Inference
A Holoscan application that needs to run inference will use an inference operator. The built-in Inference operator (InferenceOp) can be used, and several related use cases are documented in the Inference operator section below. The use cases are created using the parameter set that must be defined in the configuration file of the holoscan application. If the built-in InferenceOp doesn’t cover a specific use case, users can create their own custom inference operator as documented in Creating an Inference operator section.
The core inference functionality in the Holoscan SDK is provided by the Inference Module which is a framework that facilitates designing and executing inference and processing applications through its APIs. It is used by the built-in InferenceOp which supports the same parameters as the Inference Module. All parameters required by the Holoscan Inference Module are passed through a parameter set in the configuration file of an application.
Required parameters and related features available with the Holoscan Inference Module are listed below.
Data Buffer Parameters: Parameters are provided in the inference settings to enable data buffer locations at several stages of the inference. As shown in the figure below, three parameters
input_on_cuda,output_on_cudaandtransmit_on_cudacan be set by the user.input_on_cudarefers to the location of the data going into the inference.If value is
true, it means the input data is on the deviceIf value is
false, it means the input data is on the hostDefault value:
true
output_on_cudarefers to the data location of the inferred data.If value is
true, it means the inferred data is on the deviceIf value is
false, it means the inferred data is on the hostDefault value:
true
transmit_on_cudarefers to the data transmission.If value is
true, it means the data transmission from the inference extension will be on DeviceIf value is
false, it means the data transmission from the inference extension will be on HostDefault value:
true
Inference Parameters
backendparameter is set to eithertrtfor TensorRT,onnxrtfor Onnx runtime, ortorchfor libtorch. If there are multiple models in the inference application, all models will use the same backend. If it is desired to use different backends for different models, specify thebackend_mapparameter instead.TensorRT:
CUDA-based inference supported both on x86_64 and aarch64
End-to-end CUDA-based data buffer parameters supported.
input_on_cuda,output_on_cudaandtransmit_on_cudawill all be true for end-to-end CUDA-based data movement.input_on_cuda,output_on_cudaandtransmit_on_cudacan be eithertrueorfalse.TensorRT backend expects input models to be in
tensorrt engine fileformat oronnxformat.if models are in
tensorrt engine fileformat, parameteris_engine_pathmust be set totrue.if models are in
onnxformat, it will be automatically converted intotensorrt engine fileby the Holoscan inference module.
Torch:
CUDA and CPU based inference supported both on x86_64 and aarch64.
End-to-end CUDA-based data buffer parameters supported.
input_on_cuda,output_on_cudaandtransmit_on_cudawill all be true for end-to-end CUDA-based data movement.input_on_cuda,output_on_cudaandtransmit_on_cudacan be eithertrueorfalse.Libtorch and TorchVision are included in the Holoscan NGC container, initially built as part of the PyTorch NGC container. To use the Holoscan SDK torch backend outside of these containers, we recommend you download libtorch and torchvision binaries from Holoscan’s third-party repository.
Torch backend expects input models to be in
torchscriptformat.It is recommended to use the same version of torch for
torchscriptmodel generation, as used in the HOLOSCAN SDK on the respective architectures.Additionally, it is recommended to generate the
torchscriptmodel on the same architecture on which it will be executed. For example,torchscriptmodel must be generated onx86_64to be executed in an application running onx86_64only.
Onnx runtime:
Data flow via host only.
input_on_cuda,output_on_cudaandtransmit_on_cudamust befalse.CUDA based inference (supported on x86_64)
CPU based inference (supported on x86_64 and aarch64)
infer_on_cpuparameter is set totrueif CPU based inference is desired.The tables below demonstrate the supported features related to the data buffer and the inference with
trtandonnxrtbased backend, on x86 and aarch64 system respectively.x86
input_on_cudaoutput_on_cudatransmit_on_cudainfer_on_cpuSupported values for trttrueorfalsetrueorfalsetrueorfalsefalseSupported values for torchtrueorfalsetrueorfalsetrueorfalsetrueorfalseSupported values for onnxrtfalsefalsetrueorfalsetrueorfalseAarch64
input_on_cudaoutput_on_cudatransmit_on_cudainfer_on_cpuSupported values for trttrueorfalsetrueorfalsetrueorfalsefalseSupported values for torchtrueorfalsetrueorfalsetrueorfalsetrueorfalseSupported values for onnxrtfalsefalsetrueorfalsetruemodel_path_map: User can design single or multi AI inference pipeline by populatingmodel_path_mapin the config file.With a single entry it is single inference and with more than one entry, multi AI inference is enabled.
Each entry in
model_path_maphas a unique keyword as key (used as an identifier by the Holoscan Inference Module), and the path to the model as value.All model entries must have the models either in onnx or tensorrt engine file or torchscript format.
pre_processor_map: input tensor to the respective model is specified inpre_processor_mapin the config file.The Holoscan Inference Module supports same input for multiple models or unique input per model.
Each entry in
pre_processor_maphas a unique keyword representing the model (same as used inmodel_path_map), and a vector of tensor names as the value.The Holoscan Inference Module supports multiple input tensors per model.
inference_map: output tensors per model after inference is specified ininference_mapin the config file.Each entry in
inference_maphas a unique keyword representing the model (same as used inmodel_path_mapandpre_processor_map), and a vector of the output tensor names as the value.The Holoscan Inference Module supports multiple output tensors per model.
parallel_inference: Parallel or Sequential execution of inferences.If multiple models are input, then user can execute models in parallel.
Parameter
parallel_inferencecan be eithertrueorfalse. Default value istrue.Inferences are launched in parallel without any check of the available GPU resources, user must make sure that there is enough memory and compute available to run all the inferences in parallel.
enable_fp16: Generation of the TensorRT engine files with FP16 optionIf
backendis set totrt, and if the input models are in onnx format, then users can generate the engine file with fp16 option to accelerate inferencing.It takes few mintues to generate the engine files for the first time.
It can be either
trueorfalse. Default value isfalse.
is_engine_path: if the input models are specified in trt engine format inmodel_path_map, this flag must be set totrue. Default value isfalse.in_tensor_names: Input tensor names to be used bypre_processor_map. This parameter is optional. If absent in the parameter map, values are derived frompre_processor_map.out_tensor_names: Output tensor names to be used byinference_map. This parameter is optional. If absent in the parameter map, values are derived frominference_map.device_map: Multi-GPU inferencing is enabled ifdevice_mapis populated in the parameter set.Each entry in
device_maphas a unique keyword representing the model (same as used inmodel_path_mapandpre_processor_map), and GPU identifier as the value. This GPU ID is used to execute the inference for the specified model.GPUs specified in the
device_mapmust have P2P (peer to peer) access and they must be connected to the same PCIE configuration. If P2P access is not possible among GPUs, the host (CPU memory) will be used to transfer the data.Multi-GPU inferencing is supported for all backends.
temporal_map: Temporal inferencing is enabled iftemporal_mapis populated in the parameter set.Each entry in
temporal_maphas a unique keyword representing the model (same as used inmodel_path_mapandpre_processor_map), and frame delay as the value. Frame delay represents the frame count that are skipped by the operator in doing the inference for that particular model. A model with the value of 1, is inferred per frame. A model with a value of 10 is inferred for every 10th frame coming into the operator, which is the 1st frame, 11th frame, 21st frame and so on. Additionally, the operator will transmit the last inferred result for all the frames that are not inferred. For example, a model with a value of 10 will be inferred at 11th frame and from 12th to 20th frame, the result from 11th frame is transmitted.If the
temporal_mapis absent in the parameter set, all models are inferred for all the frames.All models are not mandatory in the
temporal_map. The missing models are inferred per frame.Temporal map based inferencing is supported for all backends.
activation_map: Dynamic inferencing can be enabled with this parameter. It is populated in the parameter set and is updated at runtime.Each entry in
activation_maphas a unique keyword representing the model (same as used inmodel_path_mapandpre_processor_map), and activation state as the value. Activation state represents whether the model will be used for inferencing or not on a given frame. Any model(s) with a value of 1 will be active and will be used for inference, and any model(s) with a value of 0 will not run. The activation map must be initialized in the parameter set for all the models that need to be activated or deactivated dynamically.When the activation state is 0 for a particular model in the
activation_map, the inference operator will not launch the inference for the model and will emits the last inferred result for the model.If the
activation_mapis absent in the parameter set, all of the models are inferred for all frames.All models are not mandatory in the
activation_map. The missing models are active on every frame.Activation map based dynamic inferencing is supported for all backends.
backend_map: Multiple backends can be used in the same application with this parameter.Each entry in
backend_maphas a unique keyword representing the model (same as used inmodel_path_map), and thebackendas the value.A sample backend_map is shown below. In the example, model_1 uses the
tensorRTbackend, and model 2 and model 3 uses thetorchbackend for inference.backend_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": "trt" "model_2_unique_identifier": "torch" "model_3_unique_identifier": "torch"
Other features: Table below illustrates other features and supported values in the current release.
Feature
Supported values
Data type float32,int32,int8Inference Backend trt,torch,onnxrtInputs per model Multiple Outputs per model Multiple GPU(s) supported Multi-GPU on same PCIE network Tensor data dimension 2, 3, 4 Model Type All onnxorall torchscriptorall trt enginetype or acombination of torch and trt engineMulti Receiver and Single Transmitter support
The Holoscan Inference Module provides an API to extract the data from multiple receivers.
The Holoscan Inference Module provides an API to transmit multiple tensors via a single transmitter.
Parameter Specification
All required inference parameters of the inference application must be specified. Below is a sample parameter set for an application that uses three models for inferencing. User must populate all required fields with appropriate values.
inference:
backend: "trt"
model_path_map:
"model_1_unique_identifier": "path_to_model_1"
"model_2_unique_identifier": "path_to_model_2"
"model_3_unique_identifier": "path_to_model_3"
pre_processor_map:
"model_1_unique_identifier": ["input_tensor_1_model_1_unique_identifier"]
"model_2_unique_identifier": ["input_tensor_1_model_2_unique_identifier"]
"model_3_unique_identifier": ["input_tensor_1_model_3_unique_identifier"]
inference_map:
"model_1_unique_identifier": ["output_tensor_1_model_1_unique_identifier"]
"model_2_unique_identifier": ["output_tensor_1_model_2_unique_identifier"]
"model_3_unique_identifier": ["output_tensor_1_model_3_unique_identifier"]
parallel_inference: true
infer_on_cpu: false
enable_fp16: false
input_on_cuda: true
output_on_cuda: true
transmit_on_cuda: true
is_engine_path: false
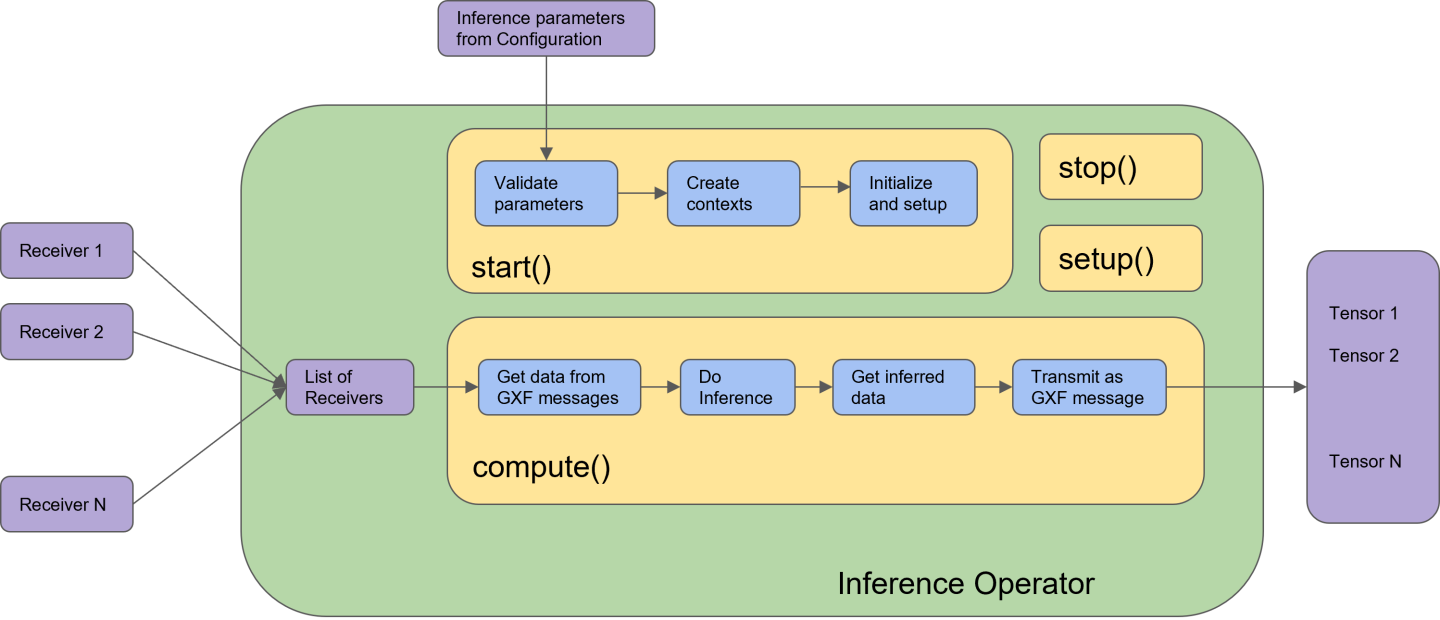
In Holoscan SDK, the built-in Inference operator (InferenceOp) is designed using the Holoscan Inference Module APIs. The Inference operator ingests the inference parameter set (from the configuration file) and the data receivers (from previous connected operators in the application), executes the inference and transmits the inferred results to the next connected operators in the application.
InferenceOp is a generic operator that serves multiple use cases via the parameter set. Parameter sets for some key use cases are listed below:
Note: Some parameters have default values set for them in the InferenceOp. For any parameters not mentioned in the example parameter sets below, their default is used by the InferenceOp. These parameters are used to enable several use cases.
Single model inference using
TensorRTbackend.backend: "trt" model_path_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": "path_to_model_1" pre_processor_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": ["input_tensor_1_model_1_unique_identifier"] inference_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": ["output_tensor_1_model_1_unique_identifier"]
Value of
backendcan be modified for other supported backends, and other parameters related to each backend. User must ensure correct model type and model path is provided into the parameter set, along with supported values of all parameters for the respective backend.In this example,
path_to_model_1must be anonnxfile, which will be converted to atensorRTengine file at first execution. During subsequent executions, the Holoscan inference module will automatically find the tensorRT engine file (ifpath_to_model_1has not changed). Additionally, if user has a pre-builttensorRTengine file,path_to_model_1must be path to the engine file and the parameteris_engine_pathmust be set totruein the parameter set.Single model inference using
TensorRTbackend with multiple outputs.backend: "trt" model_path_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": "path_to_model_1" pre_processor_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": ["input_tensor_1_model_1_unique_identifier"] inference_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": ["output_tensor_1_model_1_unique_identifier", "output_tensor_2_model_1_unique_identifier", "output_tensor_3_model_1_unique_identifier"]
As shown in example above, Holoscan Inference module automatically maps the model outputs to the named tensors in the parameter set. Users must ensure to use the named tensors in the same sequence in which the model generates the output. Similar logic holds for multiple inputs.
Single model inference using fp16 precision.
backend: "trt" model_path_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": "path_to_model_1" pre_processor_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": ["input_tensor_1_model_1_unique_identifier"] inference_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": ["output_tensor_1_model_1_unique_identifier", "output_tensor_2_model_1_unique_identifier", "output_tensor_3_model_1_unique_identifier"] enable_fp16: true
If a
tensorRTengine file is not available for fp16 precision, it will be automatically generated by the Holoscan Inference module on the first execution. The file is cached for future executions.Single model inference on CPU.
backend: "onnxrt" model_path_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": "path_to_model_1" pre_processor_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": ["input_tensor_1_model_1_unique_identifier"] inference_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": ["output_tensor_1_model_1_unique_identifier"] infer_on_cpu: true
Note that the backend can only be
onnxrtortorchfor CPU based inference.Single model inference with input/output data on Host.
backend: "trt" model_path_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": "path_to_model_1" pre_processor_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": ["input_tensor_1_model_1_unique_identifier"] inference_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": ["output_tensor_1_model_1_unique_identifier"] input_on_cuda: false output_on_cuda: false
Data in the core inference engine is passed through the host and is received on the host. Inference can happen on the GPU. Parameters
input_on_cudaandoutput_on_cudadefine the location of the data before and after inference respectively.Single model inference with data transmission via Host.
backend: "trt" model_path_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": "path_to_model_1" pre_processor_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": ["input_tensor_1_model_1_unique_identifier"] inference_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": ["output_tensor_1_model_1_unique_identifier"] transmit_on_host: true
Data from inference operator to the next connected operator in the application is transmitted via the host.
Multi model inference with a single backend.
backend: "trt" model_path_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": "path_to_model_1" "model_2_unique_identifier": "path_to_model_2" "model_3_unique_identifier": "path_to_model_3" pre_processor_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": ["input_tensor_1_model_1_unique_identifier"] "model_2_unique_identifier": ["input_tensor_1_model_2_unique_identifier"] "model_3_unique_identifier": ["input_tensor_1_model_3_unique_identifier"] inference_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": ["output_tensor_1_model_1_unique_identifier"] "model_2_unique_identifier": ["output_tensor_1_model_2_unique_identifier"] "model_3_unique_identifier": ["output_tensor_1_model_3_unique_identifier"]
By default multiple model inferences are launched in parallel. The backend specified via parameter
backendis used for all models in the application.Multi model inference with sequential inference.
backend: "trt" model_path_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": "path_to_model_1" "model_2_unique_identifier": "path_to_model_2" "model_3_unique_identifier": "path_to_model_3" pre_processor_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": ["input_tensor_1_model_1_unique_identifier"] "model_2_unique_identifier": ["input_tensor_1_model_2_unique_identifier"] "model_3_unique_identifier": ["input_tensor_1_model_3_unique_identifier"] inference_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": ["output_tensor_1_model_1_unique_identifier"] "model_2_unique_identifier": ["output_tensor_1_model_2_unique_identifier"] "model_3_unique_identifier": ["output_tensor_1_model_3_unique_identifier"] parallel_inference: false
parallel_inferenceis set totrueby default. To launch model inferences in sequence,parallel_inferencemust be set tofalse.Multi model inference with multiple backends.
backend_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": "trt" "model_2_unique_identifier": "torch" "model_3_unique_identifier": "torch" model_path_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": "path_to_model_1" "model_2_unique_identifier": "path_to_model_2" "model_3_unique_identifier": "path_to_model_3" pre_processor_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": ["input_tensor_1_model_1_unique_identifier"] "model_2_unique_identifier": ["input_tensor_1_model_2_unique_identifier"] "model_3_unique_identifier": ["input_tensor_1_model_3_unique_identifier"] inference_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": ["output_tensor_1_model_1_unique_identifier"] "model_2_unique_identifier": ["output_tensor_1_model_2_unique_identifier"] "model_3_unique_identifier": ["output_tensor_1_model_3_unique_identifier"]
In the above sample parameter set, the first model will do inference using the
tensorRTbackend, and model 2 and 3 will do inference using thetorchbackend.Note: the combination of backends in
backend_mapmust support all other parameters that will be used during the inference. For. e.g.onnxrtandtensorRTcombination with CPU based inference will not be supported.Multi model inference with a single backend on multi-GPU.
backend: "trt" device_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": "1" "model_2_unique_identifier": "0" "model_3_unique_identifier": "1" model_path_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": "path_to_model_1" "model_2_unique_identifier": "path_to_model_2" "model_3_unique_identifier": "path_to_model_3" pre_processor_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": ["input_tensor_1_model_1_unique_identifier"] "model_2_unique_identifier": ["input_tensor_1_model_2_unique_identifier"] "model_3_unique_identifier": ["input_tensor_1_model_3_unique_identifier"] inference_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": ["output_tensor_1_model_1_unique_identifier"] "model_2_unique_identifier": ["output_tensor_1_model_2_unique_identifier"] "model_3_unique_identifier": ["output_tensor_1_model_3_unique_identifier"]
In the sample above, model 1 and model 3 will do inference on the GPU with ID 1 and model 2 will do inferene on the GPU with ID 0. GPUs must have P2P (peer to peer) access among them. If it is not enabled, the Holoscan inference module enables it by default. If P2P access is not possible between GPUs, then the data transfer will happen via the Host.
Multi model inference with multiple backends on multiple GPUs.
backend_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": "trt" "model_2_unique_identifier": "torch" "model_3_unique_identifier": "torch" device_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": "1" "model_2_unique_identifier": "0" "model_3_unique_identifier": "1" model_path_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": "path_to_model_1" "model_2_unique_identifier": "path_to_model_2" "model_3_unique_identifier": "path_to_model_3" pre_processor_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": ["input_tensor_1_model_1_unique_identifier"] "model_2_unique_identifier": ["input_tensor_1_model_2_unique_identifier"] "model_3_unique_identifier": ["input_tensor_1_model_3_unique_identifier"] inference_map: "model_1_unique_identifier": ["output_tensor_1_model_1_unique_identifier"] "model_2_unique_identifier": ["output_tensor_1_model_2_unique_identifier"] "model_3_unique_identifier": ["output_tensor_1_model_3_unique_identifier"]
In the sample above, three models are used during the inference. Model 1 uses the trt backend and runs on the GPU with ID 1, model 2 uses the torch backend and runs on the GPU with ID 0, and model 3 uses the torch backend and runs on the GPU with ID 1.
The Inference operator is the core inference unit in an inference application. The built-in Inference operator (InferenceOp) can be used for inference, or users can create their own custom inference operator as explained in this section. In Holoscan SDK, the inference operator can be designed using the Holoscan Inference Module APIs.
Arguments in the code sections below are referred to as ….
Parameter Validity Check: Input inference parameters via the configuration (from step 1) are verified for correctness.
auto status = HoloInfer::inference_validity_check(...);
Inference specification creation: For a single AI, only one entry is passed into the required entries in the parameter set. There is no change in the API calls below. Single AI or multi AI is enabled based on the number of entries in the parameter specifications from the configuration (in step 1).
// Declaration of inference specifications std::shared_ptr<HoloInfer::InferenceSpecs> inference_specs_; // Creation of inference specification structure inference_specs_ = std::make_shared<HoloInfer::InferenceSpecs>(...);
Inference context creation.
// Pointer to inference context. std::unique_ptr<HoloInfer::InferContext> holoscan_infer_context_; // Create holoscan inference context holoscan_infer_context_ = std::make_unique<HoloInfer::InferContext>();
Parameter setup with inference context: All required parameters of the Holoscan Inference Module are transferred in this step, and relevant memory allocations are initiated in the inference specification.
// Set and transfer inference specification to inference context auto status = holoscan_infer_context_->set_inference_params(inference_specs_);
Data extraction and allocation: The following API is used from the Holoinfer utility to extract and allocate data for the specified tensor.
// Extract relevant data from input, and update inference specifications gxf_result_t stat = HoloInfer::get_data_per_model(...);
Inference execution
// Execute inference and populate output buffer in inference specifications auto status = holoscan_infer_context_->execute_inference(inference_specs_->data_per_model_, inference_specs_->output_per_model_);
Transmit inferred data:
// Transmit output buffers auto status = HoloInfer::transmit_data_per_model(...);
Figure below demonstrates the Inference operator in the Holoscan SDK. All blocks with blue color are the API calls from the Holoscan Inference Module.