DOCA Stream Receive Performance Application Guide
This guide outlines the implementation of the DOCA Stream Receive Performance application, built on top of the NVIDIA® BlueField® DPU.
The Stream Receive Performance application is designed to measure and evaluate RX performance using the NVIDIA DOCA RMAX library. It leverages the capabilities of DOCA RMAX and NVIDIA Rivermax to support efficient, high-performance media and data streaming.
Key Technologies
DOCA RMAX API – A component of the NVIDIA DOCA framework, optimized for networking tasks in media streaming use cases.
NVIDIA Rivermax SDK – Built to exploit BlueField DPU hardware acceleration, enabling direct data transfers between the NIC and GPU, minimizing CPU load.
This architecture delivers high throughput, ultra-low latency, and minimal CPU utilization making it an ideal solution for demanding real-time streaming workloads.
Deployment Notes
DOCA Rivermax applications must run on BlueField target DPUs with root privileges or other additional permissions and capabilities
Ensure the DPU has a valid IP address configured
Allocate an appropriate number of huge pages for optimal performance. Refer to "Rivermax Performance-oriented Development Guidelines" for details.
InfoTo access this document, join the NVIDIA Rivermax SDK developers' program and access documentation in the Rivermax Developer page.
Runtime configurations can be tuned even after the application starts, allowing dynamic performance optimization
For complete setup steps and advanced configurations, refer to DOCA RMAX documentation.
The application is designed to receive and process network packets using the DOCA library. It is structured around three core components:
Configuration management – Manages the initialization, parsing, validation, and cleanup of application configuration parameters
Global resources management – Handles the allocation and management of shared resources such as memory maps, buffer inventories, and progress engines
Stream management – Manages the lifecycle of data streams used for packet reception, including setup, execution, and teardown
The architecture comprises several key modules and their responsibilities.
Main Application
Initialization – Sets up logging, parses command-line arguments, and initializes the configuration.
Device listing – If the
--listflag is passed, it enumerates and prints available devices, then exits.Stream processing – Initializes global resources, configures the stream, and enters the packet reception loop.
Configuration Management
Initialization – Applies default values and creates the CPU affinity mask.
Argument parsing – Parses command-line arguments and updates the configuration accordingly.
Validation – Verifies that all required parameters are provided.
Destruction – Frees any configuration-related resources.
Global Resources Management
Initialization – Sets up shared memory maps, buffer inventories, and progress engines required for data handling
Destruction – Cleans up and releases global resources
Stream Management
Initialization – Configures and starts the stream, allocates memory buffers, and attaches the necessary flows
Packet reception loop – Processes incoming packets, manages events, and collects runtime statistics
Destruction – Detaches flows, stops the stream, and releases associated buffers
Application Functions and Roles
Function(s) | Role |
| Entry point of the application, handles overall flow control |
| Manage application configuration |
| Register command-line arguments |
| Manage global resources |
| Manage stream setup and teardown |
| Main loop for receiving and processing packets |
| Event handlers for packet reception and errors |
Data Structures
app_config– Holds configuration parameters for the applicationglobals– Holds global resources required by the applicationstream_data– Manages the state and data associated with streaming
Event Handling
Completion Events – Handled by
handle_completion, updates statistics and optionally dumps packet contentError Events – Handled by
handle_error, logs errors and stops the receive loop
Flow
Initialization – Set up logging, configuration, and global resources.
Device listing – Optionally list available devices.
Stream setup – Configure and initialize the stream.
Packet reception – Enter the main loop to receive and process packets.
Teardown – Clean up resources and exit.
This application leverages the following DOCA library:
The RMAX library must be compiled and run, and a Rivermax license is required to run this application, as is the case with every application using DOCA RMAX. Refer to NVIDIA Rivermax SDK page to obtain that license.
Please refer to the DOCA Installation Guide for Linux for details on how to install BlueField-related software.
The installation of DOCA's reference applications contains the sources of the applications, alongside the matching compilation instructions. This allows for compiling the applications "as-is" and provides the ability to modify the sources, then compile a new version of the application.
For more information about the applications as well as development and compilation tips, refer to the DOCA Reference Applications page.
The sources of the application can be found under the application's directory: /opt/mellanox/doca/applications/stream_receive_perf/.
Compiling All Applications
All DOCA applications are defined under a single meson project. So, by default, the compilation includes all of them.
To build all the applications together, run:
cd /opt/mellanox/doca/applications/
meson /tmp/build
ninja -C /tmp/build
doca_stream_receive_perf is created under /tmp/build/stream_receive_perf/.
Compiling Only the Current Application
To directly build only the stream receive performance application:
cd /opt/mellanox/doca/applications/ meson /tmp/build -Denable_all_applications=
false-Denable_stream_receive_perf=trueninja -C /tmp/builddoca_stream_receive_perfis created under/tmp/build/stream_receive_perf/.Alternatively, one can set the desired flags in the
meson_options.txtfile instead of providing them in the compilation command line:Edit the following flags in
/opt/mellanox/doca/applications/meson_options.txt:Set
enable_all_applicationstofalseSet
enable_stream_receive_perftotrue
The same compilation commands should be used, as were shown in the previous section:
cd /opt/mellanox/doca/applications/ meson /tmp/build ninja -C /tmp/build
doca_stream_receive_perfis created under/tmp/build/stream_receive_perf/.
Troubleshooting
Please refer to the NVIDIA BlueField Platform Software Troubleshooting Guide for any issue you may encounter with the compilation of the DOCA applications.
Prerequisites
This application can run on the target DPU only.
This application must be run with root privileges or other additional permissions and capabilities.
An IP address to the device being used must be set up .
It is recommended to have at least 800 huge pages enabled to achieve maximum performance:
dpu> echo
1000000000> /proc/sys/kernel/shmmax dpu> echo800> /proc/sys/vm/nr_hugepages
Application Execution
The stream receive performance application is provided in source form, hence a compilation is required before the application can be executed.
Application usage instructions
Usage: doca_stream_receive_perf [DOCA Flags] [Program Flags] DOCA Flags: -h, --help Print a help synopsis -v, --version Print program version information -l, --log-level Set the (numeric) log level
forthe program <10=DISABLE,20=CRITICAL,30=ERROR,40=WARNING,50=INFO,60=DEBUG,70=TRACE> --sdk-log-level Set the SDK (numeric) log levelforthe program <10=DISABLE,20=CRITICAL,30=ERROR,40=WARNING,50=INFO,60=DEBUG,70=TRACE> Program Flags: --list List available devices --scatter-type Scattering type: RAW (default) or ULP --tstamp-format Timestamp format: raw (default), free-running or synced -s, --src-ip Source address to read from -d, --dst-ip Destination address to bind to -i, --local-ip IP of the localinterfaceto receive data -p, --dst-port Destination port to read from -K, --packets Number of packets to allocate memoryfor(default262144) -y, --payload-size Packet's payload size (default1500) -e, --app-hdr-size Packet's application header size (default0) -a, --cpu-affinity Comma separated list of CPU affinity coresforthe application main thread --sleep Amount of microseconds to sleep between requests (default0) --min Block until at leastthisnumber of packets are received (default0) --max Maximum number of packets toreturnin one completion --dump Dump packet contentFor additional information, please refer to the "Command Line Flags" section below.
The above usage printout can be printed to the command line using the
-h(or--help) options:./doca_stream_receive_perf -h
CLI example for listing available devices:
./doca_stream_receive_perf --list
CLI example for receiving a stream sent from
1.1.63.5to the local NIC address1.1.64.67and port7000:./doca_stream_receive_perf --local-ip
1.1.64.67--dst-ip1.1.64.67--src-ip1.1.63.5--dst-port7000CLI example for receiving a stream receiving a stream sent on
239.0.0.1to the local NIC1.1.64.67from1.1.63.5and port7000:./doca_stream_receive_perf --local-ip
1.1.64.67--dst-ip239.0.0.1--src-ip1.1.63.5--dst-port7000CLI example for receiving a stream using header-data split mode. This example r eceives a stream sent from
1.1.63.5to the local NIC address1.1.64.67and port7000. The application header size is 20 bytes, and the payload size is 1200 bytes:./doca_stream_receive_perf --local-ip
1.1.64.67--dst-ip1.1.64.67--src-ip1.1.63.5--dst-port7000--app-hdr-size20--payload-size1200InfoSetting the application header size enables header-data split mode which separates the application header from the payload.
Command Line Flags
Flag Type | Short Flag | Long Flag | Description |
General flags |
|
| Print a help synopsis |
|
| Print program version information | |
|
| Set the log level for the application:
| |
N/A |
| Set the log level for the program:
| |
Program flags | N/A |
| List all available devices, dump their IPv4 addresses, and tell whether or not the PTP clock is supported |
N/A |
| Scattering type:
| |
N/A |
| Timestamp format:
| |
|
| Source IP address to read from | |
|
| Destination IP address to bind to | |
|
| IP of the local interface to receive data | |
|
| Destination port to read from | |
|
| Number of packets to allocate memory for (default 262144) | |
|
| Packet's payload size (default 1500) | |
|
| Packet's application header size (default 0) | |
|
| list of CPU affinity cores for the application main thread | |
N/A |
| Amount of microseconds to sleep between requests | |
N/A |
| Block until at least this number of packets are received | |
N/A |
| Maximum number of packets to return in one completion | |
N/A |
| Dump packet content |
Refer to DOCA Arg Parser for more information regarding the supported flags and execution modes.
Troubleshooting
Please refer to the NVIDIA BlueField Platform Software Troubleshooting Guide for any issue you may encounter with the installation or execution of the DOCA applications.
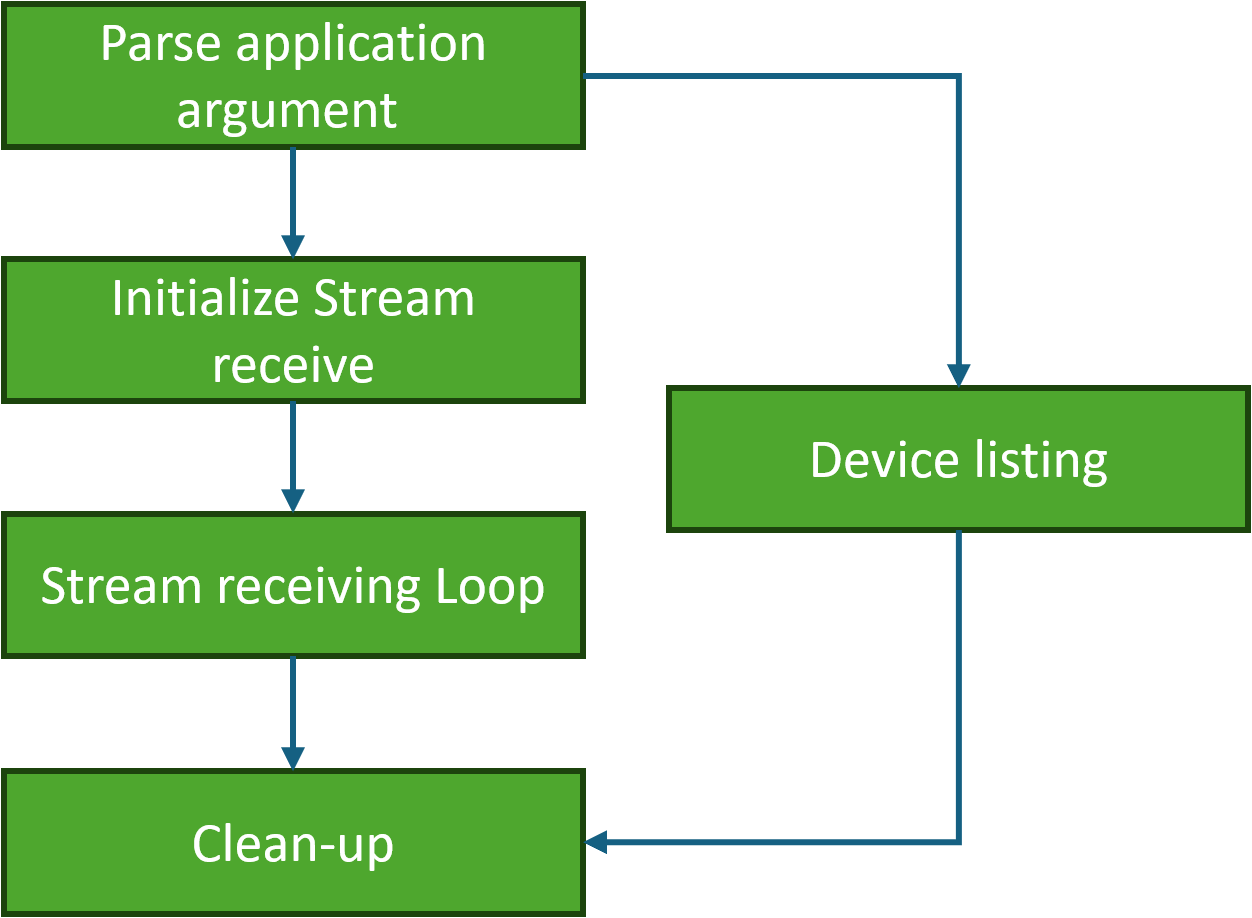
Parse application argument.
Initialize arg parser resources and register DOCA general parameters.
init_config();
Register stream receive performance application parameters.
register_argp_params();
Parse the arguments.
doca_argp_start();
Parse app parameters.
Device listing.
If the list parameter is set to true, the application lists all available devices.
Initializes the DOCA RMAX library.
doca_rmax_init();
Enumerates and lists all available devices.
list_devices();
Stream receive: if the list parameter is not set, the application proceeds to receive stream.
Mandatory Arguments Check.
mandatory_args_set();
CPU Affinity Mask (if it is set).
doca_rmax_set_cpu_affinity_mask();
Initializes the DOCA RMAX library.
doca_rmax_init();
Device opening.
open_device();
Global Resources Initialization.
init_globals();
Stream Initialization.
init_stream();
Main Loop.
run_recv_loop();
Clean-up.
Cleans up and destroys the stream.
destroy_stream();
Releases and destroys global application resources.
destroy_globals();
Closes the device.
doca_dev_close();
Releases the DOCA RMAX library.
doca_rmax_release();
Destroys the ARGP resources.
doca_argp_destroy();
Releases resources allocated by the application configuration.
destroy_config();
/opt/mellanox/doca/applications/stream_receive_perf/