YOLOv4
YOLOv4 is an object detection model that is included in the TAO Toolkit. YOLOv4 supports the following tasks:
kmeans
train
evaluate
inference
prune
export
These tasks can be invoked from the TAO Toolkit Launcher using the following convention on the command line:
tao yolo_v4 <sub_task> <args_per_subtask>
where args_per_subtask are the command line arguments required for a given subtask. Each
subtask is explained in detail below.
Below is a sample for the YOLOv4 spec file. It has 6 major components: yolov4_config,
training_config, eval_config, nms_config, augmentation_config, and
dataset_config. The format of the spec file is a protobuf text (prototxt) message, and each
of its fields can be either a basic data type or a nested message. The top-level structure of the
spec file is summarized in the table below.
random_seed: 42
yolov4_config {
big_anchor_shape: "[(114.94, 60.67), (159.06, 114.59), (297.59, 176.38)]"
mid_anchor_shape: "[(42.99, 31.91), (79.57, 31.75), (56.80, 56.93)]"
small_anchor_shape: "[(15.60, 13.88), (30.25, 20.25), (20.67, 49.63)]"
box_matching_iou: 0.25
matching_neutral_box_iou: 0.5
arch: "resnet"
nlayers: 18
arch_conv_blocks: 2
loss_loc_weight: 0.8
loss_neg_obj_weights: 100.0
loss_class_weights: 0.5
label_smoothing: 0.0
big_grid_xy_extend: 0.05
mid_grid_xy_extend: 0.1
small_grid_xy_extend: 0.2
freeze_bn: false
freeze_blocks: 0
force_relu: false
}
training_config {
batch_size_per_gpu: 8
num_epochs: 80
enable_qat: false
checkpoint_interval: 10
learning_rate {
soft_start_cosine_annealing_schedule {
min_learning_rate: 1e-7
max_learning_rate: 1e-4
soft_start: 0.3
}
}
regularizer {
type: L1
weight: 3e-5
}
optimizer {
adam {
epsilon: 1e-7
beta1: 0.9
beta2: 0.999
amsgrad: false
}
}
pretrain_model_path: "EXPERIMENT_DIR/pretrained_resnet18/tlt_pretrained_object_detection_vresnet18/resnet_18.hdf5"
}
eval_config {
average_precision_mode: SAMPLE
batch_size: 8
matching_iou_threshold: 0.5
}
nms_config {
confidence_threshold: 0.001
clustering_iou_threshold: 0.5
top_k: 200
}
augmentation_config {
hue: 0.1
saturation: 1.5
exposure:1.5
vertical_flip:0
horizontal_flip: 0.5
jitter: 0.3
output_width: 1248
output_height: 384
output_channel: 3
randomize_input_shape_period: 100
mosaic_prob: 0.5
mosaic_min_ratio:0.2
image_mean {
key: 'b'
value: 103.9
}
image_mean {
key: 'g'
value: 116.8
}
image_mean {
key: 'r'
value: 123.7
}
}
dataset_config {
data_sources: {
tfrecords_path: "/workspace/tao-experiments/data/training/tfrecords/<tfrecords pattern>"
image_directory_path: "/workspace/tao-experiments/data/training"
}
include_difficult_in_training: true
image_extension: "png"
target_class_mapping {
key: "car"
value: "car"
}
target_class_mapping {
key: "pedestrian"
value: "pedestrian"
}
target_class_mapping {
key: "cyclist"
value: "cyclist"
}
target_class_mapping {
key: "van"
value: "car"
}
target_class_mapping {
key: "person_sitting"
value: "pedestrian"
}
validation_data_sources: {
tfrecords_path: "/workspace/tao-experiments/data/val/tfrecords/<tfrecords pattern>"
image_directory_path: "/workspace/tao-experiments/data/val"
}
}
Training Config
The training configuration (training_config) defines the parameters needed for
training, evaluation, and inference. Details are summarized in the table below.
Field |
Description |
Data Type and Constraints |
Recommended/Typical Value |
batch_size_per_gpu |
The batch size for each GPU; the effective batch size is batch_size_per_gpu * num_gpus |
Unsigned int, positive |
– |
checkpoint_interval |
The number of training epochs per one model checkpoint/validation |
Unsigned int, positive |
10 |
num_epochs |
The number of epochs to train the network |
Unsigned int, positive. |
– |
enable_qat |
Whether to use quantization-aware training |
Boolean |
Note: YOLOv4 does not support loading a pruned QAT model and retraining
it with QAT disabled, or vice versa. For example, to get a pruned QAT model,
perform the initial training with QAT enabled or |
learning_rate |
One soft_start_annealing_schedule and soft_start_cosine_annealing_schedule with the following nested parameters are supported:
|
Message type |
– |
regularizer |
This parameter configures the regularizer to use while training and contains the following nested parameters:
|
Message type |
L1 (Note: NVIDIA suggests using the L1 regularizer when training a network before pruning, as L1 regularization makes the network weights more prunable.) |
optimizer |
The optimizer can be one of adam, sgd, and rmsprop. Each type has the following parameters:
The meanings of above parameters are same as those in Keras. |
Message type |
– |
pretrain_model_path |
The path to the pretrained model, if any At most, one pretrain_model_path, resume_model_path, and pruned_model_path may be present. |
String |
– |
resume_model_path |
The path to the TAO checkpoint model to resume training, if any At most, one pretrain_model_path, resume_model_path, and pruned_model_path may be present. |
String |
– |
pruned_model_path |
The path to the TAO pruned model for re-training, if any At most, one pretrain_model_path, resume_model_path, and pruned_model_path may be present. |
String |
– |
max_queue_size |
The number of prefetch batches in data loading |
Unsigned int, positive |
– |
n_workers |
The number of workers for data loading per GPU |
Unsigned int, positive |
– |
use_multiprocessing |
Whether to use multiprocessing mode of keras sequence data loader |
Boolean |
true (in case of deadlock, restart training and use False) |
The learning rate is automatically scaled with the number of GPUs used during training, or the effective learning rate is learning_rate * n_gpu.
Evaluation Config
The evaluation configuration (eval_config) defines the parameters needed for the
evaluation either during training or standalone evaluation. Details are summarized in the table
below.
Field |
Description |
Data Type and Constraints |
Recommended/Typical Value |
average_precision_mode |
Average Precision (AP) calculation mode can be either SAMPLE or INTEGRATE. SAMPLE is used as VOC metrics for VOC 2009 or before. INTEGRATE is used for VOC 2010 or after. |
ENUM type ( SAMPLE or INTEGRATE) |
SAMPLE |
matching_iou_threshold |
The lowest IoU of the predicted box and ground truth box that can be considered a match |
float |
0.5 |
NMS Config
The NMS configuration (nms_config) defines the parameters needed for the NMS postprocessing.
NMS config applies to the NMS layer of the model in training, validation, evaluation, inference,
and export. Details are summarized in the table below.
Field |
Description |
Data Type and Constraints |
Recommended/Typical Value |
confidence_threshold |
Boxes with a confidence score less than confidence_threshold are discarded before applying NMS. |
float |
0.01 |
cluster_iou_threshold |
The IoU threshold below which boxes will go through the NMS process. |
float |
0.6 |
top_k |
top_k boxes will be output after the NMS keras layer. If the number of valid boxes is less than k, the returned array will be padded with boxes whose confidence score is 0. |
Unsigned int |
200 |
infer_nms_score_bits |
The number of bits to represent the score values in NMS plugin in TensorRT OSS. The valid range is integers in [1, 10]. Setting it to any other values will make it fall back to ordinary NMS. Currently this optimized NMS plugin is only avaible in FP16 but it should also be selected by INT8 data type as there is no INT8 NMS in TensorRT OSS and hence this fastest implementation in FP16 will be selected. If falling back to ordinary NMS, the actual data type when building the engine will decide the exact precision(FP16 or FP32) to run at. |
int. In the interval [1, 10]. |
0 |
force_on_cpu |
A flag to force NMS to run on CPU. Setting it to True will force NMS to run on CPU during training. This is useful when using TFRecord dataset for validation during training since there is a known issue with TensorFlow NMS on GPU when using TFRecord dataset for validation. Note Note that this flag does not have any impact on TAO export and TensorRT/DeepStream inference. |
Boolean |
False |
Augmentation Config
The augmentation configuration (augmentation_config) defines the parameters needed for
online data augmentation. Details are summarized in the table below.
Field |
Description |
Data Type and Constraints |
Recommended/Typical Value |
hue |
Image hue to be changed within [-hue, hue] * 180.0 |
float of [0, 1] |
0.1 |
saturation |
Image saturation to be changed within [1.0 / saturation, saturation] times |
float >= 1.0 |
1.5 |
exposure |
Image exposure to be changed within [1.0 / exposure, exposure] times |
float >= 1.0 |
1.5 |
vertical_flip |
The probability of images to be vertically flipped |
float of [0, 1] |
0 |
horizontal_flip |
The probability of images to be horizontally flipped |
float of [0, 1] |
0.5 |
jitter |
The maximum jitter allowed in augmentation; “jitter” here refers to jitter augmentation in YOLO networks |
float of [0, 1] |
0.3 |
output_width |
The base output image width of augmentation pipeline |
integer, multiple of 32 |
– |
output_height |
The base output image height of augmentation pipeline |
integer, multiple of 32 |
– |
output_channel |
The number of output channels of augmentation pipeline |
1 or 3 |
– |
randomize_input_shape_period |
The batch interval to randomly change the output width and height. For value K, the augmentation pipeline will adjust output shape per K batches, and the adjusted output width/height will be within 0.6 to 1.5 times of the base width/height. Note: If K=0, the output width/height will always be the exact base width/height as configured, and training will be much faster. But the accuracy of the trained network might not be as good. |
non-negative integer |
10 |
mosaic_prob |
The probability of mosaic augmentation to be applied on one image |
float of [0, 1] |
0.5 |
mosaic_min_ratio |
The minimum ratio of width/height one sub-image should occupy |
float of (0, 0.5) |
0.2 |
image_mean |
A key/value pair to specify image mean values. If omitted, ImageNet mean will be used for image preprocessing. If set, depending on output_channel, either ‘r/g/b’ or ‘l’ key/value pair must be configured. |
dict |
– |
Dataset Config
YOLOv4 supports two data formats: the sequence format (KITTI images folder and raw labels folder)
and the tfrecords format (KITTI images folder and TFRecords). From our experience, if mosaic
augmentation is disabled (mosaic_prob=0), training with TFRecords format is faster. If mosaic
augmentation is enabled (mosaic_prob>0), training with sequence format is faster. The
train and evaluate command will determine the data format based on your
dataset_config.
The YOLOv4 dataloader assumes the training/validation split is already done and the data is
prepared in KITTI format: images and labels are in two separate folders, where each image in the
image folder has a .txt label file with the same filename in the label folder, and the
label file content follows KITTI format.
Sequence format
The following is an example dataset_config element if you want to use sequence format:
dataset_config {
data_sources: {
label_directory_path: "/workspace/tao-experiments/data/training/label_2"
image_directory_path: "/workspace/tao-experiments/data/training/image_2"
}
data_sources: {
label_directory_path: "/workspace/tao-experiments/data/training/label_3"
image_directory_path: "/workspace/tao-experiments/data/training/image_3"
}
include_difficult_in_training: true
target_class_mapping {
key: "car"
value: "car"
}
target_class_mapping {
key: "pedestrian"
value: "pedestrian"
}
target_class_mapping {
key: "cyclist"
value: "cyclist"
}
target_class_mapping {
key: "van"
value: "car"
}
target_class_mapping {
key: "person_sitting"
value: "pedestrian"
}
validation_data_sources: {
label_directory_path: "/workspace/tao-experiments/data/val/label_1"
image_directory_path: "/workspace/tao-experiments/data/val/image_1"
}
}
The parameters in dataset_config are defined as follows:
data_sources: The path to datasets to train on. If you have multiple data sources for training, you may use multipledata_sources. This field contains 2 parameters:label_directory_path: The path to the data source label folder.image_directory_path: The path to the data source image folder.
include_difficult_in_training: A flag specifying whether to include difficult boxes in training. If set tofalse, difficult boxes will be ignored. Difficult boxes are those with non-zero occlusion levels in KITTI labels.target_class_mapping: This parameter maps the class names in the labels to the target class to be trained in the network. An element is defined for every source class to target class mapping. This field was included with the intention of grouping similar class objects under one umbrella. For example, “car”, “van”, “heavy_truck”, etc. may be grouped under “automobile”. The “key” field is the value of the class name in the tfrecords file, and the “value” field corresponds to the value that the network is expected to learn.validation_data_sources: Captures the path to datasets to validate on. If you have multiple data sources for validation, you may use multiplevalidation_data_sources. Likedata_sources, this field contains two parameters.
The class names key in the target_class_mapping must be identical to the one shown
in the KITTI labels so that the correct classes are picked up for training.
TFRecords format
TFRecords format requires tfrecords for all labels. This requires running of
tao yolo_v4 dataset-convert command. The command has same functionality and argument
requirements as that of detectnet_v2 and for details of how to generate tfrecords, check
Pre-processing the Dataset in detectnet_v2.
The following is an example dataset_config element if you want to use tfrecords format.
Here, we assume your tfrecords are all generated under a folder called tfrecords, which is under
same parent folder with images and labels:
dataset_config {
data_sources: {
tfrecords_path: "/workspace/tao-experiments/data/training/tfrecords/<tfrecords pattern>"
image_directory_path: "/workspace/tao-experiments/data/training"
}
include_difficult_in_training: true
image_extension: "png"
target_class_mapping {
key: "car"
value: "car"
}
target_class_mapping {
key: "pedestrian"
value: "pedestrian"
}
target_class_mapping {
key: "cyclist"
value: "cyclist"
}
target_class_mapping {
key: "van"
value: "car"
}
target_class_mapping {
key: "person_sitting"
value: "pedestrian"
}
validation_data_sources: {
tfrecords_path: "/workspace/tao-experiments/data/val/tfrecords/<tfrecords pattern>"
image_directory_path: "/workspace/tao-experiments/data/val"
}
}
The parameters in dataset_config are defined as follows:
data_sources: The path to datasets to train on. If you have multiple data sources for training, you may use multipledata_sources. This field contains 2 parameters:tfrecords_path: The path to the data source tfrecords.image_directory_path: The path to the root directory containing the image folder.
image_extension: Image extensions of images contained in the image folder. Note, to use tfrecords format, all images must have same extensions and currently we support jpg and pngvalidation_data_sources: Captures the path to datasets to validate on. This field contains two parameters same asdata_sources. If you have multiple data sources for validation, you may use multiplevalidation_data_sources.
All other fields are same as those in sequence format dataset_config.
YOLO4 Config
The YOLOv4 configuration (yolov4_config) defines the parameters needed for building the
YOLOv4 model. Details are summarized in the table below.
Field |
Description |
Data Type and Constraints |
Recommended/Typical Value |
big_anchor_shape, mid_anchor_shape, and small_anchor_shape |
These settings should be 1-d arrays inside quotation marks. The elements of those arrays are tuples representing the pre-defined anchor shape in the order of “width, height”. The default YOLOv4 configuration has nine predefined anchor shapes. They are divided into three groups
corresponding to big, medium, and small objects. The detection output corresponding to
different groups are from different depths in the network. You should run the |
string |
Use the tao yolo_v4 kmeans command to generate those shapes |
box_matching_iou |
This field should be a float number between 0 and 1. Any anchor with at least this IoU to any ground truth boxes will be matched to the ground truth box it has the largest IoU with. In contrast with YOLOv3, one ground truth box might match to multiple anchors in YOLOv4. |
float |
0.5 |
matching_neutral_box_iou |
This field should be a float number between 0.25 and 1. Any inferred bounding box with at least this IoU to any ground truth boxes will not be treated as negative box and will be assigned 0 for its negative objectiveness loss (neutral box) |
float |
0.5 |
arch_conv_blocks |
Supported values are 0, 1, and 2. This value controls how many convolutional blocks are present among detection output layers. Set this value to 2 if you want to reproduce the meta architecture of the original YOLOv4 model paired with DarkNet 53. Note that this config setting only controls the size of the YOLO meta-architecture–the size of the feature extractor has nothing to do with this config field. |
0, 1 or 2 |
2 |
loss_loc_weight, loss_neg_obj_weights, and loss_class_weights |
These loss weights can be configured as float numbers. The YOLOv4 loss is a summation of localization loss, negative objectiveness loss, positive objectiveness loss, and classification loss. The weight of positive objectiveness loss is set to 1, while the weights of other losses are read from the config file. |
float |
loss_loc_weight: 5.0 loss_neg_obj_weights: 50.0 loss_class_weights: 1.0 |
label_smoothing |
Label smoothing applied to classification loss. |
float of [0, 0.3] |
0, 0.1, 0.2 |
big_grid_xy_extend, mid_grid_xy_extend, and small_grid_xy_extend |
These settings should be small positive floats. The calculated box center relative to the anchor box will be re-calibrated according to following: center_xy = calculated_xy * (grid_xy_extend + 1.0) - grid_xy_extend / 2.0 The default YOLOv4 has nine predefined anchor shapes. They are divided into three groups corresponding to big, medium, and small objects. The detection output corresponding to different groups are from different depths in the network. The three different grid_xy_extend configs allow users to define different grid_xy_extend values for different anchor-shape groups. The grid_xy_extend settings make it easier for the network to propose an inferenced box with a center that is close to or on the anchor border. |
float of [0, 0.3] |
0.05, 0.1, 0.2 |
arch |
The backbone for feature extraction. Currently, “resnet”, “vgg”, “darknet”, “googlenet”, “mobilenet_v1”, “mobilenet_v2”, “cspdarknet”, and “squeezenet” are supported. |
string |
resnet |
nlayers |
The number of conv layers in a specific architecture. For “resnet”, 10, 18, 34, 50 and 101 are supported. For “vgg”, 16 and 19 are supported. For “darknet” or “cspdarknet”, 19 and 53 are supported. All other networks don’t have this configuration, in which case you should just delete this config from the config file. |
Unsigned int |
– |
freeze_bn |
A flag specifying whether to freeze all batch normalization layers during training. |
Boolean |
False |
freeze_blocks |
The list of block IDs to be frozen in the model during training. You can choose to freeze some of the CNN blocks in the model to make the training more stable and/or easier to converge. The definition of a block is heuristic for a specific architecture (for example, by stride or by logical blocks in the model). However, the block ID numbers identify the blocks in the model in a sequential order so you don’t have to know the exact locations of the blocks when you do training. A general principle to keep in mind is that the smaller the block ID, the closer it is to the model input; the larger the block ID, the closer it is to the model output. You can divide the whole model into several blocks and optionally freeze a subset of it. Note that for FasterRCNN, you can only freeze the blocks that are before the ROI pooling layer. Any layer after the ROI pooling layer will not be frozen anyway. For different backbones, the number of blocks and the block ID for each block are different. It deserves some detailed explanations on how to specify the block IDs for each backbone. |
list(repeated integers)
|
– |
force_relu |
A flag specifying whether to replace all activation functions with ReLU. This is useful for training models for NVDLA. |
Boolean |
False |
The anchor shape should match most ground truth boxes in the dataset to help the network learn
bounding boxes. The YOLOv4 paper proposes using the kmeans algorithm to get the anchor shapes,
and the tao yolo_v4 kmeans command is implemented in the TAO algorithm. You should
use the output as your anchor shape in the yolov4_config spec file.
tao yolo_v4 kmeans [-h] -l <label_folders>
-i <image_folders>
-x <network base input width>
-y <network base input height>
[-n <num_clusters>]
[--max_steps <kmeans max steps>]
[--min_x <ignore boxes with width less than this value>]
[--min_y <ignore boxes with height less than this value>]
Required Arguments
-l: Paths to the training label folders. Multiple folder paths should be separated with spaces.-i: Paths to corresponding training image folders. Folder counts and orders must match label folders.-x: The base network input width. This should be theoutput_widthin the augmentation config part of your spec file.-y: The base network input height. This should be theoutput_heightin the augmentation config part of your spec file.
Optional Arguments
-n: The number of shape clusters. This defines how many shape centers the command will output. The default is 9 (3 per group and 3 groups).--max_steps: The max number of steps the kmeans algorithm should run. If the algorithm does not converge at this step, a suboptimal result will be returned. The default value is 10000.--min_x: Ignore ground truth boxes with width less than this value in a reshaped image (images are first reshaped to network base shape as -x, -y).--min_y: Ignore ground truth boxes with height less than this value in a reshaped image (images are first reshaped to network base shape as -x, -y).-h, --help: Show this help message and exit.
Train the YOLOv4 model using this command:
tao yolo_v4 train [-h] -e <experiment_spec>
-r <output_dir>
-k <key>
[--gpus <num_gpus>]
[--gpu_index <gpu_index>]
[--use_amp]
[--log_file <log_file_path>]
Required Arguments
-r, --results_dir: The path to the folder where the experiment output is written.-k, --key: The encryption key to decrypt the model.-e, --experiment_spec_file: The experiment specification file to set up the evaluation experiment. This should be the same as the training-specification file.
Optional Arguments
--gpus: The number of GPUs to use for training in a multi-GPU scenario (default: 1).--gpu_index: The GPU indices used to run the training. You can specify the indices of GPUs to use for training when the machine has multiple GPUs installed.--use_amp: A flag to enable AMP training.--log_file: THe path to the log file. The default path isstdout.-h, --help: Show this help message and exit.
Input Requirement
Input size: C * W * H (where C = 1 or 3, W >= 128, H >= 128, W, H are multiples of 32)
Image format: JPG, JPEG, PNG
Label format: KITTI detection
Sample Usage
Here’s an example of using the train command on a YOLOv4 model:
tao yolo_v4 train --gpus 2 -e /path/to/spec.txt -r /path/to/result -k $KEY
To run evaluation on a YOLOv4 model, use this command:
tao yolo_v4 evaluate [-h] -e <experiment_spec_file>
-m <model_file>
-k <key>
[--gpu_index <gpu_index>]
[--log_file <log_file_path>]
Required Arguments
-e, --experiment_spec_file: The experiment spec file to set up the evaluation experiment. This should be the same as the training-specification file.-m, --model: The path to the model file to use for evaluation. The model can be either a.tltmodel file or TensorRT engine.-k, --key: The key to load the model (not needed if the model is a TensorRT engine).
Optional Arguments
-h, --help: Show this help message and exit.--gpu_index: The GPU index used to run the evaluation. You can specify the index of a GPU to run evaluation when the machine has multiple GPUs installed. Note that evaluation can only run on a single GPU.--log_file: The path to the log file. The default path isstdout.
The inference tool for YOLOv4 networks, which may be used to visualize bboxes or generate frame-by-frame KITTI format labels on a single image or a directory of images. An example of the command for this tool is shown here:
tao yolo_v4 inference [-h] -i <input directory>
-o <output annotated image directory>
-e <experiment spec file>
-m <model file>
-k <key>
[-l <output label directory>]
[-t <visualization threshold>]
[--gpu_index <gpu_index>]
[--log_file <log_file_path>]
Required Arguments
-m, --model: The path to the trained model (TAO model) or TensorRT engine.-i, --in_image_dir: The directory of input images for inference.-o, --out_image_dir: The directory path to output annotated images.-k, --key: The key to load model (not needed if model is a TensorRT engine).-e, --config_path: Path to an experiment spec file for training.
Optional Arguments
-t, --draw_conf_thres: Threshold for drawing a bbox. default: 0.3.-h, --help: Show this help message and exit.-l, --out_label_dir: The directory to output KITTI labels.--gpu_index: The GPU index used to run the inference. We can specify the GPU index used to run evaluation when the machine has multiple GPUs installed. Note that evaluation can only run on a single GPU.--log_file: The path to the log file. The default path isstdout.
Pruning removes parameters from the model to reduce the model size without compromising the
integrity of the model itself using the tao yolo_v4 prune command.
The tao yolo_v4 prune command includes these parameters:
tao yolo_v4 prune [-h] -m <pretrained_model>
-o <output_file>
-k <key>
[-n <normalizer>]
[-eq <equalization_criterion>]
[-pg <pruning_granularity>]
[-pth <pruning threshold>]
[-nf <min_num_filters>]
[-el [<excluded_list>]
Required Arguments
-m, --model: The path to pretrained YOLOv4 model-o, --output_file: The path to the output checkpoints-k, --key: The key to load a .tlt model
Optional Arguments
-h, --help: Show this help message and exit.-n, –normalizer: Usemaxto normalize by dividing each norm by the maximum norm within a layer; useL2to normalize by dividing by the L2 norm of the vector comprising all kernel norms. The default value ismax.-eq, --equalization_criterion: Criteria to equalize the stats of inputs to an element-wise op layer or depth-wise convolutional layer. This parameter is useful for ResNets and MoblieNets. Options arearithmetic_mean,:code:geometric_mean,union, andintersection. The default value isunion.-pg, -pruning_granularity: The number of filters to remove at a time (default: 8)-pth: The threshold to compare a normalized norm against (default: 0.1)-nf, --min_num_filters: The minimum number of filters to keep per layer (default: 16)-el, --excluded_layers: A list of excluded_layers. Examples: -i item1 item2 (default: [])
After pruning, the model needs to be retrained. See Re-training the Pruned Model for more details.
Using the Prune Command
Here’s an example of using the tao yolo_v4 prune command:
tao yolo_v4 prune -m /workspace/output/weights/resnet_003.tlt \
-o /workspace/output/weights/resnet_003_pruned.tlt \
-eq union \
-pth 0.7 -k $KEY
Once the model has been pruned, there might be a slight decrease in accuracy because some
previously useful weights may have been removed. To regain accuracy,
we recommend retraining the pruned model over the same dataset. To do this, use
the tao yolo_v4 train command as documented in Training the model,
with an updated spec file that points to the newly pruned model as the pruned_model_path.
We recommend turning off the regularizer in the training_config for detectnet to recover
the accuracy when retraining a pruned model. You may do this by setting the regularizer type
to NO_REG as mentioned in the Training Config section. All
other parameters in the spec file can be carried over from the previous training.
Exporting the model decouples the training process from inference and allows conversion to
TensorRT engines outside the TAO environment. TensorRT engines are specific to each hardware
configuration and should be generated for each unique inference environment.
The exported model may be used universally across training and deployment hardware.
The exported model format is referred to as .etlt. Like .tlt, the .etlt model
format is also an encrypted model format with the same key of the .tlt model that it is
exported from. This key is required when deploying this model.
INT8 Mode Overview
TensorRT engines can be generated in INT8 mode to improve performance, but require a calibration
cache at engine creation-time. If tao yolo_v4 export is run with the --data_type
flag set to int8, the calibration cache is generated using a calibration tensor file.
Pre-generating the calibration information and caching it removes the need for calibrating the
model on the inference machine. Moving the calibration cache is usually much more convenient than
moving the calibration tensorfile since it is a much smaller file and can be moved with the
exported model. Using the calibration cache also speeds up engine creation, as building the
cache can take several minutes depending on the size of the Tensorfile and the model itself.
The export tool can generate an INT8 calibration cache by ingesting training data using either of these options:
Option 1: Using the training data loader to load the training images for INT8 calibration. This option is now the recommended approach to support multiple image directories by leveraging the training dataset loader. This also ensures two important aspects of data during calibration:
Data pre-processing in the INT8 calibration step is the same as in the training process.
The data batches are sampled randomly across the entire training dataset, thereby improving the accuracy of the INT8 model.
Option 2: Pointing the tool to a directory of images that you want to use to calibrate the model. For this option, make sure to create a sub-sampled directory of random images that best represent your training dataset.
FP16/FP32 Model
The calibration.bin is only required if you need to run inference at INT8 precision. For
FP16/FP32 based inference, the export step is much simpler. All that is required is to provide
a .tlt model from the training/retraining step to be converted into .etlt.
Exporting the Model
Here’s an example of the command line arguments of the tao yolo_v4 export command:
tao yolo_v4 export [-h]
-m <path to the .tlt model file generated by tao train>
-k <key>
[-o <path to output file>]
[--cal_data_file <path to tensor file>]
[--cal_image_dir <path to the directory images to calibrate the model]
[--cal_cache_file <path to output calibration file>]
[--data_type <Data type for the TensorRT backend during export>]
[--batches <Number of batches to calibrate over>]
[--max_batch_size <maximum trt batch size>]
[--max_workspace_size <maximum workspace size]
[--batch_size <batch size to TensorRT engine>]
[--experiment_spec <path to experiment spec file>]
[--engine_file <path to the TensorRT engine file>]
[--gen_ds_config]
[--verbose]
[--strict_type_constraints]
[--force_ptq]
[--gpu_index <gpu_index>]
[--log_file <log_file_path>]
Required Arguments
-m, --model: The path to the.tlt modelfile to be exported.-k, --key: The key used to save the.tltmodel file.-e, --experiment_spec: The path to the spec file.
Optional Arguments
-h, --help: Show this help message and exit.-o, --output_file: The path to save the exported model to. The default path is./<input_file>.etlt.--data_type: The desired engine data type. The options are {fp32,fp16,int8} The default value isfp32. A calibration cache is generated in INT8 mode. If using INT8 mode, the following INT8 arguments are required.--gen_ds_config: A Boolean flag indicating whether to generate the template DeepStream related configuration (“nvinfer_config.txt”) as well as a label file (“labels.txt”) in the same directory as theoutput_file. Note that the config file is NOT a complete configuration file and requires the user to update the sample config files in DeepStream with the parameters generated.-s, --strict_type_constraints: A Boolean flag indicating whether to apply the TensorRT strict type constraints when building the TensorRT engine.--gpu_index: The index of the (descrete) GPU for exporting the model if the machine has multiple GPUs installed. Note that export can only run on a single GPU.--log_file: The path to the log file. The default path isstdout.
INT8 Export Mode Required Arguments
--cal_data_file: The tensorfile generated for calibrating the engine. This can also be an output file if used with--cal_image_dir.--cal_image_dir: A directory of images to use for calibration.
The --cal_image_dir parameter for images applies the necessary preprocessing
to generate a tensorfile at the path mentioned in the --cal_data_file
parameter, which is in turn used for calibration. The number of generated batches in the
tensorfile is obtained from the --batches parameter value,
and the batch_size is obtained from the --batch_size
parameter value. Ensure that the directory mentioned in --cal_image_dir has at
least batch_size * batches number of images in it. The valid image extensions are
.jpg, .jpeg, and .png. In this case, the input_dimensions
of the calibration tensors are derived from the input layer of the .tlt model.
INT8 Export Optional Arguments
--cal_cache_file: The path to save the calibration cache file to. The default value is./cal.bin.--batches: The number of batches to use for calibration and inference testing. The default value is 10.--batch_size: The batch size to use for calibration. The default value is 8.--max_batch_size: The maximum batch size of the TensorRT engine. The default value is 16.--max_workspace_size: The maximum workspace size of TensorRT engine. The default value is1073741824 = 1<<30--engine_file: The path to the serialized TensorRT engine file. Note that this file is hardware specific, and cannot be generalized across GPUs. It is useful to quickly test your model accuracy using TensorRT on the host. As TensorRT engine file is hardware specific, you cannot use this engine file for deployment unless the deployment GPU is identical to the training GPU.--force_ptq: A boolean flag to force post training quantization on the exported etlt model.
When exporting a model trained with QAT enabled, the tensor scale factors to calibrate
the activations are peeled out of the model and serialized to a TensorRT readable cache file
defined by the cal_cache_file argument. However, note that the current version of
QAT doesn’t natively support DLA INT8 deployment on Jetson. To deploy
this model on a Jetson with DLA int8, use the --force_ptq flag for
TensorRT post-training quantization to generate the calibration cache file.
Sample usage
The following is a sample command to export a YOLOv4 model in INT8 mode:
tao yolo_v4 export -m /workspace/yolov4_resnet18_epoch_100.tlt \
-o /workspace/yolov4_resnet18_epoch_100_int8.etlt \
-e /workspace/yolov4_retrain_resnet18_kitti.txt \
-k $KEY \
--cal_image_dir /workspace/data/training/image_2 \
--data_type int8 \
--batch_size 8 \
--batches 10 \
--cal_cache_file /export/cal.bin \
--cal_data_file /export/cal.tensorfile
The deep learning and computer vision models that you’ve trained can be deployed on edge devices, such as a Jetson Xavier or Jetson Nano, a discrete GPU, or in the cloud with NVIDIA GPUs. TAO Toolkit has been designed to integrate with DeepStream SDK, so models trained with TAO Toolkit will work out of the box with DeepStream SDK.
DeepStream SDK is a streaming analytic toolkit to accelerate building AI-based video analytic applications. This section will describe how to deploy your trained model to DeepStream SDK.
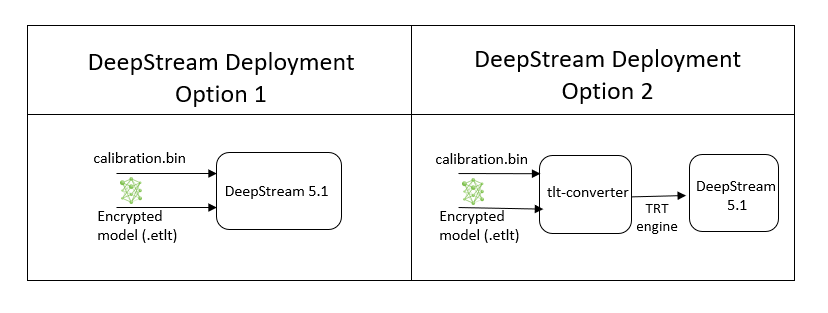
To deploy a model trained by TAO Toolkit to DeepStream we have two options:
Option 1: Integrate the
.etltmodel directly in the DeepStream app. The model file is generated by export.Option 2: Generate a device specific optimized TensorRT engine using
tao-converter. The generated TensorRT engine file can also be ingested by DeepStream.
Machine-specific optimizations are done as part of the engine creation process, so a distinct engine should be generated for each environment and hardware configuration. If the TensorRT or CUDA libraries of the inference environment are updated (including minor version updates), or if a new model is generated, new engines need to be generated. Running an engine that was generated with a different version of TensorRT and CUDA is not supported and will cause unknown behavior that affects inference speed, accuracy, and stability, or it may fail to run altogether.
Option 1 is very straightforward. The .etlt file and calibration cache are directly
used by DeepStream. DeepStream will automatically generate the TensorRT engine file and then run
inference. TensorRT engine generation can take some time depending on size of the model
and type of hardware. Engine generation can be done ahead of time with Option 2.
With option 2, the tao-converter is used to convert the .etlt file to TensorRT; this
file is then provided directly to DeepStream.
See the Exporting the Model section for more details on how to export a TAO model.
TensorRT Open Source Software (OSS)
The TensorRT OSS build is required for YOLOv4 models. This is required because several TensorRT
plugins that are required by these models are only available in TensorRT open source repo and not
in the general TensorRT release. Specifically, for YOLOv4, we need the batchTilePlugin and
batchedNMSPlugin.
If the deployment platform is x86 with an NVIDIA GPU, follow the TensorRT OSS on x86 instructions; if your deployment is on an NVIDIA Jetson platform, follow the TensorRT OSS on Jetson (ARM64) instructions.
TensorRT OSS on x86
Building TensorRT OSS on x86:
Install Cmake (>=3.13).
NoteTensorRT OSS requires cmake >= v3.13, so install cmake 3.13 if your cmake version is lower than 3.13c
sudo apt remove --purge --auto-remove cmake wget https://github.com/Kitware/CMake/releases/download/v3.13.5/cmake-3.13.5.tar.gz tar xvf cmake-3.13.5.tar.gz cd cmake-3.13.5/ ./configure make -j$(nproc) sudo make install sudo ln -s /usr/local/bin/cmake /usr/bin/cmake
Get GPU architecture. The
GPU_ARCHSvalue can be retrieved by thedeviceQueryCUDA sample:cd /usr/local/cuda/samples/1_Utilities/deviceQuery sudo make ./deviceQuery
If the
/usr/local/cuda/samplesdoesn’t exist in your system, you could downloaddeviceQuery.cppfrom this GitHub repo. Compile and rundeviceQuery.nvcc deviceQuery.cpp -o deviceQuery ./deviceQuery
This command will output something like this, which indicates the
GPU_ARCHSis75based on CUDA Capability major/minor version.Detected 2 CUDA Capable device(s) Device 0: "Tesla T4" CUDA Driver Version / Runtime Version 10.2 / 10.2 CUDA Capability Major/Minor version number: 7.5
Build TensorRT OSS:
git clone -b 21.03 https://github.com/nvidia/TensorRT cd TensorRT/ git submodule update --init --recursive export TRT_SOURCE=`pwd` cd $TRT_SOURCE mkdir -p build && cd build
NoteMake sure your
GPU_ARCHSfrom step 2 is in TensorRT OSSCMakeLists.txt. If GPU_ARCHS is not in TensorRT OSSCMakeLists.txt, add-DGPU_ARCHS=<VER>as below, where<VER>representsGPU_ARCHSfrom step 2./usr/local/bin/cmake .. -DGPU_ARCHS=xy -DTRT_LIB_DIR=/usr/lib/aarch64-linux-gnu/ -DCMAKE_C_COMPILER=/usr/bin/gcc -DTRT_BIN_DIR=`pwd`/out make nvinfer_plugin -j$(nproc)
After building ends successfully,
libnvinfer_plugin.so*will be generated under\`pwd\`/out/.Replace the original
libnvinfer_plugin.so*:sudo mv /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libnvinfer_plugin.so.7.x.y ${HOME}/libnvinfer_plugin.so.7.x.y.bak // backup original libnvinfer_plugin.so.x.y sudo cp $TRT_SOURCE/`pwd`/out/libnvinfer_plugin.so.7.m.n /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libnvinfer_plugin.so.7.x.y sudo ldconfig
TensorRT OSS on Jetson (ARM64)
Install Cmake (>=3.13)
NoteTensorRT OSS requires cmake >= v3.13, while the default cmake on Jetson/Ubuntu 18.04 is cmake 3.10.2.
Upgrade TensorRT OSS using:
sudo apt remove --purge --auto-remove cmake wget https://github.com/Kitware/CMake/releases/download/v3.13.5/cmake-3.13.5.tar.gz tar xvf cmake-3.13.5.tar.gz cd cmake-3.13.5/ ./configure make -j$(nproc) sudo make install sudo ln -s /usr/local/bin/cmake /usr/bin/cmake
Get GPU architecture based on your platform. The
GPU_ARCHSfor different Jetson platform are given in the following table.Jetson Platform
GPU_ARCHS
Nano/Tx1
53
Tx2
62
AGX Xavier/Xavier NX
72
Build TensorRT OSS:
git clone -b 21.03 https://github.com/nvidia/TensorRT cd TensorRT/ git submodule update --init --recursive export TRT_SOURCE=`pwd` cd $TRT_SOURCE mkdir -p build && cd build
NoteThe
-DGPU_ARCHS=72below is for Xavier or NX, for other Jetson platform, change72referring toGPU_ARCHSfrom step 2./usr/local/bin/cmake .. -DGPU_ARCHS=72 -DTRT_LIB_DIR=/usr/lib/aarch64-linux-gnu/ -DCMAKE_C_COMPILER=/usr/bin/gcc -DTRT_BIN_DIR=`pwd`/out make nvinfer_plugin -j$(nproc)
After building ends successfully,
libnvinfer_plugin.so*will be generated under‘pwd’/out/.Replace
"libnvinfer_plugin.so*"with the newly generated.sudo mv /usr/lib/aarch64-linux-gnu/libnvinfer_plugin.so.7.x.y ${HOME}/libnvinfer_plugin.so.7.x.y.bak // backup original libnvinfer_plugin.so.x.y sudo cp `pwd`/out/libnvinfer_plugin.so.7.m.n /usr/lib/aarch64-linux-gnu/libnvinfer_plugin.so.7.x.y sudo ldconfig
Generating an Engine Using tao-converter
The tao-converter tool is provided with the TAO Toolkit
to facilitate the deployment of TAO trained models on TensorRT and/or Deepstream.
This section elaborates on how to generate a TensorRT engine using tao-converter.
For deployment platforms with an x86-based CPU and discrete GPUs, the tao-converter
is distributed within the TAO docker. Therefore, we suggest using the docker to generate
the engine. However, this requires that the user adhere to the same minor version of
TensorRT as distributed with the docker. The TAO docker includes TensorRT version 7.2.
Instructions for x86
For an x86 platform with discrete GPUs, the default TAO package includes the tao-converter
built for TensorRT 7.2 with CUDA 11.1 and CUDNN 8.0. However, for any other version of CUDA and
TensorRT, please refer to the overview section for download. Once the
tao-converter is downloaded, follow the instructions below to generate a TensorRT engine.
Unzip the zip file on the target machine.
Install the OpenSSL package using the command:
sudo apt-get install libssl-dev
Export the following environment variables:
$ export TRT_LIB_PATH=”/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu”
$ export TRT_INC_PATH=”/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu”
Run the
tao-converterusing the sample command below and generate the engine.Instructions to build TensorRT OSS on Jetson can be found in the TensorRT OSS on x86 section above or in this GitHub repo.
Make sure to follow the output node names as mentioned in Exporting the Model
section of the respective model.
Instructions for Jetson
For the Jetson platform, the tao-converter is available to download in the NVIDIA developer zone. You may choose
the version you wish to download as listed in the overview section.
Once the tao-converter is downloaded, please follow the instructions below to generate a
TensorRT engine.
Unzip the zip file on the target machine.
Install the OpenSSL package using the command:
sudo apt-get install libssl-dev
Export the following environment variables:
$ export TRT_LIB_PATH=”/usr/lib/aarch64-linux-gnu”
$ export TRT_INC_PATH=”/usr/include/aarch64-linux-gnu”
For Jetson devices, TensorRT 7.1 comes pre-installed with Jetpack. If you are using older JetPack, upgrade to JetPack 4.4 or JetPack 4.5.
Instructions to build TensorRT OSS on Jetson can be found in the TensorRT OSS on Jetson (ARM64) section above or in this GitHub repo.
Run the
tao-converterusing the sample command below and generate the engine.
Make sure to follow the output node names as mentioned in Exporting the Model
section of the respective model.
Using the tao-converter
tao-converter [-h] -k <encryption_key>
-d <input_dimensions>
-o <comma separated output nodes>
[-c <path to calibration cache file>]
[-e <path to output engine>]
[-b <calibration batch size>]
[-m <maximum batch size of the TRT engine>]
[-t <engine datatype>]
[-w <maximum workspace size of the TRT Engine>]
[-i <input dimension ordering>]
[-p <optimization_profiles>]
[-s]
[-u <DLA_core>]
input_file
Required Arguments
input_file: The path to the.etltmodel exported usingtao yolo_v4 export.-k: The key used to encode the.tltmodel when training.-d: A comma-separated list of input dimensions that should match the dimensions used fortao yolo_v4 export.-o: A comma-separated list of output blob names that should match the output configuration used fortao yolo_v4 export. For YOLOv4, set this argument toBatchedNMS.-p: Optimization profiles for.etltmodels with dynamic shape. Use a comma-separated list of optimization profile shapes in the format<input_name>,<min_shape>,<opt_shape>,<max_shape>, where each shape has the format:<n>x<c>x<h>x<w>. The input name for YOLOv4 isInput
Optional Arguments
-e: The path to save the engine to. The default path is./saved.engine.-t: The desired engine data type. The options are {fp32,fp16,int8}. The default value isfp32. A calibration cache is generated in INT8 mode.-w: The maximum workspace size for the TensorRT engine. The default value is1073741824(1<<30).-i: The input dimension ordering; all other TAO commands use NCHW. The options are {nchw,nhwc,nc}.The default value isnchw, so you can omit this argument for YOLOv4.-s: TensorRT strict type constraints. A Boolean to apply TensorRT strict type constraints when building the TensorRT engine.-u: Specifies the DLA core index when building the TensorRT engine on Jetson devices (only needed if using DLA core).
INT8 Mode Arguments
-c: The path to the calibration cache file (only used in INT8 mode). The default value is./cal.bin.-b: The batch size used during the export step for INT8-calibration cache generation (default:8).-m: The maximum batch size for the TensorRT engine (default:16). If you encounter an out-of-memory issue, decrease the batch size accordingly. This parameter is not required for.etltmodels generated with dynamic shape (which is only possible for new models introduced since version 3.0).
Sample Output Log
Here is a sample log for exporting a YOLOv4 model:
tao-converter -k $KEY \
-d 3,384,1248 \
-o BatchedNMS \
-e /export/trt.fp16.engine \
-t fp16 \
-i nchw \
-m 8 \
/ws/yolov4_resnet18_epoch_100.etlt
Integrating the model with DeepStream
To integrate a model trained by TAO Toolkit with DeepStream, you shoud generate a device-specific
optimized TensorRT engine using tao-converter. The generated TensorRT engine file can then
be ingested by DeepStream (Currently, YOLOv4 etlt files are not supported by DeepStream).
For YOLOv4, you will need to build the TensorRT open-source plugins and custom bounding-box parser. The instructions to build TensorRT open-source plugins are provided in the TensorRT Open Source Software (OSS) section above. The instructions to build a custom bounding-box parser are provided in the Prerequisites for YOLOv4 Model section below, and the required code can be found in this GitHub repo.
To integrate the models with DeepStream, you need the following:
Download and install DeepStream SDK. The installation instructions for DeepStream are provided in the DeepStream Development Guide.
An exported
.etltmodel file and optional calibration cache for INT8 precision.A
labels.txtfile containing the labels for classes in the order in which the networks produces outputs.A sample
config_infer_*.txtfile to configure the nvinfer element in DeepStream. The nvinfer element handles everything related to TensorRT optimization and engine creation in DeepStream.
DeepStream SDK ships with an end-to-end reference application which is fully configurable. Users
can configure input sources, inference model, and output sinks. The app requires a primary object
detection model, followed by an optional secondary classification model. The reference
application is installed as deepstream-app. The graphic below shows the architecture of the
reference application.
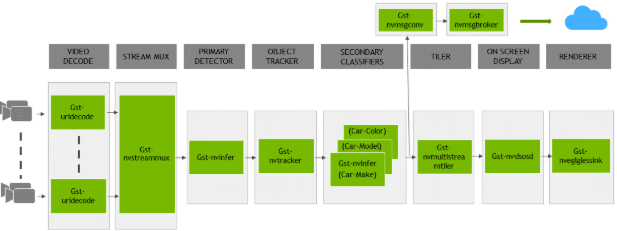
There are typically 2 or more configuration files that are used with this app. In the install
directory, the config files are located in samples/configs/deepstream-app or
sample/configs/tlt_pretrained_models. The main config file configures all the high level
parameters in the pipeline above. This would set input source and resolution, number of
inferences, tracker and output sinks. The other supporting config files are for each individual
inference engine. The inference specific config files are used to specify models, inference
resolution, batch size, number of classes and other customization. The main config file will call
all the supporting config files. Here are some config files in
samples/configs/deepstream-app for your reference.
source4_1080p_dec_infer-resnet_tracker_sgie_tiled_display_int8.txt: Main config fileconfig_infer_primary.txt: Supporting config file for primary detector in the pipeline aboveconfig_infer_secondary_*.txt: Supporting config file for secondary classifier in the pipeline above
The deepstream-app will only work with the main config file. This file will most likely
remain the same for all models and can be used directly from the DeepStream SDK will little to no
change. User will only have to modify or create config_infer_primary.txt and
config_infer_secondary_*.txt.
Integrating a YOLOv4 Model
To run a YOLOv4 model in DeepStream, you need a label file and a DeepStream configuration file. In addition, you need to compile the TensorRT 7+ Open source software and YOLOv4 bounding box parser for DeepStream.
A DeepStream sample with documentation on how to run inference using the trained YOLOv4 models from TAO Toolkit is provided on GitHub repo..
Prerequisites for YOLOv4 Model
YOLOv4 requires batchTilePlugin, resizeNearestPlugin, and batchedNMSPlugin. These plugins are available in the TensorRT open source repo, but not in TensorRT 7.0. Detailed instructions to build TensorRT OSS can be found in TensorRT Open Source Software (OSS).
YOLOv4 requires YOLOv3 custom bounding box parsers that are not built-in inside the DeepStream SDK. The source code to build YOLOv3 custom bounding box parsers is available in GitHub repo. The following instructions can be used to build bounding box parser:
Step1: Install git-lfs (git >= 1.8.2)
curl -s https://packagecloud.io/install/repositories/github/git-lfs/
script.deb.sh | sudo bash
sudo apt-get install git-lfs
git lfs install
Step 2: Download Source Code with SSH or HTTPS
git clone -b release/tlt3.0 https://github.com/NVIDIA-AI-IOT/deepstream_tlt_apps
Step 3: Build
// or Path for DS installation
export CUDA_VER=10.2 // CUDA version, e.g. 10.2
make
This generates libnvds_infercustomparser_tlt.so in the directory post_processor.
Label File
The label file is a text file containing the names of the classes that the YOLOv4 model is trained to detect. The order in which the classes are listed here must match the order in which the model predicts the output. During the training, TAO YOLOv4 will specify all class names in lower case and sort them in alphabetical order. For example, if the dataset_config is:
dataset_config {
data_sources: {
label_directory_path: "/workspace/tao-experiments/data/training/label_2"
image_directory_path: "/workspace/tao-experiments/data/training/image_2"
}
target_class_mapping {
key: "car"
value: "car"
}
target_class_mapping {
key: "person"
value: "person"
}
target_class_mapping {
key: "bicycle"
value: "bicycle"
}
validation_data_sources: {
label_directory_path: "/workspace/tao-experiments/data/val/label"
image_directory_path: "/workspace/tao-experiments/data/val/image"
}
}
Then the corresponding yolov4_labels.txt file would be:
bicycle
car
person
DeepStream Configuration File
The detection model is typically used as a primary inference engine. It can also be used as a
secondary inference engine. To run this model in the sample deepstream-app, you must modify
the existing config_infer_primary.txt file to point to this model.
Integrate the TensorRT engine file with the DeepStream app
Step 1: Generate TensorRT engine using tao-converter. Detailed instructions are provided in the Generating an engine using tao-converter section above.
Step 2: Once the engine file is generated successfully, modify the following parameters to use this engine with DeepStream.
model-engine-file=<PATH to generated TensorRT engine>
All other parameters are common between the two approaches. To use the custom bounding box parser instead of the default parsers in DeepStream, modify the following parameters in [property] section of primary infer configuration file:
parse-bbox-func-name=NvDsInferParseCustomBatchedNMSTLT
custom-lib-path=<PATH to libnvds_infercustomparser_tlt.so>
Add the label file generated above using:
labelfile-path=<YOLOv4 labels>
For all the options, see the configuration file below. To learn about what all the parameters are used for, refer to the DeepStream Development Guide.
Here’s a sample config file, pgie_yolov4_config.txt:
[property]
gpu-id=0
net-scale-factor=1.0
offsets=103.939;116.779;123.68
model-color-format=1
labelfile-path=<Path to yolov4_labels.txt>
model-engine-file=<PATH to generated TensorRT engine>
tlt-model-key=<Key to decrypt model>
infer-dims=3;384;1248
maintain-aspect-ratio=1
uff-input-order=0
uff-input-blob-name=Input
batch-size=1
## 0=FP32, 1=INT8, 2=FP16 mode
network-mode=0
num-detected-classes=3
interval=0
gie-unique-id=1
is-classifier=0
#network-type=0
#no cluster
cluster-mode=3
output-blob-names=BatchedNMS
parse-bbox-func-name=NvDsInferParseCustomBatchedNMSTLT
custom-lib-path=<Path to libnvds_infercustomparser_tlt.so>
[class-attrs-all]
pre-cluster-threshold=0.3
roi-top-offset=0
roi-bottom-offset=0
detected-min-w=0
detected-min-h=0
detected-max-w=0
detected-max-h=0