Installing Tools on Grace Hopper MGX System
This chapter describes how to install the required kernel, driver, and tools on the host. This is a one-time installation and can be skipped if the system has been configured already.
In the following sequence of steps, the target host is Supermicro Grace Hopper MGX System.
Depending on the release, tools that are installed in this section may need to be upgraded in the Installing and Upgrading cuBB SDK section.
After everything is installed and updated, refer to the cuBB Quick Start Guide for how to use the cuBB SDK.
Supermicro Server SKU: ARS-111GL-NHR (Config 2)

Top View:

Back View:

Connect a USB to Ethernet dongle to the back USB port for host internet access.
To run end-to-end test with O-RU, the BF3 fronthaul port#0 or port#1 must be connected to the fronthaul switch. Make sure the PTP is configured to use the port connected to the fronthaul switch.
To run cuBB end-to-end test with TestMAC and RU emulator, an Aerial Devkit is required to run RU emulator. The BF3 fronthaul port#1 must be connected to CX6-DX NIC port#0 on Aerial the Devkit (RU emulator server) via Mellanox 100GbE direct attach copper cable.
During the first boot, login to BMC to check the firmware inventory. Go to Dashboard -> Maintenance -> Firmware Management -> Inventory to see the current firmware versions.

Here is the list of the minimum required versions. Upgrade the firmware to the following or newer versions, if your system has older firmware.
Component |
Firmware Version |
Firmware filename |
|---|---|---|
| BMC | 1.02.01 (20231103) | BMC_SCMAST2600-ROT20-2501MS_20231103_01.02.01_STDsp.bin |
| BIOS | 1.0 (20231026) | BIOS_G1SMH-G-1D31_20231026_1.0_STDsp.bin |
| FPGA | 0.8A | FPGA_MBD-G1SMH-G-10XX1D31_20231018_00.8A.XX_STDsp.bin |
| VBIOS | 96.00.84.00.02 | g530_0206_888__9600840002-prod.fwpkg |
| EROT | 1.03.0114.0000-n01 | cec1736-ecfw-01.03.0114.0000-n01-rel-prod.fwpkg |
| CPLD Motherboard Misc | V0B | CPLD_XO3-GP03E0-10XX03E0_20231020_0B.XX.XX_STDsp.jed |
The recommended firmware update sequence is:
Power off host
Update BMC
Update CPLD motherboard misc
Update CPU ERoT
Update FPGA
A/C power cycle
Update BIOS
Update VBIOS
Reboot or Power cycle
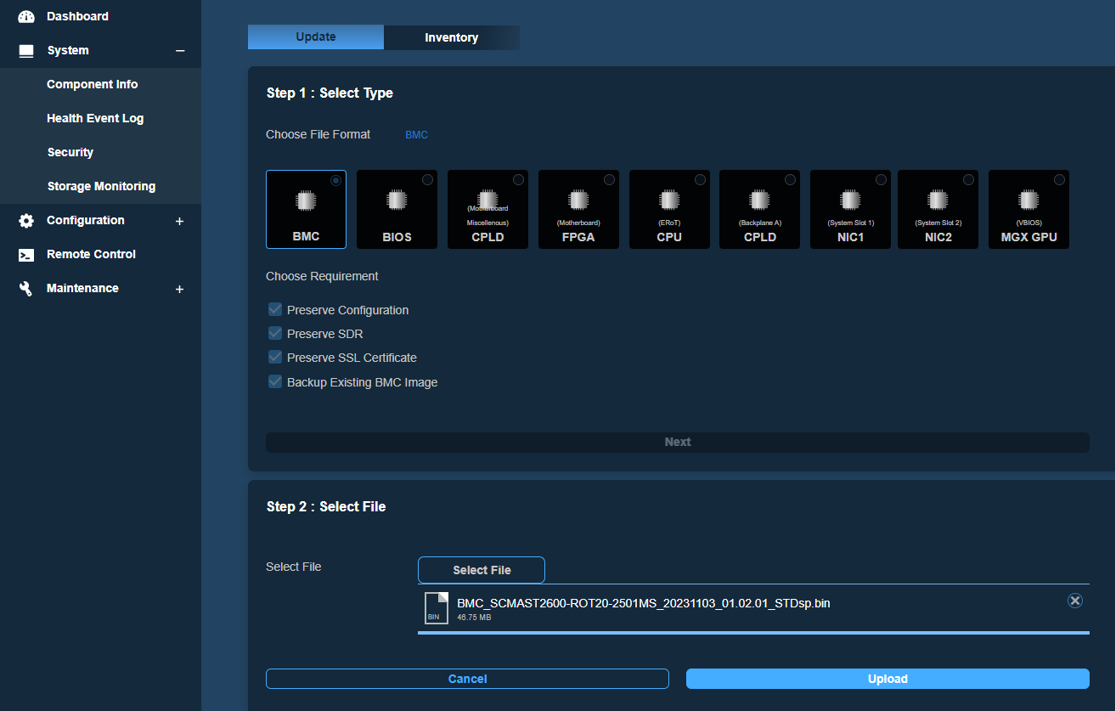
To update the firmware for a specific component, go to Dashboard -> Maintenance -> Firmware Management -> Update then select the component icon -> Next -> Select File -> Upload -> Update. For example, select BMC and its firmware file as follows:
For non-BMC firmware update, it is queued in the task list to update in next boot.

Contact NVIDIA CPM to get the above firmware files, if your system has older firmware.
Download the Ubuntu server 22.04 ISO image for ARM-based system from https://ubuntu.com/download/server/arm. Before installing the system OS, prepare a bootable USB drive contains the OS image or configure the virtual media in the BMC for remote installation. Also verify that a USB to Ethernet dongle is connected to the back USB port for host internet access.
There are two ways to configure the virtual media. One is to share the OS ISO image by Windows network sharing or Samba sharing on Linux. Then go to BMC Dashboard -> Configuration -> Virtual Media to enter the virtual media connection info including the share host ip, image path, username and password. After the connection info is saved, click the Link icon to connect.

Another way to configure virtual media, is to select the Virtual Media icon from the remote console then mount the OS ISO image to the virtual CD/DVD drive.

Reboot the system after the virtual media is configured and connected. Press F11 to enter the BIOS boot menu and select UEFI: USB CD/DVD Drive to boot with the virtual media.

Launch the SOL console from the BMC Remote Control menu. The SOL console is required to complete the Ubuntu OS installation.
The Ubuntu 22.04.3 installation media does not include a required patch for the resolution of an issue with the ast driver. The ast driver is used to interface with the BMC. The absence of this patch causes distorted output from the on-board display port and remote console. Because of this, the OS installation must be done on the SOL console. The fix is included in the NVIDIA optimized Ubuntu kernel. After installing the NVIDIA optimized Ubuntu kernel, the output of the on-board display and the remote console from BMC will be normal again.

After seeing the GRUB menu from the SOL console, select Ubuntu Server with the HWE Kernel to install the Ubuntu server OS.

Follow the Ubuntu installation process with the notable selection below:
Continue in rich mode
Continue without updating
Ubuntu Server
Install OpenSSH server
When the installation is done, the console shows Install complete and Reboot now. Reboot the system and check the following:
Check if the system time is correct to avoid apt update error.
Run the following commands to set the date and time via NTP once (this will not enable the NTP service):
sudo apt-get install ntpdate
sudo ntpdate -s pool.ntp.org
Check if the GPU and NIC are detected by the OS.
Use the following commands to determine whether the GPU and NIC are detected by the OS:
$ lspci | grep -i nvidia
# GH200 GPU
0009:01:00.0 3D controller: NVIDIA Corporation Device 2342 (rev a1)
$ lspci | grep -i mellanox
# The first BF3 NIC (Fronthaul NIC)
0000:01:00.0 Ethernet controller: Mellanox Technologies MT43244 BlueField-3 integrated ConnectX-7 network controller (rev 01)
0000:01:00.1 Ethernet controller: Mellanox Technologies MT43244 BlueField-3 integrated ConnectX-7 network controller (rev 01)
0000:01:00.2 DMA controller: Mellanox Technologies MT43244 BlueField-3 SoC Management Interface (rev 01)
# The second BF3 NIC (Backhaul NIC)
0002:01:00.0 Ethernet controller: Mellanox Technologies MT43244 BlueField-3 integrated ConnectX-7 network controller (rev 01)
0002:01:00.1 Ethernet controller: Mellanox Technologies MT43244 BlueField-3 integrated ConnectX-7 network controller (rev 01)
0002:01:00.2 DMA controller: Mellanox Technologies MT43244 BlueField-3 SoC Management Interface (rev 01)
Use the following command to change the hostname:
$ sudo hostnamectl set-hostname NEW_HOSTNAME
To display the GRUB menu during boot, create /etc/default/grub.d/menu.cfg with the following content:
$ cat <<"EOF" | sudo tee /etc/default/grub.d/menu.cfg
GRUB_TIMEOUT_STYLE=menu
GRUB_TIMEOUT=5
GRUB_TERMINAL="console serial"
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT=""
GRUB_SERIAL_COMMAND="$GRUB_SERIAL_COMMANDserial --unit=0 --speed=115200 --word=8 --parity=no --stop=1"
EOF
Edit the /etc/apt/apt.conf.d/20auto-upgrades system file, and change the “1” to “0” for both lines.
This prevents the installed version of the low latency kernel from being accidentally changed with a
subsequent software upgrade.
$ sudo nano /etc/apt/apt.conf.d/20auto-upgrades
APT::Periodic::Update-Package-Lists "0";
APT::Periodic::Unattended-Upgrade "0";
Run the following commands to install the NVIDIA optimized Ubuntu kernel.
$ sudo apt update
# NOTE: This will install the specific kernel version, not the latest NVIDIA optimized kernel.
$ sudo apt install -y linux-image-6.2.0-1012-nvidia-64k
Then, update the GRUB to change the default boot kernel. The version to use here depends on the latest version that was installed with the previous command:
# Update grub to change the default boot kernel
$ sudo sed -i 's/^GRUB_DEFAULT=.*/GRUB_DEFAULT="Advanced options for Ubuntu>Ubuntu, with Linux 6.2.0-1012-nvidia-64k"/' /etc/default/grub
Ensure the iommu.passthrough=y kernel parameter is NOT passed to the kernel. This parameter prevents the GPU driver from loading so it must be removed if it is present.
Verify that the parameter is present by running:
$ grep iommu.passthrough=y /proc/cmdline
If the parameter is present, find the file that contains this parameter and remove it. For example:
$ grep -rns iommu.passthrough /etc/default/grub*
# Remove iommu.passthrough=y from the found file
$ sudo sed -i 's/ iommu.passthrough=y//' /etc/default/<found file>
To set kernel command-line parameters, edit the GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX parameter in the grub
file /etc/default/grub.d/cmdline.cfg and append or update the parameters described below. The following kernel parameters
are optimized for GH200. To automatically append the grub file with these parameters, enter this command:
$ cat <<"EOF" | sudo tee /etc/default/grub.d/cmdline.cfg
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="$GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUXpci=realloc=off pci=pcie_bus_safe default_hugepagesz=512M hugepagesz=512M hugepages=32 tsc=reliable processor.max_cstate=0 audit=0 idle=poll rcu_nocb_poll nosoftlockup irqaffinity=0 isolcpus=managed_irq,domain,4-47 nohz_full=4-47 rcu_nocbs=4-47 earlycon module_blacklist=nouveau acpi_power_meter.force_cap_on=y numa_balancing=disable init_on_alloc=0 preempt=none"
EOF
The hugepage size is 512MB which is optimized for the 64k page size kernel on ARM.
$ sudo update-grub
$ sudo reboot
After rebooting, enter this command to verify that the kernel command-line parameters are configured properly:
$ uname -r
6.2.0-1012-nvidia-64k
$ cat /proc/cmdline
BOOT_IMAGE=/vmlinuz-6.2.0-1012-nvidia-64k root=/dev/mapper/ubuntu--vg-ubuntu--lv ro pci=realloc=off pci=pcie_bus_safe default_hugepagesz=512M hugepagesz=512M hugepages=32 tsc=reliable processor.max_cstate=0 audit=0 idle=poll rcu_nocb_poll nosoftlockup irqaffinity=0 isolcpus=managed_irq,domain,4-47 nohz_full=4-47 rcu_nocbs=4-47 earlycon module_blacklist=nouveau acpi_power_meter.force_cap_on=y numa_balancing=disable init_on_alloc=0 preempt=none
Enter this command to check if hugepages are enabled:
$ grep -i huge /proc/meminfo
AnonHugePages: 0 kB
ShmemHugePages: 0 kB
FileHugePages: 0 kB
HugePages_Total: 32
HugePages_Free: 32
HugePages_Rsvd: 0
HugePages_Surp: 0
Hugepagesize: 524288 kB
Hugetlb: 16777216 kB
Enter these commands to install the prerequisite packages:
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install -y build-essential linux-headers-$(uname -r) dkms unzip linuxptp pv apt-utils net-tools
Check if there is an existing MOFED installed on the host system.
$ ofed_info -s
MLNX_OFED_LINUX-23.07-0.5.0.0:
Uninstall MOFED if it is present.
$ sudo /usr/sbin/ofed_uninstall.sh
Download the doca-host-repo-ubuntu2204_2.5.0-0.0.1.2.5.0108.1.23.10.1.1.9.0_arm64.deb package here and copy it to the local file system on the server.
Enter the following commands to install DOCA OFED.
# Install DOCA OFED
$ sudo dpkg -i doca-host-repo-ubuntu2204_2.5.0-0.0.1.2.5.0108.1.23.10.1.1.9.0_arm64.deb
$ sudo apt update
$ sudo apt install -y doca-ofed
# To check what version of OFED you have installed
$ ofed_info -s
OFED-internal-23.10-1.1.9:
Enter the following commands to install Mellanox firmware tools.
# Install Mellanox Firmware Tools
$ export MFT_VERSION=4.26.1-3
$ wget https://www.mellanox.com/downloads/MFT/mft-$MFT_VERSION-arm64-deb.tgz
$ tar xvf mft-$MFT_VERSION-arm64-deb.tgz
$ sudo mft-$MFT_VERSION-arm64-deb/install.sh
$ sudo mst version
mst, mft 4.26.1-3, built on Nov 27 2023, 15:25:09. Git SHA Hash: N/A
$ sudo mst start
# check NIC PCIe bus addresses and network interface names
$ sudo mst status -v
MST modules:
------------
MST PCI module is not loaded
MST PCI configuration module is not loaded
PCI devices:
------------
DEVICE_TYPE MST PCI RDMA NET NUMA
BlueField3(rev:1) NA 0000:01:00.0 mlx5_0 net-enp1s0f0np0 0
BlueField3(rev:1) NA 0002:01:00.0 mlx5_2 net-enP2p1s0f0np0 0
BlueField3(rev:1) NA 0000:01:00.1 mlx5_1 net-enp1s0f1np1 0
BlueField3(rev:1) NA 0002:01:00.1 mlx5_3 net-enP2p1s0f1np1 0
Enter these commands to check the link status of port 0:
# Here is an example if the port 0 of fronthaul NIC is connected to another server or switch via a 100GbE DAC cable.
$ sudo mlxlink -d 0000:01:00.0
Operational Info
----------------
State : Active
Physical state : LinkUp
Speed : 100G
Width : 4x
FEC : Standard RS-FEC - RS(528,514)
Loopback Mode : No Loopback
Auto Negotiation : ON
Supported Info
--------------
Enabled Link Speed (Ext.) : 0x00003ff2 (200G_2X,200G_4X,100G_1X,100G_2X,100G_4X,50G_1X,50G_2X,40G,25G,10G,1G)
Supported Cable Speed (Ext.) : 0x000002f2 (100G_4X,50G_2X,40G,25G,10G,1G)
Troubleshooting Info
--------------------
Status Opcode : 0
Group Opcode : N/A
Recommendation : No issue was observed
Tool Information
----------------
Firmware Version : 32.37.1306
amBER Version : 2.13
MFT Version : mft 4.26.1-3
If the system has an older driver installed, unload the current driver modules and uninstall the old driver, using the following:
# Unload the current driver modules
$ for m in $(lsmod | awk "/^[^[:space:]]*(nvidia|nv_|gdrdrv)/ {print \$1}"); do echo Unload $m...; sudo rmmod $m; done
# Remove the driver if it was installed by runfile installer before.
$ sudo /usr/bin/nvidia-uninstall
Create the driver module config with the following recommended settings:
$ cat <<EOF | sudo tee /etc/modprobe.d/nvidia.conf
options nvidia NVreg_RegistryDwords="RMNvLinkDisableLinks=0x3FFFF;"
EOF
Run the following commands to install the NVIDIA open-source GPU kernel driver (OpenRM).
# Install NVIDIA GPU driver
$ wget https://us.download.nvidia.com/tesla/535.129.03/NVIDIA-Linux-aarch64-535.129.03.run
$ sudo sh NVIDIA-Linux-aarch64-535.129.03.run --silent -m kernel-open
# Verify that the driver is loaded successfully
$ nvidia-smi
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| NVIDIA-SMI 535.129.03 Driver Version: 535.129.03 CUDA Version: 12.2 |
|-----------------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
| GPU Name Persistence-M | Bus-Id Disp.A | Volatile Uncorr. ECC |
| Fan Temp Perf Pwr:Usage/Cap | Memory-Usage | GPU-Util Compute M. |
| | | MIG M. |
|=========================================+======================+======================|
| 0 GH200 480GB Off | 00000009:01:00.0 Off | 0 |
| N/A 40C P0 109W / 900W | 5MiB / 97871MiB | 8% Default |
| | | Disabled |
+-----------------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Processes: |
| GPU GI CI PID Type Process name GPU Memory |
| ID ID Usage |
|=======================================================================================|
| No running processes found |
+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
Run the following commands to install the GDRCopy driver. If the system has an older version installed, remove the old driver first.
GDRCopy driver must be installed after the CUDA driver.
# Check the installed GDRCopy driver version
$ apt list --installed | grep gdrdrv-dkms
# Remove the driver, if you have the older version installed.
$ sudo apt purge gdrdrv-dkms
$ sudo apt autoremove
# Install GDRCopy driver
$ wget https://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/redist/gdrcopy/CUDA%2012.2/ubuntu22_04/aarch64/gdrdrv-dkms_2.4-1_arm64.Ubuntu22_04.deb
$ sudo dpkg -i gdrdrv-dkms_2.4-1_arm64.Ubuntu22_04.deb
The full official instructions for installing Docker CE can be found here: https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/ubuntu/#install-docker-engine. The following instructions are one supported way of installing Docker CE:
To work correctly, the CUDA driver must be installed before Docker CE or nvidia-container-toolkit installation. It is recommended that you install the CUDA driver before installing Docker CE or the nvidia-container-toolkit.
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install -y ca-certificates curl gnupg
$ sudo install -m 0755 -d /etc/apt/keyrings
$ curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg
$ sudo chmod a+r /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg
$ echo \
"deb [arch="$(dpkg --print-architecture)" signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \
"$(. /etc/os-release && echo "$VERSION_CODENAME")" stable" | \
sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install -y docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-plugin
$ sudo docker run hello-world
Locate and follow the nvidia-container-toolkit install instructions.
Or use the following instructions as an alternate way to install the nvidia-container-toolkit. Version 1.14.1-1 is supported.
To work correctly, the CUDA driver must be installed before Docker CE or nvidia-container-toolkit installation. It is recommended that you install the CUDA driver before installing Docker CE or the nvidia-container-toolkit.
$ curl -fsSL https://nvidia.github.io/libnvidia-container/gpgkey | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/nvidia-container-toolkit-keyring.gpg \
&& curl -s -L https://nvidia.github.io/libnvidia-container/stable/deb/nvidia-container-toolkit.list | \
sed 's#deb https://#deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/nvidia-container-toolkit-keyring.gpg] https://#g' | \
sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nvidia-container-toolkit.list \
&& \
sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install -y nvidia-container-toolkit
$ sudo nvidia-ctk runtime configure --runtime=docker
$ sudo systemctl restart docker
$ sudo docker run --rm --runtime=nvidia --gpus all ubuntu nvidia-smi
NOTE: The following instructions are for BF3 NIC (OPN: 900-9D3B6-00CV-A; PSID: MT_0000000884) specifically. The BFB image must be updated before the NIC firmware.
# Enable MST
$ sudo mst start
$ sudo mst status
MST modules:
------------
MST PCI module is not loaded
MST PCI configuration module loaded
MST devices:
------------
/dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf0 - PCI configuration cycles access.
domain:bus:dev.fn=0000:01:00.0 addr.reg=88 data.reg=92 cr_bar.gw_offset=-1
Chip revision is: 01
/dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf1 - PCI configuration cycles access.
domain:bus:dev.fn=0002:01:00.0 addr.reg=88 data.reg=92 cr_bar.gw_offset=-1
Chip revision is: 01
# Change to DPU mode
$ sudo mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf0 -y s INTERNAL_CPU_MODEL=1 INTERNAL_CPU_OFFLOAD_ENGINE=0
$ sudo mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf1 -y s INTERNAL_CPU_MODEL=1 INTERNAL_CPU_OFFLOAD_ENGINE=0
# NOTE: Need power cycle to take effect
$ sudo reboot
# Download the BF3 BFB image
$ wget https://content.mellanox.com/BlueField/BFBs/Ubuntu22.04/DOCA_2.5.0_BSP_4.5.0_Ubuntu_22.04-1.23-10.prod.bfb
# Update the BFB image of the 1st BF3
$ sudo bfb-install -r rshim0 -b DOCA_2.5.0_BSP_4.5.0_Ubuntu_22.04-1.23-10.prod.bfb
# Update the BFB image of the 2nd BF3
$ sudo bfb-install -r rshim1 -b DOCA_2.5.0_BSP_4.5.0_Ubuntu_22.04-1.23-10.prod.bfb
Pushing bfb
1.20GiB 0:01:06 [18.5MiB/s] [
Collecting BlueField booting status. Press Ctrl+C to stop…
INFO[MISC]: PSC BL1 START
INFO[BL2]: start
INFO[BL2]: DDR POST passed
INFO[BL2]: UEFI loaded
INFO[BL31]: start
INFO[BL31]: lifecycle Production
INFO[BL31]: PTMERROR: Unknown OPN
INFO[BL31]: runtime
INFO[UEFI]: eMMC init
INFO[UEFI]: eMMC probed
INFO[UEFI]: UPVS valid
INFO[UEFI]: PMI: updates started
INFO[UEFI]: PMI: boot image update
INFO[UEFI]: PMI: updates completed, status 0
INFO[UEFI]: PCIe enum start
INFO[UEFI]: PCIe enum end
INFO[UEFI]: exit Boot Service
INFO[MISC]: Ubuntu installation started
INFO[MISC]: Installing OS image
INFO[MISC]: Installation finished
# Wait 10 minutes to ensure the card initializes properly after the BFB installation
$ sleep 600
# Download the BF3 NIC FW 32.39.2048
$ wget https://www.mellanox.com/downloads/firmware/fw-BlueField-3-rel-32_39_2048-900-9D3B6-00CV-A_Ax-NVME-20.4.1-UEFI-21.4.13-UEFI-22.4.12-UEFI-14.32.17-FlexBoot-3.7.300.signed.bin.zip
$ unzip fw-BlueField-3-rel-32_39_2048-900-9D3B6-00CV-A_Ax-NVME-20.4.1-UEFI-21.4.13-UEFI-22.4.12-UEFI-14.32.17-FlexBoot-3.7.300.signed.bin.zip
# Update the NIC FW of the 1st BF3
$ sudo flint -d /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf0 -y -i fw-BlueField-3-rel-32_39_2048-900-9D3B6-00CV-A_Ax-NVME-20.4.1-UEFI-21.4.13-UEFI-22.4.12-UEFI-14.32.17-FlexBoot-3.7.300.signed.bin b
# Update the NIC FW of the 2nd BF3
$ sudo flint -d /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf1 -y -i fw-BlueField-3-rel-32_39_2048-900-9D3B6-00CV-A_Ax-NVME-20.4.1-UEFI-21.4.13-UEFI-22.4.12-UEFI-14.32.17-FlexBoot-3.7.300.signed.bin b
Current FW version on flash: 32.37.1306
New FW version: 32.39.2048
FSMST_INITIALIZE - OK
Writing Boot image component - OK
Restoring signature - OK
# Change back to NIC mode
$ sudo mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf0 -y s INTERNAL_CPU_MODEL=1 INTERNAL_CPU_OFFLOAD_ENGINE=1
$ sudo mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf1 -y s INTERNAL_CPU_MODEL=1 INTERNAL_CPU_OFFLOAD_ENGINE=1
# NOTE: Requires a full power cycle from host with cold boot
# Verify NIC FW version after reboot
$ sudo mst start
$ sudo flint -d /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf0 q
Image type: FS4
FW Version: 32.39.2048
FW Release Date: 29.11.2023
Product Version: 32.39.2048
Rom Info: type=UEFI Virtio net version=21.4.13 cpu=AMD64,AARCH64
type=UEFI Virtio blk version=22.4.12 cpu=AMD64,AARCH64
type=UEFI version=14.32.17 cpu=AMD64,AARCH64
type=PXE version=3.7.300 cpu=AMD64
Description: UID GuidsNumber
Base GUID: 946dae0300f5a1f2 38
Base MAC: 946daef5a1f2 38
Image VSD: N/A
Device VSD: N/A
PSID: MT_0000000884
Security Attributes: secure-fw
Run the following commands to configure the BF3 NIC:
# Setting BF3 port to Ethernet mode (not Infiniband)
$ sudo mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf0 --yes set LINK_TYPE_P1=2
$ sudo mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf0 --yes set LINK_TYPE_P2=2
$ sudo mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf0 --yes set INTERNAL_CPU_MODEL=1
$ sudo mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf0 --yes set INTERNAL_CPU_PAGE_SUPPLIER=EXT_HOST_PF
$ sudo mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf0 --yes set INTERNAL_CPU_ESWITCH_MANAGER=EXT_HOST_PF
$ sudo mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf0 --yes set INTERNAL_CPU_IB_VPORT0=EXT_HOST_PF
$ sudo mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf0 --yes set INTERNAL_CPU_OFFLOAD_ENGINE=DISABLED
$ sudo mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf0 --yes set CQE_COMPRESSION=1
$ sudo mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf0 --yes set PROG_PARSE_GRAPH=1
$ sudo mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf0 --yes set ACCURATE_TX_SCHEDULER=1
$ sudo mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf0 --yes set FLEX_PARSER_PROFILE_ENABLE=4
$ sudo mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf0 --yes set REAL_TIME_CLOCK_ENABLE=1
$ sudo mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf0 --yes set EXP_ROM_VIRTIO_NET_PXE_ENABLE=0
$ sudo mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf0 --yes set EXP_ROM_VIRTIO_NET_UEFI_ARM_ENABLE=0
$ sudo mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf0 --yes set EXP_ROM_VIRTIO_NET_UEFI_x86_ENABLE=0
$ sudo mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf0 --yes set EXP_ROM_VIRTIO_BLK_UEFI_ARM_ENABLE=0
$ sudo mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf0 --yes set EXP_ROM_VIRTIO_BLK_UEFI_x86_ENABLE=0
# NOTE: Requires a full power cycle from host with cold boot
# Verify that the NIC FW changes have been applied
$ sudo mlxconfig -d /dev/mst/mt41692_pciconf0 q | grep "CQE_COMPRESSION\|PROG_PARSE_GRAPH\|ACCURATE_TX_SCHEDULER\|FLEX_PARSER_PROFILE_ENABLE\|REAL_TIME_CLOCK_ENABLE\|INTERNAL_CPU_MODEL\|LINK_TYPE_P1\|LINK_TYPE_P2\|INTERNAL_CPU_PAGE_SUPPLIER\|INTERNAL_CPU_ESWITCH_MANAGER\|INTERNAL_CPU_IB_VPORT0\|INTERNAL_CPU_OFFLOAD_ENGINE"
INTERNAL_CPU_MODEL EMBEDDED_CPU(1)
INTERNAL_CPU_PAGE_SUPPLIER EXT_HOST_PF(1)
INTERNAL_CPU_ESWITCH_MANAGER EXT_HOST_PF(1)
INTERNAL_CPU_IB_VPORT0 EXT_HOST_PF(1)
INTERNAL_CPU_OFFLOAD_ENGINE DISABLED(1)
FLEX_PARSER_PROFILE_ENABLE 4
PROG_PARSE_GRAPH True(1)
ACCURATE_TX_SCHEDULER True(1)
CQE_COMPRESSION AGGRESSIVE(1)
REAL_TIME_CLOCK_ENABLE True(1)
LINK_TYPE_P1 ETH(2)
LINK_TYPE_P2 ETH(2)
Enter these commands to configure PTP4L, assuming that enp1s0f0np0 NIC interface and CPU core 41 are used for PTP:
$ cat <<EOF | sudo tee /etc/ptp.conf
[global]
dataset_comparison G.8275.x
G.8275.defaultDS.localPriority 128
maxStepsRemoved 255
logAnnounceInterval -3
logSyncInterval -4
logMinDelayReqInterval -4
#serverOnly 0
G.8275.portDS.localPriority 128
#ptp_dst_mac 01:80:C2:00:00:0E
network_transport L2
domainNumber 25
#free_running 1
tx_timestamp_timeout 30
slaveOnly 1
clock_servo pi
#tsproc_mode filter_weight
#delay_filter moving_average
#delay_filter_length 180
#freq_est_interval 2
step_threshold 1.0
#step_window 1.0
egressLatency 28
pi_proportional_const 4.65
pi_integral_const 0.1
[enp1s0f0np0]
announceReceiptTimeout 3
delay_mechanism E2E
network_transport L2
EOF
$ cat <<EOF | sudo tee /lib/systemd/system/ptp4l.service
[Unit]
Description=Precision Time Protocol (PTP) service
Documentation=man:ptp4l
After=network.target
[Service]
Restart=always
RestartSec=5s
Type=simple
ExecStartPre=ifconfig enp1s0f0np0 up
ExecStartPre=ethtool --set-priv-flags enp1s0f0np0 tx_port_ts on
ExecStartPre=ethtool -A enp1s0f0np0 rx off tx off
ExecStartPre=ifconfig enp1s0f1np1 up
ExecStartPre=ethtool --set-priv-flags enp1s0f1np1 tx_port_ts on
ExecStartPre=ethtool -A enp1s0f1np1 rx off tx off
ExecStart=taskset -c 41 /usr/sbin/ptp4l -f /etc/ptp.conf
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
EOF
$ sudo systemctl daemon-reload
$ sudo systemctl restart ptp4l.service
$ sudo systemctl enable ptp4l.service
One server becomes the master clock, as shown below:
$ sudo systemctl status ptp4l.service
• ptp4l.service - Precision Time Protocol (PTP) service
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/ptp4l.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Tue 2023-08-08 19:37:56 UTC; 2 weeks 3 days ago
Docs: man:ptp4l
Main PID: 1120 (ptp4l)
Tasks: 1 (limit: 94533)
Memory: 460.0K
CPU: 9min 8.089s
CGroup: /system.slice/ptp4l.service
└─1120 /usr/sbin/ptp4l -f /etc/ptp.conf
Aug 09 18:12:35 aerial-devkit taskset[1120]: ptp4l[81287.043]: selected local clock b8cef6.fffe.d333be as best master
Aug 09 18:12:35 aerial-devkit taskset[1120]: ptp4l[81287.043]: port 1: assuming the grand master role
Aug 11 20:44:51 aerial-devkit taskset[1120]: ptp4l[263223.379]: timed out while polling for tx timestamp
Aug 11 20:44:51 aerial-devkit taskset[1120]: ptp4l[263223.379]: increasing tx_timestamp_timeout may correct this issue, but it is likely caused by a driver bug
Aug 11 20:44:51 aerial-devkit taskset[1120]: ptp4l[263223.379]: port 1: send sync failed
Aug 11 20:44:51 aerial-devkit taskset[1120]: ptp4l[263223.379]: port 1: MASTER to FAULTY on FAULT_DETECTED (FT_UNSPECIFIED)
Aug 11 20:45:07 aerial-devkit taskset[1120]: ptp4l[263239.522]: port 1: FAULTY to LISTENING on INIT_COMPLETE
Aug 11 20:45:08 aerial-devkit taskset[1120]: ptp4l[263239.963]: port 1: LISTENING to MASTER on ANNOUNCE_RECEIPT_TIMEOUT_EXPIRES
Aug 11 20:45:08 aerial-devkit taskset[1120]: ptp4l[263239.963]: selected local clock b8cef6.fffe.d333be as best master
Aug 11 20:45:08 aerial-devkit taskset[1120]: ptp4l[263239.963]: port 1: assuming the grand master role
The other becomes the secondary, follower clock, as shown below:
$ sudo systemctl status ptp4l.service
● ptp4l.service - Precision Time Protocol (PTP) service
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/ptp4l.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Tue 2023-11-21 17:49:00 UTC; 5 days ago
Docs: man:ptp4l
Process: 1798 ExecStartPre=ifconfig enp1s0f1np1 up (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Process: 1920 ExecStartPre=ethtool --set-priv-flags enp1s0f1np1 tx_port_ts on (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Process: 1971 ExecStartPre=ethtool -A enp1s0f1np1 rx off tx off (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 2023 (ptp4l)
Tasks: 1 (limit: 146916)
Memory: 2.7M
CPU: 6min 16.710s
CGroup: /system.slice/ptp4l.service
└─2023 /usr/sbin/ptp4l -f /etc/ptp.conf
Nov 27 05:51:18 gh-smc-cg1-qs-01 ptp4l[2023]: [475374.166] rms 2 max 4 freq -13578 +/- 11 delay -33 +/- 0
Nov 27 05:51:19 gh-smc-cg1-qs-01 ptp4l[2023]: [475375.166] rms 2 max 5 freq -13587 +/- 10 delay -34 +/- 0
Nov 27 05:51:20 gh-smc-cg1-qs-01 ptp4l[2023]: [475376.166] rms 4 max 8 freq -13584 +/- 17 delay -34 +/- 1
Nov 27 05:51:21 gh-smc-cg1-qs-01 ptp4l[2023]: [475377.166] rms 4 max 8 freq -13586 +/- 20 delay -35 +/- 1
Nov 27 05:51:22 gh-smc-cg1-qs-01 ptp4l[2023]: [475378.166] rms 4 max 7 freq -13580 +/- 18 delay -33 +/- 1
Nov 27 05:51:23 gh-smc-cg1-qs-01 ptp4l[2023]: [475379.166] rms 4 max 9 freq -13579 +/- 20 delay -34 +/- 1
Nov 27 05:51:24 gh-smc-cg1-qs-01 ptp4l[2023]: [475380.167] rms 3 max 7 freq -13584 +/- 14 delay -34 +/- 1
Nov 27 05:51:25 gh-smc-cg1-qs-01 ptp4l[2023]: [475381.167] rms 2 max 4 freq -13583 +/- 11 delay -34 +/- 1
Nov 27 05:51:26 gh-smc-cg1-qs-01 ptp4l[2023]: [475382.167] rms 3 max 5 freq -13587 +/- 14 delay -34 +/- 0
Nov 27 05:51:27 gh-smc-cg1-qs-01 ptp4l[2023]: [475383.167] rms 4 max 8 freq -13590 +/- 18 delay -33 +/- 0
Enter the commands to turn off NTP:
$ sudo timedatectl set-ntp false
$ timedatectl
Local time: Mon 2023-11-27 05:52:23 UTC
Universal time: Mon 2023-11-27 05:52:23 UTC
RTC time: Mon 2023-11-27 05:52:23
Time zone: Etc/UTC (UTC, +0000)
System clock synchronized: no
NTP service: inactive
RTC in local TZ: no
Run PHC2SYS as service:
PHC2SYS is used to synchronize the system clock to the PTP hardware clock (PHC) on the NIC. Here are the two examples of PHC2SYS configurations.
Example 1: Specify the network interface used for PTP and system clock as the slave clock. This is the default mode when the system is configured as a gNB or RU emulator to run cuBB test.
# If more than one instance is already running, kill the existing # PHC2SYS sessions. # Command used can be found in /lib/systemd/system/phc2sys.service # Update the ExecStart line to the following $ cat <<EOF | sudo tee /lib/systemd/system/phc2sys.service [Unit] Description=Synchronize system clock or PTP hardware clock (PHC) Documentation=man:phc2sys Requires=ptp4l.service After=ptp4l.service [Service] Restart=always RestartSec=5s Type=simple # Gives ptp4l a chance to stabilize ExecStartPre=sleep 2 ExecStart=/bin/sh -c "taskset -c 41 /usr/sbin/phc2sys -s /dev/ptp\$(ethtool -T enp1s0f0np0 | grep PTP | awk '{print \$4}') -c CLOCK_REALTIME -n 24 -O 0 -R 256 -u 256" [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target EOF
Example 2: Synchronize time automatically according to the current ptp4l state and synchronize the system clock to the remote master. This configuration is usually performed when the system is configured as a gNB to run E2E test in the LLS-C3 topology.
# If more than one instance is already running, kill the existing # PHC2SYS sessions. # Command used can be found in /lib/systemd/system/phc2sys.service # Update the ExecStart line to the following, the -a option will use the same interface as ptp4l and -r will synchronize the system clock $ cat <<EOF | sudo tee /lib/systemd/system/phc2sys.service [Unit] Description=Synchronize system clock or PTP hardware clock (PHC) Documentation=man:phc2sys After=ntpdate.service Requires=ptp4l.service After=ptp4l.service [Service] Restart=always RestartSec=5s Type=simple ExecStart=/usr/sbin/phc2sys -a -r -n 24 -R 256 -u 256 [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
After the PHC2SYS config file is changed, run the following:
$ sudo systemctl daemon-reload
$ sudo systemctl restart phc2sys.service
# Set to start automatically on reboot
$ sudo systemctl enable phc2sys.service
# check that the service is active and has converged to a low rms value (<30) and that the correct NIC has been selected (enp1s0f0np0):
$ sudo systemctl status phc2sys.service
● phc2sys.service - Synchronize system clock or PTP hardware clock (PHC)
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/phc2sys.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Tue 2023-11-21 17:49:02 UTC; 5 days ago
Docs: man:phc2sys
Process: 2037 ExecStartPre=sleep 2 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 2102 (sh)
Tasks: 2 (limit: 146916)
Memory: 1.9M
CPU: 25min 30.299s
CGroup: /system.slice/phc2sys.service
├─2102 /bin/sh -c "taskset -c 41 /usr/sbin/phc2sys -s /dev/ptp\$(ethtool -T enp1s0f0np0 | grep PTP | awk '{print \$4}') -c CLOCK_REALTIME -n 24 -O 0 -R 256 -u 256"
└─2108 /usr/sbin/phc2sys -s /dev/ptp0 -c CLOCK_REALTIME -n 24 -O 0 -R 256 -u 256
Nov 27 06:01:27 gh-smc-cg1-qs-01 phc2sys[2108]: [475982.933] CLOCK_REALTIME rms 8 max 20 freq -2268 +/- 25 delay 512 +/- 5
Nov 27 06:01:28 gh-smc-cg1-qs-01 phc2sys[2108]: [475983.950] CLOCK_REALTIME rms 8 max 19 freq -2279 +/- 16 delay 511 +/- 6
Nov 27 06:01:29 gh-smc-cg1-qs-01 phc2sys[2108]: [475984.966] CLOCK_REALTIME rms 8 max 21 freq -2280 +/- 33 delay 512 +/- 3
Nov 27 06:01:30 gh-smc-cg1-qs-01 phc2sys[2108]: [475985.982] CLOCK_REALTIME rms 8 max 20 freq -2274 +/- 13 delay 512 +/- 6
Nov 27 06:01:31 gh-smc-cg1-qs-01 phc2sys[2108]: [475986.998] CLOCK_REALTIME rms 8 max 20 freq -2281 +/- 18 delay 511 +/- 6
Nov 27 06:01:32 gh-smc-cg1-qs-01 phc2sys[2108]: [475988.014] CLOCK_REALTIME rms 8 max 19 freq -2293 +/- 25 delay 513 +/- 6
Nov 27 06:01:33 gh-smc-cg1-qs-01 phc2sys[2108]: [475989.031] CLOCK_REALTIME rms 8 max 19 freq -2279 +/- 12 delay 514 +/- 7
Nov 27 06:01:34 gh-smc-cg1-qs-01 phc2sys[2108]: [475990.047] CLOCK_REALTIME rms 8 max 21 freq -2280 +/- 23 delay 512 +/- 7
Nov 27 06:01:35 gh-smc-cg1-qs-01 phc2sys[2108]: [475991.063] CLOCK_REALTIME rms 8 max 19 freq -2291 +/- 20 delay 512 +/- 5
Nov 27 06:01:36 gh-smc-cg1-qs-01 phc2sys[2108]: [475992.079] CLOCK_REALTIME rms 8 max 24 freq -2281 +/- 26 delay 512 +/- 7
Verify that the system clock is synchronized:
$ timedatectl
Local time: Mon 2023-11-27 06:02:44 UTC
Universal time: Mon 2023-11-27 06:02:44 UTC
RTC time: Mon 2023-11-27 06:02:44
Time zone: Etc/UTC (UTC, +0000)
System clock synchronized: yes
NTP service: inactive
RTC in local TZ: no
Create the directory /usr/local/bin and create the /usr/local/bin/nvidia.sh file to run the commands with every reboot.
The command for “nvidia-smi lgc” expects just one GPU device (-i 0). This needs to be modified if the system uses more than one GPU.
$ cat <<"EOF" | sudo tee /usr/local/bin/nvidia.sh
#!/bin/bash
mst start
nvidia-persistenced
nvidia-smi -pm 1
nvidia-smi -i 0 -lgc $(nvidia-smi -i 0 --query-supported-clocks=graphics --format=csv,noheader,nounits | sort -h | tail -n 1)
nvidia-smi -mig 0
echo -1 > /proc/sys/kernel/sched_rt_runtime_us
EOF
Create a system service file to be loaded after network interfaces are up.
$ cat <<EOF | sudo tee /lib/systemd/system/nvidia.service
[Unit]
After=network.target
[Service]
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/nvidia.sh
[Install]
WantedBy=default.target
EOF
Set the file permissions, reload the systemd daemon, enable the service, restart the service when installing the first time, and check status.
$ sudo chmod 744 /usr/local/bin/nvidia.sh
$ sudo chmod 664 /lib/systemd/system/nvidia.service
$ sudo systemctl daemon-reload
$ sudo systemctl enable nvidia.service
$ sudo systemctl restart nvidia.service
$ systemctl status nvidia.service
The output of the last command should look like this:
$ systemctl status nvidia.service
○ nvidia.service
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/nvidia.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: inactive (dead) since Wed 2023-12-06 01:49:10 UTC; 28s ago
Process: 14572 ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/nvidia.sh (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 14572 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
CPU: 3.034s
Dec 06 01:49:06 aerial nvidia-persistenced[15545]: Started (15545)
Dec 06 01:49:09 aerial nvidia.sh[15578]: Persistence mode is already Enabled for GPU 00000009:01:00.0.
Dec 06 01:49:09 aerial nvidia.sh[15578]: All done.
Dec 06 01:49:09 aerial nvidia.sh[15583]: GPU clocks set to "(gpuClkMin 1980, gpuClkMax 1980)" for GPU 00000009:01:00.0
Dec 06 01:49:09 aerial nvidia.sh[15583]: All done.
Dec 06 01:49:09 aerial nvidia.sh[15584]: Disabled MIG Mode for GPU 00000009:01:00.0
Dec 06 01:49:09 aerial nvidia.sh[15584]: All done.
Dec 06 01:49:10 aerial nvidia-persistenced[15545]: Shutdown (15545)
Dec 06 01:49:10 aerial systemd[1]: nvidia.service: Deactivated successfully.
Dec 06 01:49:10 aerial systemd[1]: nvidia.service: Consumed 3.034s CPU time.
Ensure the cmake command line contains -DCUDA_GENCODE_ARCH_LIST=80,90 so the support of the Hopper GPU architecture is included in the resulting binaries.
The default MGX CG1 configs within the Aerial source are:
cuPHY-CP/cuphycontroller/config/cuphycontroller_F08_CG1.yaml
cuPHY-CP/cuphycontroller/config/l2_adapter_config_F08_CG1.yaml
Pass F08_CG1 to the cuphycontroller_scf executable to select them.