Deploying to DeepStream for DetectNet_v2
The deep learning and computer vision models that you’ve trained can be deployed on edge devices, such as a Jetson Xavier or Jetson Nano, a discrete GPU, or in the cloud with NVIDIA GPUs. TAO Toolkit has been designed to integrate with DeepStream SDK, so models trained with TAO Toolkit will work out of the box with DeepStream SDK.
DeepStream SDK is a streaming analytic toolkit to accelerate building AI-based video analytic applications. This section will describe how to deploy your trained model to DeepStream SDK.
To deploy a model trained by TAO Toolkit to DeepStream we have two options:
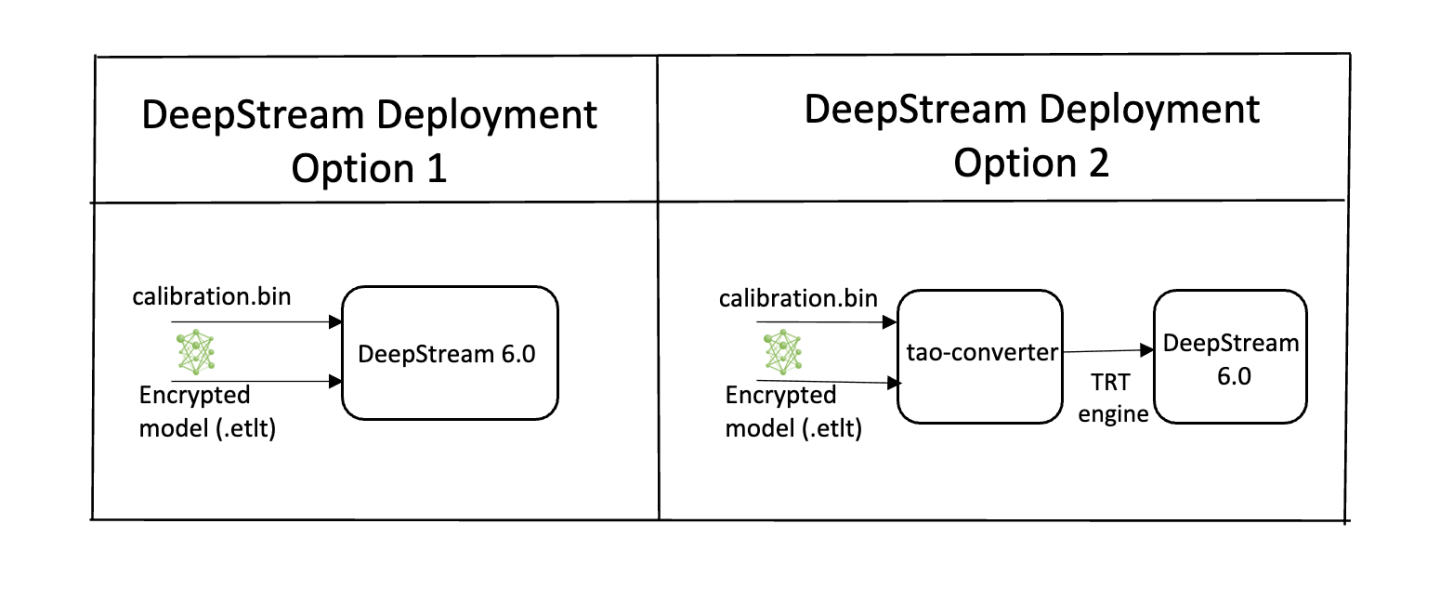
Option 1: Integrate the
.etltmodel directly in the DeepStream app. The model file is generated by export.Option 2: Generate a device-specific optimized TensorRT engine using TAO Deploy. The generated TensorRT engine file can also be ingested by DeepStream.
Option 3 (Deprecated for x86 devices): Generate a device-specific optimized TensorRT engine using TAO Converter.
Machine-specific optimizations are done as part of the engine creation process, so a distinct engine should be generated for each environment and hardware configuration. If the TensorRT or CUDA libraries of the inference environment are updated (including minor version updates), or if a new model is generated, new engines need to be generated. Running an engine that was generated with a different version of TensorRT and CUDA is not supported and will cause unknown behavior that affects inference speed, accuracy, and stability, or it may fail to run altogether.
Option 1 is very straightforward. The .etlt file and calibration cache are directly
used by DeepStream. DeepStream will automatically generate the TensorRT engine file and then run
inference. TensorRT engine generation can take some time depending on size of the model
and type of hardware.
Engine generation can be done ahead of time with Option 2: TAO Deploy is used to convert the .etlt
file to TensorRT; this file is then provided directly to DeepStream. The TAO Deploy workflow is similar to
TAO Converter, which is deprecated for x86 devices in TAO version 4.0.0 but is still required for
deployment to Jetson devices.
See the Exporting the Model section for more details on how to export a TAO model.
The label file is a text file containing the names of the classes that the DetectNet_v2 model
is trained to detect. The order in which the classes are listed here must match the order
in which the model predicts the output. The export subtask in DetectNet_v2 generates this
file when run with the --gen_ds_config flag enabled.
The detection model is typically used as a primary inference engine. It can also be used as a
secondary inference engine. To run this model in the sample deepstream-app, you must modify
the existing config_infer_primary.txt file to point to this model.
Option 1: Integrate the model (.etlt) directly in the DeepStream app.
For this option, you will need to add the following parameters in the configuration file.
The int8-calib-file is only required for INT8 precision.
tlt-encoded-model=<TLT exported .etlt>
tlt-model-key=<Model export key>
int8-calib-file=<Calibration cache file>
The tlt-encoded-model parameter points to the exported model (.etlt) from TAO Toolkit.
The tlt-model-key is the encryption key used during model export.
Option 2: Integrate the TensorRT engine file with the DeepStream app.
Generate the device-specific TensorRT engine using TAO Deploy.
After the engine file is generated, modify the following parameter to use this engine with DeepStream:
model-engine-file=<PATH to generated TensorRT engine>
All other parameters are common between the two approaches. Update the label-file-path parameter
in the configuration file with the path to the labels.txt that was generated at
export.
labelfile-path=<Classification labels>
For all options, see the configuration file below. To learn more about all the parameters, refer to the DeepStream Development Guide under the GsT-nvinfer section.
[property]
gpu-id=0
# preprocessing parameters.
net-scale-factor=0.0039215697906911373
model-color-format=0
# model paths.
int8-calib-file=<Path to optional INT8 calibration cache>
labelfile-path=<Path to detectNet_v2_labels.txt>
tlt-encoded-model=<Path to DetectNet_v2 TLT model>
tlt-model-key=<Key to decrypt the model>
infer-dims=c;h;w # where c = number of channels, h = height of the model input, w = width of model input
uff-input-order=0 # 0 implies that the input blob is in chw order
uff-input-blob-name=input_1
batch-size=4
## 0=FP32, 1=INT8, 2=FP16 mode
network-mode=0
num-detected-classes=3
interval=0
gie-unique-id=1
is-classifier=0
output-blob-names=output_cov/Sigmoid;output_bbox/BiasAdd
#enable_dbscan=0
[class-attrs-all]
threshold=0.2
group-threshold=1
## Set eps=0.7 and minBoxes for enable-dbscan=1
eps=0.2
#minBoxes=3
roi-top-offset=0
roi-bottom-offset=0
detected-min-w=0
detected-min-h=0
detected-max-w=0
detected-max-h=0