DPA HART Management Tool
NVIDIA DOCA DPA HART Management Tool
This document describes the DPA HART management tool, dpahartmgmt.
The DPA HART management tool can run either on the host machine or on the target DPU and allows users to manage the DPA's HARTs which are the basic resource of the DPA. The tool enables the resource control of HARTs to optimize computation resources usage of the DPA before using DOCA FlexIO SDK API.
Without HART allocation, a DPA software thread would lack access to the hardware pipeline/CPU time resource, and consequently not be able to execute.
dpahartmgmt serves the following main usages:
- Running a DPA software thread with
strictaffinity on a DPA HART (i.e., running a DPA thread using only the specific preselected HART). For this purpose,dpahartmgmtprovides an option to query the maximum HART ID allowed to use. - Allowing a DPA software thread to run over a DPA HART from a group of HARTs:
- Once a HART group is created, it is allocated a subset of HARTs.
dpahartmgmtprovides an ID to the created group which can be used to run DPA applications withgroupaffinity where the affinity ID would be the same as that group's ID.
- HART partition management - the ability to manage HART partitions.
When the software stack wishes to run a DPA thread with group affinity type, one of the available HARTs from the group's collection is used for the execution.
Upon boot, a default HART partition is automatically created. The default HART partition possesses all the system's HARTs. The DPA partition manager function is the only function that belongs to it and can therefore control the entire resources of the system.
When running a DPA thread with none affinity, the HART chosen for the DPA thread to run with comes from the partition's pool of HARTs. Namely, from the HARTs belonging only to the DPA device's current partition which were not assigned to any HART groups (on the current partition). If the aforementioned group of HARTs (i.e., the partition's default HART group) is empty, the DPA thread would fail to run with none affinity.
dpahartmgmt enables users to create, destroy, and query HART objects.
Top-level dpahartmgmt command syntax:
Usage: dpahartmgmt {help|version|hart_group|partition}
Type "./dpahartmgmt help" for detailed help
3.1. General Commands
- Print basic usage information for the tool:
dpahartmgmt -h
- Print a detailed help menu of the tool's commands:
dpahartmgmt help
- Print version information:
dpahartmgmt version
3.2. HART Group Commands
The commands listed in the following subsections are used to configure HART groups.
3.2.1. HART Group Command Flags and Arguments
The following table lists the flags relevant forhart_group commands. Arguments for the flags must be used within quotes (if more than one) and without extra spaces.
| Short Option | Long Option | Description |
|---|---|---|
-h |
--help |
Print out basic tool usage information. |
-d |
--dpa_device |
The device interface name (MST/PCI/RDMA/NET). |
-r |
--range_harts |
The range of HARTs to allocate a HART group or a partition. The argument must be provided within quotes. |
-g |
--id_group |
Group ID number. This number must be positive and less than or equal to the |
-n |
--name_group |
Group name; 15 character string. The argument must be provided within quotes. |
-f |
--file_groups |
Full path or only the filename if it is located in the same directory as the executable directory (where dpahartmgmt is). |
3.2.2. Info HART Group
Print information on the relevant DPA resources for the HART groups:
dpahartmgmt hart_group info --dpa_device <device>
Example:
$ sudo ./dpahartmgmt hart_group info -d mlx5_0
Max number of DPA HART groups: 15
Max number of DPA HARTs in one DPA HART group: 190
Max DPA HART number available to use: 190
Max HART group name length is 15 chars
3.2.3. Create HART Group
Create a HART group with the specified name on the provided device's partition. The HARTs indicated by the range are taken from the DPA device's HART partition.
dpahartmgmt hart_group create --dpa_device <device> --name_group <name> --range_harts <range>
Example:
$ sudo ./dpahartmgmt hart_group create -d mlx5_0 -n "HG hello world1" -r "6-8,16,55,70"
Group created successfully-
HART group name: HG hello world1, with id: 1.
Member HARTs are:
6,7,8,16,55,70
3.2.4. Destroy HART Group
Destroy a HART group that exists on the device's partition with either the provided group name or ID.
dpahartmgmt hart_group destroy --dpa_device <device> [--name_group <name> | --id_group <id>]
Example:
$ sudo ./dpahartmgmt hart_group destroy -d mlx5_0 -g 0
Group with group id: 0, was destroyed successfully
3.2.5. Query HART Group
Query HART groups residing on the provided device's partition. If one of the optional parameters is used, the command only queries the specific group and prints it if it exists:
dpahartmgmt hart_group query --dpa_device <device> [--name_group <name> | --id_group <id>]
Example:
$ sudo ./dpahartmgmt hart_group query -d mlx5_0
1) HART group name: HG hello world, with id: 0.
Member HARTs are:
6,7,8,16,55,70
In total there are 1 HART groups configured.
More options:
$ sudo ./dpahartmgmt hart_group query -d mlx5_0 -n "HG hello world"
$ sudo ./dpahartmgmt hart_group query -d mlx5_0 -g 0
3.2.6. Apply HART Group
Apply the HART groups provided in the file on the device's partition:
dpahartmgmt hart_group apply --dpa_device <device> --file_groups <file>
File format example:
{
"hart_groups": [
{ "name": "hg1", "range": "178-180"},
{ "name": "hg2", "range": "2-10"}
]
}
Example:
$ sudo ./dpahartmgmt hart_group apply -d mlx5_0 --file_groups example.json
1) HART group name: hg1, with id: 1.
Member HARTs are:
178,179,180
2) HART group name: hg2, with id: 2.
Member HARTs are:
2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10
In total there are 2 HART groups configured.
3.3. HART Partition Commands
The commands listed in the following subsections are used to configure HART partitions.
3.3.1. HART Partition Command Flags and Arguments
The following table lists the flags relevant for HARTpartition commands. Arguments for the flags must be used within quotes (if more than one) and without extra spaces.
| Short Option | Long Option | Description |
|---|---|---|
-h |
--help |
Print out basic tool usage information. |
-d |
--dpa_device |
The device interface name (MST/PCI/RDMA/NET). |
-r |
--range_harts |
The range of HARTs to allocate a HART group or a partition. The argument must be provided within quotes. |
-p |
--id_partition |
Partition ID number. This number must be positive and less than or equal to the value of |
-v |
--vhca_list |
The vHCA IDs to be associated with the partition. The argument must be provided within quotes. |
-m |
--max_num_hart_group |
The number of HART groups to reserve for the partition upon its creation. |
3.3.2. Info HART Partition
Print the relevant DPA resources of the HART partitions:
dpahartmgmt partition info --dpa_device <device>
Example:
$ sudo ./dpahartmgmt partition info -d mlx5_0
Max number of DPA HART partitions: 15
Max number of VHCAs associated with a single partition: 32
Max number of DPA HART groups: 15
Note- an allocation of a partition consumes from the number of DPA HART *groups* available to create
Max DPA HART number available to use: 190
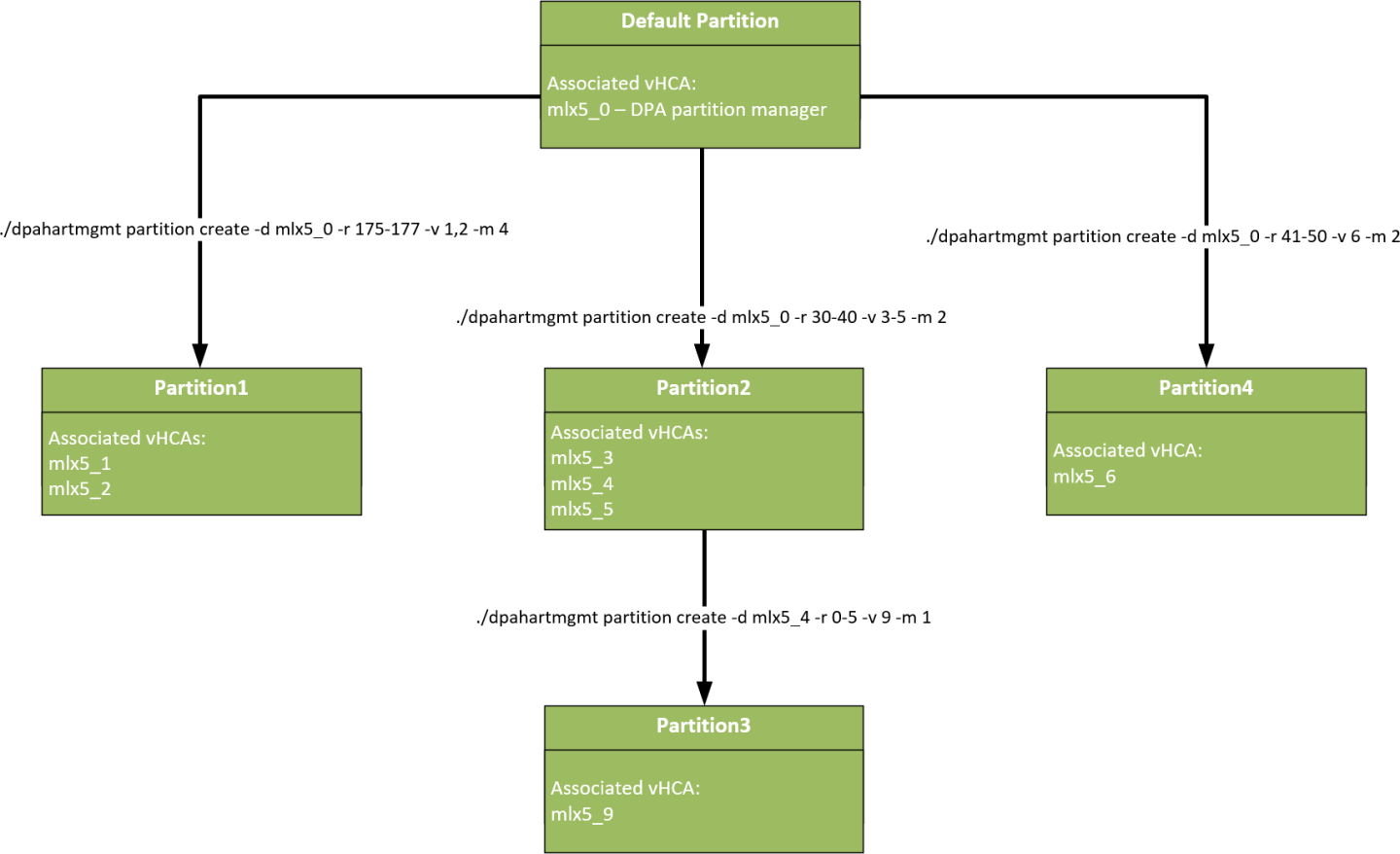
3.3.3. Create HART Partition
Create a HART partition on the DPA device:
dpahartmgmt partition create --dpa_device <device> --vhca_list <id_list> --range_harts <range> --max_num_hart_group <max_num>
Example:
$ sudo ./dpahartmgmt partition create -d mlx5_0 -v 1 -r 10-20 -m 2
Partition created successfully-
HART Partition id: 1. Maximal number of groups: 2
Number of Partition's associated VHCA ids is 1, numbers are listed below:1
Partition's member HARTs are:10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20
3.3.4. Destroy HART Partition
Destroy a HART partition that exists on the device's partition:
dpahartmgmt partition destroy --dpa_device <device> --id_partition <id>
Example:
$ sudo ./dpahartmgmt partition destroy -d mlx5_0 -p 1
Partition with partition id: 1, was destroyed successfully
3.3.5. Query HART Partition
Query HART partitions that reside on the provided device's partition and print out the partition if it exists:
dpahartmgmt partition query --dpa_device <device> [--id_partition <id>]
Example:
$ sudo ./dpahartmgmt partition query -d mlx5_0 -p 1
HART Partition id: 1. Maximal number of groups: 2
Number of Partition's associated VHCA ids is 1, numbers are listed below:1
Partition's member HARTs are:10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20
More options:
$ sudo ./dpahartmgmt partition query -d mlx5_0
- Currently,
dpahartmgmtis only supported on the DPU not the host dpahartmgmtshould run before creating a DPA process so all resources are configured ahead of time- Running the tool over a device with an existing DPA process results in failure
- The HART group name assigned by the user must be unique for every HART group on a specific partition or the HART group create command fails
- The creation of a HART partition consumes from the number of HART groups allowed on the vHCA's partition it is created on:
- 1 group for the partition itself due to a default group created for each partition
<max_num>of groups which is the user's input provided upon partition creation
- Creating groups or running DPA threads in general (with any affinity) on interfaces other than ECPF, requires a configuration of a valid partition for the specific vHCA
- Only the default partition is exposed to the real HART numbers, all other partitions the user creates use virtual HARTs
- For example, if a user creates a partition with the range of HARTs 20-40, querying the partition info from one of its virtual HCAs (vHCAs) would display HARTs from 0-20. Therefore, the HART whose real number is 39 in this example would correspond to the virtual HART number 19.
- HART overlap is not allowed on HART objects
- vHCA ID overlap is not allowed on HART partitions
- It is not possible to query vHCA IDs with
dpahartmgmt, these are assumed to be known by the user beforehand - Partition destruction fails if there are HART objects that exist on that partition
- It is not possible to know which HART has been chosen to run on
- Every vHCA sees the partition it belongs to, and its resources, as the entire world. It only sees:
- Groups and partitions it created
- The number of HARTs it was given
- The
max_num_hart_groupof the partition it belongs to
- No guarantee regarding HART group ID that will be given on group creation
- The default groups (of every partition) cannot be managed by the user
- The HART numbers available are between 0 and the max DPA HART number available to use minus 1 (the upper limit can be queried using the info command specified above)
dpahartmgmtdoes not support virtual functions (VFs)- It is not possible to create partitions on other vHCAs other than the DPA partition manager function
- There are at most 16 hardware HART group entities
Notice
This document is provided for information purposes only and shall not be regarded as a warranty of a certain functionality, condition, or quality of a product. NVIDIA Corporation nor any of its direct or indirect subsidiaries and affiliates (collectively: “NVIDIA”) make no representations or warranties, expressed or implied, as to the accuracy or completeness of the information contained in this document and assume no responsibility for any errors contained herein. NVIDIA shall have no liability for the consequences or use of such information or for any infringement of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from its use. This document is not a commitment to develop, release, or deliver any Material (defined below), code, or functionality.
NVIDIA reserves the right to make corrections, modifications, enhancements, improvements, and any other changes to this document, at any time without notice.
Customer should obtain the latest relevant information before placing orders and should verify that such information is current and complete.
NVIDIA products are sold subject to the NVIDIA standard terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgement, unless otherwise agreed in an individual sales agreement signed by authorized representatives of NVIDIA and customer (“Terms of Sale”). NVIDIA hereby expressly objects to applying any customer general terms and conditions with regards to the purchase of the NVIDIA product referenced in this document. No contractual obligations are formed either directly or indirectly by this document.
NVIDIA products are not designed, authorized, or warranted to be suitable for use in medical, military, aircraft, space, or life support equipment, nor in applications where failure or malfunction of the NVIDIA product can reasonably be expected to result in personal injury, death, or property or environmental damage. NVIDIA accepts no liability for inclusion and/or use of NVIDIA products in such equipment or applications and therefore such inclusion and/or use is at customer’s own risk.
NVIDIA makes no representation or warranty that products based on this document will be suitable for any specified use. Testing of all parameters of each product is not necessarily performed by NVIDIA. It is customer’s sole responsibility to evaluate and determine the applicability of any information contained in this document, ensure the product is suitable and fit for the application planned by customer, and perform the necessary testing for the application in order to avoid a default of the application or the product. Weaknesses in customer’s product designs may affect the quality and reliability of the NVIDIA product and may result in additional or different conditions and/or requirements beyond those contained in this document. NVIDIA accepts no liability related to any default, damage, costs, or problem which may be based on or attributable to: (i) the use of the NVIDIA product in any manner that is contrary to this document or (ii) customer product designs.
No license, either expressed or implied, is granted under any NVIDIA patent right, copyright, or other NVIDIA intellectual property right under this document. Information published by NVIDIA regarding third-party products or services does not constitute a license from NVIDIA to use such products or services or a warranty or endorsement thereof. Use of such information may require a license from a third party under the patents or other intellectual property rights of the third party, or a license from NVIDIA under the patents or other intellectual property rights of NVIDIA.
Reproduction of information in this document is permissible only if approved in advance by NVIDIA in writing, reproduced without alteration and in full compliance with all applicable export laws and regulations, and accompanied by all associated conditions, limitations, and notices.
THIS DOCUMENT AND ALL NVIDIA DESIGN SPECIFICATIONS, REFERENCE BOARDS, FILES, DRAWINGS, DIAGNOSTICS, LISTS, AND OTHER DOCUMENTS (TOGETHER AND SEPARATELY, “MATERIALS”) ARE BEING PROVIDED “AS IS.” NVIDIA MAKES NO WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED, IMPLIED, STATUTORY, OR OTHERWISE WITH RESPECT TO THE MATERIALS, AND EXPRESSLY DISCLAIMS ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF NONINFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY, AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. TO THE EXTENT NOT PROHIBITED BY LAW, IN NO EVENT WILL NVIDIA BE LIABLE FOR ANY DAMAGES, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, PUNITIVE, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, HOWEVER CAUSED AND REGARDLESS OF THE THEORY OF LIABILITY, ARISING OUT OF ANY USE OF THIS DOCUMENT, EVEN IF NVIDIA HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. Notwithstanding any damages that customer might incur for any reason whatsoever, NVIDIA’s aggregate and cumulative liability towards customer for the products described herein shall be limited in accordance with the Terms of Sale for the product.
Trademarks
NVIDIA, the NVIDIA logo, and Mellanox are trademarks and/or registered trademarks of Mellanox Technologies Ltd. and/or NVIDIA Corporation in the U.S. and in other countries. The registered trademark Linux® is used pursuant to a sublicense from the Linux Foundation, the exclusive licensee of Linus Torvalds, owner of the mark on a world¬wide basis. Other company and product names may be trademarks of the respective companies with which they are associated.
Copyright
© 2023 NVIDIA Corporation & affiliates. All rights reserved.