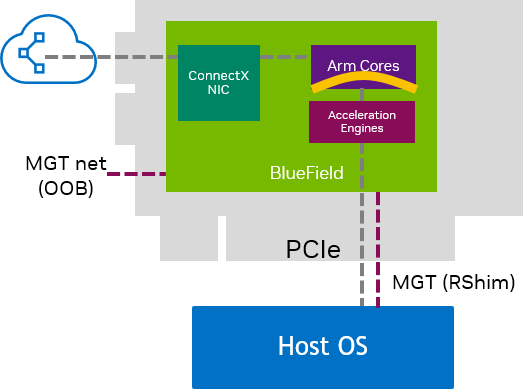
DPU Mode
Default mode for BlueField DPU
Host-trusted mode
Arm OS has embedded function (ECPF) ownership and controls the NIC's resources and data path
BlueField controls and enforces network policies with the option of enforcing storage and security policies
BlueField is the trusted function managed by the data center and host administrator
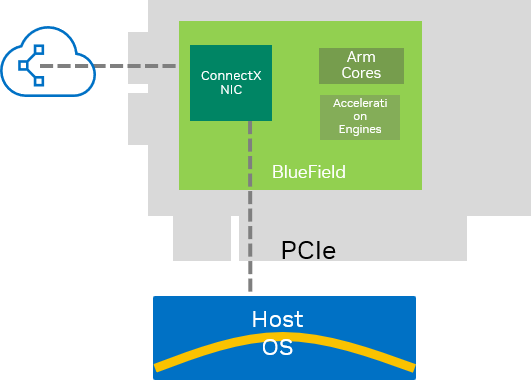
NIC Mode
Default mode for BlueField SuperNIC
BlueField behaves like a network adapter (NIC)
Host is in full control of NIC functionality
InfoAll NIC offloads (as in NVIDIA® ConnectX® offloads) are enabled and available for the host
BlueField Arm cores are halted and Arm OS stops running
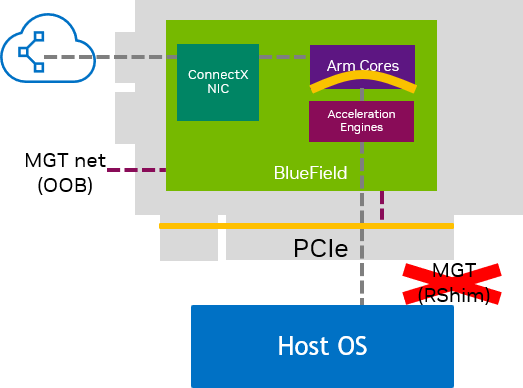
Zero-trust Mode
Arm OS has embedded function (ECPF) ownership and controls the NIC's resources and data path
BlueField controls and enforces network policies with the option of enforcing storage and security policies
Host is isolated; management from the host via PCIe edge connector is blocked
Desired, safest state
By default, BlueField boots in trusted mode. Therefore, users must change the mode to zero-trust mode.