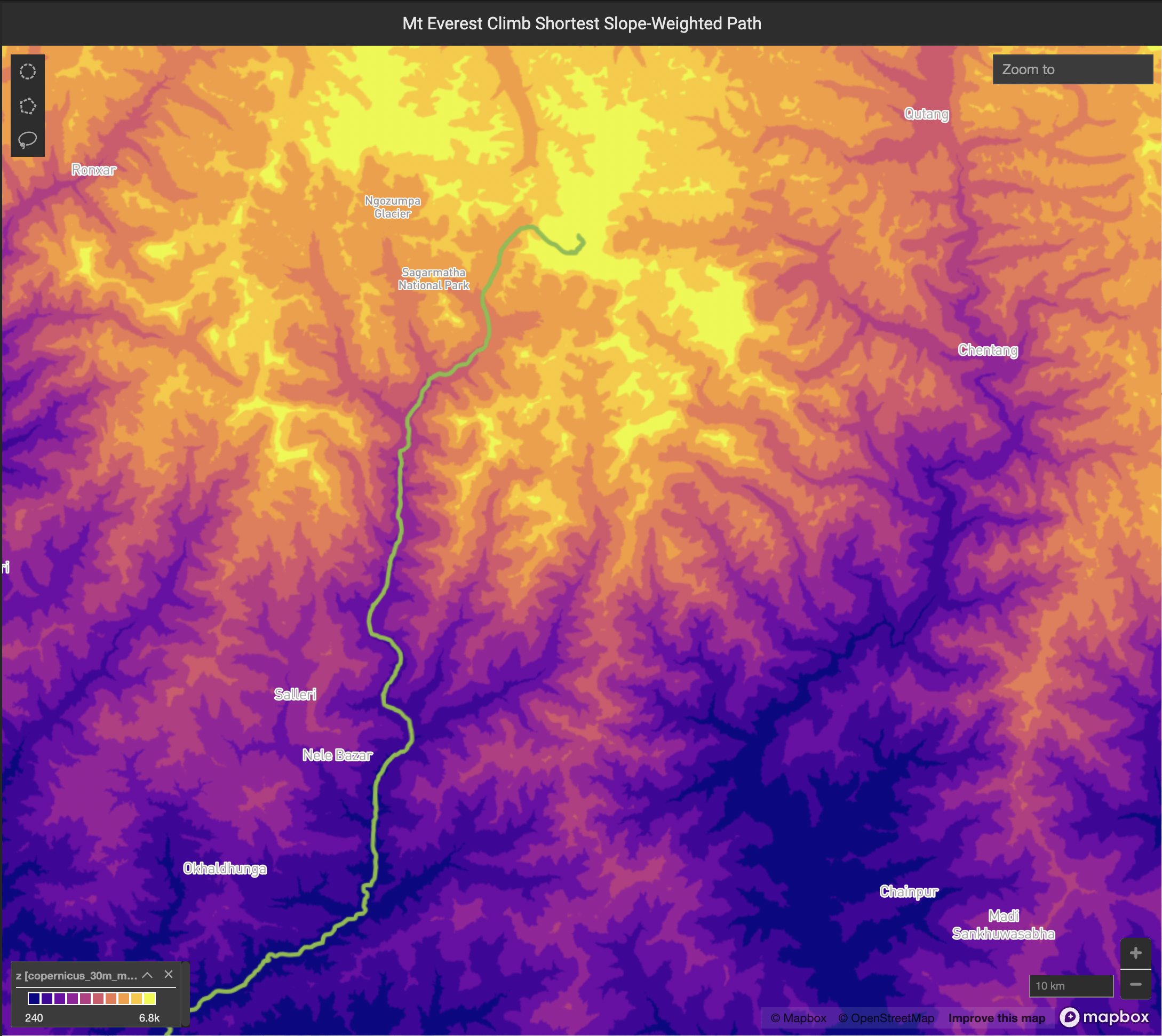
tf_raster_graph_shortest_slope_weighted_path
Aggregate point data into x/y bins of a given size in meters to form a dense spatial grid, computing the specified aggregate (using agg_type) across all points in each bin as the output value for the bin. A Gaussian average is then taken over the neighboring bins, with the number of bins specified by neighborhood_fill_radius, optionally only filling in null-valued bins if fill_only_nulls is set to true.
The graph shortest path is then computed between an origin point on the grid specified by origin_x and origin_y and a destination point on the grid specified by destination_x and destination_y, where the shortest path is weighted by the nth exponent of the computed slope between a bin and its neighbors, with the nth exponent being specified by slope_weighted_exponent. A max allowed traversable slope can be specified by slope_pct_max, such that no traversal is considered or allowed between bins with absolute computed slopes greater than the percentage specified by slope_pct_max.
Input Arguments
Output Columns