Firewall
NVIDIA DOCA Firewall Application Guide
This document provides an example of firewall implementation on top of NVIDIA® BlueField® DPU.
A firewall application is a network security application that leverages the DPU's hardware capability to monitor incoming and outgoing network traffic and allow or block packets based on a set of preconfigured rules.
The firewall application is based on DOCA Flow gRPC, used for remote programming of the DPU's hardware. The firewall can operate in two modes:
- Static mode – the firmware application gets 5-tuple traffic from the user with a JSON file for packets to be dropped. The packets that do not match any of the 5-tuple are forwarded by a hairpin pipe.
- Interactive mode – the user can add rules from the command line in real time to execute different firewall rules
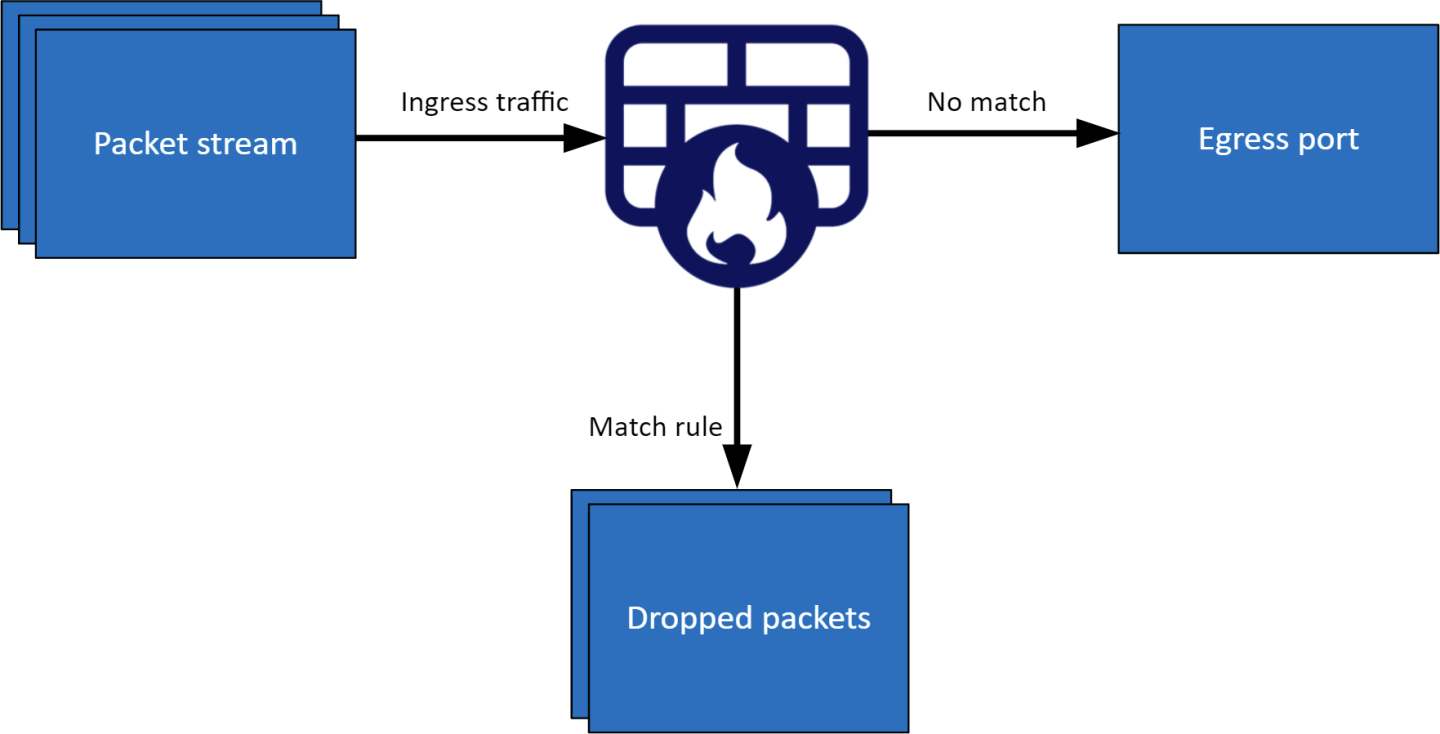
The firewall application is designed to run on the host and to use DOCA Flow gRPC client to send instructions to a server that runs on the BlueField DPU instance. The DPU intercepts ingress traffic from the wire and either drops it or forwards it to the egress port using a hairpin. The decision is made using traffic classification.
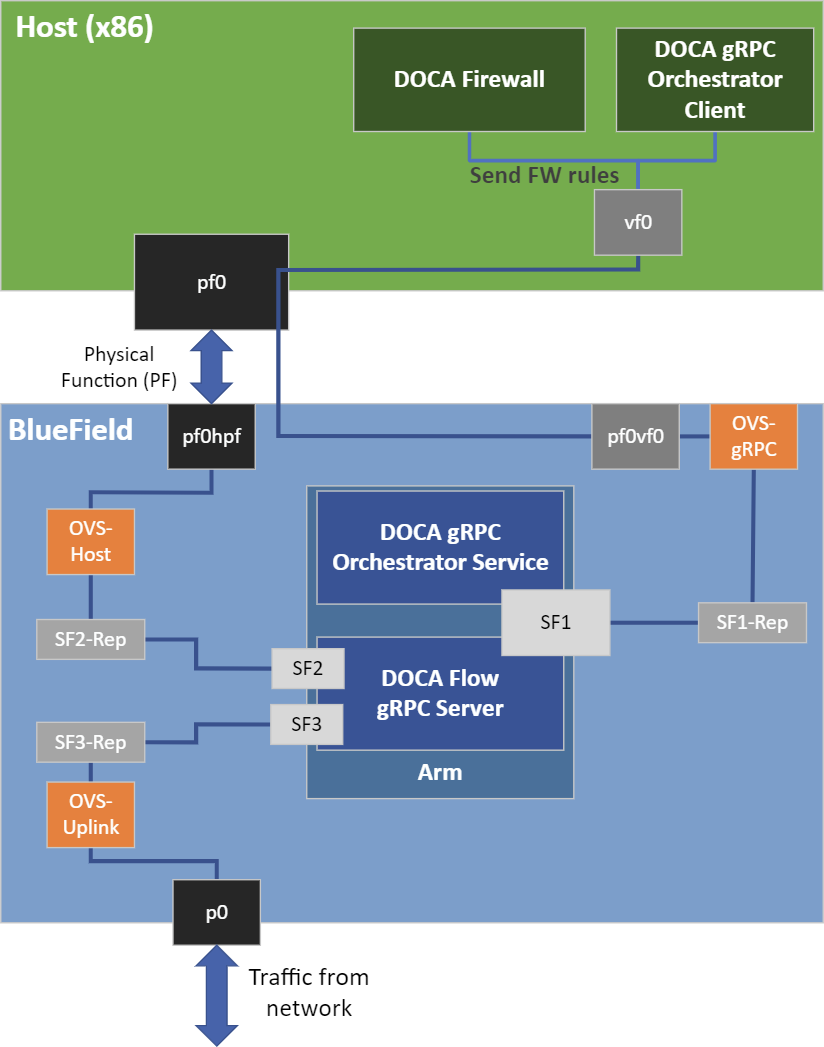
The firewall runs on top of DOCA Flow gRPC to classify packets.
3.1. Static Mode
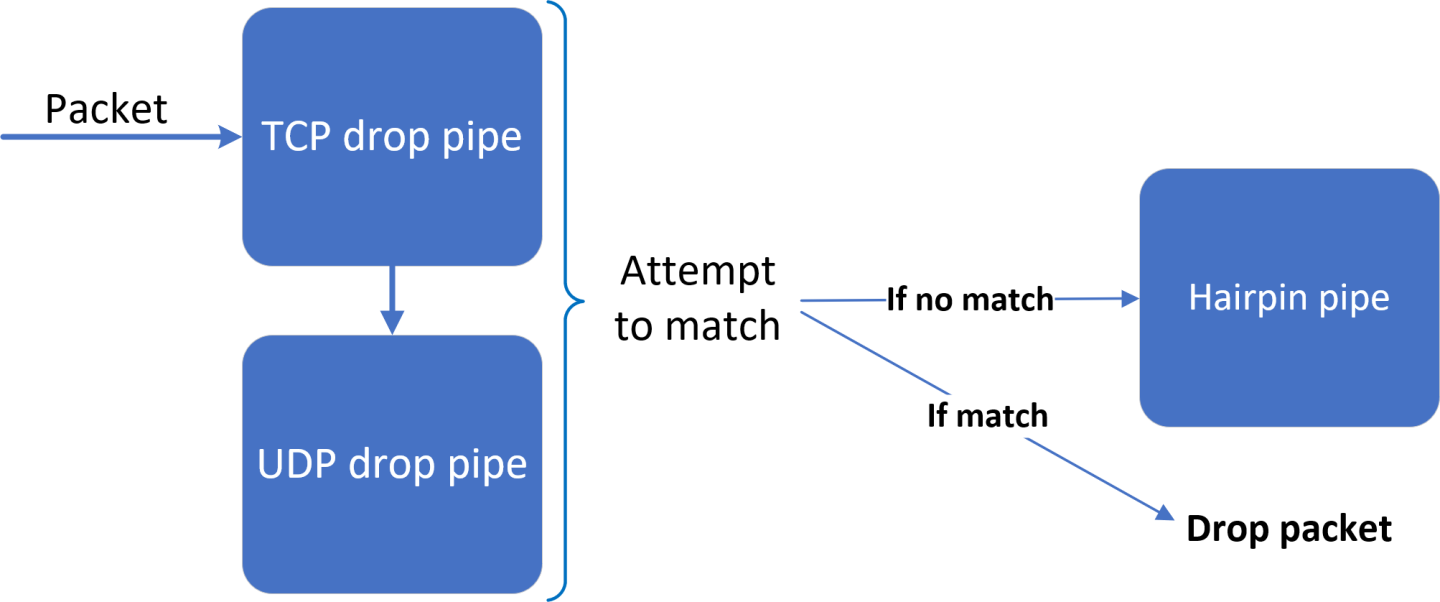
- The firewall application builds 3 pipes for each port (two drop pipes and a hairpin pipe).
- The drop pipes match only 5-tuple traffic with specific source and destination IPs and source and destination ports. One of the drop pipes matches TCP traffic and the other matches UDP. The hairpin pipe matches every packet (no misses). The drop pipes serve as root pipes and the hairpin pipe serves as a forwarding miss component to the drop pipe. Therefore, every received packet is checked first against the drop pipes. If there is a match, then it is dropped, otherwise, it is forwarded to the hairpin pipe and is then matched.
3.2. Interactive Mode
Running in interactive mode initializes 2 ports, and the user then configures the pipes and entries.
- When adding a pipe or an entry, one must run commands to create the relevant structs beforehand
- Optional parameters must be specified by the user in the command line. Otherwise, NULL is used.
- After a pipe or an entry is created successfully, the relevant ID is printed for future use
Available commands:
- create pipe port_id=[port_id][,<optional_parameters>]
- Available optional parameters: name=<pipe-name>, root_enable=[1|0], monitor=[1|0], match_mask=[1|0], fwd=[1|0], fwd_miss=[1|0],type=[basic|control]
- add entry pipe_id=<pipe_id>,pipe_queue=<pipe_queue>[,<optional_parameters>]
- Available optional parameters: monitor=[1|0], fwd=[1|0]
- add control_pipe entry priority=[priority],pipe_id=<pipe_id>,pipe_queue=<pipe_queue>[,<optional_parameters>]
- Available optional parameters: match_mask=[1|0], fwd=[1|0]
- destroy pipe port_id=[port_id],pipe_id=<pipe_id>
- rm entry pipe_queue=<pipe_queue>,entry_id=[entry_id]
- port pipes flush port_id=[port_id]
- port pipes dump port_id=[port_id],file=[file_name]
- query entry_id=[entry_id]
- create [struct] [field=value,…]
- Struct options: pipe_match, entry_match, match_mask, actions, monitor, fwd, fwd_miss
- Match struct fields:
Fields Field Options flags out_src_mac out_dst_mac out_eth_type out_vlan_id out_src_ip_type ipv4, ipv6 out_src_ip_addr out_dst_ip_type ipv4, ipv6 out_dst_ip_addr out_l4_type tcp, udp, gre out_tcp_flags FIN, SYN, RST, PSH, ACK, URG, ECE, CWR out_src_port out_dst_port tun_type vxlan-tun_id gre_key gtp_teid in_src_mac in_dst_mac in_eth_type in_vlan_id in_src_ip_type ipv4, ipv6 in_src_ip_addr in_dst_ip_type ipv4, ipv6 in_dst_ip_addr in_l4_type tcp, udp in_tcp_flags FIN, SYN, RST, PSH, ACK, URG, ECE, CWR in_src_port in_dst_port - Actions struct fields:
Fields Field Options decap true, false mod_src_mac mod_dst_mac mod_src_ip_type ipv4, ipv6 mod_src_ip_addr mod_dst_ip_type ipv4, ipv6 mod_dst_ip_addr mod_src_port mod_dst_port dec_ttl true, false has_encap true, false encap_src_mac encap_dst_mac encap_src_ip_type ipv4, ipv6 encap_src_ip_addr encap_dst_ip_type ipv4, ipv6 encap_dst_ip_addr encap_tup_type vxlan, gtpu, gre encap_vxlan-tun_id encap_gre_key encap_gtp_teid - FWD struct fields:
Fields Field Options type rss, port, pipe, drop rss_flags rss_queues num_of_queues rss_mark port_id next_pipe_id - Monitor struct fields:
- flags
- id
- cir
- cbs
- aging
- Match struct fields:
- Struct options: pipe_match, entry_match, match_mask, actions, monitor, fwd, fwd_miss
The following is an example for creating a pipe and adding an entry:
create pipe_match out_l4_type=udp,out_src_ip_type=ipv4,out_src_ip_addr=0xffffffff,out_dst_ip_type=ipv4,out_dst_ip_addr=0xffffffff
create fwd type=drop
create fwd_miss type=pipe,next_pipe_id=1
create pipe port_id=0,name=drop,root_enable=1,fwd=1,fwd_miss=1
create pipe succeed with pipe id: 2
create entry_match out_src_ip_type=ipv4,out_src_ip_addr=10.1.20.208,out_dst_ip_type=ipv4,out_dst_ip_addr=10.1.3.216
add entry pipe_id=2,pipe_queue=0
add entry succeed with entry id: 0
This application leverages the DOCA Flow library.
- Parse application argument.
doca_argp_init();
- Initialize the arg parser resources.
- Register DOCA general flags.
register_firewall_params();
- Register firewall application params.
doca_argp_start();
- Parse application flags.
- Firewall initialization.
firewall_ports_init();
- Create a new gRPC channel and initialize a stub.
- Initialize DOCA Flow and DOCA Flow ports.
- Configure firewall rules.
url_filter_init();
- When opearting in static mode:
- Initialize drop packets array from the input JSON file.
init_drop_packets();
- Create hairpin pipe for both ports. This pipe includes one entry that matches every type of packet (no misses) which is then forwarded to the egress port through a hairpin.
firewall_pipes_init();
- Creates TCP and UDP drop pipes that serve as root pipes for both ports. The built pipes have a 5-tuple match and entries from the processed JSON file that are dropped. In addition, the hairpin pipe serves as forwarding if the drop entries do not match.
- Initialize drop packets array from the input JSON file.
- When opearting in interactive mode:
- Initialize the firewall's interactive command line.
interactive_cmdline();
- Free allocated resources.
interactive_mode_cleanup();
- Initialize the firewall's interactive command line.
- When opearting in static mode:
- Refer to the following documents:
- NVIDIA DOCA Installation Guide for details on how to install BlueField-related software.
- NVIDIA DOCA Troubleshooting Guide for any issue you may encounter with the installation, compilation, or execution of DOCA applications.
- The firewall example binary is located under
/opt/mellanox/doca/applications/url_filter/bin/doca_url_filter.To build all the applications together, run:Note:Before building the application, make sure that gRPC support is enabled. Set the
enable_grpc_supportflag in/opt/mellanox/doca/applications/meson_option.txttotrue.cd /opt/mellanox/doca/applications/ meson build ninja -C build
- To build the firewall application only:
- Edit the following flags in
/opt/mellanox/doca/applications/meson_option.txt:- Set
enable_all_applicationstofalse - Set
enable_firewalltotrue
- Set
- Run the commands in step 2.
Application usage:
Usage: doca_firewall [DOCA Flags] [Program Flags] DOCA Flags: -h, --help Print a help synopsis -v, --version Print program version information -l, --log-level Set the log level for the app <CRITICAL=0, DEBUG=4> --grpc-address ip_address[:port] Set the IP address for the grpc server Program Flags: -m, --mode Set running mode {static, interactive} -r, --firewall-rules <path> Path to the JSON file with 5-tuple rules when running with static mode
Note:For additional information on the app use
-h:/opt/mellanox/doca/applications/firewall/bin/doca_firewall -h
- Edit the following flags in
- Running the application on the host:
- For instructions on running the DOCA Flow gRPC server on the BlueField, refer to NVIDIA DOCA gRPC Infrastructure User Guide.
- CLI example for running the app in interactive mode:
/opt/mellanox/doca/applications/firewall/bin/doca_firewall --grpc-address 192.168.101.2 -l 3 -m interactive
- CLI example for running the app in static mode:
/opt/mellanox/doca/applications/firewall/bin/doca_firewall --grpc-address 192.168.101.2 -l 3 -m static -d firewall_rules.json
- To run
doca_firewallusing a JSON file:doca_firewall --json [json_file]
cd /opt/mellanox/doca/applications/firewall/bin ./doca_firewall --json firewall_params.json
Refer to NVIDIA DOCA Arg Parser User Guide for more information.
| Flag Type | Short Flag | Long Flag/JSON Key | Description | JSON Content |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| General Flags | l | log-level | Set the log level for the application:
|
|
| v | version | Print program version information | N/A | |
| h | help | Print a help synopsis | N/A | |
| - | grpc-address | Set the IP address for the gRPC server |
|
|
| Program Flags | m | mode |
Set running mode {static or interactive}
Note:
|
|
| r | firewall-rules | Path to JSON rules file |
|
Notice
This document is provided for information purposes only and shall not be regarded as a warranty of a certain functionality, condition, or quality of a product. NVIDIA Corporation nor any of its direct or indirect subsidiaries and affiliates (collectively: “NVIDIA”) make no representations or warranties, expressed or implied, as to the accuracy or completeness of the information contained in this document and assume no responsibility for any errors contained herein. NVIDIA shall have no liability for the consequences or use of such information or for any infringement of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from its use. This document is not a commitment to develop, release, or deliver any Material (defined below), code, or functionality.
NVIDIA reserves the right to make corrections, modifications, enhancements, improvements, and any other changes to this document, at any time without notice.
Customer should obtain the latest relevant information before placing orders and should verify that such information is current and complete.
NVIDIA products are sold subject to the NVIDIA standard terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgement, unless otherwise agreed in an individual sales agreement signed by authorized representatives of NVIDIA and customer (“Terms of Sale”). NVIDIA hereby expressly objects to applying any customer general terms and conditions with regards to the purchase of the NVIDIA product referenced in this document. No contractual obligations are formed either directly or indirectly by this document.
NVIDIA products are not designed, authorized, or warranted to be suitable for use in medical, military, aircraft, space, or life support equipment, nor in applications where failure or malfunction of the NVIDIA product can reasonably be expected to result in personal injury, death, or property or environmental damage. NVIDIA accepts no liability for inclusion and/or use of NVIDIA products in such equipment or applications and therefore such inclusion and/or use is at customer’s own risk.
NVIDIA makes no representation or warranty that products based on this document will be suitable for any specified use. Testing of all parameters of each product is not necessarily performed by NVIDIA. It is customer’s sole responsibility to evaluate and determine the applicability of any information contained in this document, ensure the product is suitable and fit for the application planned by customer, and perform the necessary testing for the application in order to avoid a default of the application or the product. Weaknesses in customer’s product designs may affect the quality and reliability of the NVIDIA product and may result in additional or different conditions and/or requirements beyond those contained in this document. NVIDIA accepts no liability related to any default, damage, costs, or problem which may be based on or attributable to: (i) the use of the NVIDIA product in any manner that is contrary to this document or (ii) customer product designs.
No license, either expressed or implied, is granted under any NVIDIA patent right, copyright, or other NVIDIA intellectual property right under this document. Information published by NVIDIA regarding third-party products or services does not constitute a license from NVIDIA to use such products or services or a warranty or endorsement thereof. Use of such information may require a license from a third party under the patents or other intellectual property rights of the third party, or a license from NVIDIA under the patents or other intellectual property rights of NVIDIA.
Reproduction of information in this document is permissible only if approved in advance by NVIDIA in writing, reproduced without alteration and in full compliance with all applicable export laws and regulations, and accompanied by all associated conditions, limitations, and notices.
THIS DOCUMENT AND ALL NVIDIA DESIGN SPECIFICATIONS, REFERENCE BOARDS, FILES, DRAWINGS, DIAGNOSTICS, LISTS, AND OTHER DOCUMENTS (TOGETHER AND SEPARATELY, “MATERIALS”) ARE BEING PROVIDED “AS IS.” NVIDIA MAKES NO WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED, IMPLIED, STATUTORY, OR OTHERWISE WITH RESPECT TO THE MATERIALS, AND EXPRESSLY DISCLAIMS ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF NONINFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY, AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. TO THE EXTENT NOT PROHIBITED BY LAW, IN NO EVENT WILL NVIDIA BE LIABLE FOR ANY DAMAGES, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, PUNITIVE, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, HOWEVER CAUSED AND REGARDLESS OF THE THEORY OF LIABILITY, ARISING OUT OF ANY USE OF THIS DOCUMENT, EVEN IF NVIDIA HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. Notwithstanding any damages that customer might incur for any reason whatsoever, NVIDIA’s aggregate and cumulative liability towards customer for the products described herein shall be limited in accordance with the Terms of Sale for the product.
Trademarks
NVIDIA, the NVIDIA logo, and Mellanox are trademarks and/or registered trademarks of Mellanox Technologies Ltd. and/or NVIDIA Corporation in the U.S. and in other countries. The registered trademark Linux® is used pursuant to a sublicense from the Linux Foundation, the exclusive licensee of Linus Torvalds, owner of the mark on a world¬wide basis. Other company and product names may be trademarks of the respective companies with which they are associated.
Copyright
© 2022 NVIDIA Corporation & affiliates. All rights reserved.