Telemetry Client
NVIDIA DOCA Telemetry Client Reference Application Guide
This document provides a DOCA Telemetry Client implementation on top of NVIDIA® BlueField® DPU.
This document describes DOCA telemetry API example. For general information, refer to NVIDIA DOCA Telemetry Programming Guide. The telemetry application example code shows an initial recommended configuration which covers 2 use cases:
- Standard DOCA telemetry data
- DOCA telemetry for NetFlow data
The telemetry_client.c contains the basic DOCA application logic, which splits into the two cases as mentioned above:
telemetry_config.ctelemetry_netflow_config.c
Both files demonstrate the API usage and are recommended as a basis for any development that uses the DOCA telemetry API.
The telemetry client runs on the BlueField and writes telemetry data to BlueField's storage. If IPC is enabled, data is sent to the DOCA Telemetry Service (DTS) running on the same BlueField. There are 2 possibilities:
- Telemetry client runs in a container and shares the same Kubernetes pod with the DTS container, using a single
.yamlfile. ThehostIPCoption is set to false and telemetry clientipc_socketsfolder must be mounted to:/opt/mellanox/doca/services/telemetry/ipc_sockets
- Telemetry client is executed regardless of the DTA Kubernetes pod, and the pod defines
hostIPC=true. In this case, the telemetry clientipc_socketsfolder must be changed to:/opt/mellanox/doca/services/telemetry/ipc_sockets
The first scenario is preferred for production deployment as it is better in terms of security. The second scenario should be used only for debugging and development.
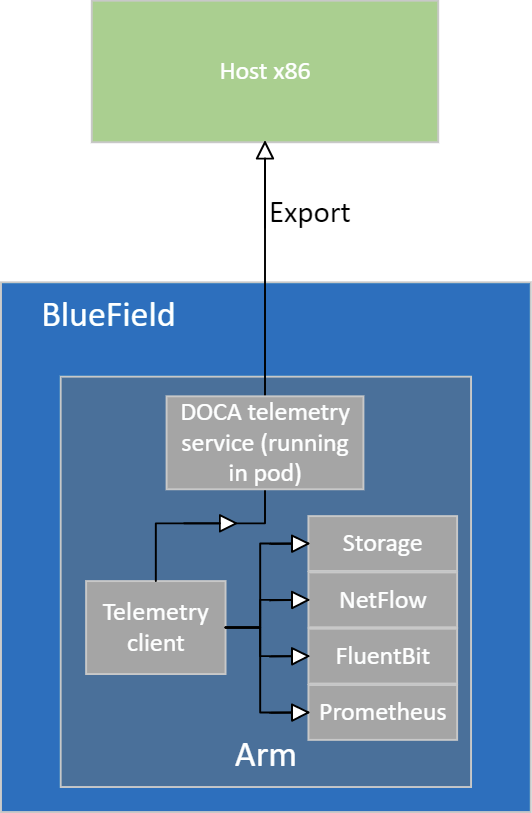
The following diagram presents example data flow:
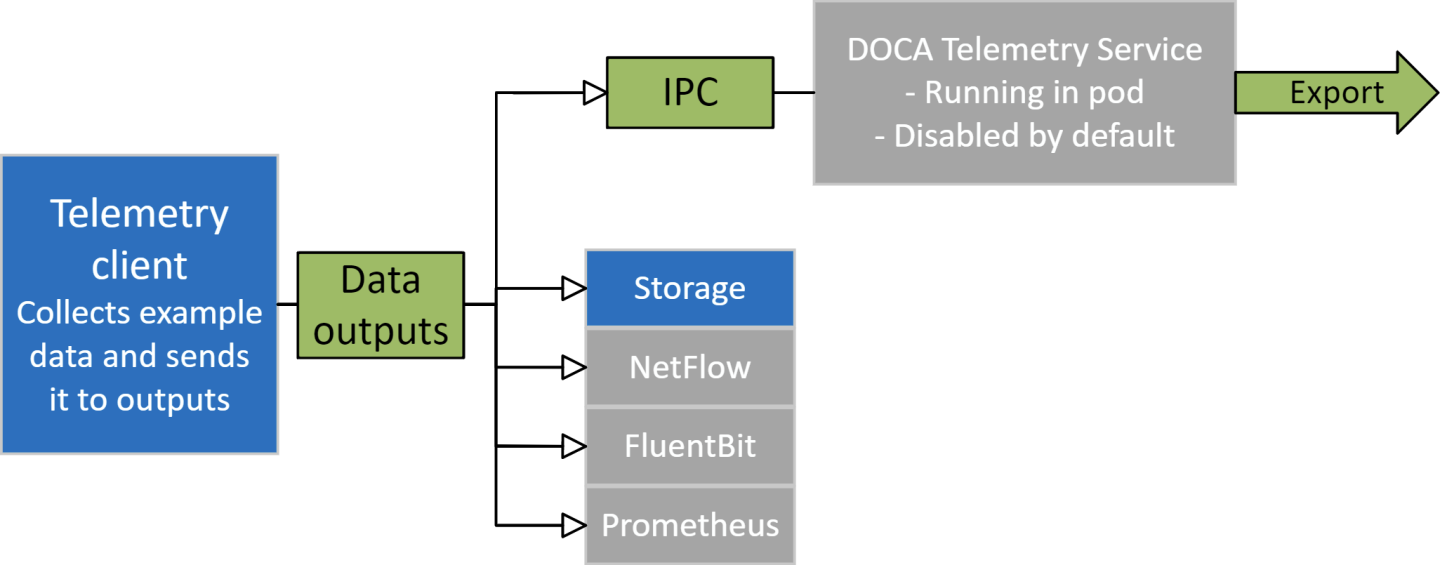
Data from telemetry client can be exported in two ways:
- Write to disk (default)
- Using inter-process communication (IPC)
By default, IPC connection to DTS is disabled and the data is written to the disk.
When the data is written to disk, it can be read with the clx_read utility (see Read Example Data). Once the user finds that data is written correctly, IPC transport can be enabled so the data is sent to DTS.
When IPS is used, telemetry client and DTS must be executed on the same node (BlueField-2/host).
DTS can export the collected data out of the node.
- Please refer to the DOCA Installation Guide for details on how to install BlueField related software.
- The telemetry client binary is located under
/opt/mellanox/doca/examples/telemetry_client/bin/doca_telemetry_client. - To re-build the application:
- Run:
cd /opt/mellanox/doca/examples/telemetry_client/src meson /tmp/build ninja -C /tmp/build
doca_telemetry_clientis created under/tmp/build. - The build process depends on the
PKG_CONFIG_PATHenvironment variable to locate the DPDK libraries. If the variable was accidently corrupted and the build fails, run the following command:- For Ubuntu:
export PKG_CONFIG_PATH=$PKG_CONFIG_PATH:/opt/mellanox/dpdk/lib/aarch64-linux-gnu/pkgconfig
- For CentOS:
export PKG_CONFIG_PATH=$PKG_CONFIG_PATH:/opt/mellanox/dpdk/lib64/pkgconfig
- For Ubuntu:
- Run:
- To run the application:
Usage: doca_telemetry_client [DOCA Flags] [Program Flags] DOCA Flags: -h, --help Print a help synopsis -l, --log-level Set the log level for the program <CRITICAL=0, DEBUG=4> Program Flags: -t, --telemetry Run DOCA telemetry example -n, --netflow Run DOCA telemetry netflow example
/opt/mellanox/doca/examples/telemetry_client/bin/doca_telemetry_client -t
For example, running with NetFlow config:/opt/mellanox/doca/examples/telemetry_client/bin/doca_telemetry_client -n
For additional information on available flags for DPDK, use-hbefore the--separator:/opt/mellanox/doca/examples/telemetry_client/bin/doca_telemetry_client -h
For additional information on the app, use-hafter the--separator:/opt/mellanox/doca/examples/telemetry_client/bin/doca_telemetry_client -- -h
In the example, data output to the file is enabled by default and is written to a predefined path which is set to ./telemetry_examle_data. The binary files are written according to the following folder structure:
{year}/{date}/{source_id}/{tag}_{timestamp}.bin
New binary files appear when the program starts or when binary file age/size restriction is reached.
$ ls -R telemetry_example_data
telemetry_example_data
├── 2021
│ └── 1007
│ └── source_1
│ └── source_1_tag_1633596291715225.bin
└── schema
├── schema_ec9d36e6844048461d96c859e176cf32.json
└── schema_f5ce72803e5583d747e1e45d0fa1241b.json
The file structure shown is printed using tree.
For the development stage, it is recommended to read data with the clx_read utility, which reads a binary file and dumps the data to stdout.
# usage: /opt/mellanox/collectx/bin/clx_read -s /path/to/schema/folder /path/to/binary/file
$ /opt/mellanox/collectx/bin/clx_read -s telemetry_example_data/schema telemetry_example_data/2021/1007/ source_1_tag_1633596291715225.bin
{
"timestamp": 1634815738799728,
"event_number": 0,
"iter_num": 0,
"string_number": 0,
"example_string": "example_str_1"
}
{
"timestamp": 1634815738799768,
"event_number": 1,
"iter_num": 0,
"string_number": 1,
"example_string": "example_str_2"
}
…
Once the user decides the data is in the correct format (i.e., all the fields are filled with the expected data), the IPC transport may be enabled.
When working on the BlueField, it is recommended to disable writing data to binary files on the disk due to existing storage restrictions of the DPU.
Notice
This document is provided for information purposes only and shall not be regarded as a warranty of a certain functionality, condition, or quality of a product. NVIDIA Corporation nor any of its direct or indirect subsidiaries and affiliates (collectively: “NVIDIA”) make no representations or warranties, expressed or implied, as to the accuracy or completeness of the information contained in this document and assume no responsibility for any errors contained herein. NVIDIA shall have no liability for the consequences or use of such information or for any infringement of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from its use. This document is not a commitment to develop, release, or deliver any Material (defined below), code, or functionality.
NVIDIA reserves the right to make corrections, modifications, enhancements, improvements, and any other changes to this document, at any time without notice.
Customer should obtain the latest relevant information before placing orders and should verify that such information is current and complete.
NVIDIA products are sold subject to the NVIDIA standard terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgement, unless otherwise agreed in an individual sales agreement signed by authorized representatives of NVIDIA and customer (“Terms of Sale”). NVIDIA hereby expressly objects to applying any customer general terms and conditions with regards to the purchase of the NVIDIA product referenced in this document. No contractual obligations are formed either directly or indirectly by this document.
NVIDIA products are not designed, authorized, or warranted to be suitable for use in medical, military, aircraft, space, or life support equipment, nor in applications where failure or malfunction of the NVIDIA product can reasonably be expected to result in personal injury, death, or property or environmental damage. NVIDIA accepts no liability for inclusion and/or use of NVIDIA products in such equipment or applications and therefore such inclusion and/or use is at customer’s own risk.
NVIDIA makes no representation or warranty that products based on this document will be suitable for any specified use. Testing of all parameters of each product is not necessarily performed by NVIDIA. It is customer’s sole responsibility to evaluate and determine the applicability of any information contained in this document, ensure the product is suitable and fit for the application planned by customer, and perform the necessary testing for the application in order to avoid a default of the application or the product. Weaknesses in customer’s product designs may affect the quality and reliability of the NVIDIA product and may result in additional or different conditions and/or requirements beyond those contained in this document. NVIDIA accepts no liability related to any default, damage, costs, or problem which may be based on or attributable to: (i) the use of the NVIDIA product in any manner that is contrary to this document or (ii) customer product designs.
No license, either expressed or implied, is granted under any NVIDIA patent right, copyright, or other NVIDIA intellectual property right under this document. Information published by NVIDIA regarding third-party products or services does not constitute a license from NVIDIA to use such products or services or a warranty or endorsement thereof. Use of such information may require a license from a third party under the patents or other intellectual property rights of the third party, or a license from NVIDIA under the patents or other intellectual property rights of NVIDIA.
Reproduction of information in this document is permissible only if approved in advance by NVIDIA in writing, reproduced without alteration and in full compliance with all applicable export laws and regulations, and accompanied by all associated conditions, limitations, and notices.
THIS DOCUMENT AND ALL NVIDIA DESIGN SPECIFICATIONS, REFERENCE BOARDS, FILES, DRAWINGS, DIAGNOSTICS, LISTS, AND OTHER DOCUMENTS (TOGETHER AND SEPARATELY, “MATERIALS”) ARE BEING PROVIDED “AS IS.” NVIDIA MAKES NO WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED, IMPLIED, STATUTORY, OR OTHERWISE WITH RESPECT TO THE MATERIALS, AND EXPRESSLY DISCLAIMS ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF NONINFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY, AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. TO THE EXTENT NOT PROHIBITED BY LAW, IN NO EVENT WILL NVIDIA BE LIABLE FOR ANY DAMAGES, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, PUNITIVE, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, HOWEVER CAUSED AND REGARDLESS OF THE THEORY OF LIABILITY, ARISING OUT OF ANY USE OF THIS DOCUMENT, EVEN IF NVIDIA HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. Notwithstanding any damages that customer might incur for any reason whatsoever, NVIDIA’s aggregate and cumulative liability towards customer for the products described herein shall be limited in accordance with the Terms of Sale for the product.
Trademarks
NVIDIA, the NVIDIA logo, and Mellanox are trademarks and/or registered trademarks of Mellanox Technologies Ltd. and/or NVIDIA Corporation in the U.S. and in other countries. The registered trademark Linux® is used pursuant to a sublicense from the Linux Foundation, the exclusive licensee of Linus Torvalds, owner of the mark on a world¬wide basis. Other company and product names may be trademarks of the respective companies with which they are associated.
Copyright
© 2022 NVIDIA Corporation & affiliates. All rights reserved.