HBN Service Configuration
To start configuring HBN, log in to the HBN container:
sudo crictl exec -it $(crictl ps | grep hbn | awk '{print $1;}') bash
Flat Files Configuration
Add network interfaces and FRR configuration files to HBN. For more more information refer to the Cumulus Linux FRRouting guide.
/etc/network/interfaces/etc/frr/frr.conf;/etc/frr/daemons
This section assumes familiarity with NVIDIA user experience (NVUE) Cumulus Linux. The following sections elaborate on HBN-specific aspects of NVUE.
NVUE Service
HBN installs NVUE by default and enables NVUE service at boot.
NVUE REST API
HBN enables the REST API with only localhost access by default. To enable REST API access, refer to Enable REST API Access.
You can run cURL commands from the command line. Use the default HBN username, nvidia, and password which you must be update when enabling the REST API using the HBN preparation script.
To change the default password for the nvidia user or to add additional users for NVUE access, refer to section HBN NVUE User Credentials.
REST API example:
curl -u 'nvidia:nvidia' --insecure https://<mgmt_ip>:8765/nvue_v1/vrf/default/router/bgp
{
"configured-neighbors": 2,
"established-neighbors": 2,
"router-id": "10.10.10.201"
}
NVUE REST API Management Through CLI
To enable the REST API service:
nv set system api state enabled
To disable the REST API service:
nv set system api state disabled
To bind the REST API service to a specific address:
nv set system api listening-address <localhost|ipv4|ipv6|0.0.0.0>
For information about using the NVUE REST API, refer to the NVUE API documentation .
NVUE REST API in DOCA Platform Framework
For information on DOCA Platform Framework (DPF), refer to DOCA Framework.
This section explains how to configure external access to the HBN NVUE REST API in a DOCA Platform Framework (DPF) environment.
By default, the NVUE REST API is only accessible from within the cluster (i.e., via localhost). To expose the API to external networks, you must configure Kubernetes NodePort and set the appropriate listening address.
Enabling External Access to the NVUE REST API
Configure NodePort in DPUService – Add the following section under
spec.serviceConfiguration.helmChart.valuesin yourDPUServiceConfigurationYAML:service: type: NodePort nodePort:
30765Set the API listening address – To bind the API to all available HBN IP addresses (for example, for external access), configure the following:
configuration: startupYAMLJ2: | - set: system: api: listening-address:
0.0.0.0: {}Verify API accessibility – Use
curlto confirm that the NVUE REST API is reachable:curl -k -u
'username:password'https://<node-ip>:<nodePort>/nvue_v1/interface/Check service status – To check the NodePort service status:
kubectl get svc -n <your-namespace>
Example: Combined DPUServiceConfiguration and DPUServiceTemplate
The following is a sample manifest to deploy HBN with the NVUE REST API enabled:
---
apiVersion: svc.dpu.nvidia.com/v1alpha1
kind: DPUServiceConfiguration
metadata:
name: doca-hbn
namespace: dpf-operator-system
spec:
deploymentServiceName: "doca-hbn"
serviceConfiguration:
helmChart:
values:
service:
nodePort: 30765
type: NodePort
configuration:
user:
create: true
password:
secretKey: password
secretName: hbn-user-password
username: nvidia
perDPUValuesYAML: |
- hostnamePattern: "*"
startupYAMLJ2: |
- header:
model: bluefield
nvue-api-version: nvue_v1
rev-id: 1.0
version: HBN 3.1.0
- set:
system:
api:
listening-address:
0.0.0.0: {}
Security Considerations
Authentication
Always use valid username/password authentication.
Use HTTPS to secure all REST API communications.
The default credentials are
nvidia:nvidia.It is strongly recommended to change the default credentials using the user creation procedure described below.
User Creation/Update Procedure for NVUE REST API
The user should not interact directly with the DPU cluster in DPF.
Create a password secret on the host cluster:
kubectl -n dpf-operator-system create secret generic hbn-user-password \ --from-literal=password=<new-password>
Propagate the secret to the DPU cluster (label the secret so that it is made available to the DPU):
kubectl -n dpf-operator-system label secret hbn-user-password \ dpu.nvidia.com/image-pull-secret=
""Update the user configuration in the helm values your service YAML:
configuration: user: create:
trueusername:"your-username"password: secretName:"hbn-user-password"#Must match the secret name from Step1secretKey:"password"#Must match the key in the secret # Optional settings shell:"/bin/bash"homeDir:"/home/your-username"additionalGroups: ["group1","group2"] uid:"1000"gid:"1000"
User Creation Configuration Options
The following options can be used to configure user creation or update in the spec.serviceConfiguration.helmChart.values.configuration.user section.
Option | Required | Description |
| Yes | Enables user creation or update. Default is |
| Yes | Username for the new user, or existing user in case of an update |
| Yes | Name of the Kubernetes secret that stores the password |
| Yes | Key within the secret that contains the password value |
| No | Shell assigned to the user (e.g., |
| No | Path to the user’s home directory |
| No | List of additional groups to assign the user to (e.g., |
| No | User ID |
| No | Group ID |
NVUE CLI
For information about using the NVUE CLI, refer to the NVUE CLI documentation
NVUE Startup Configuration File
When the network configuration is saved using NVUE, HBN writes the configuration to the /etc/nvue.d/startup.yaml file.
The startup configuration is applied by following the supervisor daemon at boot time. nvued-startup will appear in an EXITED state after applying the startup configuration:
# supervisorctl status nvued-startup
nvued-startup EXITED Apr 17 10:04 AM
nv config apply startup applies the yaml configuration saved at /etc/nvue.d/. nv config save saves the running configuration to /etc/nvue.d/startup.yaml.
HBN Default Configuration
After a fresh HBN installation, the default /etc/network/interfaces file should contain only the declaration of a loopback interface:
source /etc/network/interfaces.d/*.intf
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
FRR configuration files are also present in /etc/frr/ but configurations are not enabled.
Layer-3 Routing
Next-hop IDs and Next-hop Groups
In HBN, route programming utilizes next-hop IDs to specify a route's next-hop. For routes with multiple paths, next-hop groups are used to identify equal-cost multi-path (ECMP) next-hop sets. This grouping enables the system to efficiently process and modify route and next-hop objects, improving scalability, network convergence, and performance. You may notice changes in the display of route information in the output of kernel operational commands.
Native Routing with BGP and ECMP
HBN supports unicast routing with BGP and ECMP for IPv4 and IPv6 traffic. ECMP is achieved by distributing traffic using hash calculation based on the source IP , destination IP, and protocol type of the IP header.
For TCP and UDP packets, the source and destination ports are also included.
ECMP Example
ECMP is implemented any time routes have multiple paths over uplinks or host ports. For example, 20.20.20.0/24 has 2 paths using both uplinks, so a path is selected based on a hash of the IP headers.
# ip route show 20.20.20.0/24
20.20.20.0/24 nhid 106 proto bgp metric 20
# ip nexthop show group id 106
id 106 group 105/107 proto zebra
# ip nexthop show id 105
id 105 via fe80::202:ff:fe00:7 dev p0_if scope link proto zebra
# ip nexthop show id 107
id 107 via fe80::202:ff:fe00:c dev p1_if scope link proto zebra
HBN supports up to 64 paths for ECMP
Sample NVUE Configuration for Native Routing with Host-facing Ports as Access
nv set interface lo ip address 10.10.10.1/32
nv set interface lo ip address 2010:10:10::1/128
nv set interface vlan100 type svi
nv set interface vlan100 vlan 100
nv set interface vlan100 base-interface br_default
nv set interface vlan100 ip address 2030:30:30::1/64
nv set interface vlan100 ip address 30.30.30.1/24
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 100
nv set interface pf0hpf_if,pf1hpf_if bridge domain br_default access 100
nv set vrf default router bgp router-id 10.10.10.1
nv set vrf default router bgp autonomous-system 65501
nv set vrf default router bgp path-selection multipath aspath-ignore on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
Sample NVUE Configuration for Native Routing with Host-facing Ports as Trunk
nv set interface lo ip address 10.10.10.1/32
nv set interface lo ip address 2010:10:10::1/128
nv set interface vlan100 type svi
nv set interface vlan100 vlan 100
nv set interface vlan100 base-interface br_default
nv set interface vlan100 ip address 2030:30:30::1/64
nv set interface vlan100 ip address 30.30.30.1/24
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 100
nv set interface pf0hpf_if,pf1hpf_if bridge domain br_default
nv set vrf default router bgp router-id 10.10.10.1
nv set vrf default router bgp autonomous-system 65501
nv set vrf default router bgp path-selection multipath aspath-ignore on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
Sample Flat Files Configuration for Native Routing with Host-facing Ports as Access
Example /etc/network/interfaces configuration:
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
address 10.10.10.1/32
address 2010:10:10::1/128
auto p0_if
iface p0_if
auto p1_if
iface p1_if
auto pf0hpf_if
iface pf0hpf_if
bridge-access 100
auto pf1hpf_if
iface pf1hpf_if
bridge-access 100
auto vlan100
iface vlan100
address 2030:30:30::1/64
address 30.30.30.1/24
vlan-raw-device br_default
vlan-id 100
auto br_default
iface br_default
bridge-ports pf0hpf_if pf1hpf_if
bridge-vlan-aware yes
bridge-vids 100
bridge-pvid 1
Sample Flat Files Configuration for Native Routing with Host-facing Ports as Trunk
Example /etc/network/interfaces configuration:
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
address 10.10.10.1/32
address 2010:10:10::1/128
auto p0_if
iface p0_if
auto p1_if
iface p1_if
auto pf0hpf_if
iface pf0hpf_if
auto pf1hpf_if
iface pf1hpf_if
auto vlan100
iface vlan100
address 2030:30:30::1/64
address 30.30.30.1/24
vlan-raw-device br_default
vlan-id 100
auto br_default
iface br_default
bridge-ports pf0hpf_if pf1hpf_if
bridge-vlan-aware yes
bridge-vids 100
bridge-pvid 1
Example /etc/frr/daemons configuration:
bgpd=yes
vtysh_enable=yes
FRR Config file @ /etc/frr/frr.conf -
!
frr version 7.5+cl5.3.0u0
frr defaults datacenter
hostname BLUEFIELD2
log syslog informational
no zebra nexthop kernel enable
!
router bgp 65501
bgp router-id 10.10.10.1
bgp bestpath as-path multipath-relax
neighbor p0_if interface remote-as external
neighbor p0_if advertisement-interval 0
neighbor p0_if timers 3 9
neighbor p0_if timers connect 10
neighbor p1_if interface remote-as external
neighbor p1_if advertisement-interval 0
neighbor p1_if timers 3 9
neighbor p1_if timers connect 10
!
address-family ipv4 unicast
redistribute connected
maximum-paths 64
maximum-paths ibgp 64
exit-address-family
!
address-family ipv6 unicast
redistribute connected
neighbor p0_if activate
neighbor p1_if activate
maximum-paths 64
maximum-paths ibgp 64
exit-address-family
!
line vty
!
end
Direct Routing on Host-facing Interfaces
Host-facing interfaces (PFs and VFs) are not limited to being part of the bridge for routing. HBN supports L3-only configuration with direct routing on host-facing PFs and VFs.
Sample NVUE Configuration
nv set interface pf0hpf_if ip address 30.30.11.1/24
nv set interface pf0hpf_if ip address 2030:30:11::1/64
nv set interface pf0vf0_if ip address 30.30.13.1/24
nv set interface pf0vf0_if ip address 2030:30:13::1/64
Sample Flat File Configuration
auto pf0hpf_if
iface pf0hpf_if
address 2030:30:11::1/64
address 30.30.11.1/24
auto pf0vf0_if
iface pf0vf0_if
address 2030:30:13::1/64
address 30.30.13.1/24
BGP Peering with the Host
HBN supports the ability to establish a BGP session between the host and the HBN service running on BlueField Arm and allow the host to announce arbitrary route prefixes through the BlueField into the underlay fabric. The host can use any standard BGP protocol stack implementation to establish BGP peering with HBN.
Traffic to and from endpoints on the host gets offloaded.
Both IPv4 and IPv6 unicast AFI/SAFI are supported.
It is possible to apply route filtering for these prefixes to limit the potential security impact in this configuration.
Sample NVUE Configuration for Host BGP Peering
The following code block shows configuration to peer to host at 45.3.0.4 and 2001:cafe:1ead::4. The BGP session can be established using IPv4 or IPv6 address.
Either of these sessions can support IPv4 unicast and IPv6 unicast AFI/SAFI.
NVUE configuration for peering with host:
nv set vrf default router bgp autonomous-system 63642
nv set vrf default router bgp enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 45.3.0.4 nexthop-connected-check off
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 45.3.0.4 peer-group dpu_host
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 45.3.0.4 type numbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 2001:cafe:1ead::4 nexthop-connected-check off
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 2001:cafe:1ead::4 peer-group dpu_host
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 2001:cafe:1ead::4 type numbered
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group dpu_host address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group dpu_host address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group dpu_host remote-as external
Sample Flat Files Configuration for Host BGP peering
The following block shows configuration to peer to host at 45.3.0.4 and 2001:cafe:1ead::4. The BGP session can be established using IPv4 or IPv6 address.
frr.conf file:
router bgp 63642
bgp router-id 27.0.0.4
bgp bestpath as-path multipath-relax
neighbor dpu_host peer-group
neighbor dpu_host remote-as external
neighbor dpu_host advertisement-interval 0
neighbor dpu_host timers 3 9
neighbor dpu_host timers connect 10
neighbor dpu_host disable-connected-check
neighbor fabric peer-group
neighbor fabric remote-as external
neighbor fabric advertisement-interval 0
neighbor fabric timers 3 9
neighbor fabric timers connect 10
neighbor 45.3.0.4 peer-group dpu_host
neighbor 2001:cafe:1ead::4 peer-group dpu_host
neighbor p0_if interface peer-group fabric
neighbor p1_if interface peer-group fabric
!
address-family ipv4 unicast
neighbor dpu_host activate
!
address-family ipv6 unicast
neighbor dpu_host activate
Sample FRR configuration on the Host
Any BGP implementation can be used on the host to peer to HBN and advertise endpoints. The following is an example using FRR BGP:
Sample FRR configuration on the host:
bf2-s12# sh run
Building configuration...
Current configuration:
!
frr version 7.2.1
frr defaults traditional
hostname bf2-s12
no ip forwarding
no ipv6 forwarding
!
router bgp 1000008
!
router bgp 1000008 vrf v_200_2000
neighbor 45.3.0.2 remote-as external
neighbor 2001:cafe:1ead::2 remote-as external
!
address-family ipv4 unicast
redistribute connected
exit-address-family
!
address-family ipv6 unicast
redistribute connected
neighbor 45.3.0.2 activate
neighbor 2001:cafe:1ead::2 activate
exit-address-family
!
line vty
!
end
Sample interfaces configuration on the host:
root@bf2-s12:/home/cumulus# ifquery -a
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
address 27.0.0.7/32
address 2001:c000:10ff:f00d::7/128
auto v_200_2000
iface v_200_2000
address 60.1.0.1
address 60.1.0.2
address 60.1.0.3
address 2001:60:1::1
address 2001:60:1::2
address 2001:60:1::3
vrf-table auto
auto ens1f0np0
iface ens1f0np0
address 45.3.0.4/24
address 2001:cafe:1ead::4/64
gateway 45.3.0.1
gateway 2001:cafe:1ead::1
vrf v_200_2000
hwaddress 00:03:00:08:00:12
mtu 9162
VRF Route Leaking
VRFs are typically used when multiple independent routing and forwarding tables are desirable. However, users may want to reach destinations in one VRF from another VRF, as in the following cases:
To make a service, such as a firewall available to multiple VRFs
To enable routing to external networks or the Internet for multiple VRFs, where the external network itself is reachable through a specific VRF
Route leaking can be used to reach remote destinations as well as directly connected destinations in another VRF. Multiple VRFs can import routes from a single source VRF, and a VRF can import routes from multiple source VRFs. This can be used when a single VRF provides connectivity to external networks or a shared service for other VRFs. It is possible to control the routes leaked dynamically across VRFs with a route map.
When route leaking is used:
The
redistributecommand (notnetworkcommand) must be used in BGP to leak non-BGP routes (connected or static routes)It is not possible to leak routes between the default and non-default VRF
3769309 – Ping or other IP traffic from a locally connected host in vrfX to a local interface IP address on the BlueField/HBN in vrfY does not work, even if VRF route-leaking is enabled between these two VRFs.
In the following example commands, routes in the BGP routing table of VRF BLUE dynamically leak into VRF RED:
nv set vrf RED router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-import from-vrf list BLUE
nv config apply
The following example commands delete leaked routes from VRF BLUE to VRF
RED:
nv unset vrf RED router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-import from-vrf list BLUE
nv config apply
To exclude certain prefixes from the import process, configure the prefixes in a route map.
The following example configures a route map to match the source protocol BGP and imports the routes from VRF
BLUE
to VRF RED. For the imported routes, the community is 11:11 in VRF RED.
nv set vrf RED router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-import from-vrf list BLUE
nv set router policy route-map BLUEtoRED rule 10 match type ipv4
nv set router policy route-map BLUEtoRED rule 10 match source-protocol bgp
nv set router policy route-map BLUEtoRED rule 10 action permit
nv set router policy route-map BLUEtoRED rule 10 set community 11:11
nv set vrf RED router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-import from-vrf route-map BLUEtoRED
nv config
To check the status of the VRF route leaking, run:
NVUE command:
nv show vrf <vrf-name> router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-
importVtysh command:
show ip bgp vrf <vrf-name> ipv4|ipv6 unicast route-leak command.
For example:
nv show vrf RED router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-
importoperational applied -------------- ------------ --------- from-vrf enable on route-map BLUEtoRED [list] BLUE BLUE [route-target]10.10.10.1:3
To show more detailed status information, the following NVUE commands are available:
nv show vrf <vrf-name> router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-import from-vrfnv show vrf <vrf-name> router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-import from-vrf listnv show vrf <vrf-name> router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-import from-vrf list <leak-vrf-id>
To view the BGP routing table, run:
NVUE command:
nv show vrf <vrf-name> router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast
Vtysh command:
show ip bgp vrf <vrf-name> ipv4|ipv6 unicast
To view the FRR IP routing table, run:
Vtysh command:
show ip route vrf <vrf-name>
Or:
net show route vrf <vrf-name>
InfoThese commands show all routes, including routes leaked from other VRFs.
VLAN Subinterfaces
A VLAN subinterface is a VLAN device on an interface. The VLAN ID appends to the parent interface using dot (.) VLAN notation which is a standard way to specify a VLAN device in Linux.
For example:
A VLAN with ID 100 which is a subinterface of
p0_ifis annotated asp0_if.100The subinterface
p0_if.100only receives packets that have a VLAN 100 tag on portp0_ifAny packets transmitted from
p0_if.100would have VLAN tag 100
In HBN, VLAN subinterfaces can be created on uplink ports as well as on the host-facing PF and VF ports. A VLAN subinterface only receives traffic tagged for that VLAN.
VLAN subinterfaces are L3 interfaces and should not be added to a bridge.
In the following example, uplink subinterface on p0_if with VLAN ID 10 and a host facing subinterface on VF ports pf1vf0_if with VLAN ID 999 are created. The host-facing subinterface is also assigned with IPv4 and IPv6 addresses.
Subinterface configuration using NVUE commands:
nv set interface p0_if.10 base-interface p0_if
nv set interface p0_if.10 type sub
nv set interface p0_if.10 vlan 10
nv set interface pf1vf0_if type swp
nv set interface pf1vf0_if.999 base-interface pf1vf0_if
nv set interface pf1vf0_if.999 type sub
nv set interface pf1vf0_if.999 vlan 999
nv set interface pf1vf0_if ip address 30.30.14.1/24
nv set interface pf1vf0_if ip address 2030:30:14::1/64
Same configuration using sample flat file in /etc/network/interfaces:
subinterface configuration e/n/i file
auto p0_if.10
iface p0_if.10
auto pf1vf0_if.999
iface pf1vf0_if.999
address 2030:30:40::1/64
address 30.30.40.1/24
Ethernet Virtual Private Network – EVPN
HBN supports VXLAN with EVPN control plane for intra-subnet bridging (L2) services for IPv4 and IPv6 traffic in the overlay. For the underlay, only IPv4 or BGP unnumbered configuration is supported.
HBN supports VXLAN encapsulation only over uplink parent interfaces.
Single VXLAN Device
With a single VXLAN device, a set of VXLAN network identifiers (VNIs) represents a single device model. The single VXLAN device has a set of attributes that belong to the VXLAN construct. Individual VNIs include VLAN-to-VNI mapping which allows users to specify which VLANs are associated with which VNIs. A single VXLAN device simplifies the configuration and reduces the overhead by replacing multiple traditional VXLAN devices with a single VXLAN device.
Users may configure a single VXLAN device automatically with NVUE, or manually by editing the /etc/network/interfaces file. When users configure a single VXLAN device with NVUE, NVUE creates a unique name for the device in the following format using the bridge name as the hash key: vxlan<id>.
This example configuration performs the following steps:
Creates a single VXLAN device (vxlan21).
Maps VLAN 10 to VNI 10 and VLAN 20 to VNI 20.
Adds the VXLAN device to the default bridge.
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set bridge domain bridge vlan 10 vni 10
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set bridge domain bridge vlan 20 vni 20
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv set nve vxlan source address 10.10.10.1
cumulus@leaf01:~$ nv config apply
Alternately, edit the
/etc/network/interfaces
files, then run the
ifreload -a
command to apply the SVD configuration:
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
vxlan-local-tunnelip 10.10.10.1
auto vxlan21
iface vxlan21
bridge-vlan-vni-map 10=10 20=20
bridge-learning off
auto bridge
iface bridge
bridge-vlan-aware yes
bridge-ports vxlan21 pf0hpf_if pf1hpf_if
bridge-vids 10 20
bridge-pvid 1
Do not use a combination of single and traditional VXLAN devices.
Sample Switch Configuration for EVPN
The following is a sample NVUE config for underlay switches (NVIDIA Spectrum with Cumulus Linux) to enable EVPN deployments with HBN. It assumes that the uplinks on all BlueField devices are connected to ports swp1-4 on the switch.
nv set evpn enable on
nv set router bgp enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp autonomous-system 63640
nv set vrf default router bgp enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp1 peer-group fabric
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp1 type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp2 peer-group fabric
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp2 type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp3 peer-group fabric
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp3 type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp4 peer-group fabric
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp4 type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp path-selection multipath aspath-ignore on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family l2vpn-evpn add-path-tx off
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp router-id 27.0.0.10
nv set interface lo ip address 2001:c000:10ff:f00d::10/128
nv set interface lo ip address 27.0.0.10/32
nv set interface lo type loopback
nv set interface swp1,swp2,swp3,swp4 type swp
Layer-2 EVPN
Sample NVUE Configuration for L2 EVPN with Host-facing Ports as Access
The following is a sample NVUE configuration which has L2-VNIs (2000, 2001) for EVPN bridging on BlueField.
nv set bridge domain br_default encap 802.1Q
nv set bridge domain br_default type vlan-aware
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 200 vni 2000 flooding enable auto
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 200 vni 2000 mac-learning off
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 201 vni 2001 flooding enable auto
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 201 vni 2001 mac-learning off
nv set evpn enable on
nv set nve vxlan arp-nd-suppress on
nv set nve vxlan enable on
nv set nve vxlan mac-learning off
nv set nve vxlan source address 27.0.0.4
nv set router bgp enable on
nv set system global anycast-mac 44:38:39:42:42:07
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp autonomous-system 63642
nv set vrf default router bgp enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if peer-group fabric
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if peer-group fabric
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp path-selection multipath aspath-ignore on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family ipv4-unicast policy outbound route-map MY_ORIGIN_ASPATH_ONLY
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family ipv6-unicast policy outbound route-map MY_ORIGIN_ASPATH_ONLY
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family l2vpn-evpn add-path-tx off
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp router-id 27.0.0.4
nv set interface lo ip address 2001:c000:10ff:f00d::4/128
nv set interface lo ip address 27.0.0.4/32
nv set interface lo type loopback
nv set interface p0_if,p1_if,pf0hpf_if,pf1hpf_if type swp
nv set interface pf0hpf_if bridge domain br_default access 200
nv set interface pf1hpf_if bridge domain br_default access 201
nv set interface vlan200-201 base-interface br_default
nv set interface vlan200-201 ip ipv4 forward on
nv set interface vlan200-201 ip ipv6 forward on
nv set interface vlan200-201 ip vrr enable on
nv set interface vlan200-201 ip vrr state up
nv set interface vlan200-201 link mtu 9050
nv set interface vlan200-201 type svi
nv set interface vlan200 ip address 2001:cafe:1ead::3/64
nv set interface vlan200 ip address 45.3.0.2/24
nv set interface vlan200 ip vrr address 2001:cafe:1ead::1/64
nv set interface vlan200 ip vrr address 45.3.0.1/24
nv set interface vlan200 vlan 200
nv set interface vlan201 ip address 2001:cafe:1ead:1::3/64
nv set interface vlan201 ip address 45.3.1.2/24
nv set interface vlan201 ip vrr address 2001:cafe:1ead:1::1/64
nv set interface vlan201 ip vrr address 45.3.1.1/24
nv set interface vlan201 vlan 201
Sample NVUE Configuration for L2 EVPN with Host-facing Ports as Trunk
The following is a sample NVUE configuration which has L2-VNIs (2000, 2001) for EVPN bridging on BlueField.
nv set bridge domain br_default encap 802.1Q
nv set bridge domain br_default type vlan-aware
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 200 vni 2000 flooding enable auto
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 200 vni 2000 mac-learning off
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 201 vni 2001 flooding enable auto
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 201 vni 2001 mac-learning off
nv set evpn enable on
nv set nve vxlan arp-nd-suppress on
nv set nve vxlan enable on
nv set nve vxlan mac-learning off
nv set nve vxlan source address 27.0.0.4
nv set router bgp enable on
nv set system global anycast-mac 44:38:39:42:42:07
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp autonomous-system 63642
nv set vrf default router bgp enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if peer-group fabric
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if peer-group fabric
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp path-selection multipath aspath-ignore on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family ipv4-unicast policy outbound route-map MY_ORIGIN_ASPATH_ONLY
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family ipv6-unicast policy outbound route-map MY_ORIGIN_ASPATH_ONLY
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family l2vpn-evpn add-path-tx off
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp router-id 27.0.0.4
nv set interface lo ip address 2001:c000:10ff:f00d::4/128
nv set interface lo ip address 27.0.0.4/32
nv set interface lo type loopback
nv set interface p0_if,p1_if,pf0hpf_if,pf1hpf_if type swp
nv set interface pf0hpf_if bridge domain br_default
nv set interface pf1hpf_if bridge domain br_default
nv set interface vlan200-201 base-interface br_default
nv set interface vlan200-201 ip ipv4 forward on
nv set interface vlan200-201 ip ipv6 forward on
nv set interface vlan200-201 ip vrr enable on
nv set interface vlan200-201 ip vrr state up
nv set interface vlan200-201 link mtu 9050
nv set interface vlan200-201 type svi
nv set interface vlan200 ip address 2001:cafe:1ead::3/64
nv set interface vlan200 ip address 45.3.0.2/24
nv set interface vlan200 ip vrr address 2001:cafe:1ead::1/64
nv set interface vlan200 ip vrr address 45.3.0.1/24
nv set interface vlan200 vlan 200
nv set interface vlan201 ip address 2001:cafe:1ead:1::3/64
nv set interface vlan201 ip address 45.3.1.2/24
nv set interface vlan201 ip vrr address 2001:cafe:1ead:1::1/64
nv set interface vlan201 ip vrr address 45.3.1.1/24
nv set interface vlan201 vlan 201
Sample Flat Files Configuration for L2 EVPN with Host-facing Ports as Access
The following is a sample flat files configuration which has L2-VNIs (vx-2000, vx-2001) for EVPN bridging on BlueField. This file is located at /etc/network/interfaces:
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
address 2001:c000:10ff:f00d::4/128
address 27.0.0.4/32
vxlan-local-tunnelip 27.0.0.4
auto p0_if
iface p0_if
auto p1_if
iface p1_if
auto pf0hpf_if
iface pf0hpf_if
bridge-access 200
auto pf1hpf_if
iface pf1hpf_if
bridge-access 201
auto vlan200
iface vlan200
address 2001:cafe:1ead::3/64
address 45.3.0.2/24
mtu 9050
address-virtual 00:00:5e:00:01:01 2001:cafe:1ead::1/64 45.3.0.1/24
vlan-raw-device br_default
vlan-id 200
auto vlan201
iface vlan201
address 2001:cafe:1ead:1::3/64
address 45.3.1.2/24
mtu 9050
address-virtual 00:00:5e:00:01:01 2001:cafe:1ead:1::1/64 45.3.1.1/24
vlan-raw-device br_default
vlan-id 201
auto vxlan48
iface vxlan48
bridge-vlan-vni-map 200=2000 201=2001
217=2017
bridge-learning off
auto br_default
iface br_default
bridge-ports pf0hpf_if pf1hpf_if vxlan48
bridge-vlan-aware yes
bridge-vids 200 201
bridge-pvid 1
Sample Flat Files Configuration for L2 EVPN with Host-facing Ports as Trunk
The following is a sample flat files configuration which has L2-VNIs (vx-2000, vx-2001) for EVPN bridging on BlueField. This file is located at /etc/network/interfaces:
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
address 2001:c000:10ff:f00d::4/128
address 27.0.0.4/32
vxlan-local-tunnelip 27.0.0.4
auto p0_if
iface p0_if
auto p1_if
iface p1_if
auto pf0hpf_if
iface pf0hpf_if
auto pf1hpf_if
iface pf1hpf_if
auto vlan200
iface vlan200
address 2001:cafe:1ead::3/64
address 45.3.0.2/24
mtu 9050
address-virtual 00:00:5e:00:01:01 2001:cafe:1ead::1/64 45.3.0.1/24
vlan-raw-device br_default
vlan-id 200
auto vlan201
iface vlan201
address 2001:cafe:1ead:1::3/64
address 45.3.1.2/24
mtu 9050
address-virtual 00:00:5e:00:01:01 2001:cafe:1ead:1::1/64 45.3.1.1/24
vlan-raw-device br_default
vlan-id 201
auto vxlan48
iface vxlan48
bridge-vlan-vni-map 200=2000 201=2001
217=2017
bridge-learning off
auto br_default
iface br_default
bridge-ports pf0hpf_if pf1hpf_if vxlan48
bridge-vlan-aware yes
bridge-vids 200 201
bridge-pvid 1
This file tells the frr package which daemon to start and is located at /etc/frr/daemons:
bgpd=yes
ospfd=no
ospf6d=no
isisd=no
pimd=no
ldpd=no
pbrd=no
vrrpd=no
fabricd=no
nhrpd=no
eigrpd=no
babeld=no
sharpd=no
fabricd=no
ripngd=no
ripd=no
vtysh_enable=yes
zebra_options=" -M cumulus_mlag -M snmp -A 127.0.0.1 -s 90000000"
bgpd_options=" -M snmp -A 127.0.0.1"
ospfd_options=" -M snmp -A 127.0.0.1"
ospf6d_options=" -M snmp -A ::1"
ripd_options=" -A 127.0.0.1"
ripngd_options=" -A ::1"
isisd_options=" -A 127.0.0.1"
pimd_options=" -A 127.0.0.1"
ldpd_options=" -A 127.0.0.1"
nhrpd_options=" -A 127.0.0.1"
eigrpd_options=" -A 127.0.0.1"
babeld_options=" -A 127.0.0.1"
sharpd_options=" -A 127.0.0.1"
pbrd_options=" -A 127.0.0.1"
staticd_options="-A 127.0.0.1"
fabricd_options="-A 127.0.0.1"
vrrpd_options=" -A 127.0.0.1"
frr_profile="datacenter"
FRR configuration file is located at /etc/frr/frr.conf:
!---- Cumulus Defaults ----
frr defaults datacenter
log syslog informational
no zebra nexthop kernel enable
vrf default
outer bgp 63642 vrf default
bgp router-id 27.0.0.4
bgp bestpath as-path multipath-relax
timers bgp 3 9
bgp deterministic-med
! Neighbors
neighbor fabric peer-group
neighbor fabric remote-as external
neighbor fabric timers 3 9
neighbor fabric timers connect 10
neighbor fabric advertisement-interval 0
neighbor p0_if interface peer-group fabric
neighbor p1_if interface peer-group fabric
address-family ipv4 unicast
maximum-paths ibgp 64
maximum-paths 64
distance bgp 20 200 200
neighbor fabric activate
exit-address-family
address-family ipv6 unicast
maximum-paths ibgp 64
maximum-paths 64
distance bgp 20 200 200
neighbor fabric activate
exit-address-family
address-family l2vpn evpn
advertise-all-vni
neighbor fabric activate
exit-address-family
Layer-3 EVPN with Symmetric Routing
In distributed symmetric routing, each VXLAN endpoint (VTEP) acts as a layer-3 gateway, performing routing for its attached hosts. However, both the ingress VTEP and egress VTEP route the packets (similar to traditional routing behavior of routing to a next-hop router). In a VXLAN encapsulated packet, the inner destination MAC address is the router MAC address of the egress VTEP to indicate that the egress VTEP is the next hop and that it must also perform the routing.
All routing happens in the context of a tenant (VRF). For a packet that the ingress VTEP receives from a locally attached host, the SVI interface corresponding to the VLAN determines the VRF. For a packet that the egress VTEP receives over the VXLAN tunnel, the VNI in the packet has to specify the VRF. For symmetric routing, this is a VNI corresponding to the tenant and is different from either the source VNI or the destination VNI. This VNI is a layer-3 VNI or interconnecting VNI. The regular VNI, which maps a VLAN, is the layer-2 VNI.
Refer to the Cumulus Linux Symmetric Routing .
HBN uses a one-to-one mapping between an L3 VNI and a tenant (VRF).
The VRF to L3 VNI mapping must be consistent across all VTEPs.
An L3 VNI and an L2 VNI cannot have the same ID.
In an EVPN symmetric routing configuration, when the switch announces a type-2 (MAC/IP) route, in addition to containing two VNIs (L2 and L3 VNIs), the route also contains separate route targets (RTs) for L2 and L3. The L3 RT associates the route with the tenant VRF. By default, this is auto-derived using the L3 VNI instead of the L2 VNI. However, this is configurable.
Sample NVUE Configuration for L3 EVPN with Host-facing Ports as Access
If using NVUE to configure EVPN symmetric routing, the following is a sample configuration using NVUE commands:
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 111 vni 1000111
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 112 vni 1000112
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 213 vni 1000213
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 214 vni 1000214
nv set evpn enable on
nv set interface lo ip address 6.0.0.19/32
nv set interface lo type loopback
nv set interface p0_if description 'alias p0_if to leaf-21 swp3'
nv set interface p0_if,p1_if,pf0hpf_if,pf0vf0_if,pf1hpf_if,pf1vf0_if type swp
nv set interface p1_if description 'alias p1_if to leaf-22 swp3'
nv set interface pf0hpf_if bridge domain br_default access 111
nv set interface pf0hpf_if description 'alias pf0hpf_if to host-211 ens2f0np0'
nv set interface pf0vf0_if bridge domain br_default access 112
nv set interface pf0vf0_if description 'alias pf0vf0_if to host-211 ens2f0np0v0'
nv set interface pf1hpf_if bridge domain br_default access 213
nv set interface pf1hpf_if description 'alias pf1hpf_if to host-211 ens2f1np1'
nv set interface pf1vf0_if bridge domain br_default access 214
nv set interface pf1vf0_if description 'alias pf1vf0_if to host-211 ens2f1np0v0'
nv set interface vlan111 ip address 60.1.1.21/24
nv set interface vlan111 ip address 2060:1:1:1::21/64
nv set interface vlan111 ip vrr address 60.1.1.250/24
nv set interface vlan111 ip vrr address 2060:1:1:1::250/64
nv set interface vlan111 vlan 111
nv set interface vlan111,213 ip vrf vrf2
nv set interface vlan111-112,213-214 ip vrr enable on
nv set interface vlan111-112,213-214 ip vrr mac-address 00:00:5e:00:01:01
nv set interface vlan111-112,213-214 ip ipv4 forward on
nv set interface vlan111-112,213-214 ip ipv6 forward on
nv set interface vlan111-112,213-214 type svi
nv set interface vlan112 ip address 50.1.1.21/24
nv set interface vlan112 ip address 2050:1:1:1::21/64
nv set interface vlan112 ip vrr address 50.1.1.250/24
nv set interface vlan112 ip vrr address 2050:1:1:1::250/64
nv set interface vlan112 vlan 112
nv set interface vlan112,214 ip vrf vrf1
nv set interface vlan213 ip address 60.1.210.21/24
nv set interface vlan213 ip address 2060:1:1:210::21/64
nv set interface vlan213 ip vrr address 60.1.210.250/24
nv set interface vlan213 ip vrr address 2060:1:1:210::250/64
nv set interface vlan213 vlan 213
nv set interface vlan214 ip address 50.1.210.21/24
nv set interface vlan214 ip address 2050:1:1:210::21/64
nv set interface vlan214 ip vrr address 50.1.210.250/24
nv set interface vlan214 ip vrr address 2050:1:1:210::250/64
nv set interface vlan214 vlan 214
nv set nve vxlan arp-nd-suppress on
nv set nve vxlan enable on
nv set nve vxlan source address 6.0.0.19
nv set platform
nv set router bgp enable on
nv set router policy route-map ALLOW_LOBR rule 10 action permit
nv set router policy route-map ALLOW_LOBR rule 10 match interface lo
nv set router policy route-map ALLOW_LOBR rule 20 action permit
nv set router policy route-map ALLOW_LOBR rule 20 match interface br_default
nv set router policy route-map ALLOW_VRF1 rule 10 action permit
nv set router policy route-map ALLOW_VRF1 rule 10 match interface vrf1
nv set router policy route-map ALLOW_VRF2 rule 10 action permit
nv set router policy route-map ALLOW_VRF2 rule 10 match interface vrf2
nv set router vrr enable on
nv set system global system-mac 00:01:00:00:1e:03
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast multipaths ebgp 16
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected route-map ALLOW_LOBR
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp autonomous-system 650019
nv set vrf default router bgp enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if address-family l2vpn-evpn add-path-tx off
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if peer-group TOR_LEAF_SPINE
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if address-family l2vpn-evpn add-path-tx off
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if peer-group TOR_LEAF_SPINE
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp path-selection multipath aspath-ignore on
nv set vrf default router bgp path-selection routerid-compare on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group TOR_LEAF_SPINE address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp router-id 6.0.0.19
nv set vrf vrf1 evpn enable on
nv set vrf vrf1 evpn vni 104001
nv set vrf vrf1 loopback ip address 50.1.21.21/32
nv set vrf vrf1 loopback ip address 2050:50:50:21::21/128
nv set vrf vrf1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf vrf1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf vrf1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected route-map ALLOW_VRF1
nv set vrf vrf1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf vrf1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf vrf1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf vrf1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected route-map ALLOW_VRF1
nv set vrf vrf1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf vrf1 router bgp autonomous-system 650019
nv set vrf vrf1 router bgp enable on
nv set vrf vrf1 router bgp router-id 50.1.21.21
nv set vrf vrf2 evpn enable on
nv set vrf vrf2 evpn vni 104002
nv set vrf vrf2 loopback ip address 60.1.21.21/32
nv set vrf vrf2 loopback ip address 2060:60:60:21::21/128
nv set vrf vrf2 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf vrf2 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf vrf2 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected route-map ALLOW_VRF2
nv set vrf vrf2 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf vrf2 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf vrf2 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf vrf2 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected route-map ALLOW_VRF2
nv set vrf vrf2 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf vrf2 router bgp autonomous-system 650019
nv set vrf vrf2 router bgp enable on
nv set vrf vrf2 router bgp router-id 60.1.21.21
Sample NVUE Configuration for L3 EVPN with Host-facing Ports as Trunk
If using NVUE to configure EVPN symmetric routing, the following is a sample configuration using NVUE commands:
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 111 vni 1000111
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 112 vni 1000112
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 213 vni 1000213
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 214 vni 1000214
nv set evpn enable on
nv set interface lo ip address 6.0.0.19/32
nv set interface lo type loopback
nv set interface p0_if description 'alias p0_if to leaf-21 swp3'
nv set interface p0_if,p1_if,pf0hpf_if,pf0vf0_if,pf1hpf_if,pf1vf0_if type swp
nv set interface p1_if description 'alias p1_if to leaf-22 swp3'
nv set interface pf0hpf_if bridge domain br_default
nv set interface pf0hpf_if description 'alias pf0hpf_if to host-211 ens2f0np0'
nv set interface pf0vf0_if bridge domain br_default
nv set interface pf0vf0_if description 'alias pf0vf0_if to host-211 ens2f0np0v0'
nv set interface pf1hpf_if bridge domain br_default
nv set interface pf1hpf_if description 'alias pf1hpf_if to host-211 ens2f1np1'
nv set interface pf1vf0_if bridge domain br_default
nv set interface pf1vf0_if description 'alias pf1vf0_if to host-211 ens2f1np0v0'
nv set interface vlan111 ip address 60.1.1.21/24
nv set interface vlan111 ip address 2060:1:1:1::21/64
nv set interface vlan111 ip vrr address 60.1.1.250/24
nv set interface vlan111 ip vrr address 2060:1:1:1::250/64
nv set interface vlan111 vlan 111
nv set interface vlan111,213 ip vrf vrf2
nv set interface vlan111-112,213-214 ip vrr enable on
nv set interface vlan111-112,213-214 ip vrr mac-address 00:00:5e:00:01:01
nv set interface vlan111-112,213-214 ip ipv4 forward on
nv set interface vlan111-112,213-214 ip ipv6 forward on
nv set interface vlan111-112,213-214 type svi
nv set interface vlan112 ip address 50.1.1.21/24
nv set interface vlan112 ip address 2050:1:1:1::21/64
nv set interface vlan112 ip vrr address 50.1.1.250/24
nv set interface vlan112 ip vrr address 2050:1:1:1::250/64
nv set interface vlan112 vlan 112
nv set interface vlan112,214 ip vrf vrf1
nv set interface vlan213 ip address 60.1.210.21/24
nv set interface vlan213 ip address 2060:1:1:210::21/64
nv set interface vlan213 ip vrr address 60.1.210.250/24
nv set interface vlan213 ip vrr address 2060:1:1:210::250/64
nv set interface vlan213 vlan 213
nv set interface vlan214 ip address 50.1.210.21/24
nv set interface vlan214 ip address 2050:1:1:210::21/64
nv set interface vlan214 ip vrr address 50.1.210.250/24
nv set interface vlan214 ip vrr address 2050:1:1:210::250/64
nv set interface vlan214 vlan 214
nv set nve vxlan arp-nd-suppress on
nv set nve vxlan enable on
nv set nve vxlan source address 6.0.0.19
nv set platform
nv set router bgp enable on
nv set router policy route-map ALLOW_LOBR rule 10 action permit
nv set router policy route-map ALLOW_LOBR rule 10 match interface lo
nv set router policy route-map ALLOW_LOBR rule 20 action permit
nv set router policy route-map ALLOW_LOBR rule 20 match interface br_default
nv set router policy route-map ALLOW_VRF1 rule 10 action permit
nv set router policy route-map ALLOW_VRF1 rule 10 match interface vrf1
nv set router policy route-map ALLOW_VRF2 rule 10 action permit
nv set router policy route-map ALLOW_VRF2 rule 10 match interface vrf2
nv set router vrr enable on
nv set system global system-mac 00:01:00:00:1e:03
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast multipaths ebgp 16
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected route-map ALLOW_LOBR
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp autonomous-system 650019
nv set vrf default router bgp enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if address-family l2vpn-evpn add-path-tx off
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if peer-group TOR_LEAF_SPINE
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if address-family l2vpn-evpn add-path-tx off
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if peer-group TOR_LEAF_SPINE
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp path-selection multipath aspath-ignore on
nv set vrf default router bgp path-selection routerid-compare on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group TOR_LEAF_SPINE address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp router-id 6.0.0.19
nv set vrf vrf1 evpn enable on
nv set vrf vrf1 evpn vni 104001
nv set vrf vrf1 loopback ip address 50.1.21.21/32
nv set vrf vrf1 loopback ip address 2050:50:50:21::21/128
nv set vrf vrf1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf vrf1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf vrf1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected route-map ALLOW_VRF1
nv set vrf vrf1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf vrf1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf vrf1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf vrf1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected route-map ALLOW_VRF1
nv set vrf vrf1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf vrf1 router bgp autonomous-system 650019
nv set vrf vrf1 router bgp enable on
nv set vrf vrf1 router bgp router-id 50.1.21.21
nv set vrf vrf2 evpn enable on
nv set vrf vrf2 evpn vni 104002
nv set vrf vrf2 loopback ip address 60.1.21.21/32
nv set vrf vrf2 loopback ip address 2060:60:60:21::21/128
nv set vrf vrf2 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf vrf2 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf vrf2 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected route-map ALLOW_VRF2
nv set vrf vrf2 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf vrf2 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf vrf2 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf vrf2 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected route-map ALLOW_VRF2
nv set vrf vrf2 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf vrf2 router bgp autonomous-system 650019
nv set vrf vrf2 router bgp enable on
nv set vrf vrf2 router bgp router-id 60.1.21.21
Sample Flat Files Configuration for L3 EVPN for Host-facing Interfaces as Access
The following is a sample flat file configuration which has L2 VNIs and L3 VNIs for EVPN bridging and symmetric routing on BlueField.
This file is located in /etc/network/interfaces:
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
address 6.0.0.19/32
vxlan-local-tunnelip 6.0.0.19
auto vrf1
iface vrf1
address 2050:50:50:21::21/128
address 50.1.21.21/32
vrf-table auto
auto vrf2
iface vrf2
address 2060:60:60:21::21/128
address 60.1.21.21/32
vrf-table auto
auto p0_if
iface p0_if
alias alias p0_if to leaf-21 swp3
auto p1_if
iface p1_if
alias alias p1_if to leaf-22 swp3
auto pf0hpf_if
iface pf0hpf_if
alias alias pf0hpf_if to host-211 ens2f0np0
bridge-access 111
auto pf0vf0_if
iface pf0vf0_if
alias alias pf0vf0_if to host-211 ens2f0np0v0
bridge-access 112
auto pf1hpf_if
iface pf1hpf_if
alias alias pf1hpf_if to host-211 ens2f1np1
bridge-access 213
auto pf1vf0_if
iface pf1vf0_if
alias alias pf1vf0_if to host-211 ens2f1np0v0
bridge-access 214
auto vlan111
iface vlan111
address 2060:1:1:1::21/64
address 60.1.1.21/24
address-virtual 00:00:5e:00:01:01 2060:1:1:1::250/64 60.1.1.250/24
hwaddress 00:01:00:00:1e:03
vrf vrf2
vlan-raw-device br_default
vlan-id 111
auto vlan112
iface vlan112
address 2050:1:1:1::21/64
address 50.1.1.21/24
address-virtual 00:00:5e:00:01:01 2050:1:1:1::250/64 50.1.1.250/24
hwaddress 00:01:00:00:1e:03
vrf vrf1
vlan-raw-device br_default
vlan-id 112
auto vlan213
iface vlan213
address 2060:1:1:210::21/64
address 60.1.210.21/24
address-virtual 00:00:5e:00:01:01 2060:1:1:210::250/64 60.1.210.250/24
hwaddress 00:01:00:00:1e:03
vrf vrf2
vlan-raw-device br_default
vlan-id 213
auto vlan214
iface vlan214
address 2050:1:1:210::21/64
address 50.1.210.21/24
address-virtual 00:00:5e:00:01:01 2050:1:1:210::250/64 50.1.210.250/24
hwaddress 00:01:00:00:1e:03
vrf vrf1
vlan-raw-device br_default
vlan-id 214
auto vlan4058_l3
iface vlan4058_l3
vrf vrf1
vlan-raw-device br_default
address-virtual none
vlan-id 4058
auto vlan4059_l3
iface vlan4059_l3
vrf vrf2
vlan-raw-device br_default
address-virtual none
vlan-id 4059
auto vxlan48
iface vxlan48
bridge-vlan-vni-map 111=1000111 112=1000112 213=1000213 214=1000214 4058=104001 4059=104002
bridge-learning off
auto br_default
iface br_default
bridge-ports pf0hpf_if pf0vf0_if pf1hpf_if pf1vf0_if vxlan48
hwaddress 00:01:00:00:1e:03
bridge-vlan-aware yes
bridge-vids 111 112 213 214
bridge-pvid 1
Sample Flat Files Configuration for L3 EVPN for Host-facing Interfaces as Trunk
The following is a sample flat file configuration which has L2 VNIs and L3 VNIs for EVPN bridging and symmetric routing on BlueField.
This file is located in /etc/network/interfaces:
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
address 6.0.0.19/32
vxlan-local-tunnelip 6.0.0.19
auto vrf1
iface vrf1
address 2050:50:50:21::21/128
address 50.1.21.21/32
vrf-table auto
auto vrf2
iface vrf2
address 2060:60:60:21::21/128
address 60.1.21.21/32
vrf-table auto
auto p0_if
iface p0_if
alias alias p0_if to leaf-21 swp3
auto p1_if
iface p1_if
alias alias p1_if to leaf-22 swp3
auto pf0hpf_if
iface pf0hpf_if
alias alias pf0hpf_if to host-211 ens2f0np0
auto pf0vf0_if
iface pf0vf0_if
alias alias pf0vf0_if to host-211 ens2f0np0v0
auto pf1hpf_if
iface pf1hpf_if
alias alias pf1hpf_if to host-211 ens2f1np1
auto pf1vf0_if
iface pf1vf0_if
alias alias pf1vf0_if to host-211 ens2f1np0v0
auto vlan111
iface vlan111
address 2060:1:1:1::21/64
address 60.1.1.21/24
address-virtual 00:00:5e:00:01:01 2060:1:1:1::250/64 60.1.1.250/24
hwaddress 00:01:00:00:1e:03
vrf vrf2
vlan-raw-device br_default
vlan-id 111
auto vlan112
iface vlan112
address 2050:1:1:1::21/64
address 50.1.1.21/24
address-virtual 00:00:5e:00:01:01 2050:1:1:1::250/64 50.1.1.250/24
hwaddress 00:01:00:00:1e:03
vrf vrf1
vlan-raw-device br_default
vlan-id 112
auto vlan213
iface vlan213
address 2060:1:1:210::21/64
address 60.1.210.21/24
address-virtual 00:00:5e:00:01:01 2060:1:1:210::250/64 60.1.210.250/24
hwaddress 00:01:00:00:1e:03
vrf vrf2
vlan-raw-device br_default
vlan-id 213
auto vlan214
iface vlan214
address 2050:1:1:210::21/64
address 50.1.210.21/24
address-virtual 00:00:5e:00:01:01 2050:1:1:210::250/64 50.1.210.250/24
hwaddress 00:01:00:00:1e:03
vrf vrf1
vlan-raw-device br_default
vlan-id 214
auto vlan4058_l3
iface vlan4058_l3
vrf vrf1
vlan-raw-device br_default
address-virtual none
vlan-id 4058
auto vlan4059_l3
iface vlan4059_l3
vrf vrf2
vlan-raw-device br_default
address-virtual none
vlan-id 4059
auto vxlan48
iface vxlan48
bridge-vlan-vni-map 111=1000111 112=1000112 213=1000213 214=1000214 4058=104001 4059=104002
bridge-learning off
auto br_default
iface br_default
bridge-ports pf0hpf_if pf0vf0_if pf1hpf_if pf1vf0_if vxlan48
hwaddress 00:01:00:00:1e:03
bridge-vlan-aware yes
bridge-vids 111 112 213 214
bridge-pvid 1
The FRR configuration is located in /etc/frr/frr.conf:
frr version 8.4.3
frr defaults datacenter
hostname doca-hbn-service-bf3-s05-1-ipmi
log syslog informational
no zebra nexthop kernel enable
service integrated-vtysh-config
!
vrf vrf1
vni 104001
exit-vrf
!
vrf vrf2
vni 104002
exit-vrf
!
router bgp 650019
bgp router-id 6.0.0.19
bgp bestpath as-path multipath-relax
bgp bestpath compare-routerid
neighbor TOR_LEAF_SPINE peer-group
neighbor TOR_LEAF_SPINE advertisement-interval 0
neighbor TOR_LEAF_SPINE timers 3 9
neighbor TOR_LEAF_SPINE timers connect 10
neighbor p0_if interface peer-group TOR_LEAF_SPINE
neighbor p0_if remote-as external
neighbor p0_if advertisement-interval 0
neighbor p0_if timers 3 9
neighbor p0_if timers connect 10
neighbor p1_if interface peer-group TOR_LEAF_SPINE
neighbor p1_if remote-as external
neighbor p1_if advertisement-interval 0
neighbor p1_if timers 3 9
neighbor p1_if timers connect 10
!
address-family ipv4 unicast
redistribute connected route-map ALLOW_LOBR
maximum-paths 16
maximum-paths ibgp 64
exit-address-family
!
address-family l2vpn evpn
neighbor p0_if activate
neighbor p1_if activate
advertise-all-vni
exit-address-family
exit
!
router bgp 650019 vrf vrf1
bgp router-id 50.1.21.21
!
address-family ipv4 unicast
redistribute connected route-map ALLOW_VRF1
maximum-paths 64
maximum-paths ibgp 64
exit-address-family
!
address-family ipv6 unicast
redistribute connected route-map ALLOW_VRF1
maximum-paths 64
maximum-paths ibgp 64
exit-address-family
!
address-family l2vpn evpn
advertise ipv4 unicast
advertise ipv6 unicast
exit-address-family
exit
!
router bgp 650019 vrf vrf2
bgp router-id 60.1.21.21
!
address-family ipv4 unicast
redistribute connected route-map ALLOW_VRF2
maximum-paths 64
maximum-paths ibgp 64
exit-address-family
!
address-family ipv6 unicast
redistribute connected route-map ALLOW_VRF2
maximum-paths 64
maximum-paths ibgp 64
exit-address-family
!
address-family l2vpn evpn
advertise ipv4 unicast
advertise ipv6 unicast
exit-address-family
exit
!
route-map ALLOW_LOBR permit 10
match interface lo
exit
!
route-map ALLOW_LOBR permit 20
match interface br_default
exit
!
route-map ALLOW_VRF1 permit 10
match interface vrf1
exit
!
route-map ALLOW_VRF2 permit 10
match interface vrf2
exit
Multi-hop eBGP Peering for EVPN (Route Server in Symmetric EVPN Routing)
eBGP multi-hop peering for EVPN support in a route server-like role in EVPN topology, allows the deployment of EVPN on any cloud that supports IP transport.
R oute servers and BF/HBN VTEPs are connected via the IP cloud. That is:
Switches in the cloud provider need not be EVPN-aware
Switches in the provider fabric provide IPv4 and IPv6 transport and do not have to support EVPN
Sample Route Server Configuration for EVPN
The following is a sample configuration of an Ubuntu server running FRR 9.0 stable, configured as EVPN route server and an HBN VTEP that is peering to two spine switches for IP connectivity and 3 Route servers for EVPN overlay control.
root@sn1:/home/cumulus# uname -a
Linux sn1 5.15.0-88-generic #98-Ubuntu SMP Mon Oct 2 15:18:56 UTC 2023 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
root@sn1:/home/cumulus# dpkg -l frr
Desired=Unknown/Install/Remove/Purge/Hold
| Status=Not/Inst/Conf-files/Unpacked/halF-conf/Half-inst/trig-aWait/Trig-pend
|/ Err?=(none)/Reinst-required (Status,Err: uppercase=bad)
||/ Name Version Architecture Description
+++-==============-=====================-============-=============================================================
ii frr 9.0.1-0~ubuntu22.04.1 amd64 FRRouting suite of internet protocols (BGP, OSPF, IS-IS, ...)
root@sn1:/home/cumulus#
FRR configuration (frr.conf):
sn1# sh run
Building configuration...
Current configuration:
!
frr version 9.0.1
frr defaults datacenter
hostname sn1
no ip forwarding
no ipv6 forwarding
service integrated-vtysh-config
!
router bgp 4200065507
bgp router-id 6.0.0.7
timers bgp 60 180
neighbor rclients peer-group
neighbor rclients remote-as external
neighbor rclients ebgp-multihop 10
neighbor rclients update-source lo
neighbor rclients advertisement-interval 0
neighbor rclients timers 3 9
neighbor rclients timers connect 10
neighbor rcsuper peer-group
neighbor rcsuper remote-as external
neighbor rcsuper advertisement-interval 0
neighbor rcsuper timers 3 9
neighbor rcsuper timers connect 10
neighbor swp1 interface peer-group rcsuper
bgp listen range 6.0.0.0/24 peer-group rclients
!
address-family ipv4 unicast
redistribute connected
neighbor fabric route-map pass in
neighbor fabric route-map pass out
no neighbor rclients activate
maximum-paths 64
maximum-paths ibgp 64
exit-address-family
!
address-family l2vpn evpn
neighbor rclients activate
neighbor rcsuper activate
exit-address-family
exit
!
route-map pass permit 10
set community 11:11 additive
exit
!
end
sn1#
Interfaces configuration (/etc/network/interfaces):
root@sn1:/home/cumulus# ifquery -a
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
address 6.0.0.7/32
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
auto swp1
iface swp1
auto eth0
iface eth0
address 192.168.0.15/24
gateway 192.168.0.2
root@sn1:/home/cumulus#
Sample HBN Configuration for Deployments with EVPN Route Server
root@doca-hbn-service-bf2-s12-1-ipmi:/tmp# nv config show -o commands
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 101 vni 10101
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 102 vni 10102
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 201 vni 10201
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 202 vni 10202
nv set evpn enable on
nv set evpn route-advertise svi-ip off
nv set interface ilan3200 ip vrf internet1
nv set interface ilan3200 vlan 3200
nv set interface ilan3200,slan3201,vlan101-102,201-202,3001-3002 base-interface br_default
nv set interface ilan3200,slan3201,vlan101-102,201-202,3001-3002 type svi
nv set interface lo ip address 6.0.0.13/32
nv set interface lo ip address 2001::13/128
nv set interface lo type loopback
nv set interface p0_if,p1_if,pf0hpf_if,pf0vf0_if,pf0vf1_if,pf0vf2_if,pf0vf3_if,pf1hpf_if type swp
nv set interface pf0vf0_if bridge domain br_default access 101
nv set interface pf0vf1_if bridge domain br_default access 102
nv set interface pf0vf2_if bridge domain br_default access 201
nv set interface pf0vf3_if bridge domain br_default access 202
nv set interface slan3201 ip vrf special1
nv set interface slan3201 vlan 3201
nv set interface vlan101 ip address 21.1.0.13/16
nv set interface vlan101 ip address 2020:0:1:1::13/64
nv set interface vlan101 ip vrr address 21.1.0.250/16
nv set interface vlan101 ip vrr address 2020:0:1:1::250/64
nv set interface vlan101 ip vrr mac-address 00:00:01:00:00:65
nv set interface vlan101 vlan 101
nv set interface vlan101-102,201-202 ip vrr enable on
nv set interface vlan101-102,3001 ip vrf tenant1
nv set interface vlan102 ip address 21.2.0.13/16
nv set interface vlan102 ip address 2020:0:1:2::13/64
nv set interface vlan102 ip vrr address 21.2.0.250/16
nv set interface vlan102 ip vrr address 2020:0:1:2::250/64
nv set interface vlan102 ip vrr mac-address 00:00:01:00:00:66
nv set interface vlan102 vlan 102
nv set interface vlan201 ip address 22.1.0.13/16
nv set interface vlan201 ip address 2020:0:2:1::13/64
nv set interface vlan201 ip vrr address 22.1.0.250/16
nv set interface vlan201 ip vrr address 2020:0:2:1::250/64
nv set interface vlan201 ip vrr mac-address 00:00:02:00:00:c9
nv set interface vlan201 vlan 201
nv set interface vlan201-202,3002 ip vrf tenant2
nv set interface vlan202 ip address 22.2.0.13/16
nv set interface vlan202 ip address 2020:0:2:2::13/64
nv set interface vlan202 ip vrr address 22.2.0.250/16
nv set interface vlan202 ip vrr address 2020:0:2:2::250/64
nv set interface vlan202 ip vrr mac-address 00:00:02:00:00:ca
nv set interface vlan202 vlan 202
nv set interface vlan3001 vlan 3001
nv set interface vlan3002 vlan 3002
nv set nve vxlan arp-nd-suppress on
nv set nve vxlan enable on
nv set nve vxlan source address 6.0.0.13
nv set platform
nv set router bgp autonomous-system 4200065011
nv set router bgp enable on
nv set router bgp router-id 6.0.0.13
nv set router vrr enable on
nv set system config snippet
nv set system global
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 6.0.0.7 peer-group rservers
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 6.0.0.7 type numbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 6.0.0.8 peer-group rservers
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 6.0.0.8 type numbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 6.0.0.9 peer-group rservers
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 6.0.0.9 type numbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if peer-group fabric
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if peer-group fabric
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rservers address-family ipv4-unicast enable off
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rservers address-family l2vpn-evpn add-path-tx off
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rservers address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rservers multihop-ttl 3
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rservers remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rservers update-source lo
nv set vrf internet1 evpn enable on
nv set vrf internet1 evpn vni 42000
nv set vrf internet1 loopback ip address 8.1.0.13/32
nv set vrf internet1 loopback ip address 2008:0:1::13/64
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp enable on
nv set vrf special1 evpn enable on
nv set vrf special1 evpn vni 42001
nv set vrf special1 loopback ip address 9.1.0.13/32
nv set vrf special1 loopback ip address 2009:0:1::13/64
nv set vrf special1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf special1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf special1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf special1 router bgp enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 evpn vni 30001
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp router-id 6.0.0.13
nv set vrf tenant2 evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant2 evpn vni 30002
nv set vrf tenant2 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant2 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf tenant2 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant2 router bgp enable on
nv set vrf tenant2 router bgp router-id 6.0.0.13
root@doca-hbn-service-bf2-s12-1-ipmi:/tmp#
Verifying BGP sessions in HBN:
doca-hbn-service-bf2-s12-1-ipmi# sh bgp sum
IPv4 Unicast Summary (VRF default):
BGP router identifier 6.0.0.13, local AS number 4200065011 vrf-id 0
BGP table version 20
RIB entries 21, using 4032 bytes of memory
Peers 2, using 40 KiB of memory
Peer groups 2, using 128 bytes of memory
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd PfxSnt Desc
spine11(p0_if) 4 65201 30617 30620 0 0 0 1d01h30m 9 11 N/A
spine12(p1_if) 4 65201 30620 30623 0 0 0 1d01h30m 9 11 N/A
Total number of neighbors 2
IPv6 Unicast Summary (VRF default):
BGP router identifier 6.0.0.13, local AS number 4200065011 vrf-id 0
BGP table version 0
RIB entries 0, using 0 bytes of memory
Peers 2, using 40 KiB of memory
Peer groups 2, using 128 bytes of memory
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd PfxSnt Desc
spine11(p0_if) 4 65201 30617 30620 0 0 0 1d01h30m 0 0 N/A
spine12(p1_if) 4 65201 30620 30623 0 0 0 1d01h30m 0 0 N/A
Total number of neighbors 2
L2VPN EVPN Summary (VRF default):
BGP router identifier 6.0.0.13, local AS number 4200065011 vrf-id 0
BGP table version 0
RIB entries 79, using 15 KiB of memory
Peers 3, using 60 KiB of memory
Peer groups 2, using 128 bytes of memory
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd PfxSnt Desc
sn1(6.0.0.7) 4 4200065507 31410 31231 0 0 0 00:27:51 69 95 N/A
sn2(6.0.0.8) 4 4200065508 31169 31062 0 0 0 02:34:47 69 95 N/A
sn3(6.0.0.9) 4 4200065509 31285 31059 0 0 0 02:34:47 69 95 N/A
Total number of neighbors 3
doca-hbn-service-bf2-s12-1-ipmi#
The command output shows that the HBN has BGP sessions with spine switches exchanging IPv4/IPv6 unicast. BGP sessions with route servers sn1, sn2, and sn3 only exchanging L2VPN EVPN AFI/SAFI.
Downstream VNI (DVNI)
Downstream VNI (symmetric EVPN route leaking) allows users to leak remote EVPN routes without having the source tenant VRF locally configured. A common use case is where upstream switches learn the L3VNI from downstream leaf switches and impose the learned L3VNI to the traffic VXLAN routed to the associated VRF. This eliminates the need to configure L3VNI-SVI interfaces on all leaf switches and enables shared service and hub-and-spoke scenarios .
To configure access to a shared service in a specific VRF, users must:
Configure route-target import statements, effectively leaking routes from remote tenants to the shared VRF.
Import shared VRF's route-target at the remote nodes.
The route target import or export statement takes the following format:
route-target import|export <asn>:<vni>
For example:
route-target import 65101:6000
For route target import statements, users can use route-target import ANY:<vni> for NVUE commands or route-target import *:<vni> in the /etc/frr/frr.conf file. ANY in NVUE commands or the asterisk (*) in the /etc/frr/frr.conf file use any ASN (a
utonomous system number
) as a wildcard.
The NVUE commands are as follows:
To configure a route import statement:
nv set vrf <vrf> router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target <asn>:<vni>
To configure a route export statement:
nv set vrf <vrf> router bgp route-export from-evpn route-target <asn>:<vni>
Important considerations when implementing DVNI configuration:
EVPN symmetric mode supports downstream VNI with L3 VNIs and single VXLAN devices only
You can configure multiple import and export route targets in a VRF
You cannot leak (import) overlapping tenant prefixes into the same destination VRF
If symmetric EVPN configuration is using automatic import/export (which is often the case), when DVNI is configured, automatic import of a tenant's
VNI
is disabled which isolates the
VRF
from the tenant. To avoid this issue, add route-import from-evpn route-target auto to the command line.
DVNI Configurations for Shared Internet Service
Configuration example here considers a scenario where External/Internet connectivity is available via a firewall (FW), which is connected to a shared VRF (vrf external in this example).
The routes on super spine switches have external VRF configured in which the route-targets from remote tenants are imported.
On BlueField devices with HBN, a local tenant VRF imports route-target corresponding to the shared external VRF.
L3VNI:
Tenant | L3VNI | |
tenant1 | 30001 | On HBN VTEPs |
tenant2 | 30002 | On HBN VTEPs |
tenant3 | 30003 | On HBN VTEPs |
tenant4 | 30004 | On HBN VTEPs |
tenant5 | 30005 | On HBN VTEPs |
tenant6 | 30006 | On HBN VTEPs |
external | 60000 | Configured on superspines and connects to external world |
On BlueField devices with HBN, every tenant VRF on HBN one must import VNI of shared external VRF:
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target ANY:60000
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target auto
nv set vrf tenant2 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target ANY:60000
nv set vrf tenant2 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target auto
nv set vrf tenant3 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target ANY:60000
nv set vrf tenant3 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target auto
nv set vrf tenant4 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target ANY:60000
nv set vrf tenant4 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target auto
nv set vrf tenant5 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target ANY:60000
nv set vrf tenant5 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target auto
nv set vrf tenant6 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target ANY:60000
nv set vrf tenant6 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target auto
root@doca-hbn-service-bf3-s06-1-ipmi:/tmp#
On super spine switches (SS1 in this example), every remote tenant VRF that needs access to shared services has to be leaked to the shared external VRF.
nv set vrf external router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target ANY:30001
nv set vrf external router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target ANY:30002
nv set vrf external router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target ANY:30003
nv set vrf external router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target ANY:30004
nv set vrf external router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target ANY:30005
nv set vrf external router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target ANY:30006
nv set vrf external router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target auto
root@superspine1:mgmt:/home/cumulus#
All super spines in this case need this configuration.
DVNI Leaked Routes in VRF Table of HBN
Each super spine here is advertising reachability providing 4-way overlay ECMP.
Kernel table for all tenant VRFs, showing the imported shared service:
root@doca-hbn-service-bf3-s06-1-ipmi:/tmp# ip -4 route show table all 6.0.0.4/32
6.0.0.4 table tenant1 proto bgp metric 20
nexthop encap ip id 60000 src 0.0.0.0 dst 6.0.0.12 ttl 0 tos 0 via 6.0.0.12 dev vxlan48 weight 1 onlink
nexthop encap ip id 60000 src 0.0.0.0 dst 6.0.0.13 ttl 0 tos 0 via 6.0.0.13 dev vxlan48 weight 1 onlink
nexthop encap ip id 60000 src 0.0.0.0 dst 6.0.0.14 ttl 0 tos 0 via 6.0.0.14 dev vxlan48 weight 1 onlink
nexthop encap ip id 60000 src 0.0.0.0 dst 6.0.0.15 ttl 0 tos 0 via 6.0.0.15 dev vxlan48 weight 1 onlink
6.0.0.4 table tenant2 proto bgp metric 20
nexthop encap ip id 60000 src 0.0.0.0 dst 6.0.0.12 ttl 0 tos 0 via 6.0.0.12 dev vxlan48 weight 1 onlink
nexthop encap ip id 60000 src 0.0.0.0 dst 6.0.0.13 ttl 0 tos 0 via 6.0.0.13 dev vxlan48 weight 1 onlink
nexthop encap ip id 60000 src 0.0.0.0 dst 6.0.0.14 ttl 0 tos 0 via 6.0.0.14 dev vxlan48 weight 1 onlink
nexthop encap ip id 60000 src 0.0.0.0 dst 6.0.0.15 ttl 0 tos 0 via 6.0.0.15 dev vxlan48 weight 1 onlink
6.0.0.4 table tenant3 proto bgp metric 20
nexthop encap ip id 60000 src 0.0.0.0 dst 6.0.0.12 ttl 0 tos 0 via 6.0.0.12 dev vxlan48 weight 1 onlink
nexthop encap ip id 60000 src 0.0.0.0 dst 6.0.0.13 ttl 0 tos 0 via 6.0.0.13 dev vxlan48 weight 1 onlink
nexthop encap ip id 60000 src 0.0.0.0 dst 6.0.0.14 ttl 0 tos 0 via 6.0.0.14 dev vxlan48 weight 1 onlink
nexthop encap ip id 60000 src 0.0.0.0 dst 6.0.0.15 ttl 0 tos 0 via 6.0.0.15 dev vxlan48 weight 1 onlink
6.0.0.4 table tenant4 proto bgp metric 20
nexthop encap ip id 60000 src 0.0.0.0 dst 6.0.0.12 ttl 0 tos 0 via 6.0.0.12 dev vxlan48 weight 1 onlink
nexthop encap ip id 60000 src 0.0.0.0 dst 6.0.0.13 ttl 0 tos 0 via 6.0.0.13 dev vxlan48 weight 1 onlink
nexthop encap ip id 60000 src 0.0.0.0 dst 6.0.0.14 ttl 0 tos 0 via 6.0.0.14 dev vxlan48 weight 1 onlink
nexthop encap ip id 60000 src 0.0.0.0 dst 6.0.0.15 ttl 0 tos 0 via 6.0.0.15 dev vxlan48 weight 1 onlink
6.0.0.4 table tenant5 proto bgp metric 20
nexthop encap ip id 60000 src 0.0.0.0 dst 6.0.0.12 ttl 0 tos 0 via 6.0.0.12 dev vxlan48 weight 1 onlink
nexthop encap ip id 60000 src 0.0.0.0 dst 6.0.0.13 ttl 0 tos 0 via 6.0.0.13 dev vxlan48 weight 1 onlink
nexthop encap ip id 60000 src 0.0.0.0 dst 6.0.0.14 ttl 0 tos 0 via 6.0.0.14 dev vxlan48 weight 1 onlink
nexthop encap ip id 60000 src 0.0.0.0 dst 6.0.0.15 ttl 0 tos 0 via 6.0.0.15 dev vxlan48 weight 1 onlink
6.0.0.4 table tenant6 proto bgp metric 20
nexthop encap ip id 60000 src 0.0.0.0 dst 6.0.0.12 ttl 0 tos 0 via 6.0.0.12 dev vxlan48 weight 1 onlink
nexthop encap ip id 60000 src 0.0.0.0 dst 6.0.0.13 ttl 0 tos 0 via 6.0.0.13 dev vxlan48 weight 1 onlink
nexthop encap ip id 60000 src 0.0.0.0 dst 6.0.0.14 ttl 0 tos 0 via 6.0.0.14 dev vxlan48 weight 1 onlink
nexthop encap ip id 60000 src 0.0.0.0 dst 6.0.0.15 ttl 0 tos 0 via 6.0.0.15 dev vxlan48 weight 1 onlink
root@doca-hbn-service-bf3-s06-1-ipmi:/tmp#
FRR RIB table:
root@doca-hbn-service-bf3-s06-1-ipmi:/tmp# vtysh
Hello, this is FRRouting (version 8.4.3).
Copyright 1996-2005 Kunihiro Ishiguro, et al.
doca-hbn-service-bf3-s06-1-ipmi# sh ip route vrf tenant1
Codes: K - kernel route, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP,
O - OSPF, I - IS-IS, B - BGP, E - EIGRP, N - NHRP,
T - Table, A - Babel, D - SHARP, F - PBR, f - OpenFabric,
Z - FRR,
> - selected route, * - FIB route, q - queued, r - rejected, b - backup
t - trapped, o - offload failure
VRF tenant1:
K>* 0.0.0.0/0 [255/8192] unreachable (ICMP unreachable), 00:10:36
B>* 6.0.0.4/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.12, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:38
* via 6.0.0.13, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:38
* via 6.0.0.14, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:38
* via 6.0.0.15, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:38
B>* 6.6.0.12/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.12, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:38
B>* 6.6.0.13/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.13, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:38
B>* 6.6.0.14/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.14, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:38
B>* 6.6.0.15/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.15, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:38
B>* 7.1.0.6/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.6, vlan4052_l3 onlink, weight 1, 00:05:37
C>* 7.1.0.16/32 is directly connected, tenant1, 00:10:36
B>* 7.1.0.18/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.18, vlan4052_l3 onlink, weight 1, 00:05:37
B>* 7.1.0.20/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.20, vlan4052_l3 onlink, weight 1, 00:05:37
C>* 21.1.0.0/16 is directly connected, vlan101, 00:10:36
C * 21.1.0.0/16 [0/1024] is directly connected, vlan101-v0, 00:10:36
C * 21.2.0.0/16 [0/1024] is directly connected, vlan102-v0, 00:10:36
C>* 21.2.0.0/16 is directly connected, vlan102, 00:10:36
B>* 101.12.4.0/24 [20/0] via 6.0.0.12, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:38
B>* 101.13.4.0/24 [20/0] via 6.0.0.13, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:38
B>* 101.14.4.0/24 [20/0] via 6.0.0.14, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:38
B>* 101.15.4.0/24 [20/0] via 6.0.0.15, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:38
doca-hbn-service-bf3-s06-1-ipmi# sh ip route vrf all
Codes: K - kernel route, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP,
O - OSPF, I - IS-IS, B - BGP, E - EIGRP, N - NHRP,
T - Table, A - Babel, D - SHARP, F - PBR, f - OpenFabric,
Z - FRR,
> - selected route, * - FIB route, q - queued, r - rejected, b - backup
t - trapped, o - offload failure
VRF default:
B>* 6.0.0.6/32 [20/0] via fe80::202:ff:fe00:1f, p0_if, weight 1, 00:06:47
* via fe80::202:ff:fe00:27, p1_if, weight 1, 00:06:47
B>* 6.0.0.7/32 [20/0] via fe80::202:ff:fe00:1f, p0_if, weight 1, 00:05:48
* via fe80::202:ff:fe00:27, p1_if, weight 1, 00:05:48
B>* 6.0.0.8/32 [20/0] via fe80::202:ff:fe00:1f, p0_if, weight 1, 00:05:38
* via fe80::202:ff:fe00:27, p1_if, weight 1, 00:05:38
B>* 6.0.0.9/32 [20/0] via fe80::202:ff:fe00:1f, p0_if, weight 1, 00:05:28
* via fe80::202:ff:fe00:27, p1_if, weight 1, 00:05:28
B>* 6.0.0.10/32 [20/0] via fe80::202:ff:fe00:1f, p0_if, weight 1, 00:06:49
B>* 6.0.0.11/32 [20/0] via fe80::202:ff:fe00:27, p1_if, weight 1, 00:06:47
B>* 6.0.0.12/32 [20/0] via fe80::202:ff:fe00:1f, p0_if, weight 1, 00:06:47
* via fe80::202:ff:fe00:27, p1_if, weight 1, 00:06:47
B>* 6.0.0.13/32 [20/0] via fe80::202:ff:fe00:1f, p0_if, weight 1, 00:06:47
* via fe80::202:ff:fe00:27, p1_if, weight 1, 00:06:47
B>* 6.0.0.14/32 [20/0] via fe80::202:ff:fe00:1f, p0_if, weight 1, 00:06:47
* via fe80::202:ff:fe00:27, p1_if, weight 1, 00:06:47
B>* 6.0.0.15/32 [20/0] via fe80::202:ff:fe00:1f, p0_if, weight 1, 00:06:47
* via fe80::202:ff:fe00:27, p1_if, weight 1, 00:06:47
C>* 6.0.0.16/32 is directly connected, lo, 00:10:42
B>* 6.0.0.18/32 [20/0] via fe80::202:ff:fe00:1f, p0_if, weight 1, 00:06:47
* via fe80::202:ff:fe00:27, p1_if, weight 1, 00:06:47
B>* 6.0.0.20/32 [20/0] via fe80::202:ff:fe00:1f, p0_if, weight 1, 00:06:47
* via fe80::202:ff:fe00:27, p1_if, weight 1, 00:06:47
B>* 192.168.0.0/24 [20/0] via fe80::202:ff:fe00:1f, p0_if, weight 1, 00:05:48
* via fe80::202:ff:fe00:27, p1_if, weight 1, 00:05:48
VRF internet1:
K>* 0.0.0.0/0 [255/8192] unreachable (ICMP unreachable), 00:10:42
B>* 8.1.0.6/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.6, vlan4004_l3 onlink, weight 1, 00:05:43
C>* 8.1.0.16/32 is directly connected, internet1, 00:10:42
B>* 8.1.0.18/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.18, vlan4004_l3 onlink, weight 1, 00:05:43
B>* 8.1.0.20/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.20, vlan4004_l3 onlink, weight 1, 00:05:43
VRF mgmt:
K>* 0.0.0.0/0 [255/8192] unreachable (ICMP unreachable), 00:10:42
C>* 10.88.0.0/16 is directly connected, eth0, 00:10:42
VRF special1:
K>* 0.0.0.0/0 [255/8192] unreachable (ICMP unreachable), 00:10:42
B>* 9.1.0.6/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.6, vlan4033_l3 onlink, weight 1, 00:05:43
C>* 9.1.0.16/32 is directly connected, special1, 00:10:42
B>* 9.1.0.18/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.18, vlan4033_l3 onlink, weight 1, 00:05:43
B>* 9.1.0.20/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.20, vlan4033_l3 onlink, weight 1, 00:05:43
VRF tenant1:
K>* 0.0.0.0/0 [255/8192] unreachable (ICMP unreachable), 00:10:42
B>* 6.0.0.4/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.12, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
* via 6.0.0.13, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
* via 6.0.0.14, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
* via 6.0.0.15, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 6.6.0.12/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.12, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 6.6.0.13/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.13, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 6.6.0.14/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.14, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 6.6.0.15/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.15, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 7.1.0.6/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.6, vlan4052_l3 onlink, weight 1, 00:05:43
C>* 7.1.0.16/32 is directly connected, tenant1, 00:10:42
B>* 7.1.0.18/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.18, vlan4052_l3 onlink, weight 1, 00:05:43
B>* 7.1.0.20/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.20, vlan4052_l3 onlink, weight 1, 00:05:43
C>* 21.1.0.0/16 is directly connected, vlan101, 00:10:42
C * 21.1.0.0/16 [0/1024] is directly connected, vlan101-v0, 00:10:42
C * 21.2.0.0/16 [0/1024] is directly connected, vlan102-v0, 00:10:42
C>* 21.2.0.0/16 is directly connected, vlan102, 00:10:42
B>* 101.12.4.0/24 [20/0] via 6.0.0.12, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 101.13.4.0/24 [20/0] via 6.0.0.13, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 101.14.4.0/24 [20/0] via 6.0.0.14, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 101.15.4.0/24 [20/0] via 6.0.0.15, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
VRF tenant2:
K>* 0.0.0.0/0 [255/8192] unreachable (ICMP unreachable), 00:10:42
B>* 6.0.0.4/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.12, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
* via 6.0.0.13, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
* via 6.0.0.14, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
* via 6.0.0.15, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 6.6.0.12/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.12, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 6.6.0.13/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.13, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 6.6.0.14/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.14, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 6.6.0.15/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.15, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 7.2.0.6/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.6, vlan4037_l3 onlink, weight 1, 00:05:43
C>* 7.2.0.16/32 is directly connected, tenant2, 00:10:42
B>* 7.2.0.18/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.18, vlan4037_l3 onlink, weight 1, 00:05:43
B>* 7.2.0.20/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.20, vlan4037_l3 onlink, weight 1, 00:05:43
C * 22.1.0.0/16 [0/1024] is directly connected, vlan201-v0, 00:10:42
C>* 22.1.0.0/16 is directly connected, vlan201, 00:10:42
C * 22.2.0.0/16 [0/1024] is directly connected, vlan202-v0, 00:10:42
C>* 22.2.0.0/16 is directly connected, vlan202, 00:10:42
B>* 101.12.4.0/24 [20/0] via 6.0.0.12, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 101.13.4.0/24 [20/0] via 6.0.0.13, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 101.14.4.0/24 [20/0] via 6.0.0.14, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 101.15.4.0/24 [20/0] via 6.0.0.15, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
VRF tenant3:
K>* 0.0.0.0/0 [255/8192] unreachable (ICMP unreachable), 00:10:42
B>* 6.0.0.4/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.12, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
* via 6.0.0.13, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
* via 6.0.0.14, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
* via 6.0.0.15, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 6.6.0.12/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.12, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 6.6.0.13/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.13, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 6.6.0.14/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.14, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 6.6.0.15/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.15, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 7.3.0.6/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.6, vlan4022_l3 onlink, weight 1, 00:05:43
C>* 7.3.0.16/32 is directly connected, tenant3, 00:10:42
B>* 7.3.0.18/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.18, vlan4022_l3 onlink, weight 1, 00:05:43
B>* 7.3.0.20/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.20, vlan4022_l3 onlink, weight 1, 00:05:43
C>* 23.17.0.0/16 is directly connected, pf0vf4_if.3, 00:10:42
B>* 23.19.0.0/16 [20/0] via 6.0.0.18, vlan4022_l3 onlink, weight 1, 00:05:43
B>* 23.21.0.0/16 [20/0] via 6.0.0.20, vlan4022_l3 onlink, weight 1, 00:05:43
B>* 101.12.4.0/24 [20/0] via 6.0.0.12, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 101.13.4.0/24 [20/0] via 6.0.0.13, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 101.14.4.0/24 [20/0] via 6.0.0.14, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 101.15.4.0/24 [20/0] via 6.0.0.15, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
VRF tenant4:
K>* 0.0.0.0/0 [255/8192] unreachable (ICMP unreachable), 00:10:42
B>* 6.0.0.4/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.12, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
* via 6.0.0.13, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
* via 6.0.0.14, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
* via 6.0.0.15, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 6.6.0.12/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.12, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 6.6.0.13/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.13, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 6.6.0.14/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.14, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 6.6.0.15/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.15, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 7.4.0.6/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.6, vlan4017_l3 onlink, weight 1, 00:05:43
C>* 7.4.0.16/32 is directly connected, tenant4, 00:10:42
B>* 7.4.0.18/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.18, vlan4017_l3 onlink, weight 1, 00:05:43
B>* 7.4.0.20/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.20, vlan4017_l3 onlink, weight 1, 00:05:43
C>* 24.17.0.0/16 is directly connected, pf0vf4_if.4, 00:10:42
B>* 24.19.0.0/16 [20/0] via 6.0.0.18, vlan4017_l3 onlink, weight 1, 00:05:43
B>* 24.21.0.0/16 [20/0] via 6.0.0.20, vlan4017_l3 onlink, weight 1, 00:05:43
B>* 101.12.4.0/24 [20/0] via 6.0.0.12, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 101.13.4.0/24 [20/0] via 6.0.0.13, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 101.14.4.0/24 [20/0] via 6.0.0.14, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 101.15.4.0/24 [20/0] via 6.0.0.15, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
VRF tenant5:
K>* 0.0.0.0/0 [255/8192] unreachable (ICMP unreachable), 00:10:42
B>* 6.0.0.4/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.12, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
* via 6.0.0.13, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
* via 6.0.0.14, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
* via 6.0.0.15, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 6.6.0.12/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.12, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 6.6.0.13/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.13, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 6.6.0.14/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.14, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 6.6.0.15/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.15, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 7.5.0.6/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.6, vlan4046_l3 onlink, weight 1, 00:05:43
C>* 7.5.0.16/32 is directly connected, tenant5, 00:10:42
B>* 7.5.0.18/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.18, vlan4046_l3 onlink, weight 1, 00:05:43
B>* 7.5.0.20/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.20, vlan4046_l3 onlink, weight 1, 00:05:43
C>* 25.17.0.0/16 is directly connected, pf0vf4_if.5, 00:10:42
B>* 25.19.0.0/16 [20/0] via 6.0.0.18, vlan4046_l3 onlink, weight 1, 00:05:43
B>* 25.21.0.0/16 [20/0] via 6.0.0.20, vlan4046_l3 onlink, weight 1, 00:05:43
B>* 101.12.4.0/24 [20/0] via 6.0.0.12, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 101.13.4.0/24 [20/0] via 6.0.0.13, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 101.14.4.0/24 [20/0] via 6.0.0.14, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 101.15.4.0/24 [20/0] via 6.0.0.15, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
VRF tenant6:
K>* 0.0.0.0/0 [255/8192] unreachable (ICMP unreachable), 00:10:42
B>* 6.0.0.4/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.12, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
* via 6.0.0.13, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
* via 6.0.0.14, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
* via 6.0.0.15, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 6.6.0.12/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.12, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 6.6.0.13/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.13, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 6.6.0.14/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.14, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 6.6.0.15/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.15, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 7.6.0.6/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.6, vlan4041_l3 onlink, weight 1, 00:05:43
C>* 7.6.0.16/32 is directly connected, tenant6, 00:10:42
B>* 7.6.0.18/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.18, vlan4041_l3 onlink, weight 1, 00:05:43
B>* 7.6.0.20/32 [20/0] via 6.0.0.20, vlan4041_l3 onlink, weight 1, 00:05:43
C>* 26.17.0.0/16 is directly connected, pf0vf4_if.6, 00:10:42
B>* 26.19.0.0/16 [20/0] via 6.0.0.18, vlan4041_l3 onlink, weight 1, 00:05:43
B>* 26.21.0.0/16 [20/0] via 6.0.0.20, vlan4041_l3 onlink, weight 1, 00:05:43
B>* 101.12.4.0/24 [20/0] via 6.0.0.12, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 101.13.4.0/24 [20/0] via 6.0.0.13, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 101.14.4.0/24 [20/0] via 6.0.0.14, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
B>* 101.15.4.0/24 [20/0] via 6.0.0.15, vxlan48 (vrf default) onlink, label 60000, weight 1, 00:05:44
doca-hbn-service-bf3-s06-1-ipmi#
DVNI Debugging
BGP/Zebra debug:
May 7 20:59:49 doca-hbn-service-bf3-s06-1-ipmi bgpd[1775018]: [GKC5Y-XBAX9] vrf tenant1: import evpn prefix [5]:[0]:[32]:[6.0.0.4] parent 0xaaaafda63a90 flags 0x410
May 7 20:59:49 doca-hbn-service-bf3-s06-1-ipmi bgpd[1775018]: [KZNVF-SX7KT] ... new pi dest 0xaaaafe524650 (l 2) pi 0xaaaafe5ae400 (l 1, f 0x4010)
May 7 20:59:49 doca-hbn-service-bf3-s06-1-ipmi bgpd[1775018]: [GKC5Y-XBAX9] vrf tenant2: import evpn prefix [5]:[0]:[32]:[6.0.0.4] parent 0xaaaafda63a90 flags 0x410
May 7 20:59:49 doca-hbn-service-bf3-s06-1-ipmi bgpd[1775018]: [KZNVF-SX7KT] ... new pi dest 0xaaaafe51c420 (l 2) pi 0xaaaafe55d230 (l 1, f 0x4010)
May 7 20:59:49 doca-hbn-service-bf3-s06-1-ipmi bgpd[1775018]: [GKC5Y-XBAX9] vrf tenant3: import evpn prefix [5]:[0]:[32]:[6.0.0.4] parent 0xaaaafda63a90 flags 0x410
May 7 20:59:49 doca-hbn-service-bf3-s06-1-ipmi bgpd[1775018]: [KZNVF-SX7KT] ... new pi dest 0xaaaafe51a670 (l 2) pi 0xaaaafe674820 (l 1, f 0x4010)
May 7 20:59:49 doca-hbn-service-bf3-s06-1-ipmi bgpd[1775018]: [GKC5Y-XBAX9] vrf tenant4: import evpn prefix [5]:[0]:[32]:[6.0.0.4] parent 0xaaaafda63a90 flags 0x410
May 7 20:59:49 doca-hbn-service-bf3-s06-1-ipmi bgpd[1775018]: [KZNVF-SX7KT] ... new pi dest 0xaaaafe519fb0 (l 2) pi 0xaaaafe675e40 (l 1, f 0x4010)
May 7 20:59:49 doca-hbn-service-bf3-s06-1-ipmi bgpd[1775018]: [GKC5Y-XBAX9] vrf tenant5: import evpn prefix [5]:[0]:[32]:[6.0.0.4] parent 0xaaaafda63a90 flags 0x410
May 7 20:59:49 doca-hbn-service-bf3-s06-1-ipmi bgpd[1775018]: [KZNVF-SX7KT] ... new pi dest 0xaaaafe55ae50 (l 2) pi 0xaaaafe5482f0 (l 1, f 0x4010)
May 7 20:59:49 doca-hbn-service-bf3-s06-1-ipmi bgpd[1775018]: [GKC5Y-XBAX9] vrf tenant6: import evpn prefix [5]:[0]:[32]:[6.0.0.4] parent 0xaaaafda63a90 flags 0x410
May 7 20:59:49 doca-hbn-service-bf3-s06-1-ipmi bgpd[1775018]: [KZNVF-SX7KT] ... new pi dest 0xaaaafdaf3590 (l 2) pi 0xaaaafe48fbf0 (l 1, f 0x4010)
DVNI table:
root@doca-hbn-service-bf3-s06-1-ipmi:/tmp# cat /cumulus/nl2docad/run/software-tables/15
{
"table": {
"id": 15,
"name": "HAL Downstream-VNI Table ",
"count": 1,
"records": [
{
"vni": 60000,
"fid": 4098,
"mark-for-del": 0,
"vtep-users":
{
"count": 4,
"vtep-user-list": [
{
"dest-vtep": "6.0.0.12",
"dest-mac": "44:38:39:f0:00:12",
"is-dmac-null": 0,
"ref-cnt": 36
},
{
"dest-vtep": "6.0.0.14",
"dest-mac": "44:38:39:f0:00:14",
"is-dmac-null": 0,
"ref-cnt": 36
},
{
"dest-vtep": "6.0.0.13",
"dest-mac": "44:38:39:f0:00:13",
"is-dmac-null": 0,
"ref-cnt": 36
},
{
"dest-vtep": "6.0.0.15",
"dest-mac": "44:38:39:f0:00:15",
"is-dmac-null": 0,
"ref-cnt": 36
}
]
}
}
]
}
}root@doca-hbn-service-bf3-s06-1-ipmi:/tmp#
Sample DVNI Configuration
HBN configuration example for BlueField devices:
root@doca-hbn-service-bf3-s06-1-ipmi:/tmp# nv config show -o commands
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 101 vni 10101
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 102 vni 10102
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 201 vni 10201
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 202 vni 10202
nv set evpn enable on
nv set evpn route-advertise svi-ip off
nv set interface ilan3200 ip vrf internet1
nv set interface ilan3200 vlan 3200
nv set interface ilan3200,slan3201,vlan101-102,201-202,3001-3006 base-interface br_default
nv set interface ilan3200,slan3201,vlan101-102,201-202,3001-3006 type svi
nv set interface lo ip address 6.0.0.16/32
nv set interface lo ip address 2001::16/128
nv set interface lo type loopback
nv set interface p0_if,p1_if,pf0hpf_if,pf0vf0_if,pf0vf1_if,pf0vf2_if,pf0vf3_if,pf0vf4_if,pf1hpf_if type swp
nv set interface pf0vf0_if bridge domain br_default access 101
nv set interface pf0vf1_if bridge domain br_default access 102
nv set interface pf0vf2_if bridge domain br_default access 201
nv set interface pf0vf3_if bridge domain br_default access 202
nv set interface pf0vf4_if.3 ip address 23.17.0.16/16
nv set interface pf0vf4_if.3 ip address 2020:0:3:17::16/64
nv set interface pf0vf4_if.3 vlan 3
nv set interface pf0vf4_if.3,vlan3003 ip vrf tenant3
nv set interface pf0vf4_if.3-6 base-interface pf0vf4_if
nv set interface pf0vf4_if.3-6 type sub
nv set interface pf0vf4_if.4 ip address 24.17.0.16/16
nv set interface pf0vf4_if.4 ip address 2020:0:4:17::16/64
nv set interface pf0vf4_if.4 vlan 4
nv set interface pf0vf4_if.4,vlan3004 ip vrf tenant4
nv set interface pf0vf4_if.5 ip address 25.17.0.16/16
nv set interface pf0vf4_if.5 ip address 2020:0:5:17::16/64
nv set interface pf0vf4_if.5 vlan 5
nv set interface pf0vf4_if.5,vlan3005 ip vrf tenant5
nv set interface pf0vf4_if.6 ip address 26.17.0.16/16
nv set interface pf0vf4_if.6 ip address 2020:0:6:17::16/64
nv set interface pf0vf4_if.6 vlan 6
nv set interface pf0vf4_if.6,vlan3006 ip vrf tenant6
nv set interface slan3201 ip vrf special1
nv set interface slan3201 vlan 3201
nv set interface vlan101 ip address 21.1.0.16/16
nv set interface vlan101 ip address 2020:0:1:1::16/64
nv set interface vlan101 ip vrr address 21.1.0.250/16
nv set interface vlan101 ip vrr address 2020:0:1:1::250/64
nv set interface vlan101 ip vrr mac-address 00:00:01:00:00:65
nv set interface vlan101 vlan 101
nv set interface vlan101-102,201-202 ip vrr enable on
nv set interface vlan101-102,3001 ip vrf tenant1
nv set interface vlan102 ip address 21.2.0.16/16
nv set interface vlan102 ip address 2020:0:1:2::16/64
nv set interface vlan102 ip vrr address 21.2.0.250/16
nv set interface vlan102 ip vrr address 2020:0:1:2::250/64
nv set interface vlan102 ip vrr mac-address 00:00:01:00:00:66
nv set interface vlan102 vlan 102
nv set interface vlan201 ip address 22.1.0.16/16
nv set interface vlan201 ip address 2020:0:2:1::16/64
nv set interface vlan201 ip vrr address 22.1.0.250/16
nv set interface vlan201 ip vrr address 2020:0:2:1::250/64
nv set interface vlan201 ip vrr mac-address 00:00:02:00:00:c9
nv set interface vlan201 vlan 201
nv set interface vlan201-202,3002 ip vrf tenant2
nv set interface vlan202 ip address 22.2.0.16/16
nv set interface vlan202 ip address 2020:0:2:2::16/64
nv set interface vlan202 ip vrr address 22.2.0.250/16
nv set interface vlan202 ip vrr address 2020:0:2:2::250/64
nv set interface vlan202 ip vrr mac-address 00:00:02:00:00:ca
nv set interface vlan202 vlan 202
nv set interface vlan3001 vlan 3001
nv set interface vlan3002 vlan 3002
nv set interface vlan3003 vlan 3003
nv set interface vlan3004 vlan 3004
nv set interface vlan3005 vlan 3005
nv set interface vlan3006 vlan 3006
nv set nve vxlan arp-nd-suppress on
nv set nve vxlan enable on
nv set nve vxlan source address 6.0.0.16
nv set platform
nv set router bgp autonomous-system 65011
nv set router bgp enable on
nv set router bgp router-id 6.0.0.16
nv set router vrr enable on
nv set system config snippet
nv set system global
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 6.0.0.7 peer-group rservers
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 6.0.0.7 type numbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 6.0.0.8 peer-group rservers
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 6.0.0.8 type numbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 6.0.0.9 peer-group rservers
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 6.0.0.9 type numbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if peer-group fabric
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if peer-group fabric
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric bfd detect-multiplier 3
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric bfd enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric bfd min-rx-interval 1000
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric bfd min-tx-interval 1000
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rservers address-family ipv4-unicast enable off
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rservers address-family l2vpn-evpn add-path-tx off
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rservers address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rservers multihop-ttl 10
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rservers remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rservers update-source lo
nv set vrf internet1 evpn enable on
nv set vrf internet1 evpn vni 42000
nv set vrf internet1 loopback ip address 8.1.0.16/32
nv set vrf internet1 loopback ip address 2008:0:1::16/64
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp enable on
nv set vrf special1 evpn enable on
nv set vrf special1 evpn vni 42001
nv set vrf special1 loopback ip address 9.1.0.16/32
nv set vrf special1 loopback ip address 2009:0:1::16/64
nv set vrf special1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf special1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf special1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf special1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf special1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf special1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf special1 router bgp enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 evpn vni 30001
nv set vrf tenant1 loopback ip address 7.1.0.16/32
nv set vrf tenant1 loopback ip address 2007:0:1::16/64
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp neighbor 21.1.0.17 peer-group hostgroup
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp neighbor 21.1.0.17 type numbered
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp peer-group hostgroup address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp peer-group hostgroup address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp peer-group hostgroup remote-as external
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target ANY:60000
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target auto
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp router-id 6.0.0.16
nv set vrf tenant2 evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant2 evpn vni 30002
nv set vrf tenant2 loopback ip address 7.2.0.16/32
nv set vrf tenant2 loopback ip address 2007:0:2::16/64
nv set vrf tenant2 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant2 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf tenant2 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant2 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant2 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf tenant2 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant2 router bgp enable on
nv set vrf tenant2 router bgp neighbor 22.1.0.17 peer-group hostgroup
nv set vrf tenant2 router bgp neighbor 22.1.0.17 type numbered
nv set vrf tenant2 router bgp peer-group hostgroup address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant2 router bgp peer-group hostgroup address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant2 router bgp peer-group hostgroup remote-as external
nv set vrf tenant2 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target ANY:60000
nv set vrf tenant2 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target auto
nv set vrf tenant2 router bgp router-id 6.0.0.16
nv set vrf tenant3 evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant3 evpn vni 30003
nv set vrf tenant3 loopback ip address 7.3.0.16/32
nv set vrf tenant3 loopback ip address 2007:0:3::16/64
nv set vrf tenant3 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant3 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf tenant3 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant3 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant3 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf tenant3 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant3 router bgp enable on
nv set vrf tenant3 router bgp neighbor 23.17.0.17 peer-group hostgroup
nv set vrf tenant3 router bgp neighbor 23.17.0.17 type numbered
nv set vrf tenant3 router bgp peer-group hostgroup address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant3 router bgp peer-group hostgroup address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant3 router bgp peer-group hostgroup remote-as external
nv set vrf tenant3 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target ANY:60000
nv set vrf tenant3 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target auto
nv set vrf tenant3 router bgp router-id 6.0.0.16
nv set vrf tenant3 table auto
nv set vrf tenant4 evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant4 evpn vni 30004
nv set vrf tenant4 loopback ip address 7.4.0.16/32
nv set vrf tenant4 loopback ip address 2007:0:4::16/64
nv set vrf tenant4 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant4 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf tenant4 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant4 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant4 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf tenant4 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant4 router bgp enable on
nv set vrf tenant4 router bgp neighbor 24.17.0.17 peer-group hostgroup
nv set vrf tenant4 router bgp neighbor 24.17.0.17 type numbered
nv set vrf tenant4 router bgp peer-group hostgroup address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant4 router bgp peer-group hostgroup address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant4 router bgp peer-group hostgroup remote-as external
nv set vrf tenant4 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target ANY:60000
nv set vrf tenant4 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target auto
nv set vrf tenant4 router bgp router-id 6.0.0.16
nv set vrf tenant4 table auto
nv set vrf tenant5 evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant5 evpn vni 30005
nv set vrf tenant5 loopback ip address 7.5.0.16/32
nv set vrf tenant5 loopback ip address 2007:0:5::16/64
nv set vrf tenant5 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant5 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf tenant5 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant5 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant5 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf tenant5 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant5 router bgp enable on
nv set vrf tenant5 router bgp neighbor 25.17.0.17 peer-group hostgroup
nv set vrf tenant5 router bgp neighbor 25.17.0.17 type numbered
nv set vrf tenant5 router bgp peer-group hostgroup address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant5 router bgp peer-group hostgroup address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant5 router bgp peer-group hostgroup remote-as external
nv set vrf tenant5 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target ANY:60000
nv set vrf tenant5 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target auto
nv set vrf tenant5 router bgp router-id 6.0.0.16
nv set vrf tenant5 table auto
nv set vrf tenant6 evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant6 evpn vni 30006
nv set vrf tenant6 loopback ip address 7.6.0.16/32
nv set vrf tenant6 loopback ip address 2007:0:6::16/64
nv set vrf tenant6 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant6 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf tenant6 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant6 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant6 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf tenant6 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant6 router bgp enable on
nv set vrf tenant6 router bgp neighbor 26.17.0.17 peer-group hostgroup
nv set vrf tenant6 router bgp neighbor 26.17.0.17 type numbered
nv set vrf tenant6 router bgp peer-group hostgroup address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant6 router bgp peer-group hostgroup address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant6 router bgp peer-group hostgroup remote-as external
nv set vrf tenant6 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target ANY:60000
nv set vrf tenant6 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target auto
nv set vrf tenant6 router bgp router-id 6.0.0.16
nv set vrf tenant6 table auto
root@doca-hbn-service-bf3-s06-1-ipmi:/tmp#
SS1 switch configuration example:
root@superspine1:mgmt:/home/cumulus# nv config show -o commands
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 101 vni 10101
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 102 vni 10102
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 201 vni 10201
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 202 vni 10202
nv set evpn enable on
nv set interface eth0 ip address 192.168.0.15/24
nv set interface eth0 ip gateway 192.168.0.2
nv set interface eth0 type eth
nv set interface lo ip address 6.0.0.12/32
nv set interface lo ip address 2001::12/128
nv set interface lo type loopback
nv set interface swp1-6 type swp
nv set interface swp6 ip address 101.12.4.12/24
nv set interface swp6 ip address 2101:12::4:12/112
nv set interface swp6 ip vrf external
nv set nve vxlan arp-nd-suppress on
nv set nve vxlan enable on
nv set nve vxlan source address 6.0.0.12
nv set platform
nv set router bgp autonomous-system 65300
nv set router bgp enable on
nv set router bgp router-id 6.0.0.12
nv set system config snippet
nv set system global system-mac 44:38:39:f0:00:12
nv set system hostname superspine1
nv set system ssh-server permit-root-login enabled
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp1 peer-group fabric
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp1 type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp2 peer-group fabric
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp2 type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp3 peer-group rservers
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp3 type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp4 peer-group rservers
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp4 type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp5 peer-group rservers
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp5 type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric bfd detect-multiplier 3
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric bfd enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric bfd min-rx-interval 1000
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric bfd min-tx-interval 1000
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rservers address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rservers address-family l2vpn-evpn add-path-tx off
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rservers address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rservers remote-as external
nv set vrf external evpn enable on
nv set vrf external evpn vni 60000
nv set vrf external loopback ip address 6.6.0.12/32
nv set vrf external loopback ip address 2006:0:6::12/64
nv set vrf external router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf external router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf external router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf external router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf external router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf external router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf external router bgp address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf external router bgp enable on
nv set vrf external router bgp neighbor swp6 peer-group peer-group-fw
nv set vrf external router bgp neighbor swp6 type unnumbered
nv set vrf external router bgp peer-group peer-group-fw address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf external router bgp peer-group peer-group-fw address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf external router bgp peer-group peer-group-fw remote-as external
nv set vrf external router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target ANY:30001
nv set vrf external router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target ANY:30002
nv set vrf external router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target ANY:30003
nv set vrf external router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target ANY:30004
nv set vrf external router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target ANY:30005
nv set vrf external router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target ANY:30006
nv set vrf external router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target auto
root@superspine1:mgmt:/home/cumulus#
Gateway Application Using Downstream VNI and Subinterface
A DPU running the HBN service can be deployed in the role of a border gateway using a combination of HBN features, specifically, EVPN symmetric routing, downstream VNI, VRF route-leaking, and VLAN sub-interfaces. Such a border gateway can do the northbound traffic handoff (to external networks or the Internet) for one or more tenants. In this gateway configuration, the BlueField's uplinks must carry both the tenant traffic which would be in the "overlay" and VXLAN-encapsulated, as well as traffic to and from the external network or Internet, which would be direct-routed in the "underlay". This is accomplished by configuring and running VXLAN-EVPN on the uplink interfaces while configuring and using additional VLAN sub-interfaces on those same uplinks for the traffic to and from external networks. These VLAN sub-interfaces would be configured into an Internet or external VRF for separation from the VXLAN-encapsulated traffic which is carried over the default VRF.
With a BlueField running HBN able to act as a border gateway, there is no longer a dependence on physical switches and routers to terminate VXLAN traffic and perform this role, hence the requirements on the underlying network is simply to provide end-to-end IP/UDP connectivity and facilitate the setup of overlay networks on top. Additionally, multiple border gateways can be easily deployed in the network, including dedicated gateways per tenant or shared gateways for groups of tenants.
Since HBN currently does not support network address translation (NAT), a dedicated border gateway must be deployed per tenant, for those tenants that have overlapping IP addresses.
For more details and configuration of some of the key features that together enable the border gateway functionality, refer to sections on Downstream VNIs and VLAN Subinterfaces.
Gateway Application Example
The following topology diagram and associated configuration snippets show two different use cases of border gateway deployment:
tenant1is an example of a tenant hosted on a server(s) with a non-gateway BlueField, using a dedicated border gateway on BlueField Gw-HBN1 for Internet connectivity. Traffic flow to and from the Internet for this tenant is m arked in pink.gw_tenant1is an example of a tenant hosted on a server(s) with a gateway BlueField. In this case, the border gateway for this tenant is provided by BlueField Gw-HBN2. Traffic flow to and from the Internet for this tenant is depicted in blue .
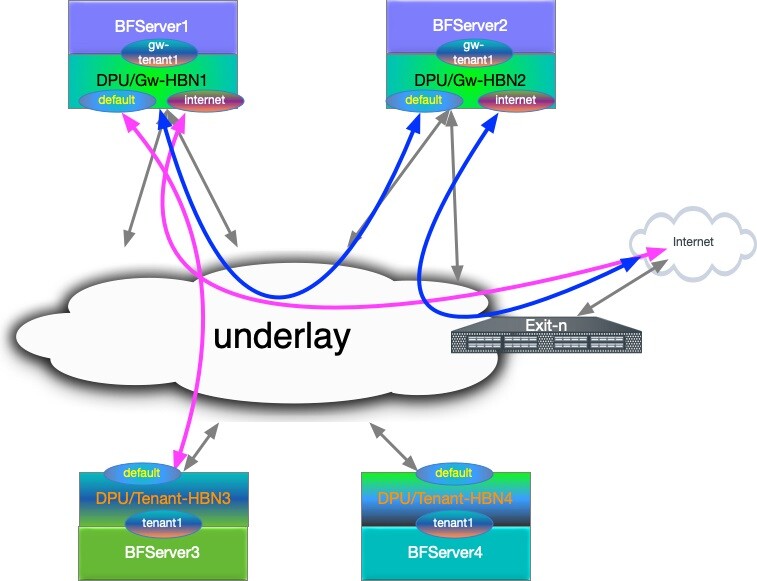
L3 VNI Origin Map
HBN | VRF | L3 VNI |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configuration Snippet for Internet VRF
Internet VRF is established in BGP sessions using sub-interface features with underlay switches (i.e.,
p0_if.60andp1_if.60)The Internet VRF also imports all the tenant VRFs (local and remote) using the downstream VNI feature with from-EVPN syntax
nv set interface p0_if.60,p1_if.60,vlan10 ip vrf internet1
nv set vrf internet1 evpn enable on
nv set vrf internet1 evpn vni 10000
nv set vrf internet1 loopback ip address 6.2.0.1/32
nv set vrf internet1 loopback ip address 2001:cafe:feed::1/128
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp autonomous-system 65552
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp neighbor p0_if.60 capabilities source-address internet1
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp neighbor p0_if.60 peer-group l3_pg1
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp neighbor p0_if.60 type unnumbered
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp neighbor p1_if.60 capabilities source-address internet1
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp neighbor p1_if.60 peer-group l3_pg1
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp neighbor p1_if.60 type unnumbered
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp peer-group l3_pg1 address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp peer-group l3_pg1 address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp peer-group l3_pg1 remote-as external
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp route-export to-evpn route-target 65552:10000
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target ANY:20000
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target ANY:30000
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target auto
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp router-id 27.0.0.5
Configuration Snippet for Gateway Local Tenant
gw_tenantis stretched across 2 gateway and connected using L3 VNIgw_tenanthas multiple SVIs, which are represented asvlan30andvlan31SVIsInternet L3 VNI is imported using DVNI. The example also explicitly adds route targets using auto.
gw_tenant VRF:
nv set interface vlan30-31 ip vrf gw_tenant1
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 evpn enable on
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 evpn vni 30000
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 loopback ip address 15.3.0.1/32
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 loopback ip address 2001:bad:c0de::1/128
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp autonomous-system 65552
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp enable on
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp route-export to-evpn route-target 65552:30000
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target ANY:10000
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target auto
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp router-id 27.0.0.5
Configuration Snippet for Remote Tenant
tenant1is stretched across 2 remote HBN VTEP and connected using L3 VNItenant1is importing Internet L3 VNI routes intenant1and adding its own using route-target auto
Tenant VRF:
nv set interface vlan20-21 ip vrf tenant1
nv set vrf tenant1 evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 evpn vni 20000
nv set vrf tenant1 loopback ip address 15.1.0.1/32
nv set vrf tenant1 loopback ip address 2001:c001:c0de::1/128
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp autonomous-system 6300656
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp route-export to-evpn route-target 6300656:20000
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target ANY:10000
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target auto
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp router-id 27.0.0.17
HBN Accelerated Routing Plan
The following subsections pick a few IP endpoints from the code snippets above and examine their route distribution.
The gateway devices have a remote tenant
Internet route is injected using the default originator from the exit node
Gateway-1 Route Info
BGP sharing the uplink via a sub-interface feature in the Internet VRF.
gateway1 - External Routes Internet VRF
root
@doca-hbn-service # ip -4route showdefaultvrf internet1defaultnhid248proto bgp metric20root@doca-hbn-service-bf2-s12-1-ipmi:~# ip -6route showdefaultvrf internet1defaultnhid248proto bgp metric20pref medium root@doca-hbn-service # ip nexthop get id248; ip nexthop get id249; ip nexthop get id250id248group249/250proto zebra id249via fe80::202:ff:fe00:1d dev p0_if.60scope link proto zebra id250via fe80::202:ff:fe00:26dev p1_if.60scope link proto zebraLocal Tenant routing information: The Internet is reached using L3 VNI via a peer gateway.
gateway1 - External Routes gw_tenant VRF
root
@hbn:/# ip -4route show vrf gw_tenant1defaultdefaultencap ip id10000src0.0.0.0dst27.0.0.7ttl0tos0via27.0.0.7dev vxlan48 proto bgp metric20onlink root@hbn:/# ip -6route show vrf gw_tenant1defaultdefaultencap ip id10000src0.0.0.0dst27.0.0.7ttl0tos0via ::ffff:27.0.0.7dev vxlan48 proto bgp metric20onlink pref mediumRemote tenant routing reachability via
gateway1using DVNI CFG.Considering an IP endpoint from the remote
tenant1VRF on Tenant-HBN3.gateway1 - Routes Internet VRF
root
@hbn:/# ip -4route show vrf internet115.1.0.1/3215.1.0.1encap ip id20000src0.0.0.0dst27.0.0.17ttl0tos0via27.0.0.17dev vxlan48 proto bgp metric20onlink root@hbn:/# ip -6route show vrf internet12001:c001:c0de::1/1282001:c001:c0de::1encap ip id20000src0.0.0.0dst27.0.0.17ttl0tos0via ::ffff:27.0.0.17dev vxlan48 proto bgp metric20onlink pref medium
Tenant-HBN3 Route Info
IP endpoint as
gateway1VRF loopback and DVNI handoff for the VNI is reaching thegateway1node.tenant-hbn3 - Routes tenant VRF
root
@hbn:/# ip -4route show vrf tenant16.2.0.1/326.2.0.1encap ip id10000src0.0.0.0dst27.0.0.5ttl0tos0via27.0.0.5dev vxlan48 proto bgp metric20onlink root@hbn:/# ip -6route show vrf tenant12001:cafe:feed::1/1282001:cafe:feed::1encap ip id10000src0.0.0.0dst27.0.0.5ttl0tos0via ::ffff:27.0.0.5dev vxlan48 proto bgp metric20onlink pref mediumInternet VRF default route is reaching the remote tenant VRF.
tenant-hbn3 external - Routes tenant VRF
root
@hbn:/# ip -4route show vrf tenant1defaultdefaultproto bgp metric20nexthop encap ip id10000src0.0.0.0dst27.0.0.5ttl0tos0via27.0.0.5dev vxlan48 weight1onlink nexthop encap ip id10000src0.0.0.0dst27.0.0.7ttl0tos0via27.0.0.7dev vxlan48 weight1onlink root@hbn:/# ip -6route show vrf tenant1defaultdefaultproto bgp metric20pref medium nexthop encap ip id10000src0.0.0.0dst27.0.0.5ttl0tos0via ::ffff:27.0.0.5dev vxlan48 weight1onlink nexthop encap ip id10000src0.0.0.0dst27.0.0.7ttl0tos0via ::ffff:27.0.0.7dev vxlan48 weight1onlink
Gateway and Tenant Complete Configuration Example
Gateway-1 Full Configuration
Gateway-HBN-1
nv set bridge domain br_default encap 802.1Q
nv set bridge domain br_default type vlan-aware
nv set bridge domain br_default untagged 1
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10,30-31
nv set evpn enable on
nv set interface lo ip address 27.0.0.5/32
nv set interface lo ip address 2001:c001:ff:f00d::5/128
nv set interface lo type loopback
nv set interface p0_if,p1_if,pf0hpf_if,pf0vf0_if,pf0vf1_if,pf0vf2_if,pf0vf3_if,pf0vf4_if,pf1hpf_if type swp
nv set interface p0_if.60 base-interface p0_if
nv set interface p0_if.60,p1_if.60 type sub
nv set interface p0_if.60,p1_if.60 vlan 60
nv set interface p0_if.60,p1_if.60,vlan10 ip vrf internet1
nv set interface p1_if.60 base-interface p1_if
nv set interface pf0hpf_if bridge domain br_default access 30
nv set interface pf0vf0_if bridge domain br_default access 31
nv set interface vlan10 ip address 12.2.0.1/24
nv set interface vlan10 ip address 2001:c001:d00d::1/96
nv set interface vlan10 vlan 10
nv set interface vlan10,30-31 ip ipv4 forward on
nv set interface vlan10,30-31 ip ipv6 forward on
nv set interface vlan10,30-31 type svi
nv set interface vlan30 ip address 45.3.0.1/24
nv set interface vlan30 ip address 2001:b055:b00c::1/96
nv set interface vlan30 vlan 30
nv set interface vlan30-31 ip vrf gw_tenant1
nv set interface vlan31 ip address 45.3.1.1/24
nv set interface vlan31 ip address 2001:b055:b00c::1:0:1/96
nv set interface vlan31 vlan 31
nv set nve vxlan arp-nd-suppress on
nv set nve vxlan enable on
nv set nve vxlan mac-learning off
nv set nve vxlan source address 27.0.0.5
nv set platform
nv set router bgp enable on
nv set system config snippet
nv set system global anycast-mac 44:38:39:42:42:17
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp autonomous-system 65552
nv set vrf default router bgp enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 27.0.0.11 peer-group rs_client
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 27.0.0.11 type numbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 27.0.0.12 peer-group rs_client
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 27.0.0.12 type numbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if capabilities source-address lo
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if peer-group fabric
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if capabilities source-address lo
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if peer-group fabric
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp path-selection multipath aspath-ignore on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family l2vpn-evpn add-path-tx off
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family l2vpn-evpn enable off
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric timers connection-retry 5
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric timers hold 30
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric timers keepalive 10
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rs_client address-family ipv4-unicast enable off
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rs_client address-family ipv6-unicast enable off
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rs_client address-family l2vpn-evpn add-path-tx off
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rs_client address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rs_client multihop-ttl 5
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rs_client remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rs_client timers connection-retry 5
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rs_client timers hold 30
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rs_client timers keepalive 10
nv set vrf default router bgp router-id 27.0.0.5
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 evpn enable on
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 evpn vni 30000
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 loopback ip address 15.3.0.1/32
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 loopback ip address 2001:bad:c0de::1/128
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp autonomous-system 65552
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp enable on
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp route-export to-evpn route-target 65552:30000
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target ANY:10000
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target auto
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp router-id 27.0.0.5
nv set vrf internet1 evpn enable on
nv set vrf internet1 evpn vni 10000
nv set vrf internet1 loopback ip address 6.2.0.1/32
nv set vrf internet1 loopback ip address 2001:cafe:feed::1/128
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp autonomous-system 65552
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp neighbor p0_if.60 capabilities source-address internet1
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp neighbor p0_if.60 peer-group l3_pg1
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp neighbor p0_if.60 type unnumbered
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp neighbor p1_if.60 capabilities source-address internet1
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp neighbor p1_if.60 peer-group l3_pg1
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp neighbor p1_if.60 type unnumbered
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp peer-group l3_pg1 address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp peer-group l3_pg1 address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp peer-group l3_pg1 remote-as external
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp route-export to-evpn route-target 65552:10000
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target ANY:20000
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target ANY:30000
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target auto
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp router-id 27.0.0.5
Gateway-2 Full Configuration
Gateway-HBN-2
nv set bridge domain br_default encap 802.1Q
nv set bridge domain br_default type vlan-aware
nv set bridge domain br_default untagged 1
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 10,30-31
nv set evpn enable on
nv set interface lo ip address 27.0.0.7/32
nv set interface lo ip address 2001:c001:ff:f00d::7/128
nv set interface lo type loopback
nv set interface p0_if,p1_if,pf0hpf_if,pf0vf0_if,pf0vf1_if,pf0vf2_if,pf0vf3_if,pf0vf4_if,pf1hpf_if type swp
nv set interface p0_if.60 base-interface p0_if
nv set interface p0_if.60,p1_if.60 type sub
nv set interface p0_if.60,p1_if.60 vlan 60
nv set interface p0_if.60,p1_if.60,vlan10 ip vrf internet1
nv set interface p1_if.60 base-interface p1_if
nv set interface pf0hpf_if bridge domain br_default access 30
nv set interface pf0vf0_if bridge domain br_default access 31
nv set interface vlan10 ip address 12.2.1.1/24
nv set interface vlan10 ip address 2001:c001:d00d::1:0:1/96
nv set interface vlan10 vlan 10
nv set interface vlan10,30-31 ip ipv4 forward on
nv set interface vlan10,30-31 ip ipv6 forward on
nv set interface vlan10,30-31 type svi
nv set interface vlan30 ip address 45.3.2.1/24
nv set interface vlan30 ip address 2001:b055:b00c::2:0:1/96
nv set interface vlan30 vlan 30
nv set interface vlan30-31 ip vrf gw_tenant1
nv set interface vlan31 ip address 45.3.3.1/24
nv set interface vlan31 ip address 2001:b055:b00c::3:0:1/96
nv set interface vlan31 vlan 31
nv set nve vxlan arp-nd-suppress on
nv set nve vxlan enable on
nv set nve vxlan mac-learning off
nv set nve vxlan source address 27.0.0.7
nv set platform
nv set router bgp enable on
nv set system config snippet
nv set system global anycast-mac 44:38:39:42:42:19
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp autonomous-system 65554
nv set vrf default router bgp enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 27.0.0.11 peer-group rs_client
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 27.0.0.11 type numbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 27.0.0.12 peer-group rs_client
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 27.0.0.12 type numbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if capabilities source-address lo
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if peer-group fabric
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if capabilities source-address lo
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if peer-group fabric
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp path-selection multipath aspath-ignore on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family l2vpn-evpn add-path-tx off
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family l2vpn-evpn enable off
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric timers connection-retry 5
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric timers hold 30
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric timers keepalive 10
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rs_client address-family ipv4-unicast enable off
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rs_client address-family ipv6-unicast enable off
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rs_client address-family l2vpn-evpn add-path-tx off
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rs_client address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rs_client multihop-ttl 5
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rs_client remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rs_client timers connection-retry 5
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rs_client timers hold 30
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rs_client timers keepalive 10
nv set vrf default router bgp router-id 27.0.0.7
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 evpn enable on
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 evpn vni 30000
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 loopback ip address 15.3.0.2/32
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 loopback ip address 2001:bad:c0de::2/128
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp autonomous-system 65554
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp enable on
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp route-export to-evpn route-target 65554:30000
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target ANY:10000
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target auto
nv set vrf gw_tenant1 router bgp router-id 27.0.0.7
nv set vrf internet1 evpn enable on
nv set vrf internet1 evpn vni 10000
nv set vrf internet1 loopback ip address 6.2.0.2/32
nv set vrf internet1 loopback ip address 2001:cafe:feed::2/128
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp autonomous-system 65554
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp neighbor p0_if.60 capabilities source-address internet1
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp neighbor p0_if.60 peer-group l3_pg1
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp neighbor p0_if.60 type unnumbered
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp neighbor p1_if.60 capabilities source-address internet1
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp neighbor p1_if.60 peer-group l3_pg1
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp neighbor p1_if.60 type unnumbered
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp peer-group l3_pg1 address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp peer-group l3_pg1 address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp peer-group l3_pg1 remote-as external
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp route-export to-evpn route-target 65554:10000
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target ANY:20000
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target ANY:30000
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target auto
nv set vrf internet1 router bgp router-id 27.0.0.7
Tenant-HBN-3 Full Configuration
Tenant-HBN-3
nv set bridge domain br_default encap 802.1Q
nv set bridge domain br_default type vlan-aware
nv set bridge domain br_default untagged 1
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 20-21
nv set evpn enable on
nv set interface lo ip address 27.0.0.17/32
nv set interface lo ip address 2001:c001:ff:f00d::11/128
nv set interface lo type loopback
nv set interface p0-1,pf0hpf,pf0vf0-12,pf1hpf,pf1vf0-4 type swp
nv set interface pf0hpf bridge domain br_default access 20
nv set interface pf0vf0 bridge domain br_default access 21
nv set interface vlan20 ip address 45.1.0.1/24
nv set interface vlan20 ip address 2001:c001:b00c::1/96
nv set interface vlan20 vlan 20
nv set interface vlan20-21 ip ipv4 forward on
nv set interface vlan20-21 ip ipv6 forward on
nv set interface vlan20-21 ip vrf tenant1
nv set interface vlan20-21 type svi
nv set interface vlan21 ip address 45.1.1.1/24
nv set interface vlan21 ip address 2001:c001:b00c::1:0:1/96
nv set interface vlan21 vlan 21
nv set nve vxlan arp-nd-suppress on
nv set nve vxlan enable on
nv set nve vxlan mac-learning off
nv set nve vxlan source address 27.0.0.17
nv set platform
nv set router bgp enable on
nv set system global anycast-mac 44:38:39:42:42:21
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp autonomous-system 6300656
nv set vrf default router bgp enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 27.0.0.11 peer-group rs_client
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 27.0.0.11 type numbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 27.0.0.12 peer-group rs_client
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 27.0.0.12 type numbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0 capabilities source-address lo
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0 peer-group fabric
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0 type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1 capabilities source-address lo
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1 peer-group fabric
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1 type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp path-selection multipath aspath-ignore on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family l2vpn-evpn add-path-tx off
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family l2vpn-evpn enable off
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric timers connection-retry 5
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric timers hold 30
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric timers keepalive 10
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rs_client address-family ipv4-unicast enable off
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rs_client address-family ipv6-unicast enable off
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rs_client address-family l2vpn-evpn add-path-tx off
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rs_client address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rs_client multihop-ttl 5
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rs_client remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rs_client timers connection-retry 5
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rs_client timers hold 30
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rs_client timers keepalive 10
nv set vrf default router bgp router-id 27.0.0.17
nv set vrf tenant1 evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 evpn vni 20000
nv set vrf tenant1 loopback ip address 15.1.0.1/32
nv set vrf tenant1 loopback ip address 2001:c001:c0de::1/128
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp autonomous-system 6300656
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp route-export to-evpn route-target 6300656:20000
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target ANY:10000
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target auto
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp router-id 27.0.0.17
Tenant-HBN-4 Full Configuration
Tenant-HBN4
nv set bridge domain br_default encap 802.1Q
nv set bridge domain br_default type vlan-aware
nv set bridge domain br_default untagged 1
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 20-21
nv set evpn enable on
nv set interface lo ip address 27.0.0.19/32
nv set interface lo ip address 2001:c001:ff:f00d::13/128
nv set interface lo type loopback
nv set interface p0-1,pf0hpf,pf0vf0-12,pf1hpf,pf1vf0-4 type swp
nv set interface pf0hpf bridge domain br_default access 20
nv set interface pf0vf0 bridge domain br_default access 21
nv set interface vlan20 ip address 45.1.2.1/24
nv set interface vlan20 ip address 2001:c001:b00c::2:0:1/96
nv set interface vlan20 vlan 20
nv set interface vlan20-21 ip ipv4 forward on
nv set interface vlan20-21 ip ipv6 forward on
nv set interface vlan20-21 ip vrf tenant1
nv set interface vlan20-21 type svi
nv set interface vlan21 ip address 45.1.3.1/24
nv set interface vlan21 ip address 2001:c001:b00c::3:0:1/96
nv set interface vlan21 vlan 21
nv set nve vxlan arp-nd-suppress on
nv set nve vxlan enable on
nv set nve vxlan mac-learning off
nv set nve vxlan source address 27.0.0.19
nv set platform
nv set router bgp enable on
nv set system global anycast-mac 44:38:39:42:42:23
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp autonomous-system 6300658
nv set vrf default router bgp enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 27.0.0.11 peer-group rs_client
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 27.0.0.11 type numbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 27.0.0.12 peer-group rs_client
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 27.0.0.12 type numbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0 capabilities source-address lo
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0 peer-group fabric
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0 type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1 capabilities source-address lo
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1 peer-group fabric
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1 type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp path-selection multipath aspath-ignore on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family l2vpn-evpn add-path-tx off
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family l2vpn-evpn enable off
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric timers connection-retry 5
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric timers hold 30
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric timers keepalive 10
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rs_client address-family ipv4-unicast enable off
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rs_client address-family ipv6-unicast enable off
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rs_client address-family l2vpn-evpn add-path-tx off
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rs_client address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rs_client multihop-ttl 5
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rs_client remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rs_client timers connection-retry 5
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rs_client timers hold 30
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rs_client timers keepalive 10
nv set vrf default router bgp router-id 27.0.0.19
nv set vrf tenant1 evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 evpn vni 20000
nv set vrf tenant1 loopback ip address 15.1.0.2/32
nv set vrf tenant1 loopback ip address 2001:c001:c0de::2/128
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp autonomous-system 6300658
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp route-export to-evpn route-target 6300658:20000
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target ANY:10000
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp route-import from-evpn route-target auto
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp router-id 27.0.0.19
Access Control Lists
Access Control Lists (ACLs) are a set of rules that are used to filter network traffic. These rules are used to specify the traffic flows that must be permitted or blocked at networking device interfaces. There are two types of ACLs:
Stateless ACLs – rules that are applied to individual packets. They inspect each packet individually and permit/block the packets based on the packet header information and the match criteria specified by the rule.
Stateful ACLs – rules that are applied to traffic sessions/connections. They inspect each packet with respect to the state of the session/connection to which the packet belongs to determine whether to permit/block the packet.
Stateless ACLs
HBN supports configuration of stateless ACLs for IPv4 packets, IPv6 packets, and Ethernet (MAC) frames. The following examples depict how stateless ACLs are configured for each case, with NVUE and with flat files (cl-acltool).
Stateless ACLs can be bound to host representor ports (for e.g., pf0hpf_if, pf0vf0_if, etc.) and sub-interfaces of host representor ports (pf0hpf_if.500, pf0vf0_if.999, etc).
NVUE Examples for Stateless ACLs
NVUE IPv4 ACLs Example
The following is an example of an ingress IPv4 ACL that permits DHCP request packets ingressing on the pf0vf1_if.999 interface towards the DHCP server:
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv set acl acl1_ingress type ipv4
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv set acl acl1_ingress rule 100 match ip protocol udp
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv set acl acl1_ingress rule 100 match ip dest-port 67
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv set acl acl1_ingress rule 100 match ip source-port 68
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv set acl acl1_ingress rule 100 action permit
Bind the ingress IPv4 ACL to host representor port pf0vf1_if.999 of BlueField in the inbound direction:
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv set interface pf0vf1_if.999 acl acl1_ingress inbound
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv config apply
The following is an example of an egress IPv4 ACL that permits DHCP reply packets egressing out of the pf0vf1_if.999 port towards the DHCP client:
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv set acl acl2_egress type ipv4
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv set acl acl2_egress rule 200 match ip protocol udp
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv set acl acl2_egress rule 200 match ip dest-port 68
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv set acl acl2_egress rule 200 match ip source-port 67
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv set acl acl2_egress rule 200 action permit
Bind the egress IPv4 ACL to host representor port pf0vf1_if.999 of BlueField in the outbound direction:
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv set interface pf0vf1_if.999 acl acl2_egress outbound
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv config apply
NVUE IPv6 ACLs Example
The following is an example of an ingress IPv6 ACL that permits traffic with matching dest-ip and protocol tcp ingress on port pf0hpf_if:
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv set acl acl5_ingress type ipv6
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv set acl acl5_ingress rule 100 match ip protocol tcp
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv set acl acl5_ingress rule 100 match ip dest-ip 48:2034::80:9
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv set acl acl5_ingress rule 100 action permit
Bind the ingress IPv6 ACL to host representor port pf0hpf_if of BlueField in the inbound direction:
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv set interface pf0hpf_if acl acl5_ingress inbound
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv config apply
The following is an example of an egress IPv6 ACL that permits traffic with matching source-ip and protocol tcp egressing out of port pf0hpf_if:
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv set acl acl6_egress type ipv6
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv set acl acl6_egress rule 101 match ip protocol tcp
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv set acl acl6_egress rule 101 match ip source-ip 48:2034::80:9
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv set acl acl6_egress rule 101 action permit
Bind the egress IPv6 ACL to host representor port pf0hpf_if of BlueField in the outbound direction:
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv set interface pf0hpf_if acl acl6_egress outbound
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv config apply
NVUE MAC ACLs Example
The following is an example of an ingress MAC ACL that permits traffic with matching source-mac and dest-mac ingressing to port pf0hpf_if:
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv set acl acl3_ingress type mac
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv set acl acl3_ingress rule 1 match mac source-mac 00:00:00:00:00:0a
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv set acl acl3_ingress rule 1 match mac dest-mac 00:00:00:00:00:0b
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv set interface pf0hpf_if acl acl3_ingress inbound
Bind the ingress MAC ACL to host representor port pf0hpf_if of BlueField in the inbound direction:
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv set interface pf0hpf_if acl acl3_ingress inbound
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv config apply
The following is an example of an egress MAC ACL that permits traffic with matching source-mac and dest-mac egressing out of port pf0hpf_if:
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv set acl acl4_egress type mac
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv set acl acl4_egress rule 2 match mac source-mac 00:00:00:00:00:0b
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv set acl acl4_egress rule 2 match mac dest-mac 00:00:00:00:00:0a
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv set acl acl4_egress rule 2 action permit
Bind the egress MAC ACL to host representor port pf0hpf_if of BlueField in the outbound direction:
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv set interface pf0hpf_if acl acl4_egress outbound
root@hbn01-host01:~# nv config apply
Flat Files (cl-acltool) Examples for Stateless ACLs
For the same examples cited above, the following are the corresponding ACL rules which must be configured under /etc/cumulus/acl/policy.d/<rule_name.rules> followed by invoking cl-acltool -i. The rules in /etc/cumulus/acl/policy.d/<rule_name.rules> are configured using Linux iptables/ip6tables/ebtables.
Flat Files IPv4 ACLs Example
The following example configures an ingress IPv4 ACL rule matching with DHCP request under /etc/cumulus/acl/policy.d/<rule_name.rules> with the ingress interface as the host representor of BlueField followed by invoking cl-acltool -i:
[iptables]
## ACL acl1_ingress in dir inbound on interface pf1vf1_if.999 ##
-t filter -A FORWARD -m physdev --physdev-in pf1vf1_if.999 -p udp --sport 68 --dport 67 -j ACCEPT
The following example configures an egress IPv4 ACL rule matching with DHCP reply under /etc/cumulus/acl/policy.d/<rule_name.rules> with the egress interface as the host representor of BlueField followed by invoking cl-acltool -i:
[iptables]
## ACL acl2_egress in dir outbound on interface pf1vf1_if.999 ##
-t filter -A FORWARD -m physdev --physdev-out pf1vf1_if.999 -p udp --sport 67 --dport 68 -j ACCEPT
Flat File IPv6 ACLs Example
The following example configures an ingress IPv6 ACL rule matching with dest-ip and tcp protocol under /etc/cumulus/acl/policy.d/<rule_name.rules> with the ingress interface as the host representor of BlueField followed by invoking cl-acltool -i:
[ip6tables]
## ACL acl5_ingress in dir inbound on interface pf0hpf_if ##
-t filter -A FORWARD -m physdev --physdev-in pf0hpf_if -d 48:2034::80:9 -p tcp -j ACCEPT
The following example configures an egress IPv6 ACL rule matching with source-ip and tcp protocol under /etc/cumulus/acl/policy.d/<rule_name.rules> with the egress interface as the host representor of BlueField followed by invoking cl-acltool -i:
[ip6tables]
## ACL acl6_egress in dir outbound on interface pf0hpf_if ##
-t filter -A FORWARD -m physdev --physdev-out pf0hpf_if -s 48:2034::80:9 -p tcp -j ACCEPT
Flat Files MAC ACLs Example
The following example configures an ingress MAC ACL rule matching with source-mac and dest-mac under /etc/cumulus/acl/policy.d/<rule_name.rules> with the ingress interface as the host representor of BlueField followed by invoking cl-acltool -i:
[ebtables]
## ACL acl3_ingress in dir inbound on interface pf0hpf_if ##
-t filter -A FORWARD -m physdev --physdev-in pf0hpf_if -s 00:00:00:00:00:0a/ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff -d 00:00:00:00:00:0b/ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff -j ACCEPT
The following example configures an egress MAC ACL rule matching with source-mac and dest-mac under /etc/cumulus/acl/policy.d/<rule_name.rules> with egress interface as host representor of BlueField followed by invoking cl-acltool -i:
[ebtables]
## ACL acl4_egress in dir outbound on interface pf0hpf_if ##
-t filter -A FORWARD -m physdev --physdev-out pf0hpf_if -s 00:00:00:00:00:0b/ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff -d 00:00:00:00:00:0a/ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff -j ACCEPT
Stateful ACLs
Stateful ACLs facilitate monitoring and tracking traffic flows to enforce per-flow traffic filtering (unlike stateless ACLs which filter traffic on a per-packet basis). HBN supports stateful ACLs using reflexive ACL mechanism. Reflexive ACL mechanism is used to allow initiation of connections from "within" the network to "outside" the network and allow only replies to the initiated connections from "outside" the network (or vice versa).
HBN supports stateful ACL configuration for IPv4 traffic. Stateful ACL configuration is supported for TCP, UDP, and ICMP protocols.
Stateful ACLs can be bound to host representor ports (for e.g., pf0hpf_if, pf0vf0_if, etc.) and sub-interfaces of host representor ports (pf0hpf_if.500, pf0vf0_if.999, etc).
Stateful ACLs can be applied for native routed traffic (north-south underlay routed traffic in EVPN deployments), EVPN bridged traffic (east-west overlay bridged/L2 traffic in EVPN deployments) and EVPN routed traffic (east-west overlay routed traffic in EVPN deployments). Stateful ACLs applied for native routed traffic are called "Native-L3 stateful ACLs". Stateful ACLs applied for EVPN bridged traffic and EVPN routed traffic are called "EVPN-L2 stateful ACLs" and "EVPN-L3 stateful ACLs", respectively.
Stateful ACLs in HBN are enabled by default. To enable stateful ACL functionality, use the following NVUE commands:
root@hbn03-host00:~# nv set system reflexive-acl enable
root@hbn03-host00:~# nv config apply
If using flat-file configuration (and not NVUE), edit the file /etc/cumulus/nl2docad.d/acl.conf and set the knob rflx.reflexive_acl_enable to TRUE. To apply this change, execute:
root@hbn03-host00:~# supervisorctl start nl2doca-reload
NVUE Example for Stateful ACLs
The following is an example of allowing HTTP (TCP) connection originated by the host, where BlueField is hosted, to an HTTP server (with the IP address 11.11.11.11) on an external network. Two sets of ACLs matching with CONNTRACK state must be configured for a CONNTRACK entry to be established in the kernel which would be offloaded to hardware:
Configure an ACL rule matching TCP/HTTP connection/flow details with CONNTRACK state of NEW, ESTABLISHED and bind it to the SVI in the inbound direction.
Configure an ACL rule matching TCP/HTTP connection/flow details with CONNTRACK state of ESTABLISHED and bind it to the SVI in the outbound direction.
Stateful ACLs should be bound to a physical interface. In this example, the physical interface is pf1vf7_if.
Configure the ingress ACL rule:
root@hbn03-host00:~# nv set acl allow_tcp_conn_from_host rule 11 action permit root@hbn03-host00:~# nv set acl allow_tcp_conn_from_host rule 11 match conntrack new root@hbn03-host00:~# nv set acl allow_tcp_conn_from_host rule 11 match conntrack established root@hbn03-host00:~# nv set acl allow_tcp_conn_from_host rule 11 match ip dest-ip 11.11.11.11/32 root@hbn03-host00:~# nv set acl allow_tcp_conn_from_host rule 11 match ip dest-port 80 root@hbn03-host00:~# nv set acl allow_tcp_conn_from_host rule 11 match ip protocol tcp root@hbn03-host00:~# nv set acl allow_tcp_conn_from_host type ipv4
Bind this ACL to the physical interface in the inbound direction:
root@hbn03-host00:~# nv set interface pf1vf7_if acl allow_tcp_conn_from_host inbound root@hbn03-host00:~# nv config apply
Configure the egress ACL rule:
root@hbn03-host00:~# nv set acl allow_tcp_resp_from_server rule 21 action permit root@hbn03-host00:~# nv set acl allow_tcp_resp_from_server rule 21 match conntrack established root@hbn03-host00:~# nv set acl allow_tcp_resp_from_server rule 21 match ip protocol tcp root@hbn03-host00:~# nv set acl allow_tcp_resp_from_server type ipv4 root@hbn03-host00:~# nv config apply
Bind this ACL to the physical interface in the outbound direction:
root@hbn03-host00:~# nv set interface pf1vf7_if acl allow_tcp_resp_from_server outbound root@hbn03-host00:~# nv config apply
Flat Files (cl-acltool) Example for Stateful ACLs
For the same NVUE example for stateful ACLs cited above (HTTP server at IP address 11.11.11.11 on an external network), the following are the corresponding ACL rules which must be configured under /etc/cumulus/acl/policy.d/<rule_name.rules> followed by invoking cl-acltool -i to install the rules in BlueField hardware.
Configure an ingress ACL rule matching with TCP flow details and CONNTRACK state of NEW, ESTABLISHED under
/etc/cumulus/acl/policy.d/stateful_acl.ruleswith the ingress interface as the SVI followed by invokingcl-acltool -i:[iptables] ## ACL allow_tcp_conn_from_host in dir inbound on interface pf1vf7_if ## -t filter -A FORWARD -m physdev --physdev-in pf1vf7_if -p tcp –d 11.11.11.11/32 --dport 80 -m conntrack --ctstate EST,NEW -j ACCEPT -m mark --mark 0xdead
Configure an egress ACL rule matching the TCP flow and CONNTRACK state of ESTABLISHED, RELATED under
/etc/cumulus/acl/policy.d/stateful_acl.rulesfile with the egress interface as SVI followed by invokingcl-acltool -i:[iptables] ## ACL allow_tcp_resp_from_server in dir outbound on interface pf1vf7_if ## -t filter -A FORWARD -m physdev --physdev-out pf1vf7_if -p tcp -s 11.11.11.11/32 --sport 80 -m conntrack --ctstate EST -j ACCEPT -m mark --mark 0xdead
Network Address Translation
Network address translation (NAT) allows a network to use one set of IP addresses for internal traffic and another set for external traffic. Besides preventing the depletion of IPv4 addresses, NAT enables the use of private address space internally while still providing access to the Internet. NAT essentially consists of a set of rules for translating between public and private IP addresses and ports. Both static and dynamic NAT rules are configured on outbound or inbound uplink interfaces or sub-interfaces of uplink ports. These NAT rules should be applied on all public egress and ingress facing uplink interfaces and their sub-interfaces.
HBN supports Source NAT (SNAT), which allows traffic from the private network to reach public networks by changing the packet's source address. HBN also supports Destination NAT (DNAT), which allows incoming traffic from public networks to reach private networks by changing the packet's destination address. HBN SNAT and DNAT are supported for IPv4 and three protocols: ICMP, TCP, and UDP.
SNAT and DNAT can be configured in two types:
Static NAT – Provides a permanent mapping between one private IP address and a single public address. Static NAT is stateless and does not use connection tracking. Static NAT is enabled by default and supports port address translation (PAT) with a one-to-one mapping between private and public ports. The static NAT mapping rules are not flushed or timed out from rule tables.
Dynamic NAT – This is a stateful NAT which uses the OVS connection tracking infrastructure to monitor NAT connections. Dynamic NAT is disabled by default, and users must enable dynamic mode before setting up dynamic NAT rules (see section "Dynamic NAT Configuration"). Dynamic NAT maps private IP addresses to a range of public addresses and supports port ranges for PAT. Users are responsible for managing the pool of IP addresses and ports used in the configuration of dynamic NAT and PAT. It is recommended to use a NAT IP address range that is a power of two.
Source NAT (SNAT)
Static SNAT Configuration
Static NAT is enabled by default and is stateless.
NVUE Examples for Static SNAT
NVUE ICMP Example
The following is an example of an SNAT rule translating ICMP packets matching source IP 30.30.30.2 to source IP 100.100.100.2:
nv set acl acl_1 rule 1 action source-nat translate-ip 100.100.100.1
nv set acl acl_1 rule 1 match ip protocol icmp
nv set acl acl_1 rule 1 match ip source-ip 30.30.30.2
nv set acl acl_1 type ipv4
Bind the egress ICMP NAT ACL uplink port p0_if and p1_if of BlueField in the outbound direction:
nv set interface p0_if acl acl_1 outbound
nv set interface p1_if acl acl_1 outbound
NVUE UDP with PAT Example
The following is an example of an SNAT rule translating UDP packets matching source IP 21.1.0.18 and source port 10011 to source IP 199.5.1.1 and source port 11011:
nv set acl stnatpat rule 1 action source-nat translate-ip 199.5.1.1
nv set acl stnatpat rule 1 action source-nat translate-port 11011
nv set acl stnatpat rule 1 match ip protocol udp
nv set acl stnatpat rule 1 match ip source-ip 21.1.0.18
nv set acl stnatpat rule 1 match ip source-port 10011
nv set acl stnatpat type ipv4
Bind the egress UDP NAT ACL to uplink port p0_if.10 and p1_if.10 of BlueField in the outbound direction:
nv set interface p0_if.10,p1_if.10 acl stnatpat outbound
Flat Files (cl-acltool) Example for Static SNAT
[iptables]
## ACL acl_1 in dir outbound on interface p0_if ##
-t nat -A POSTROUTING -m physdev --physdev-out p0_if -s 30.30.30.2 -p icmp -j SNAT --to-source 100.100.100.1 -m mark --mark 0xdead
## ACL acl_1 in dir outbound on interface p1_if ##
-t nat -A POSTROUTING -m physdev --physdev-out p1_if -s 30.30.30.2 -p icmp -j SNAT --to-source 100.100.100.1 -m mark --mark 0xdead
## ACL stnatpat in dir outbound on interface p0_if.10 ##
-t nat -A POSTROUTING -o p0_if.10 -s 21.1.0.18 -p udp --sport 10011 -j SNAT --to-source 199.5.1.1:11011 -m mark --mark 0xdead
## ACL stnatpat in dir outbound on interface p1_if.10 ##
-t nat -A POSTROUTING -o p1_if.10 -s 21.1.0.18 -p udp --sport 10011 -j SNAT --to-source 199.5.1.1:11011 -m mark --mark 0xdead
Dynamic NAT Configuration
Dynamic NAT is stateful and relies on underlying connection tracking.
Enabling NVUE Dynamic NAT
nv set system nat mode dynamic
NVUE Examples for Dynamic SNAT
NVUE Dynamic SNAT with TCP
The following is an example of an SNAT rule translating TCP packets matching source IP 21.1.0.0/16 to an IP range of 199.10.0.1 to 199.10.255.254:
nv set acl dnat1 rule 1 action source-nat translate-ip 199.10.0.1 to 199.10.255.254
nv set acl dnat1 rule 1 match ip protocol tcp
nv set acl dnat1 rule 1 match ip source-ip 21.1.0.0/16
nv set acl dnat1 type ipv4
Bind the egress TCP NAT to uplink sub-interfaces p0_if.10 and p1_if.10:
nv set interface p0_if.10,p1_if.10 acl dnat1 outbound
NVUE Dynamic SNAT with TCP and PAT
The following is an example of an SNAT rule translating TCP packets matching source IP 30.30.30.0/29 and source port 5000 to an IP range 100.100.100.8 to 100.100.100.15 and source port 10000:
nv set acl acl_2 rule 1 action source-nat translate-ip 100.100.100.8 to 100.100.100.15
nv set acl acl_2 rule 1 action source-nat translate-port 10000
nv set acl acl_2 rule 1 match ip protocol tcp
nv set acl acl_2 rule 1 match ip source-ip 30.30.30.0/29
nv set acl acl_2 rule 1 match ip source-port 5000
nv set acl acl_2 type ipv4
Bind the egress TCP NAT to uplink sub-interfaces p0_if and p1_if:
nv set interface p0_if,p1_if acl acl_2 outbound
Flat Files (cl-acltool) Example for Dynamic SNAT
## ACL dnat1 in dir outbound on interface p0_if.10 ##
-t nat -A POSTROUTING -o p0_if.10 -s 21.1.0.0/16 -p tcp -j SNAT --to-source 199.10.0.1-199.10.255.254 -m mark --mark 0xdead
## ACL dnat1 in dir outbound on interface p1_if.10 ##
-t nat -A POSTROUTING -o p1_if.10 -s 21.1.0.0/16 -p tcp -j SNAT --to-source 199.10.0.1-199.10.255.254 -m mark --mark 0xdead
## ACL acl_2 in dir outbound on interface p0_if ##
-t nat -A POSTROUTING -m physdev --physdev-out p0_if -s 30.30.30.0/29 -p tcp --sport 5000 -j SNAT --to-source 100.100.100.8-100.100.100.15:10000 -m mark --mark 0xdead
## ACL acl_2 in dir outbound on interface p1_if ##
-t nat -A POSTROUTING -m physdev --physdev-out p1_if -s 30.30.30.0/29 -p tcp --sport 5000 -j SNAT --to-source 100.100.100.8-100.100.100.15:10000 -m mark --mark 0xdead
The following is an example where a pool of private IP addresses is translated to a public address using a unique port number from the available range:
nv set acl dnatpat1 rule 1 action source-nat translate-ip 199.9.1.1
nv set acl dnatpat1 rule 1 match ip protocol tcp
nv set acl dnatpat1 rule 1 match ip source-ip 21.1.0.0/16
nv set acl dnatpat1 rule 1 action source-nat translate-port 10001-24000
nv set acl dnatpat1 type ipv4
nv set interface p0_if.10,p1_if.10 acl dnatpat1 outbound
Destination NAT (DNAT)
Static DNAT Configuration
Static NAT is enabled by default and is stateless.
NVUE Examples for Static DNAT
NVUE ICMP Example
The following is an example of an SNAT rule translating ICMP packets matching incoming destination IP 100.100.100.1 to destination IP 30.30.30.2
nv set acl acl_1 rule 1 action dest-nat translate-ip 30.30.30.2
nv set acl acl_1 rule 1 match ip protocol icmp
nv set acl acl_1 rule 1 match ip dest-ip 100.100.100.1
nv set acl acl_1 type ipv4
Bind the ingress ICMP NAT ACL to uplink port p0_if and p1_if of BlueField in the inbound direction:
nv set interface p0_if acl acl_1 inbound
nv set interface p1_if acl acl_1 inbound
NVUE UDP with PAT example
Flat Files (cl-acltool) Example for Static DNAT
## ACL acl_1 in dir inbound on interface p0_if ##
-t nat -A PREROUTING -m physdev --physdev-in p0_if -d 100.100.100.1 -p icmp -j DNAT --to-destination 30.30.30.2 -m mark --mark 0xdead
## ACL acl_1 in dir inbound on interface p1_if ##
-t nat -A PREROUTING -m physdev --physdev-in p1_if -d 100.100.100.1 -p icmp -j DNAT --to-destination 30.30.30.2 -m mark --mark 0xdead
Dynamic DNAT configuration
This is common configuration for DNAT and SNAT so please see section "Dynamic NAT Configuration".
Enabling NVUE Dynamic DNAT
NVUE Examples for Dynamic DNAT
NVUE Dynamic DNAT with TCP and PAT
The following is an example of an D NAT rule translating TCP packets matching destination IP 100.100.100.1/29 and destination port 5000 to an IP range 30.30.30.1 to 30.30.30.6 and translated destination port 1234:
nv set acl acl_3 rule 1 action dest-nat translate-ip 30.30.30.1 to 30.30.30.6
nv set acl acl_3 rule 1 action dest-nat translate-port 1234
nv set acl acl_3 rule 1 match ip protocol tcp
nv set acl acl_3 rule 1 match ip dest-ip 100.100.100.1/29
nv set acl acl_3 rule 1 match ip dest-port 5000
nv set acl acl_3 type ipv4
Bind the ingress TCP NAT ACL to uplink sub-interfaces
p0_if
and
p1_if
:
nv set interface p0_if acl acl_6 inbound
nv set interface p1_if acl acl_6 inbound
Flat Files (cl-acltool) Example for Dynamic DNAT
## ACL acl_6 in dir inbound on interface p0_if ##
-t nat -A PREROUTING -m physdev --physdev-in p0_if -d 100.100.100.1/29 -p udp -j DNAT --to-destination 30.30.30.1-30.30.30.6 -m mark --mark 0xdead
## ACL acl_6 in dir inbound on interface p1_if ##
-t nat -A PREROUTING -m physdev --physdev-in p1_if -d 100.100.100.1/29 -p udp -j DNAT --to-destination 30.30.30.1-30.30.30.6 -m mark --mark 0xdead
More examples of dynamic DNAT with NVUE
In practice multiple rules can be combined as well as multiple dnat acl can be applied to same uplink ports.
ICMP
nv set acl dyndnaticmp rule 1 action dest-nat translate-ip 21.1.0.19 to 21.1.0.20
nv set acl dyndnaticmp rule 1 match ip dest-ip 199.101.6.0/30
nv set acl dyndnaticmp rule 1 match ip protocol icmp
nv set acl dyndnaticmp rule 2 action dest-nat translate-ip 120.19.0.19 to 120.19.0.20
nv set acl dyndnaticmp rule 2 match ip dest-ip 199.101.6.4/30
nv set acl dyndnaticmp rule 2 match ip protocol icmp
nv set acl dyndnaticmp rule 3 action dest-nat translate-ip 21.1.0.15 to 21.1.0.16
nv set acl dyndnaticmp rule 3 match ip dest-ip 199.101.6.8/30
nv set acl dyndnaticmp rule 3 match ip protocol icmp
nv set acl dyndnaticmp type ipv4
TCP
nv set acl dyndnattcp rule 1 action dest-nat translate-ip 21.1.0.19 to 21.1.0.20
nv set acl dyndnattcp rule 1 match ip dest-ip 199.101.7.0/30
nv set acl dyndnattcp rule 1 match ip protocol tcp
nv set acl dyndnattcp rule 2 action dest-nat translate-ip 120.19.0.19 to 120.19.0.20
nv set acl dyndnattcp rule 2 match ip dest-ip 199.101.7.4/30
nv set acl dyndnattcp rule 2 match ip protocol tcp
nv set acl dyndnattcp rule 3 action dest-nat translate-ip 21.1.0.15 to 21.1.0.16
nv set acl dyndnattcp rule 3 match ip dest-ip 199.101.7.8/30
nv set acl dyndnattcp rule 3 match ip protocol tcp
nv set acl dyndnattcp type ipv4
UDP
nv set acl dyndnatudp rule 1 action dest-nat translate-ip 21.1.0.19 to 21.1.0.20
nv set acl dyndnatudp rule 1 match ip dest-ip 199.101.8.0/30
nv set acl dyndnatudp rule 1 match ip protocol udp
nv set acl dyndnatudp rule 2 action dest-nat translate-ip 120.19.0.19 to 120.19.0.20
nv set acl dyndnatudp rule 2 match ip dest-ip 199.101.8.4/30
nv set acl dyndnatudp rule 2 match ip protocol udp
nv set acl dyndnatudp rule 3 action dest-nat translate-ip 21.1.0.15 to 21.1.0.16
nv set acl dyndnatudp rule 3 match ip dest-ip 199.101.8.8/30
nv set acl dyndnatudp rule 3 match ip protocol udp
nv set acl dyndnatudp type ipv4
Applying these to uplink ports
nv set interface p0_if.10,p1_if.10 acl dyndnaticmp inbound
nv set interface p0_if.10,p1_if.10 acl dyndnattcp inbound
nv set interface p0_if.10,p1_if.10 acl dyndnatudp inbound
Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) for BGP
BFD functionality is derived from the upstream FRRouting (FRR) suite, which includes a dedicated daemon called bfdd.
HBN supports BFD for BGP from 3.0.0 release. Single-Hop (UDP port 3784) and Multi-Hop (UDP port 4784) BFD supports are present for both IPv4 and IPv6. Asynchronous Mode (Periodically send BFD Control Packets to one another) is the default and only mode supported. BFD Echo Function is NOT supported.
BFD Configuration
BFD configuration has two parts , BFD profile configuration and BFD profile attachment to client like BGP.
BFD Profile Configuration
We have follwing profile settings for BFD sessions and it is present under "nv set/unset/show router bfd profile <profile-name> " command.
Sr. No. | Command | Details | Range | Default |
1. | detect-multiplier | 1-255 | 3 | |
2. | receive-interval | Configures the minimum interval that this system is capable of receiving control packets. | 10-4294967ms | 300ms |
3. | transmit-interval | The minimum transmission interval (less jitter) that this system wants to use to send BFD control packets. | 10-4294967ms | 300 ms |
4. | shutdown | Enables or disables the peer. | on/off | off |
5. | passive-mode | Mark session as passive: a passive session will not attempt to start the connection and will wait for control packets from peer before it begins replying. | on/off | off |
6. | minimum-ttl | For multi hop sessions only: configure the minimum expected TTL for an incoming BFD control packet. | 1-254 | 254 |
nv set router bfd profile pf1 detect-multiplier 21
nv set router bfd profile pf1 min-rx-interval 100
nv set router bfd profile pf1 min-tx-interval 100
nv set router bfd profile pf1 minimum-ttl 253
nv set router bfd profile pf1 passive-mode on
nv set router bfd profile pf1 shutdown on
BGP Configuration for BFD
Apply BFD profile with BGP neighbor/peer-group. This will create/update BFD session for the respective BGP neighbor/peer-group.
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if.100 bfd profile pf1
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 6000::23 bfd profile pf1
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group EBGP_MHOP_V4 bfd profile pf1
BFD Show Commands
Following commands can be used to display BFD sessions.
root@doca-hbn-service-bf3-s13-1-ipmi:/etc/cumulus/sougatab/frr-bfd-upgrade-debs# nv show vrf default router bfd peers --view=brief
MHop - Multihop, Local - Local, Peer - Peer, Interface - Interface, State -
State, Passive - Passive Mode, Time - Up/Down Time, Type - Config Type
LocalId MHop Local Peer Interface State Passive Time Type
---------- ----- ------------------------- -------------------- --------- ----- ------- ---------- -------
417705214 True 6.0.0.24 6.0.0.23 down False 6:19:46:05 dynamic
770667106 False fe80::a288:c2ff:fe2c:5253 fe80::202:ff:fe00:33 p1_if down False 0:03:23:27 dynamic
918556010 False fe80::a288:c2ff:fe2c:5252 fe80::202:ff:fe00:2f p0_if.100 up False 6:19:38:53 dynamic
1668048197 True 6000::24 6000::23 down False 6:19:46:05 dynamic
3190546666 False fe80::a288:c2ff:fe2c:5252 fe80::202:ff:fe00:2f p0_if.101 up False 6:19:38:53 dynamic
root@doca-hbn-service-bf3-s13-1-ipmi:/etc/cumulus/sougatab/frr-bfd-upgrade-debs# nv show vrf default router bfd peers --view=standard
MHop - Multihop, Local - Local, Peer - Peer, Interface - Interface, State -
State, Passive - Passive Mode, Time - Up/Down Time, Type - Config Type, MinTTL -
Minimum TTL, Multiplier - Detect Multiplier, MinRx - Min Rx Interval, MinTx -
Min Tx Interval, CtrlIn - Control Packet Input, CtrlOut - Control Packet Output
LocalId MHop Local Peer Interface State Passive Time Type MinTTL Multiplier MinRx MinTx CtrlIn CtrlOut
---------- ----- ------------------------- -------------------- --------- ----- ------- ---------- ------- ------ ---------- ----- ----- ------- -------
417705214 True 6.0.0.24 6.0.0.23 down False 6:19:46:14 dynamic 251 21 100 100 12517 698545
770667106 False fe80::a288:c2ff:fe2c:5253 fe80::202:ff:fe00:33 p1_if down False 0:03:23:36 dynamic 22 102 102 0 13950
918556010 False fe80::a288:c2ff:fe2c:5252 fe80::202:ff:fe00:2f p0_if.100 up False 6:19:39:02 dynamic 21 100 100 3270251 3448733
1668048197 True 6000::24 6000::23 down False 6:19:46:14 dynamic 251 21 100 100 12373 698358
3190546666 False fe80::a288:c2ff:fe2c:5252 fe80::202:ff:fe00:2f p0_if.101 up False 6:19:39:02 dynamic 22 102 102 3270331 3448614
root@doca-hbn-service-bf3-s13-1-ipmi:/etc/cumulus/sougatab/frr-bfd-upgrade-debs# nv show vrf default router bfd peers --view=detail
MHop - Multihop, Local - Local, Peer - Peer, Interface - Interface, State -
State, RemoteId - Remote ID, Passive - Passive Mode, Time - Up/Down Time, Type -
Config Type, MinTTL - Minimum TTL, Diag - Diagnostic, RemoteDiag - Remote
Diagnostic, Multiplier - Detect Multiplier, MinRx - Min Rx Interval, MinTx - Min
Tx Interval, RemoteMultiplier - Remote Detect Multiplier, RemoteRx - Remote Rx
Interval, RemoteTx - Remote Tx Interval, EchoRx - Echo Rx Interval, EchoTx -
Echo Tx Interval, RemoteEchoRx - Remote Echo Rx Interval, RTTMin - RTT Min,
RTMax - RTT Max, RTTAvg - RTT Avg, CtrlIn - Control Packet Input, CtrlOut -
Control Packet Output, EchoIn - Echo Packet Input, EchoOut - Echo Packet Output,
Up - Session Up, Down - Session Down, Zebra - Zebra Notification
LocalId MHop Local Peer Interface State RemoteId Passive Time Type MinTTL Diag RemoteDiag Multiplier MinRx MinTx RemoteMultiplier RemoteRx RemoteTx EchoRx EchoTx RemoteEchoRx RTTMin RTMax RTTAvg CtrlIn CtrlOut EchoIn EchoOut Up Down Zebra
---------- ----- ------------------------- -------------------- --------- ----- -------- ------- ---------- ------- ------ ------------------------- ---------- ---------- ----- ----- ---------------- -------- -------- ------ ------ ------------ ------ ----- ------ ------- ------- ------ ------- -- ---- -----
417705214 True 6.0.0.24 6.0.0.23 down 0 False 6:19:46:19 dynamic 251 control-detection-expired ok 21 100 100 30 300 300 50 0 50 0 0 0 12517 698550 0 0 1 1 3
770667106 False fe80::a288:c2ff:fe2c:5253 fe80::202:ff:fe00:33 p1_if down 0 False 0:03:23:41 dynamic ok ok 22 102 102 3 1000 1000 50 0 0 0 0 0 0 13954 0 0 0 0 1
918556010 False fe80::a288:c2ff:fe2c:5252 fe80::202:ff:fe00:2f p0_if.100 up 6 False 6:19:39:07 dynamic ok ok 21 100 100 20 200 200 50 0 0 0 0 0 3270275 3448759 0 0 2 1 5
1668048197 True 6000::24 6000::23 down 0 False 6:19:46:19 dynamic 251 control-detection-expired ok 21 100 100 30 300 300 50 0 50 0 0 0 12373 698363 0 0 1 1 7
3190546666 False fe80::a288:c2ff:fe2c:5252 fe80::202:ff:fe00:2f p0_if.101 up 7 False 6:19:39:07 dynamic ok ok 22 102 102 20 200 200 50 0 0 0 0 0 3270354 3448640 0 0 2 1 6
Sample BFD and BGP Configurations for a HBN Node <--> CumulusLinux Node Connection
HBN:
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 111 vni 1000111
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 112 vni 1000112
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 213 vni 1000213
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 214 vni 1000214
nv set evpn enable on
nv set interface lo ip address 6.0.0.24/32
nv set interface lo ip address 2006:20:20::24/128
nv set interface lo ip address 6000::24/128
nv set interface lo type loopback
nv set interface p0_if description 'alias p0_if to leaf-21 swp3'
nv set interface p0_if,p1_if,pf0hpf_if,pf0vf0_if,pf1hpf_if,pf1vf0_if type swp
nv set interface p0_if.100 vlan 100
nv set interface p0_if.100-101 base-interface p0_if
nv set interface p0_if.100-101 type sub
nv set interface p0_if.101 vlan 101
nv set interface p1_if description 'alias p1_if to leaf-22 swp3'
nv set interface pf0hpf_if bridge domain br_default access 111
nv set interface pf0hpf_if description 'alias pf0hpf_if to host-211 c1_0np0'
nv set interface pf0vf0_if bridge domain br_default access 112
nv set interface pf0vf0_if description 'alias pf0vf0_if to host-211 c1_0np0v0'
nv set interface pf1hpf_if bridge domain br_default access 213
nv set interface pf1hpf_if description 'alias pf1hpf_if to host-211 c1_1np1'
nv set interface pf1vf0_if bridge domain br_default access 214
nv set interface pf1vf0_if description 'alias pf1vf0_if to host-211 c1_1np0v0'
nv set interface vlan111 ip address 60.1.1.21/24
nv set interface vlan111 ip address 2060:1:1:1::21/64
nv set interface vlan111 ip vrr address 60.1.1.250/24
nv set interface vlan111 ip vrr address 2060:1:1:1::250/64
nv set interface vlan111 vlan 111
nv set interface vlan111,213 ip vrf vrf2
nv set interface vlan111-112,213-214 ip ipv4 forward on
nv set interface vlan111-112,213-214 ip ipv6 forward on
nv set interface vlan111-112,213-214 ip vrr enable on
nv set interface vlan111-112,213-214 ip vrr mac-address 00:00:5e:00:01:01
nv set interface vlan111-112,213-214 type svi
nv set interface vlan112 ip address 50.1.1.21/24
nv set interface vlan112 ip address 2050:1:1:1::21/64
nv set interface vlan112 ip vrr address 50.1.1.250/24
nv set interface vlan112 ip vrr address 2050:1:1:1::250/64
nv set interface vlan112 vlan 112
nv set interface vlan112,214 ip vrf vrf1
nv set interface vlan213 ip address 60.1.210.21/24
nv set interface vlan213 ip address 2060:1:1:210::21/64
nv set interface vlan213 ip vrr address 60.1.210.250/24
nv set interface vlan213 ip vrr address 2060:1:1:210::250/64
nv set interface vlan213 vlan 213
nv set interface vlan214 ip address 50.1.210.21/24
nv set interface vlan214 ip address 2050:1:1:210::21/64
nv set interface vlan214 ip vrr address 50.1.210.250/24
nv set interface vlan214 ip vrr address 2050:1:1:210::250/64
nv set interface vlan214 vlan 214
nv set nve vxlan arp-nd-suppress on
nv set nve vxlan enable on
nv set nve vxlan source address 6.0.0.24
nv set platform
nv set router bfd profile pf1 detect-multiplier 21
nv set router bfd profile pf1 min-rx-interval 100
nv set router bfd profile pf1 min-tx-interval 100
nv set router bfd profile pf2 detect-multiplier 22
nv set router bfd profile pf2 min-rx-interval 102
nv set router bfd profile pf2 min-tx-interval 102
nv set router bgp enable on
nv set router policy route-map ALLOW_LO rule 10 action permit
nv set router policy route-map ALLOW_LO rule 10 match interface lo
nv set router policy route-map ALLOW_LOBR rule 10 action permit
nv set router policy route-map ALLOW_LOBR rule 10 match interface lo
nv set router policy route-map ALLOW_LOBR rule 20 action permit
nv set router policy route-map ALLOW_LOBR rule 20 match interface br_default
nv set router vrr enable on
nv set system config snippet frr.conf 'log file /var/log/hbn/frr/bgpd.log'
nv set system global system-mac 00:01:00:00:1e:01
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast multipaths ebgp 16
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected route-map ALLOW_LOBR
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast multipaths ebgp 16
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected route-map ALLOW_LOBR
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp autonomous-system 650024
nv set vrf default router bgp enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 6.0.0.23 bfd profile pf1
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 6.0.0.23 multihop-ttl 5
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 6.0.0.23 remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 6.0.0.23 type numbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 6.0.0.26 peer-group EBGP_MHOP_V4
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 6.0.0.26 type numbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 6000::23 address-family ipv4-unicast enable off
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 6000::23 address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 6000::23 bfd profile pf1
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 6000::23 multihop-ttl 5
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 6000::23 remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 6000::23 type numbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 6000::26 peer-group EBGP_MHOP_V6
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 6000::26 type numbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if address-family l2vpn-evpn add-path-tx off
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if peer-group TOR_LEAF_SPINE
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if.100 address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if.100 address-family l2vpn-evpn add-path-tx off
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if.100 address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if.100 bfd profile pf1
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if.100 peer-group TOR_LEAF_SPINE
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if.100 remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if.100 type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if.101 address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if.101 address-family l2vpn-evpn add-path-tx off
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if.101 address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if.101 peer-group TOR_LEAF_SPINE
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if.101 remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if.101 type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if address-family l2vpn-evpn add-path-tx off
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if peer-group TOR_LEAF_SPINE
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp path-selection multipath aspath-ignore on
nv set vrf default router bgp path-selection routerid-compare on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group EBGP_MHOP_V4 bfd profile pf2
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group EBGP_MHOP_V4 multihop-ttl 5
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group EBGP_MHOP_V4 remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group EBGP_MHOP_V6 address-family ipv4-unicast enable off
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group EBGP_MHOP_V6 address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group EBGP_MHOP_V6 bfd profile pf2
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group EBGP_MHOP_V6 multihop-ttl 5
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group EBGP_MHOP_V6 remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group TOR_LEAF_SPINE address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group TOR_LEAF_SPINE address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group TOR_LEAF_SPINE bfd profile pf2
nv set vrf default router bgp router-id 6.0.0.24
nv set vrf default router rib ipv4 protocol static fib-filter fib2
nv set vrf vrf1 evpn enable on
nv set vrf vrf1 evpn vni 104001
nv set vrf vrf2 evpn enable on
nv set vrf vrf2 evpn vni 104002
CL:
nv set bridge domain
nv set interface eth0 ip address 192.168.0.15/24
nv set interface eth0 ip gateway 192.168.0.2
nv set interface eth0 type eth
nv set interface lo ip address 6.0.0.20/32
nv set interface lo ip address 2006:20:20::20/128
nv set interface lo ip address 6000::20/128
nv set interface lo type loopback
nv set interface swp2 description 'alias swp2 to spine-2 swp3'
nv set interface swp2-4 link auto-negotiate off
nv set interface swp2-4 link duplex full
nv set interface swp2-4 link speed 200G
nv set interface swp2-4 type swp
nv set interface swp2.100,swp3.100 vlan 100
nv set interface swp2.100-103 base-interface swp2
nv set interface swp2.100-103,swp3.100-101 type sub
nv set interface swp2.101,swp3.101 vlan 101
nv set interface swp2.102 vlan 102
nv set interface swp2.103 ip address 23.0.103.1/24
nv set interface swp2.103 router ospf enable on
nv set interface swp2.103 router ospf passive off
nv set interface swp2.103 vlan 103
nv set interface swp3 description 'alias swp3 to bfs-21 p0'
nv set interface swp3.100-101 base-interface swp3
nv set interface swp4 description 'alias swp4 to bfs-22 p0'
nv set platform
nv set router bgp enable on
nv set router ospf enable on
nv set router policy route-map ALLOW_LO rule 10 action permit
nv set router policy route-map ALLOW_LO rule 10 match interface lo
nv set router policy route-map ALLOW_LOBR rule 10 action permit
nv set router policy route-map ALLOW_LOBR rule 10 match interface lo
nv set router policy route-map ALLOW_LOBR rule 20 action permit
nv set router policy route-map ALLOW_LOBR rule 20 match interface br_default
nv set system aaa user cumulus hashed-password '*'
nv set system aaa user cumulus role system-admin
nv set system config auto-save state enabled
nv set system config snippet frr.conf 'log syslog
log file /var/log/hbn/frr/bgp_bfd.log'
nv set system control-plane acl acl-default-dos inbound
nv set system control-plane acl acl-default-whitelist inbound
nv set system hostname leaf-21
nv set system ssh-server permit-root-login enabled
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast multipaths ebgp 16
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected route-map ALLOW_LOBR
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast multipaths ebgp 16
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected route-map ALLOW_LOBR
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp autonomous-system 650020
nv set vrf default router bgp enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp2.100 address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp2.100 address-family l2vpn-evpn add-path-tx off
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp2.100 address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp2.100 peer-group TOR_LEAF_SPINE
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp2.100 remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp2.100 type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp3.100 address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp3.100 address-family l2vpn-evpn add-path-tx off
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp3.100 address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp3.100 bfd detect-multiplier 20
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp3.100 bfd enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp3.100 bfd min-rx-interval 200
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp3.100 bfd min-tx-interval 200
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp3.100 peer-group TOR_LEAF_SPINE
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp3.100 remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp3.100 type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp3.101 address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp3.101 address-family l2vpn-evpn add-path-tx off
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp3.101 address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp3.101 bfd detect-multiplier 20
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp3.101 bfd enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp3.101 bfd min-rx-interval 200
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp3.101 bfd min-tx-interval 200
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp3.101 peer-group TOR_LEAF_SPINE
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp3.101 remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp3.101 type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp4 address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp4 address-family l2vpn-evpn add-path-tx off
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp4 address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp4 bfd detect-multiplier 20
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp4 bfd enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp4 bfd min-rx-interval 200
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp4 bfd min-tx-interval 200
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp4 peer-group TOR_LEAF_SPINE
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp4 remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp4 type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp path-selection multipath aspath-ignore on
nv set vrf default router bgp path-selection routerid-compare on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group TOR_LEAF_SPINE address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group TOR_LEAF_SPINE address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group TOR_LEAF_SPINE capabilities extended-nexthop on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group TOR_LEAF_SPINE timers connection-retry 10
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group TOR_LEAF_SPINE timers hold 9
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group TOR_LEAF_SPINE timers keepalive 3
nv set vrf default router bgp router-id 6.0.0.20
nv set vrf default router ospf area 0 network 23.0.103.0/24
nv set vrf default router ospf enable on
nv set vrf default router ospf router-id 6.0.0.20
nv set vrf vrf1 evpn enable on
nv set vrf vrf1 evpn vni 104001
nv set vrf vrf2 evpn enable on
nv set vrf vrf2 evpn vni 104002
Example topology with hbn, route server and BF Host using BFD
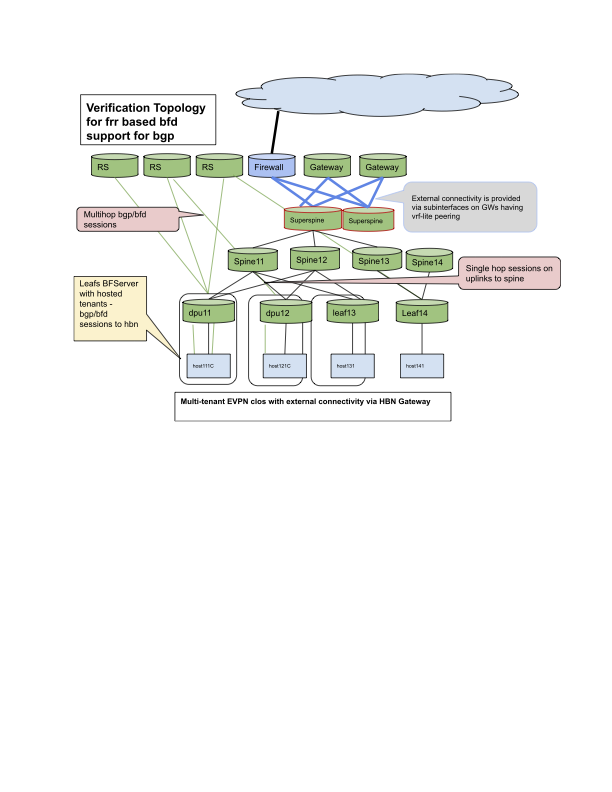
In this example HBN running on dpu11 peers with
route servers using multihop BFD in default vrf for EVPN
host11C using singlehop BFD in each tenant vrf
tenant1 uses svi for bgp/bfd session
tenant2 uses subinterface to peer to host
Configuration
DPU1 HBN configuration
HBN (DPU1)
root@doca-hbn-service-bf3-s09-1-ipmi:/tmp# nv config show -o commands
nv set bridge domain br_default vlan 101 vni 10101
nv set evpn enable on
nv set evpn route-advertise svi-ip off
nv set interface lo ip address 6.0.0.9/32
nv set interface lo ip address 2001::9/128
nv set interface lo type loopback
nv set interface p0_if,p1_if,pf0hpf_if,pf0vf0_if,pf0vf1_if,pf0vf2_if,pf0vf3_if,pf0vf4_if,pf0vf5_if,pf0vf6_if,pf0vf7_if,pf0vf8_if,pf0vf9_if,pf1hpf_if,pf1vf0_if,pf1vf1_if type swp
nv set interface pf0vf0_if bridge domain br_default access 101
nv set interface pf0vf1_if.2 base-interface pf0vf1_if
nv set interface pf0vf1_if.2 ip address 22.10.0.9/16
nv set interface pf0vf1_if.2 ip address 2020:0:2:10::9/64
nv set interface pf0vf1_if.2 type sub
nv set interface pf0vf1_if.2 vlan 2
nv set interface pf0vf1_if.2,vlan3002 ip vrf tenant2
nv set interface vlan101 ip address 21.1.0.9/16
nv set interface vlan101 ip address 2020:0:1:1::9/64
nv set interface vlan101 ip vrr address 21.1.0.250/16
nv set interface vlan101 ip vrr address 2020:0:1:1::250/64
nv set interface vlan101 ip vrr enable on
nv set interface vlan101 ip vrr mac-address 00:00:01:00:00:65
nv set interface vlan101 vlan 101
nv set interface vlan101,3001 ip vrf tenant1
nv set interface vlan101,3001-3002 base-interface br_default
nv set interface vlan101,3001-3002 type svi
nv set interface vlan3001 vlan 3001
nv set interface vlan3002 vlan 3002
nv set nve vxlan arp-nd-suppress on
nv set nve vxlan enable on
nv set nve vxlan source address 6.0.0.9
nv set platform
nv set router bfd profile fabric-bfd-profile detect-multiplier 3
nv set router bfd profile fabric-bfd-profile min-rx-interval 300
nv set router bfd profile fabric-bfd-profile min-tx-interval 300
nv set router bfd profile fabric-bfd-profile minimum-ttl 1
nv set router bfd profile fabric-bfd-profile passive-mode off
nv set router bfd profile fabric-bfd-profile shutdown off
nv set router bfd profile hostT1-bfd-profile detect-multiplier 3
nv set router bfd profile hostT1-bfd-profile min-rx-interval 300
nv set router bfd profile hostT1-bfd-profile min-tx-interval 300
nv set router bfd profile hostT1-bfd-profile minimum-ttl 1
nv set router bfd profile hostT1-bfd-profile passive-mode off
nv set router bfd profile hostT1-bfd-profile shutdown off
nv set router bfd profile hostT2-bfd-profile detect-multiplier 3
nv set router bfd profile hostT2-bfd-profile min-rx-interval 300
nv set router bfd profile hostT2-bfd-profile min-tx-interval 300
nv set router bfd profile hostT2-bfd-profile minimum-ttl 1
nv set router bfd profile hostT2-bfd-profile passive-mode off
nv set router bfd profile hostT2-bfd-profile shutdown off
nv set router bfd profile ppp1
nv set router bfd profile rserver-bfd-profile detect-multiplier 3
nv set router bfd profile rserver-bfd-profile min-rx-interval 300
nv set router bfd profile rserver-bfd-profile min-tx-interval 300
nv set router bfd profile rserver-bfd-profile minimum-ttl 1
nv set router bfd profile rserver-bfd-profile passive-mode off
nv set router bfd profile rserver-bfd-profile shutdown off
nv set router bgp autonomous-system 65011
nv set router bgp enable on
nv set router bgp router-id 6.0.0.9
nv set router vrr enable on
nv set system config snippet
nv set system global
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 6.0.0.5 peer-group rservers
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 6.0.0.5 type numbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if peer-group fabric
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p0_if type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if peer-group fabric
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor p1_if type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric bfd profile fabric-bfd-profile
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rservers address-family ipv4-unicast enable off
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rservers address-family l2vpn-evpn add-path-tx off
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rservers address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rservers bfd profile rserver-bfd-profile
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rservers multihop-ttl 10
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rservers remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rservers update-source lo
nv set vrf tenant1 evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 evpn vni 30001
nv set vrf tenant1 loopback ip address 7.1.0.9/32
nv set vrf tenant1 loopback ip address 2007:0:1::9/64
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp neighbor 21.1.0.10 peer-group hostgroup
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp neighbor 21.1.0.10 type numbered
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp peer-group hostgroup address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp peer-group hostgroup address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp peer-group hostgroup bfd profile hostT1-bfd-profile
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp peer-group hostgroup remote-as external
nv set vrf tenant1 router bgp router-id 6.0.0.9
nv set vrf tenant2 evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant2 evpn vni 30002
nv set vrf tenant2 loopback ip address 7.2.0.9/32
nv set vrf tenant2 loopback ip address 2007:0:2::9/64
nv set vrf tenant2 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant2 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf tenant2 router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant2 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant2 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf tenant2 router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast route-export to-evpn enable on
nv set vrf tenant2 router bgp enable on
nv set vrf tenant2 router bgp neighbor 22.10.0.10 peer-group hostgroup
nv set vrf tenant2 router bgp neighbor 22.10.0.10 type numbered
nv set vrf tenant2 router bgp peer-group hostgroup address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant2 router bgp peer-group hostgroup address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf tenant2 router bgp peer-group hostgroup bfd profile hostT2-bfd-profile
nv set vrf tenant2 router bgp peer-group hostgroup remote-as external
nv set vrf tenant2 router bgp router-id 6.0.0.9
nv set vrf tenant2 table auto
root@doca-hbn-service-bf3-s09-1-ipmi:/tmp#
Host11C configuration
Host is running frr that has support for BFD:
Host Requirements
root@bf3-s09:/home/cumulus# dpkg -l | grep frr
ii frr 8.4.4-1.1ubuntu6.3 amd64 FRRouting suite of internet protocols (BGP, OSPF, IS-IS, ...)
ii frr-pythontools 8.4.4-1.1ubuntu6.3 all FRRouting suite - Python tools
root@bf3-s09:/home/cumulus#
root@bf3-s09:/home/cumulus# cat /etc/os-release
PRETTY_NAME="Ubuntu 24.04.2 LTS"
NAME="Ubuntu"
VERSION_ID="24.04"
VERSION="24.04.2 LTS (Noble Numbat)"
VERSION_CODENAME=noble
ID=ubuntu
ID_LIKE=debian
HOME_URL="https://www.ubuntu.com/"
SUPPORT_URL="https://help.ubuntu.com/"
BUG_REPORT_URL="https://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/"
PRIVACY_POLICY_URL="https://www.ubuntu.com/legal/terms-and-policies/privacy-policy"
UBUNTU_CODENAME=noble
LOGO=ubuntu-logo
root@bf3-s09:/home/cumulus#
Host FRR configuration
bf3-s09# sh run
Building configuration...
Current configuration:
!
frr version 8.4.4
frr defaults datacenter
hostname bf3-s09
log syslog informational
no ip forwarding
no ipv6 forwarding
service integrated-vtysh-config
!
router bgp 1000010
exit
!
router bgp 1000010 vrf tenant1_101
neighbor 21.1.0.9 remote-as external
neighbor 21.1.0.9 bfd
neighbor 21.1.0.9 bfd profile host-bfd-profile
!
address-family ipv4 unicast
redistribute connected
exit-address-family
!
address-family ipv6 unicast
redistribute connected
neighbor 21.1.0.9 activate
exit-address-family
exit
!
router bgp 1000010 vrf tenant2
neighbor 22.10.0.9 remote-as external
neighbor 22.10.0.9 bfd
neighbor 22.10.0.9 bfd profile host-bfd-profile
!
address-family ipv4 unicast
redistribute connected
exit-address-family
!
address-family ipv6 unicast
redistribute connected
neighbor 22.10.0.9 activate
exit-address-family
exit
!
bfd
profile host-bfd-profile
transmit-interval 301
receive-interval 301
minimum-ttl 1
exit
!
exit
!
end
bf3-s09#
Host11C vrf and interface configuration
root@bf3-s09:/home/cumulus# ip vrf list
Name Table
-----------------------
tenant1_101 1001
tenant2 1002
root@bf3-s09:/home/cumulus# ifquery -a
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
address 10.0.0.10/32
address 2000::10/128
auto tenant1_101
iface tenant1_101
vrf-table auto
auto tenant2
iface tenant2
vrf-table auto
auto c1_0np0
iface c1_0np0
auto c1_0v0
iface c1_0v0
address 21.1.0.10/16
address 2020:0:1:1::10/64
gateway 21.1.0.9
gateway 2020:0:1:1::9
vrf tenant1_101
hwaddress 00:03:00:0a:0a:00
auto c1_0v1
iface c1_0v1
auto c1_0v2
iface c1_0v2
auto c1_0v3
iface c1_0v3
auto c1_0v4
iface c1_0v4
auto c1_0v5
iface c1_0v5
auto c1_0v6
iface c1_0v6
auto c1_0v7
iface c1_0v7
auto c1_0v8
iface c1_0v8
auto c1_0v9
iface c1_0v9
auto c1_1np1
iface c1_1np1
auto c1_1v0
iface c1_1v0
auto c1_1v1
iface c1_1v1
auto c1_0v1.2
iface c1_0v1.2
address 22.10.0.10/16
address 2020:0:2:10::10/64
gateway 22.10.0.9
gateway 2020:0:2:10::9
vrf tenant2
root@bf3-s09:/home/cumulus#
show commands
BFD peers
root@doca-hbn-service-bf3-s09-1-ipmi:/tmp# nv show vrf tenant2 router bfd peer
MHop - Multihop, Local - Local, Peer - Peer, Interface - Interface, State -
State, Passive - Passive Mode, Time - Up/Down Time, Type - Config Type
LocalId MHop Local Peer Interface State Passive Time Type
---------- ----- --------- ---------- ----------- ----- ------- ---------- -------
1672363941 False 22.10.0.9 22.10.0.10 pf0vf1_if.2 up False 1:15:55:07 dynamic
root@doca-hbn-service-bf3-s09-1-ipmi:/tmp# nv show vrf tenant1 router bfd peer
MHop - Multihop, Local - Local, Peer - Peer, Interface - Interface, State -
State, Passive - Passive Mode, Time - Up/Down Time, Type - Config Type
LocalId MHop Local Peer Interface State Passive Time Type
---------- ----- -------- --------- --------- ----- ------- ---------- -------
3647797911 False 21.1.0.9 21.1.0.10 vlan101 up False 1:15:55:17 dynamic
root@doca-hbn-service-bf3-s09-1-ipmi:/tmp# nv show vrf default router bfd peer
MHop - Multihop, Local - Local, Peer - Peer, Interface - Interface, State -
State, Passive - Passive Mode, Time - Up/Down Time, Type - Config Type
LocalId MHop Local Peer Interface State Passive Time Type
---------- ----- ------------------------- ------------------- --------- ----- ------- ---------- -------
1241890423 False fe80::5aa2:e1ff:fe62:f81e fe80::202:ff:fe00:a p0_if up False 1:15:55:27 dynamic
1280361828 False fe80::5aa2:e1ff:fe62:f81f fe80::202:ff:fe00:d p1_if up False 1:15:55:27 dynamic
1936332380 True 6.0.0.9 6.0.0.5 up False 1:15:55:26 dynamic
root@doca-hbn-service-bf3-s09-1-ipmi:/tmp#
Route Server SN1 configuration
In this example route server is running CumulusLinux 5.12
RS SN1 configuration
root@sn1:mgmt:/var/home/cumulus# nv config show -o commands
nv set bridge domain
nv set interface eth0 ip address 192.168.0.15/24
nv set interface eth0 ip gateway 192.168.0.2
nv set interface eth0 type eth
nv set interface lo ip address 6.0.0.5/32
nv set interface lo ip address 2001::5/128
nv set interface lo type loopback
nv set interface swp1 type swp
nv set platform
nv set router bgp autonomous-system 65505
nv set router bgp enable on
nv set router bgp router-id 6.0.0.5
nv set system aaa user cumulus hashed-password '*'
nv set system aaa user cumulus role system-admin
nv set system config auto-save state enabled
nv set system config snippet
nv set system control-plane acl acl-default-dos inbound
nv set system control-plane acl acl-default-whitelist inbound
nv set system hostname sn1
nv set system ssh-server permit-root-login enabled
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv4-unicast redistribute connected enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 6.0.0.4 peer-group rclients
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 6.0.0.4 type numbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 6.0.0.9 peer-group rclients
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor 6.0.0.9 type numbered
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp1 peer-group rcsuper
nv set vrf default router bgp neighbor swp1 type unnumbered
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric address-family ipv6-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric bfd enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group fabric remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rclients address-family ipv4-unicast attribute-mod nexthop off
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rclients address-family ipv4-unicast enable off
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rclients address-family l2vpn-evpn add-path-tx off
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rclients address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rclients bfd enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rclients multihop-ttl 10
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rclients remote-as external
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rclients update-source lo
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rcsuper address-family ipv4-unicast enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rcsuper address-family l2vpn-evpn add-path-tx off
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rcsuper address-family l2vpn-evpn enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rcsuper bfd enable on
nv set vrf default router bgp peer-group rcsuper remote-as external
root@sn1:mgmt:/var/home/cumulus#
Route Server SN1 - bgp and bfd sessions
root@sn1:mgmt:/var/home/cumulus# nv show vrf
Name Table Summary
------- ----- -----------------------
default 254 IP Address: 127.0.0.1/8
IP Address: 2001::5/128
IP Address: 6.0.0.5/32
IP Address: ::1/128
mgmt 1001 IP Address: 127.0.0.1/8
IP Address: 127.0.1.1/8
IP Address: ::1/128
root@sn1:mgmt:/var/home/cumulus# nv show vrf default router bgp neighbor
AS - Remote Autonomous System, PeerEstablishedTime - Peer established time in
UTC format, UpTime - Last connection reset time in days,hours:min:sec, Afi-Safi
- Address family, PfxSent - Transmitted prefix counter, PfxRcvd - Recieved
prefix counter
Neighbor AS State PeerEstablishedTime UpTime MsgRcvd MsgSent Afi-Safi PfxSent PfxRcvd
-------- ----- ----------- -------------------- -------- ------- ------- ------------ ------- -------
6.0.0.4 65012 established 2025-04-23T04:52:24Z 14:38:47 46720 46727 l2vpn-evpn 32 10
6.0.0.9 65011 established 2025-04-23T04:58:14Z 14:33:33 46729 46759 l2vpn-evpn 32 13
swp1 65300 established 2025-04-23T04:41:41Z 14:49:12 46743 46745 ipv4-unicast 6 5
l2vpn-evpn 32 9
root@sn1:mgmt:/var/home/cumulus#
root@sn1:mgmt:/var/home/cumulus# ptmctl -b
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
port peer state local type diag vrf
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
swp1 fe80::202:ff:fe00:11 Up fe80::202:ff:fe00:8 singlehop N/A N/A
N/A 6.0.0.4 Up 6.0.0.5 multihop N/A N/A
N/A 6.0.0.9 Up 6.0.0.5 multihop N/A N/A
root@sn1:mgmt:/var/home/cumulus#
Control plane policing (CoPP)
Control plane policing is a mechanism to guard the control plane. This is achieved by policing the traffic coming towards the control plane. Control plane constitutes of routers, management protocol handlers and system services. CoPP ensures only necessary traffic reaches to the control plane without exceeding predefined packet rate. CoPP uses filtering and rate limiting traffic coming towards control plane. This prevents overloading of CPU and other system resources with excessive packets i.e. Denial of service (DoS) attacks. The excess traffic is rate limited and dropped according to predefined or user defined configurations. CoPP configuration is applied globally to the control plane.
We have following separate policers for each protocol or group of packets. Unit of each value is in packet per second.
Sr. No. | Policer Name | Protocol | Default State | Default Rate | Default Burst |
1. | arp | ARP, RARP | Enabled | 800 | 800 |
2. | bgp | BGP | Enabled | 2000 | 2000 |
3. | bfd | BFD | Enabled | 2000 | 2000 |
4. | icmp | ICMP, ICMPv6 | Enabled | 1000 | 1000 |
5. | icmp6-neigh | IPv6 NDP | Enabled | 1000 | 1000 |
6. | dhcp | DHCPv4, DHCPv6 | Enabled | 2000 | 2000 |
7. | ip2me | All other IPv4 or IPv6 traffic destined for HBN | Enabled | 1000 | 1000 |
8. | catch-all | All other traffic not matched by above rules | Enabled | 100 | 100 |
We enabled the CoPP configuration on HBN by default with predefined values.
CoPP configuration
Enabling a policer
In this example we are enabling a bgp policer.
nv set system control-plane policer bgp enable on
Updating a policer
In this example we are changing the rate and burst of the bgp policer.
nv set system control-plane policer bgp rate 3000
nv set system control-plane policer bgp burst 3000
Disabling a policer
nv set system control-plane policer bgp enable off
CoPP show commands
CoPP summary
Following CLI shows the summary of all the policers. This includes the configurations and respective statistics
nv show system control-plane policer
Corresponding sample output
Policer State Policer Rate Policer Burst To CPU Pkts To CPU Bytes Violated Packets Violated Bytes
----------- ----- ------------ ------------- ----------- ------------ ---------------- --------------
arp on 800 800 1327 133663 0 0
bfd on 2000 2000 0 0 0 0
bgp on 2000 2000 167470 16689652 0 0
catch-all on 100 100 0 0 0 0
dhcp on 2000 2000 0 0 0 0
icmp on 1000 1000 0 0 0 0
icmp6-neigh on 1000 1000 426605 36641706 0 0
ip2me on 1000 1000 0 0 0 0
Show CLI for a specific policer
Following CLI shows details of individual policer. In this specific example bgp policer details will be shown
nv show system control-plane policer bgp
Corresponding sample output
operational applied
---------------- ----------- -------
state on on
burst 3000 3000
rate 3000 3000
statistics
to-cpu-pkts 167686
to-cpu-bytes 16710895
violated-pkts 0
violated-bytes 0
DHCP Relay on HBN
DHCP is a client server protocol that automatically provides IP hosts with IP addresses and other related configuration information. A DHCP relay (agent) is a host that forwards DHCP packets between clients and servers. DHCP relays forward requests and replies between clients and servers that are not on the same physical subnet.
DHCP relay can be configured using either flat file (supervisord configuration) or through NVUE.
Configuration
HBN is a non-systemd based container. Therefore, the DHCP relay must be configured as explained in the following subsections.
Flat File Configuration (Supervisord)
The HBN initialization script installs default configuration files on BlueField in /var/lib/hbn/etc/supervisor/conf.d/. BlueField directory is mounted to /etc/supervisor/conf.d which achieves configuration persistence.
By default, DHCP relay is disabled. Default configuration applies to one instance of DHCPv4 relay and DHCPv6 relay in the default VRF.
NVUE Configuration
The user can use NVUE to configure and maintain DHCPv4 and DHCPv6 relays with CLI and REST API. NVUE generates all the required configurations and maintains the relay service.
DHCPv4 Relay Configuration
NVUE Example
The following configuration starts a relay service which listens for the DHCP messages on p0_if, p1_if, and vlan482 and relays the requests to DHCP server 10.89.0.1 with gateway-interface as lo.
nv set service dhcp-relay default gateway-interface lo
nv set service dhcp-relay default interface p0_if
nv set service dhcp-relay default interface p1_if
nv set service dhcp-relay default interface vlan482 downstream
nv set service dhcp-relay default server 10.89.0.1
Flat Files Example
[program: isc-dhcp-relay-default]
command = /usr/sbin/dhcrelay --nl -d -i p0_if -i p1_if -id vlan482 -U lo 10.89.0.1
autostart = true
autorestart = unexpected
startsecs = 3
startretries = 3
exitcodes = 0
stopsignal = TERM
stopwaitsecs = 3
Where:
Option | Description |
| Network interface to listen on for requests and replies |
| Upstream network interface |
| Downstream network interface |
| Gateway IP address interface. Use |
| Debug logging. Location: |
| Append an agent option field to each request before forwarding it to the server with default values for |
| Set a custom remote ID string (max of 255 chars). To use this option, you must also enable the |
| Set the underlying physical interface which receives the packet as the |
DHCPv4 Relay Option 82
NVUE Example
The following NVUE command is used to enable option 82 insertion in DHCP packets with default values:
nv set service dhcp-relay default agent enable on
To provide a custom remote-id (e.g., host10) using NVUE:
nv set service dhcp-relay default agent remote-id host10
To use the underlying physical interface on which the request is received as circuit-id using NVUE:
nv set service dhcp-relay default agent use-pif-circuit-id enable on
Flat Files Example
[program: isc-dhcp-relay-default]
command = /usr/sbin/dhcrelay --nl -d -i p0_if -i p1_if -id vlan482 -U lo -a --use-pif-circuit-id -r host10 10.89.0.1
autostart = true
autorestart = unexpected
startsecs = 3
startretries = 3
exitcodes = 0
stopsignal = TERM
stopwaitsecs = 3
DHCPv6 Relay Configuration
NVUE Example
The following NVUE command starts the DHCPv6 Relay service which listens for DHCPv6 requests on vlan482 and sends relayed DHCPv6 requests towards p0_if and p1_if.
nv set service dhcp-relay6 default interface downstream vlan482
nv set service dhcp-relay6 default interface upstream p0_if
nv set service dhcp-relay6 default interface upstream p1_if
Flat Files Example
[program: isc-dhcp-relay6-default]
command = /usr/sbin/dhcrelay --nl -6 -d -l vlan482 -u p0_if -u p1_if
autostart = true
autorestart = unexpected
startsecs = 3
startretries = 3
exitcodes = 0
stopsignal = TERM
stopwaitsecs = 3
Where:
Option | Description |
| Downstream interface. Use |
| Upstream interface. Use |
| IPv6 |
| Debug logging located at |
DHCP Relay and VRF Considerations
DHCP relay can be spawned inside a VRF context to handle the DHCP requests in that VRF. There can only be 1 instance each of DHCPv4 relay and DHCPv6 relay per VRF. To achieve that, the user can follow these guidelines:
DHCPv4 on default VRF:
/usr/sbin/dhcrelay --nl -i <interface> -U [address]%%<interface> <server_ip>
DHCPv4 on VRF:
/usr/sbin/ip vrf exec <vrf> /usr/sbin/dhcrelay –-nl -i <interface> -U [address]%%<interface> <server_ip>
DHCPv6 on default VRF:
/usr/sbin/dhcrelay --nl -6 -l <interface> -u <interface>
DHCPv6 on VRF:
/usr/sbin/ip vrf exec <vrf> /usr/sbin/dhcrelay --nl -6 -l <interface> -u <interface>