Ethernet Programming Guide
NVIDIA DOCA Ethernet Programming Guide
This guide provides an overview and configuration instructions for the DOCA ETH API.
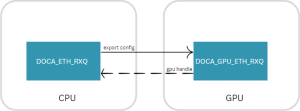
The DOCA ETH library comprises two APIs that represent two DOCA objects, namely DOCA_ETH_RXQ and DOCA_ETH_TXQ.
The control path API is handled on the host CPU side by the library. DOCA_ETH_RXQ/DOCA_ETH_TXQ are configured on the CPU and then exported to the GPU which performs its data path.
DOCA_ETH_RXQ offers an API to receive packets on an RX queue. The doca_eth_rxq object allows developers to receive Ethernet packets in CPU/GPU memory that they have allocated beforehand (Ethernet receive packets buffer). The library collects the user configuration, creates a receive queue object on the GPU memory (using the DOCA_GPU sub-device), and coordinates with the network card (NIC) to receive packets directly into GPU memory.
DOCA_ETH_TXQ provides an API to send packets on a TX queue. The library collects the user configuration and creates a send queue object on the GPU memory (using the DOCA_GPU sub-device) and exports its configuration to the GPU, enabling developers to send packets on this queue from the GPU side.
DOCA Ethernet library (Tx/Rx) is supported on the DPU control path and GPU as data path (see GPUNetIO library).
The machine must meet the following prerequisites:
- DOCA version 2.0.2 or greater
- BlueField software 4.0.2 or greater
- BlueField-3 firmware 32.37.1000 or greater
- BlueField-2 firmware 24.37.1000 or greater
This chapter provides a detailed description of the specific structures and operations related to the DOCA ETH control path API for general initialization, setup, and clean-up.
7.1. DOCA ETH RXQ
The doca_eth_rxq object allows querying device capabilities, setting object properties, creating and configuring an instance of doca_eth_rxq, and destroying it when no longer needed.
7.1.1. Querying Device Capabilities
Querying device capabilities provides information on the derived DOCA Ethernet limitations and enables users to set the properties of a doca_eth_rxq object accordingly.
The following subsections describe the functions which allow querying the device capabilities.
7.1.1.1. doca_eth_rxq_get_max_packet_size_supported()
This function queries the maximum packet size supported by the device. Any packet size bigger than this value is not accepted when trying to start the doca_eth_rxq object.
doca_error_t doca_eth_rxq_get_max_packet_size_supported(const struct doca_devinfo *devinfo, uint16_t *max_packet_size);
-
devinfo [in] -
Pointer to a
doca_devinfoinstance. -
max_packet_size [out] - Maximum packet size.
- Returns
-
doca_error_tvalue.DOCA_SUCCESSif successful or an error value upon failure. Possible error values are documented in the header file.
7.1.1.2. doca_eth_rxq_get_type_supported()
This function checks if an RX queue type is supported by the device.
doca_error_t doca_eth_rxq_get_type_supported(const struct doca_devinfo *devinfo, enum doca_eth_rxq_type type, uint8_t *type_supported);
-
devinfo [in] -
Pointer to a
doca_devinfoinstance. -
type [in] - RX queue type (the values are documented in the header file).
-
type_supported [out] - Flag to indicate if the type is supported.
- Returns
-
doca_error_tvalue.DOCA_SUCCESSif successful or an error value upon failure. Possible error values are documented in the header file.
7.1.2. Creating and Configuring DOCA_ETH_RXQ
7.1.2.1. doca_eth_rxq_create()
This function creates an instance of doca_eth_rxq.
doca_error_t doca_eth_rxq_create(struct doca_eth_rxq **eth_rxq);
-
eth_rxq [out] -
Pointer to the newly created
doca_eth_rxqinstance. - Returns
-
doca_error_tvalue.DOCA_SUCCESSif successful or an error value upon failure. Possible error values are documented in the header file.
7.1.2.2. doca_eth_rxq_destroy()
This function destroys a doca_eth_rxq instance.
doca_error_t doca_eth_rxq_destroy(struct doca_eth_rxq *eth_rxq);
-
eth_rxq [in] -
Pointer to the
doca_eth_rxqto be destroyed. - Returns
-
doca_error_tvalue.DOCA_SUCCESSif successful or an error value upon failure. Possible error values are documented in the header file.
7.1.2.3. doca_eth_rxq_set_num_packets()
This function sets the number of packets the RX queue can hold.
doca_error_t doca_eth_rxq_set_num_packets(struct doca_eth_rxq *eth_rxq, uint32_t num_packets);
-
eth_rxq [in] -
Pointer to the
doca_eth_rxqinstance. -
num_packets [in] - Maximum number of packets the queue can hold in the context.
- Returns
-
doca_error_tvalue.DOCA_SUCCESSif successful or an error value upon failure. Possible error values are documented in the header file.
7.1.2.4. doca_eth_rxq_set_max_packet_size()
This function sets the maximum Ethernet packet size the RX queue can accommodate.
doca_error_t doca_eth_rxq_set_max_packet_size(struct doca_eth_rxq *eth_rxq, uint16_t max_pkt_sz);
-
eth_rxq [in] -
Pointer to the
doca_eth_rxqinstance. -
max_pkt_sz [in] - Maximum packet size the RX queue can handle in the context.
- Returns
-
doca_error_tvalue.DOCA_SUCCESSif successful or an error value upon failure. Possible error values are documented in the header file.
7.1.2.5. doca_eth_rxq_set_type()
This function sets the RX queue type.
doca_error_t doca_eth_rxq_set_type(struct doca_eth_rxq *eth_rxq, enum doca_eth_rxq_type type);
-
eth_rxq [in] -
Pointer to the
doca_eth_rxqinstance. -
type [in] - Type of the RX queue. Possible values are documented in the header file.
- Returns
-
doca_error_tvalue.DOCA_SUCCESSif successful or an error value upon failure. Possible error values are documented in the header file.
7.1.2.6. doca_eth_rxq_get_flow_queue_id()
This function retrieves the DPDK queue ID of the receive queue, which can be used in rte_flow or doca_flow.
doca_error_t doca_eth_rxq_get_flow_queue_id(struct doca_eth_rxq *eth_rxq, uint16_t *flow_queue_id);
-
eth_rxq [in] -
Pointer to the
doca_eth_rxqinstance. -
flow_queue_id [out] -
Queue ID, which can be used in
rte_flowordoca_flow. - Returns
-
doca_error_tvalue.DOCA_SUCCESSif successful or an error value upon failure. Possible error values are documented in the header file.
7.1.2.7. doca_eth_rxq_get_gpu_handle()
This function retrieves the GPU handle of a doca_eth_rxq instance.
The following is the expected flow:
- Bind the context to a GPU device using
doca_ctx_set_data_path_on_gpu(). - Start the context using
doca_ctx_start(). - Call
doca_eth_rxq_get_gpu_handle()to retrieve thegpu_handle.
doca_error_t doca_eth_rxq_get_gpu_handle(const struct doca_eth_rxq *eth_rxq, struct doca_gpu_eth_rxq **eth_rxq_ext);
-
eth_rxq [in] -
Pointer to the
doca_eth_rxqinstance. -
eth_rxq_ext [out] -
Handle for the DOCA GPU
eth_rxq. - Returns
-
doca_error_tvalue.DOCA_SUCCESSif successful or an error value upon failure. Possible error values are documented in the header file.
7.1.2.8. doca_eth_rxq_get_pkt_buffer_size()
This function retrieves the size for the Ethernet packet buffer of a doca_eth_rxq.
doca_error_t doca_eth_rxq_get_pkt_buffer_size(const struct doca_eth_rxq *eth_rxq, uint32_t *size);
-
eth_rxq [in] -
Pointer to the
doca_eth_rxqinstance. -
size [out] - Required size for the Ethernet packet buffer.
- Returns
-
doca_error_tvalue.DOCA_SUCCESSif successful or an error value upon failure. Possible error values are documented in the header file.
7.1.2.9. doca_eth_rxq_set_pkt_buffer()
This function sets the Ethernet packet buffer of a doca_eth_rxq.
doca_error_t doca_eth_rxq_set_pkt_buffer(struct doca_eth_rxq *eth_rxq, struct doca_mmap *mmap, uint32_t offset, uint32_t size);
-
eth_rxq [in] -
Pointer to the
doca_eth_rxqinstance. -
mmap [in] - Mmap with the memrange for the Ethernet packet buffer.
-
size [in] - Size of the Ethernet packet buffer.
- Returns
-
doca_error_tvalue.DOCA_SUCCESSif successful or an error value upon failure. Possible error values are documented in the header file.
7.2. DOCA ETH TXQ
The doca_eth_txq object allows querying device capabilities, setting object properties, creating and configuring an instance of doca_eth_txq, and destroying it when no longer needed.
7.2.1. Querying Device Capabilities
Querying device capabilities provides users with information regarding the derived DOCA Eth limitations and enables them to set the properties of a doca_eth_txq object accordingly.
The following subsections describe the functions which allow querying the device capabilities.
7.2.1.1. doca_eth_txq_get_max_queue_size_supported()
This function queries the maximum queue size supported by the device. Any queue size bigger than this value is not accepted when trying to start the doca_eth_txq object.
doca_error_t doca_eth_txq_get_max_queue_size_supported(const struct doca_devinfo *devinfo, uint32_t *max_queue_size);
-
devinfo [in] -
Pointer to a
doca_devinfoinstance. -
max_queue_size [out] - Maximum queue size supported by the device.
- Returns
-
doca_error_tvalue.DOCA_SUCCESSif successful or an error value upon failure. Possible error values are documented in the header file.
7.2.1.2. doca_eth_txq_get_type_supported()
This function checks if a TX queue type is supported by the device.
doca_error_t doca_eth_txq_get_type_supported(const struct doca_devinfo *devinfo, enum doca_eth_txq_type type, uint8_t *type_supported);
-
devinfo [in] -
Pointer to a
doca_devinfoinstance. -
type [in] - TX queue type.
-
type_supported [out] - Flag to indicate if the type is supported.
- Returns
-
doca_error_tvalue.DOCA_SUCCESSif successful or an error value upon failure. Possible error values are documented in the header file.
7.2.1.3. doca_eth_txq_get_chksum_offload_supported()
This function checks if checksum offload is supported by the device.
doca_error_t doca_eth_txq_get_chksum_offload_supported(const struct doca_devinfo *devinfo, uint8_t *offload_supported);
-
devinfo [in] -
Pointer to a
doca_devinfoinstance. -
offload_supported [out] - Flag to indicate if checksum offload is supported.
- Returns
-
doca_error_tvalue.DOCA_SUCCESSif successful or an error value upon failure. Possible error values are documented in the header file.
7.2.1.4. doca_eth_txq_get_wait_on_time_offload_supported()
This function checks if wait-on-time offload is supported by the device.
doca_error_t doca_eth_txq_get_wait_on_time_offload_supported(const struct doca_dev *dev, enum doca_eth_wait_on_time *wait_on_time_mode);
-
dev [in] -
Pointer to a
doca_devinstance. -
wait_on_time_mode [out] - Wait-on-time mode supported by the device. Valid mode values are documented in the header file.
- Returns
-
doca_error_tvalue.DOCA_SUCCESSif successful or an error value upon failure. Possible error values are documented in the header file.
7.2.2. Creating and Configuring DOCA_ETH_TXQ
7.2.2.1. doca_eth_txq_create()
This function creates an instance of doca_eth_txq.
doca_error_t doca_eth_txq_create(struct doca_eth_txq **eth_txq);
-
eth_txq [out] -
Pointer to the newly created
doca_eth_txqinstance. - Returns
-
doca_error_tvalue.DOCA_SUCCESSif successful or an error value upon failure. Possible error values are documented in the header file.
7.2.2.2. doca_eth_txq_destroy()
This function destroys a doca_eth_txq instance.
doca_error_t doca_eth_txq_destroy(struct doca_eth_txq *eth_txq);
-
eth_txq [in] -
Pointer to the
doca_eth_txqinstance to destroy. - Returns
-
doca_error_tvalue.DOCA_SUCCESSif successful or an error value upon failure. Possible error values are documented in the header file.
7.2.2.3. doca_eth_txq_set_queue_size()
This function sets the size of the TX queue.
doca_error_t doca_eth_txq_set_queue_size(struct doca_eth_txq *eth_txq, uint32_t size);
-
eth_txq [in] -
Pointer to the
doca_eth_txqinstance. -
size [in] - TX queue size.
- Returns
-
doca_error_tvalue.DOCA_SUCCESSif successful or an error value upon failure. Possible error values are documented in the header file.
7.2.2.4. doca_eth_txq_set_type()
This function sets the TX queue type.
doca_error_t doca_eth_txq_set_type(struct doca_eth_txq *eth_txq, enum doca_eth_txq_type type);
-
eth_txq [in] -
Pointer to the
doca_eth_txqinstance. -
type [in] - Type of the TX queue. Possible values are documented in the header file.
- Returns
-
doca_error_tvalue.DOCA_SUCCESSif successful or an error value upon failure. Possible error values are documented in the header file.
7.2.2.5. doca_eth_txq_set_l4_chksum_offload()
This function sets offload for the calculation of TCP/UDP checksum (L4) on transmitted packets.
doca_error_t doca_eth_txq_set_l4_chksum_offload(struct doca_eth_txq *eth_txq);
-
eth_txq [in] -
Pointer to the
doca_eth_txqinstance. - Returns
-
doca_error_tvalue.DOCA_SUCCESSif successful or an error value upon failure. Possible error values are documented in the header file.
7.2.2.6. doca_eth_txq_set_l3_chksum_offload()
This function sets offload for the calculation of IPv4 checksum (L3) on transmitted packets.
doca_error_t doca_eth_txq_set_l3_chksum_offload(struct doca_eth_txq *eth_txq);
-
eth_txq [in] -
Pointer to the
doca_eth_txqinstance. - Returns
-
doca_error_tvalue.DOCA_SUCCESSif successful or an error value upon failure. Possible error values are documented in the header file.
7.2.2.7. doca_eth_txq_set_wait_on_time_offload()
This function retrieves the GPU handle of a doca_eth_txq instance.
doca_error_t doca_eth_txq_set_wait_on_time_offload(struct doca_eth_txq *eth_txq);
-
eth_txq [in] -
Pointer to the
doca_eth_txqinstance. - Returns
-
doca_error_tvalue.DOCA_SUCCESSif successful or an error value upon failure. Possible error values are documented in the header file.
7.2.2.8. doca_eth_txq_get_gpu_handle()
This function retrieves the GPU handle of a doca_eth_txq instance.
The following is the expected flow:
- Bind the context to a GPU device using
doca_ctx_set_data_path_on_gpu(). - Start the context using
doca_ctx_start(). - Call
doca_eth_txq_get_gpu_handle()to retrieve thegpu_handle.
doca_error_t doca_eth_txq_get_gpu_handle(const struct doca_eth_txq *eth_txq, struct doca_gpu_eth_txq **eth_txq_ext);
-
eth_txq [in] -
Pointer to the
doca_eth_txqinstance. -
eth_txq_ext [out] -
Handle for the DOCA GPU
eth_rxq. - Returns
-
doca_error_tvalue.DOCA_SUCCESSif successful or an error value upon failure. Possible error values are documented in the header file.
Notice
This document is provided for information purposes only and shall not be regarded as a warranty of a certain functionality, condition, or quality of a product. NVIDIA Corporation nor any of its direct or indirect subsidiaries and affiliates (collectively: “NVIDIA”) make no representations or warranties, expressed or implied, as to the accuracy or completeness of the information contained in this document and assume no responsibility for any errors contained herein. NVIDIA shall have no liability for the consequences or use of such information or for any infringement of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from its use. This document is not a commitment to develop, release, or deliver any Material (defined below), code, or functionality.
NVIDIA reserves the right to make corrections, modifications, enhancements, improvements, and any other changes to this document, at any time without notice.
Customer should obtain the latest relevant information before placing orders and should verify that such information is current and complete.
NVIDIA products are sold subject to the NVIDIA standard terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgement, unless otherwise agreed in an individual sales agreement signed by authorized representatives of NVIDIA and customer (“Terms of Sale”). NVIDIA hereby expressly objects to applying any customer general terms and conditions with regards to the purchase of the NVIDIA product referenced in this document. No contractual obligations are formed either directly or indirectly by this document.
NVIDIA products are not designed, authorized, or warranted to be suitable for use in medical, military, aircraft, space, or life support equipment, nor in applications where failure or malfunction of the NVIDIA product can reasonably be expected to result in personal injury, death, or property or environmental damage. NVIDIA accepts no liability for inclusion and/or use of NVIDIA products in such equipment or applications and therefore such inclusion and/or use is at customer’s own risk.
NVIDIA makes no representation or warranty that products based on this document will be suitable for any specified use. Testing of all parameters of each product is not necessarily performed by NVIDIA. It is customer’s sole responsibility to evaluate and determine the applicability of any information contained in this document, ensure the product is suitable and fit for the application planned by customer, and perform the necessary testing for the application in order to avoid a default of the application or the product. Weaknesses in customer’s product designs may affect the quality and reliability of the NVIDIA product and may result in additional or different conditions and/or requirements beyond those contained in this document. NVIDIA accepts no liability related to any default, damage, costs, or problem which may be based on or attributable to: (i) the use of the NVIDIA product in any manner that is contrary to this document or (ii) customer product designs.
No license, either expressed or implied, is granted under any NVIDIA patent right, copyright, or other NVIDIA intellectual property right under this document. Information published by NVIDIA regarding third-party products or services does not constitute a license from NVIDIA to use such products or services or a warranty or endorsement thereof. Use of such information may require a license from a third party under the patents or other intellectual property rights of the third party, or a license from NVIDIA under the patents or other intellectual property rights of NVIDIA.
Reproduction of information in this document is permissible only if approved in advance by NVIDIA in writing, reproduced without alteration and in full compliance with all applicable export laws and regulations, and accompanied by all associated conditions, limitations, and notices.
THIS DOCUMENT AND ALL NVIDIA DESIGN SPECIFICATIONS, REFERENCE BOARDS, FILES, DRAWINGS, DIAGNOSTICS, LISTS, AND OTHER DOCUMENTS (TOGETHER AND SEPARATELY, “MATERIALS”) ARE BEING PROVIDED “AS IS.” NVIDIA MAKES NO WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED, IMPLIED, STATUTORY, OR OTHERWISE WITH RESPECT TO THE MATERIALS, AND EXPRESSLY DISCLAIMS ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF NONINFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY, AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. TO THE EXTENT NOT PROHIBITED BY LAW, IN NO EVENT WILL NVIDIA BE LIABLE FOR ANY DAMAGES, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, PUNITIVE, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, HOWEVER CAUSED AND REGARDLESS OF THE THEORY OF LIABILITY, ARISING OUT OF ANY USE OF THIS DOCUMENT, EVEN IF NVIDIA HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. Notwithstanding any damages that customer might incur for any reason whatsoever, NVIDIA’s aggregate and cumulative liability towards customer for the products described herein shall be limited in accordance with the Terms of Sale for the product.
Trademarks
NVIDIA, the NVIDIA logo, and Mellanox are trademarks and/or registered trademarks of Mellanox Technologies Ltd. and/or NVIDIA Corporation in the U.S. and in other countries. The registered trademark Linux® is used pursuant to a sublicense from the Linux Foundation, the exclusive licensee of Linus Torvalds, owner of the mark on a world¬wide basis. Other company and product names may be trademarks of the respective companies with which they are associated.
Copyright
© 2023 NVIDIA Corporation & affiliates. All rights reserved.