Software Overview
Parabricks is a software suite for genomic analysis. It delivers major improvements in throughput time for common analytical tasks in genomics, including germline and somatic analysis. The core of the Parabricks software is its data pipeline, which takes raw data and transforms it according to the user's requirements.
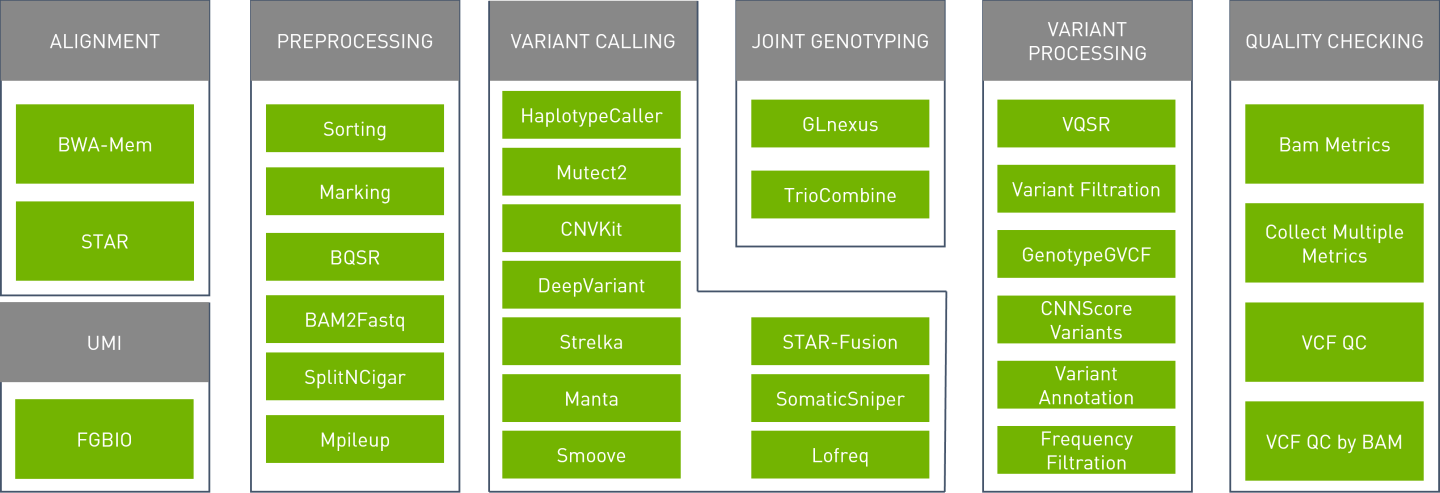
Parabricks supports the tools shown below:
Parabricks supports the pipelines shown below:

The Parabricks software can be configured to run specific accelerated tools or run full pipelines that are commonly used. The standalone tools page covers individual tools and the pipelines page discuses how to run commonly used pipelines.
NVIDIA Parabricks pipelines have been tested on Dell, HPE, IBM, and NVIDIA servers at Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, and Microsoft Azure.
Software Tools
The following standalone tools can be used with the NVIDIA Clara Parabricks Pipelines software. Click on a tool name for tool-specific options.
Tool |
Details |
Annotates existing BAM files with UMIs (Unique Molecular Indices) from a separate FASTQ file |
|
Apply BQSR report to a bam file and generate new bam file |
|
Tool for the detection of gene fusions from RNA-Seq data |
|
Convert a BAM to FASTQ |
|
Collect WGS Metrics on a bam file |
|
Sort BAM file |
|
Call variants from mpileup output |
|
Consequence prediction for genomic variants |
|
Generate BCF/VCF pileup for one or multiple BAM files |
|
Collect BQSR report on a BAM file |
|
Generate variant scores using a Convolutional Neural Network |
|
Run CNVkit with accelerated coverage calculation from read depths |
|
Collect multiple classes of metrics on a bam file |
|
Calls consensus sequences from reads with the same unique molecular tag |
|
Annotate variants based on a dbsnp |
|
Run GPU-DeepTrio for calling de novo variants |
|
Run GPU-DeepVariant for calling germline variants |
|
Perform sample demultiplexing on FASTQs |
|
Calls consensus sequences from reads with the same double-stranded source molecule |
|
A tool for estimating large repeats in the bam |
|
Run bwa mem, co-ordinate sorting, marking duplicates and Base Quality Score Recalibration |
|
Convert FASTQs to an unaligned BAM file |
|
Filter a VCF by allele frequency or allele count |
|
Convert a GVCF to VCF |
|
Merge and joint-call input gVCF files, emitting multi-sample BCF |
|
Groups reads together that appear to have come from the same original molecule |
|
Run GPU-HaplotypeCaller for calling germline variants |
|
Index a GVCF file |
|
Quantify abundances of transcripts from bulk and single-cell RNA-Seq data |
|
Call variants with high sensitivity, predicting variants below the average base-call quality |
|
Call variants from BAM file |
|
Analyze germline variation in small sets of individuals and somatic variation in tumor/normal sample pairs |
|
Call somatic variants with accelerated MuSE variant caller |
|
Run GPU-Mutect2 for tumor-normal analysis |
|
Generate the final vcf output of doing mutect pon |
|
Build an index for pon file, which is the prerequisite to do mutect pon |
|
Run RNA-seq data through the fq2bam pipeline |
|
Generate text pileup for one or multiple BAM files |
|
Adds and/or fixes mate information on paired-end reads |
|
Call and genotype SVs for short reads |
|
Annotate variants in a VCF file with VCF or GTF databases |
|
Identify single nucleotide positions that are different between tumor and normal BAM files |
|
Run the somaticsniper variant caller workflow |
|
Split reads in a BAM file that contain Ns in their cigar string |
|
Identify candidate fusion transcripts supported by Illumina reads |
|
Analyze germline variation in small cohorts and somatic variation in tumor/normal sample pairs |
|
Run the strelka variant caller workflow |
|
Combine GVCF of 2 or 3 samples |
|
This UMI pipeline is based on Fulcrum Genomics toolkit, processes sequencing reads with molecular barcodes (also known as Unique Molecular Indices, UMIs), which provide impressive error correction and increased accuracy using a sequencing consensus read level |
|
Filter a VCF using a boolean expression |
|
Annotate a VCF using dbsnp and annotation files |
|
Generate QC plots on a VCF file |
|
Generate a summaryfile using samtoolsmpileup that can be used for plotting/report generation |
|
Create union and intersection VCFs based on a minimum number of variant callers supporting a variant |
|
Build a recalibration model to score variant quality and apply a score cutoff to filter variants |
Pipelines
In Clara Parabricks, each pipeline is a collection of several individual tools that are commonly used together, all wrapped up as a single tool. For example, the deepvariant_germline takes FASTA and FASTQ files as input and produces a VCF and BAM file as output. Internally, it runs BWA mem alignment, performs coordinate sorting, marks duplicates, and then runs DeepVariant.
The following standalone pipelines can be used with the NVIDIA Clara Parabricks Pipelines software. Click on a tool name for tool-specific options.
Tool |
Details |
Run the germline pipeline from FASTQ to VCF using a deep neural network analysis |
|
(BETA) Run the de novo mutation pipeline with three samples for de novo variant detection |
|
Run the germline pipeline from FASTQ to VCF |
|
Run the germline pipeline from FASTQ to VCF with correct ploidy values for human sex chromosome handling |
|
Run the GATK Best Practices pipeline for RNA-seq data from FASTQ to VCF |
|
Run the somatic pipeline from FASTQ to VCF |
Compatible CPU Software Versions
Clara Parabricks produces the same results as the following tools:
Tool |
Version |
arriba |
2.1.0 |
bcftools |
1.10.2 |
BWA |
0.7.15 |
cnvkit |
0.9.7 |
Deepvariant |
1.1 |
Expansion Hunter |
5.0.0 |
fgbio |
1.4.0 |
GATK |
4.2.0.0 |
glnexus |
1.2.7 |
Kallisto |
0.46.2 |
lofreq |
2.1.5 |
manta |
1.6.0 |
samtools |
1.10 |
somaticsniper |
1.0.5.0 |
STAR |
2.7.2a |
STAR-Fusion |
1.7.0 |
strelka |
2.9.0 |